The document discusses asynchronous programming in Python using asyncio. It begins with motivational quotes about asynchronous programming. It then provides examples of using coroutines, tasks/futures, and event loops in asyncio. It demonstrates how asyncio avoids blocking the event loop by executing slow functions in a thread pool. The document concludes by mentioning ThreadPoolExecutor and aioHTTP as topics to explore next.












![pen4education
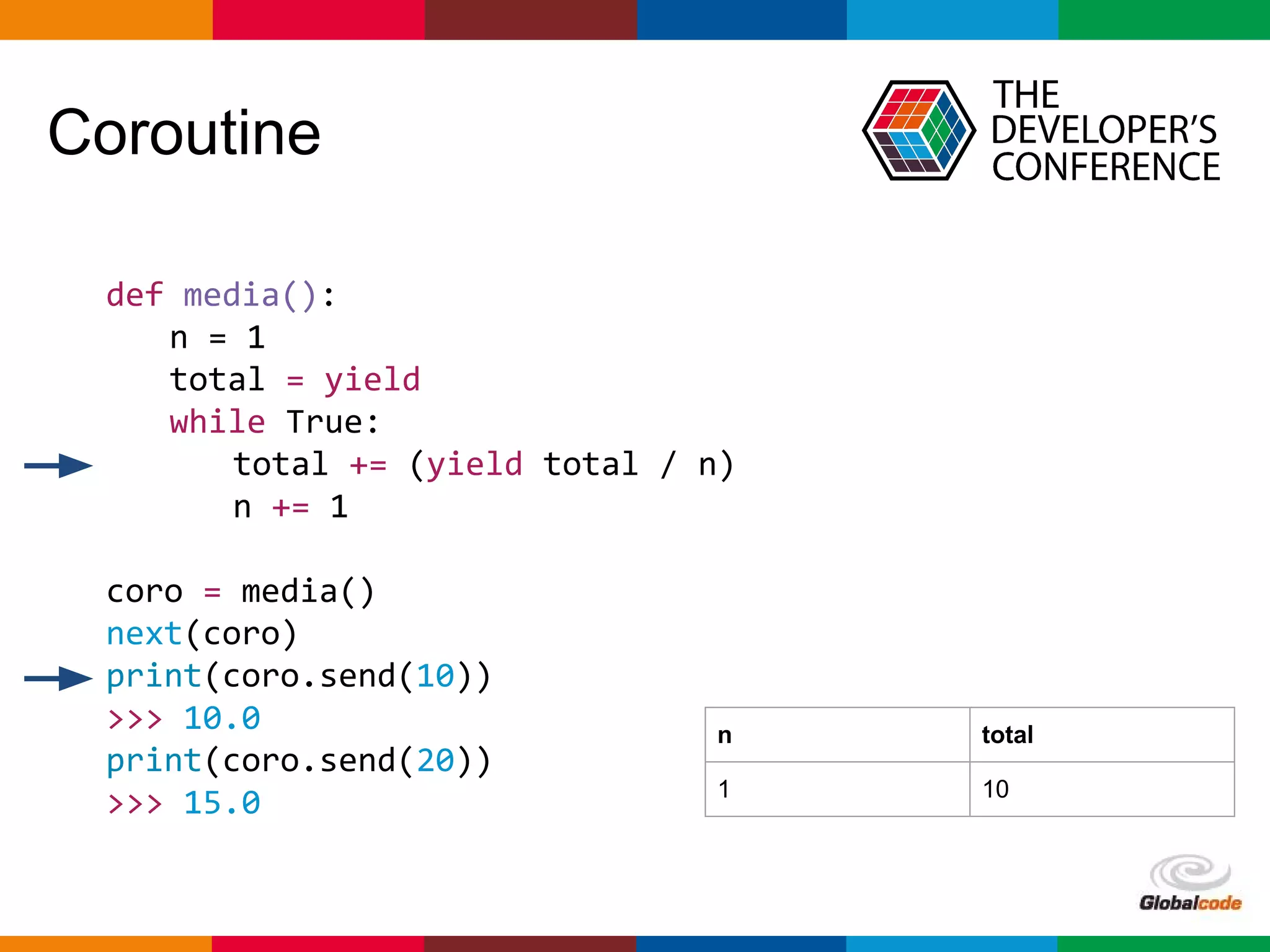
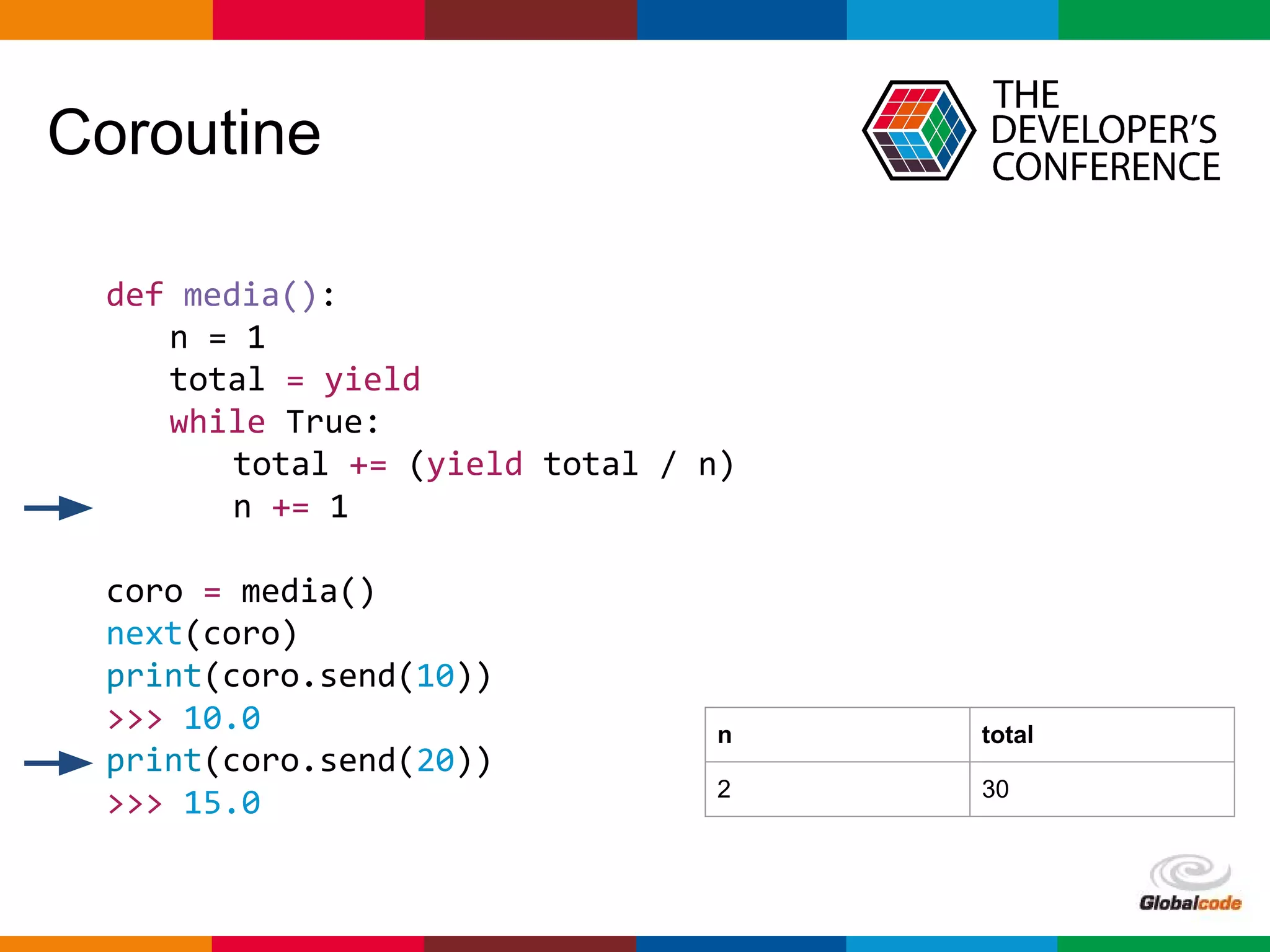
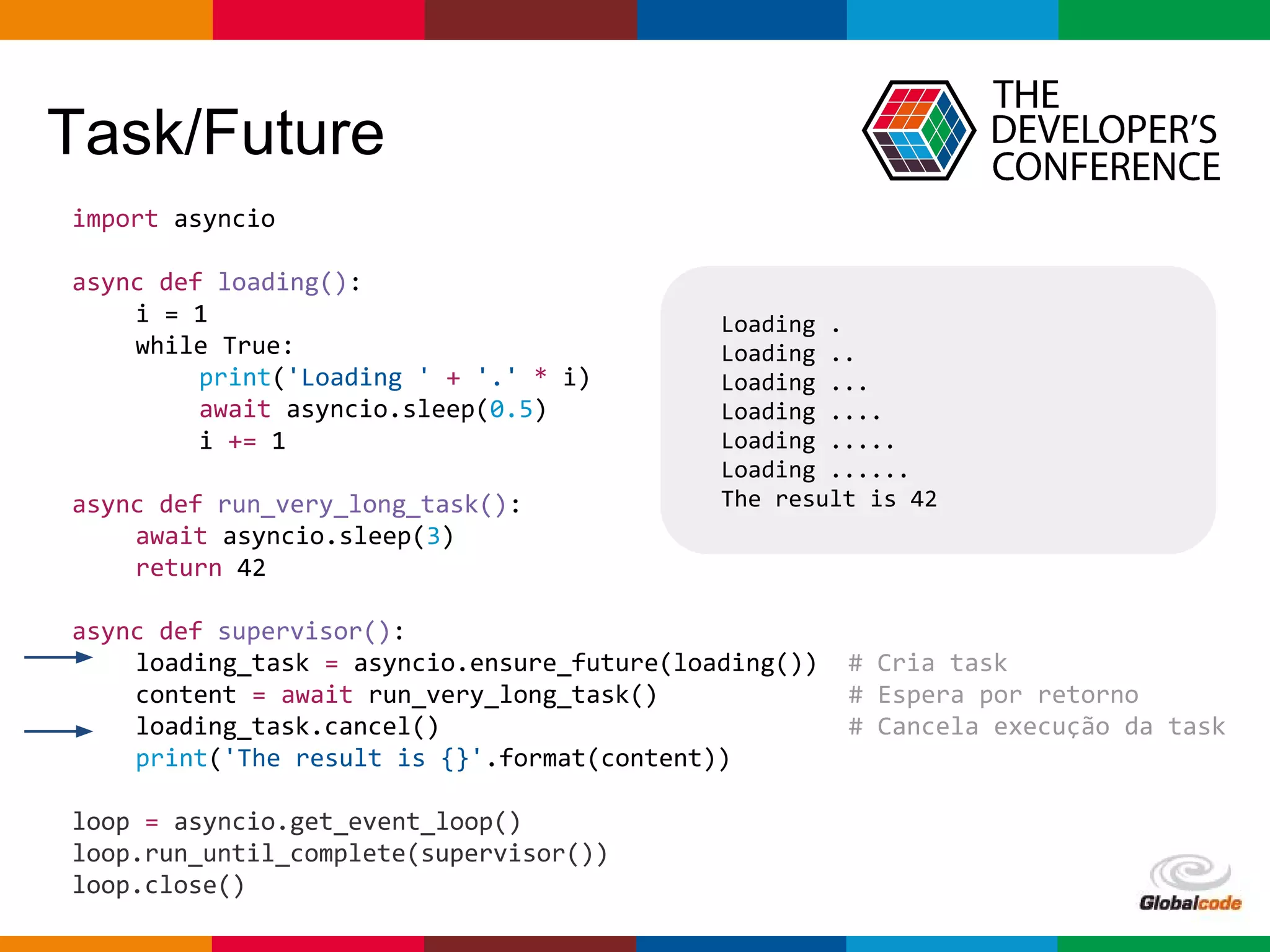
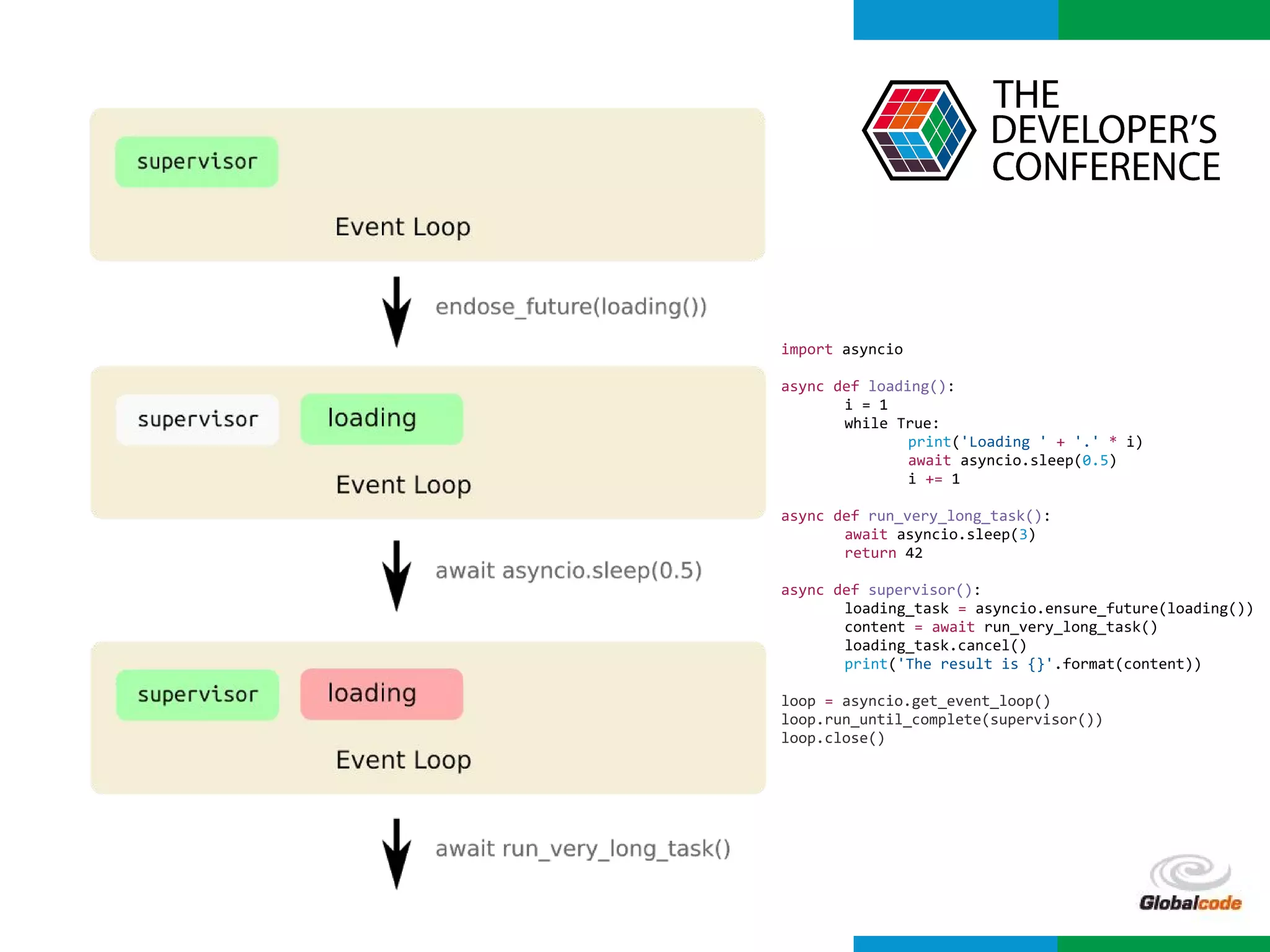
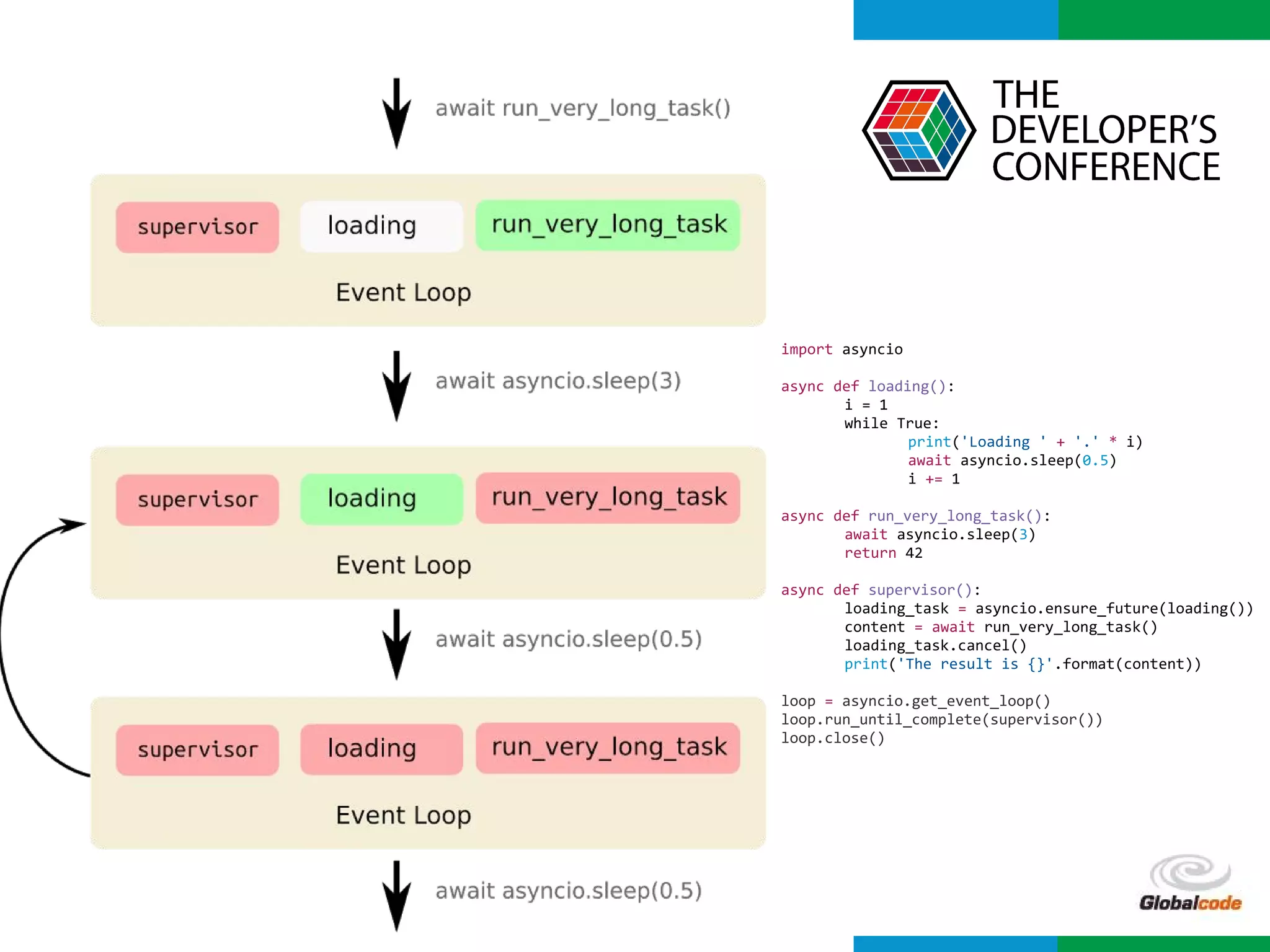
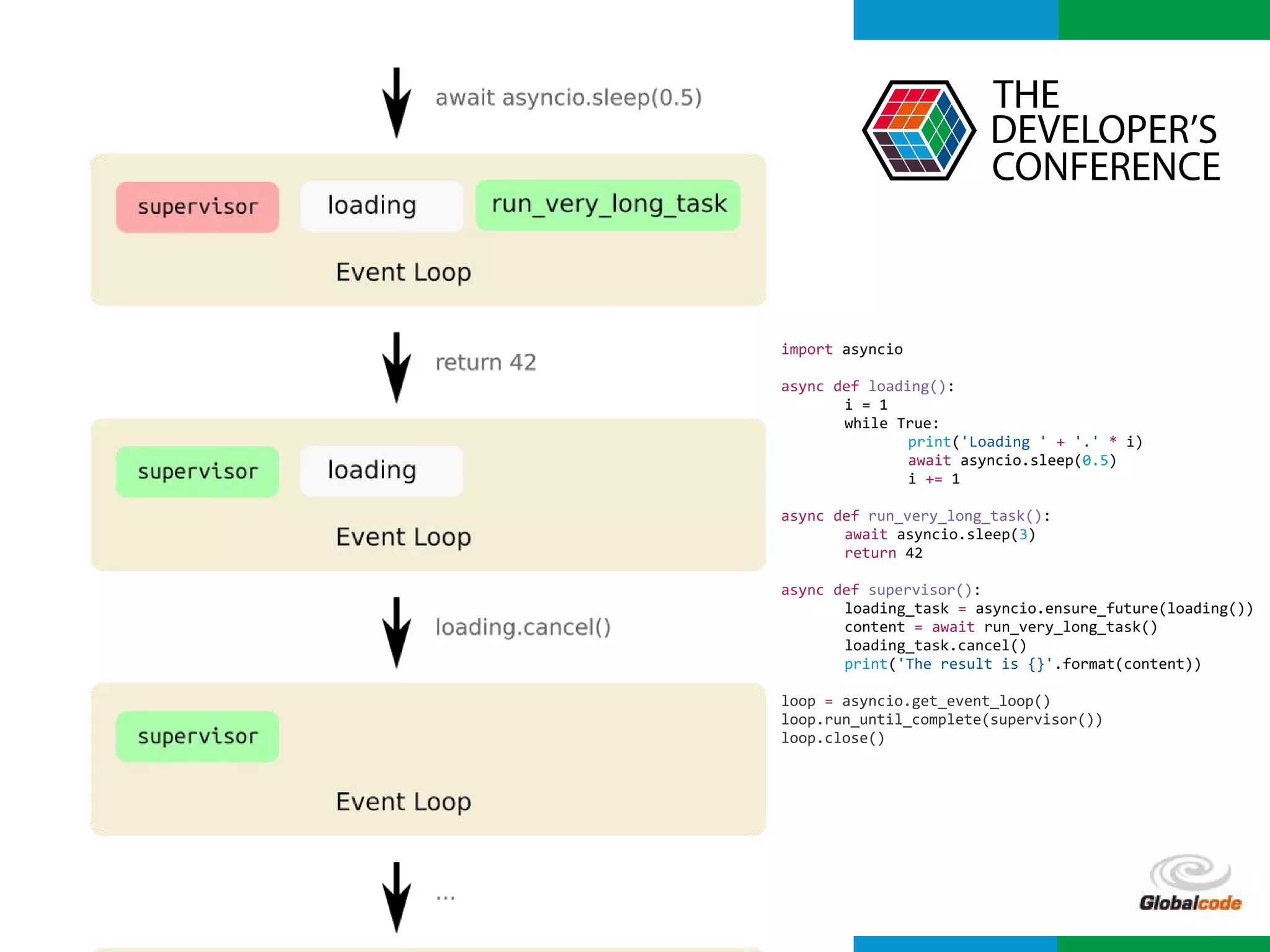
import asyncio
import time
def slow_function():
time.sleep(3)
return 42
async def test1():
slow_function()
print('Finish test1')
async def test2():
for i in range(0, 10):
print(i)
await asyncio.sleep(0.5)
print('Finish test2')
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait([
test1(),
test2()
]))
Bloqueio do Loop
Finish test1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Finish test2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/palestra-tdc-python-asyncio1-160711004039/75/Seu-primeiro-loop-com-Python-AsyncIO-TDC-2016-25-2048.jpg)
![pen4education
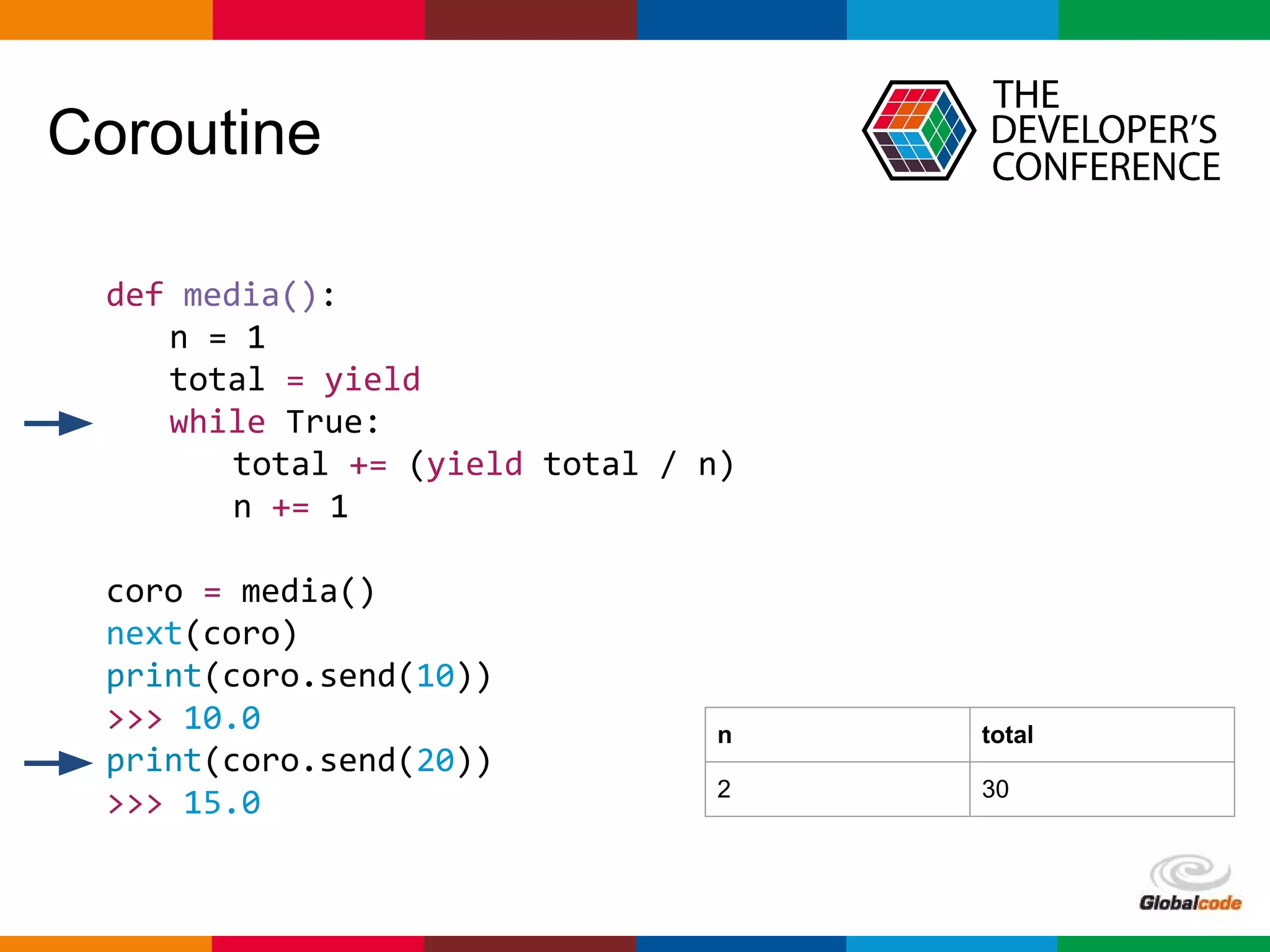
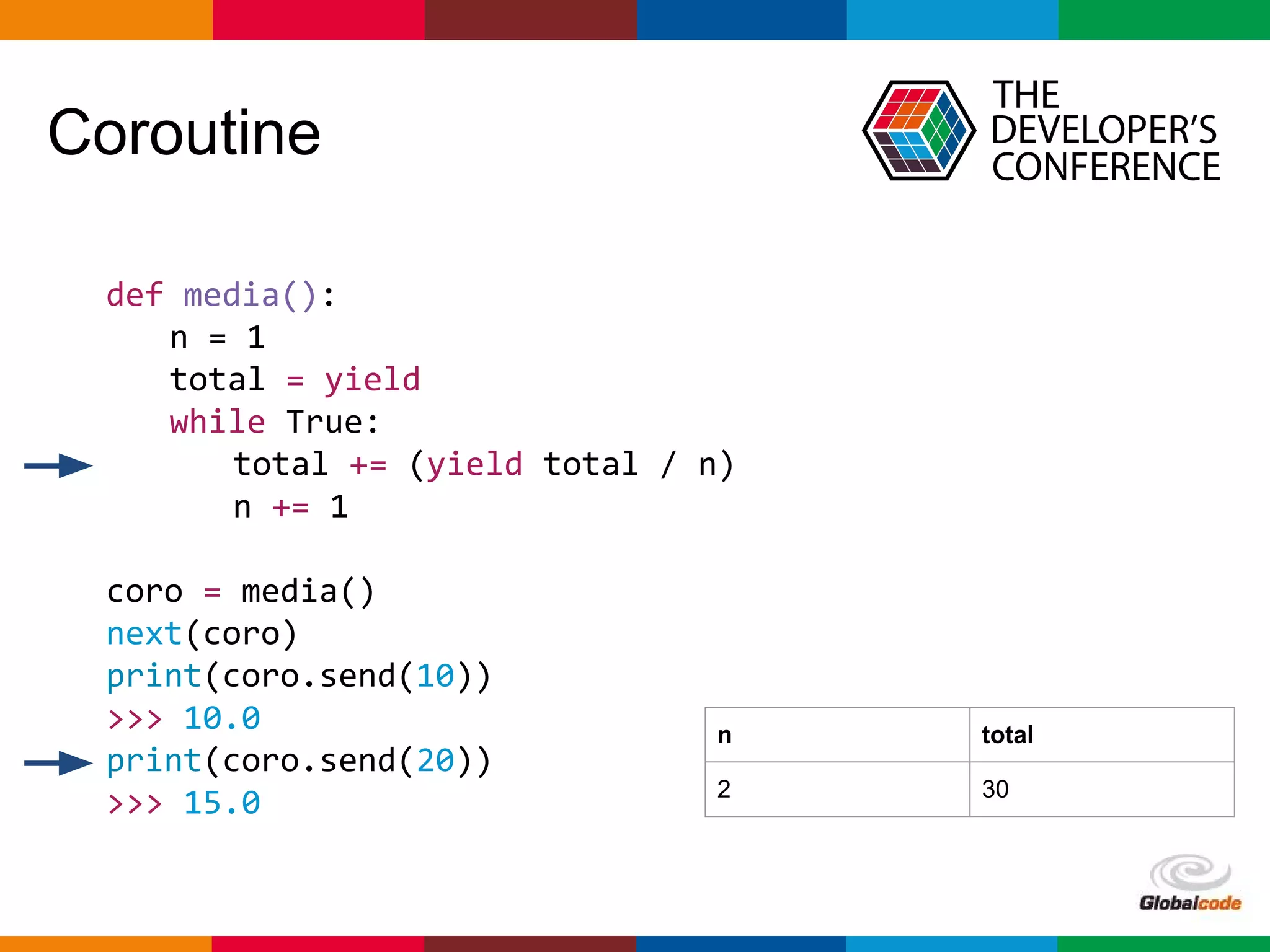
import asyncio
import time
def slow_function():
time.sleep(3)
return 42
async def test1():
await loop.run_in_executor(None, slow_function)
print('Finish test1')
async def test2():
for i in range(0, 10):
print(i)
await asyncio.sleep(0.5)
print('Finish test2')
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait([
test1(),
test2()
]))
Bloqueio do Loop
0
1
2
3
4
5
Finish test1
6
7
8
9
Finish test2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/palestra-tdc-python-asyncio1-160711004039/75/Seu-primeiro-loop-com-Python-AsyncIO-TDC-2016-26-2048.jpg)

