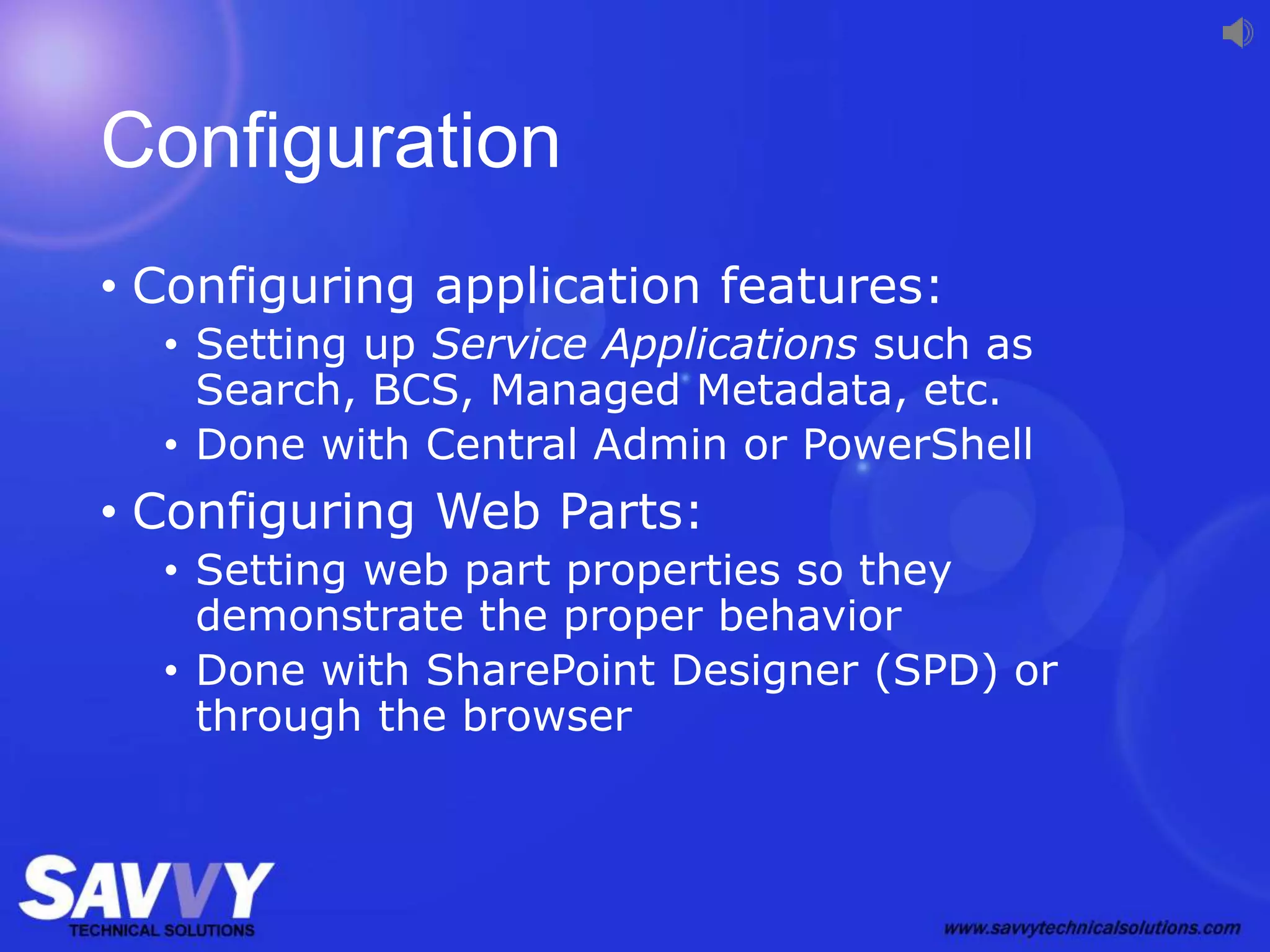
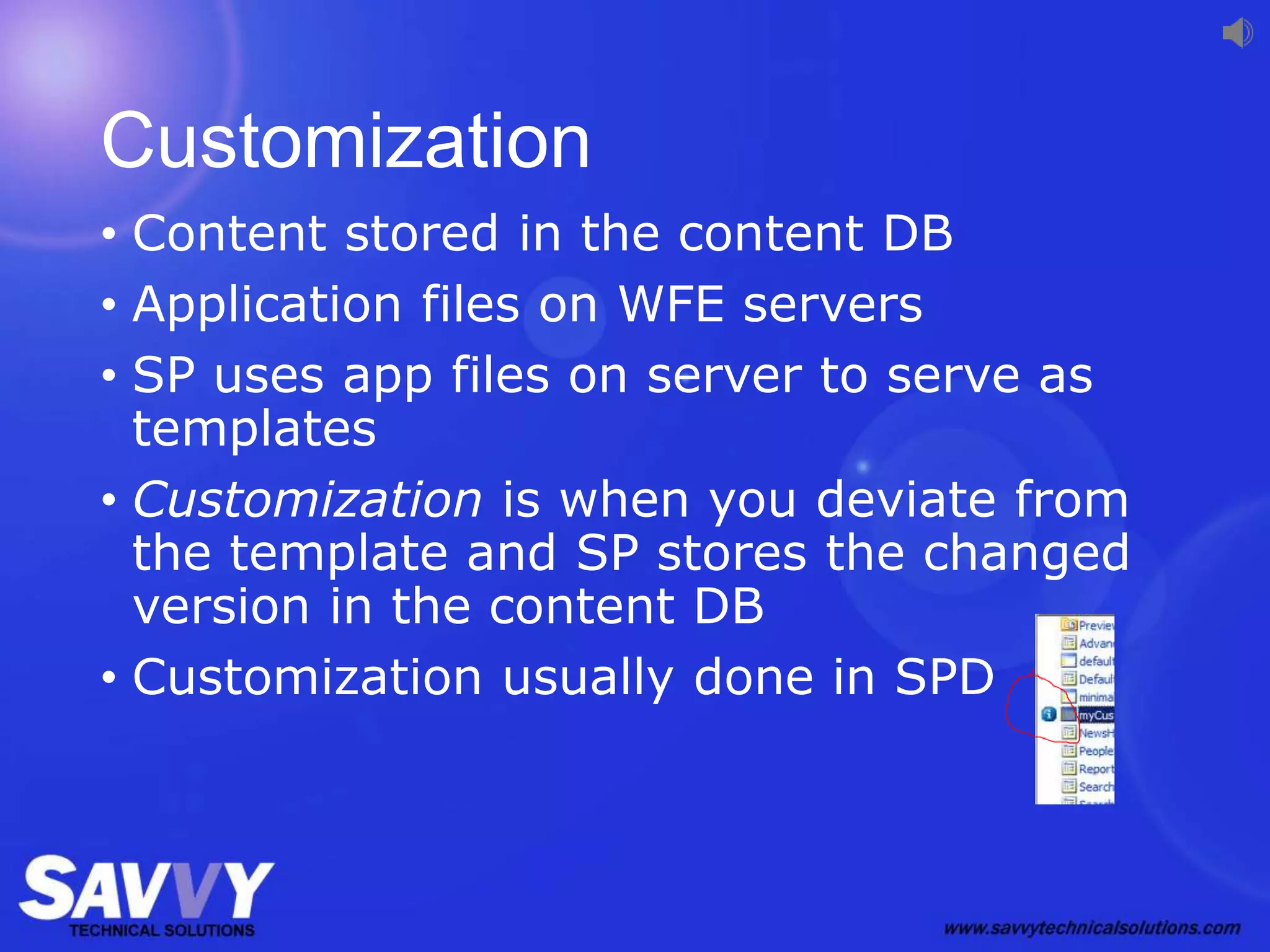
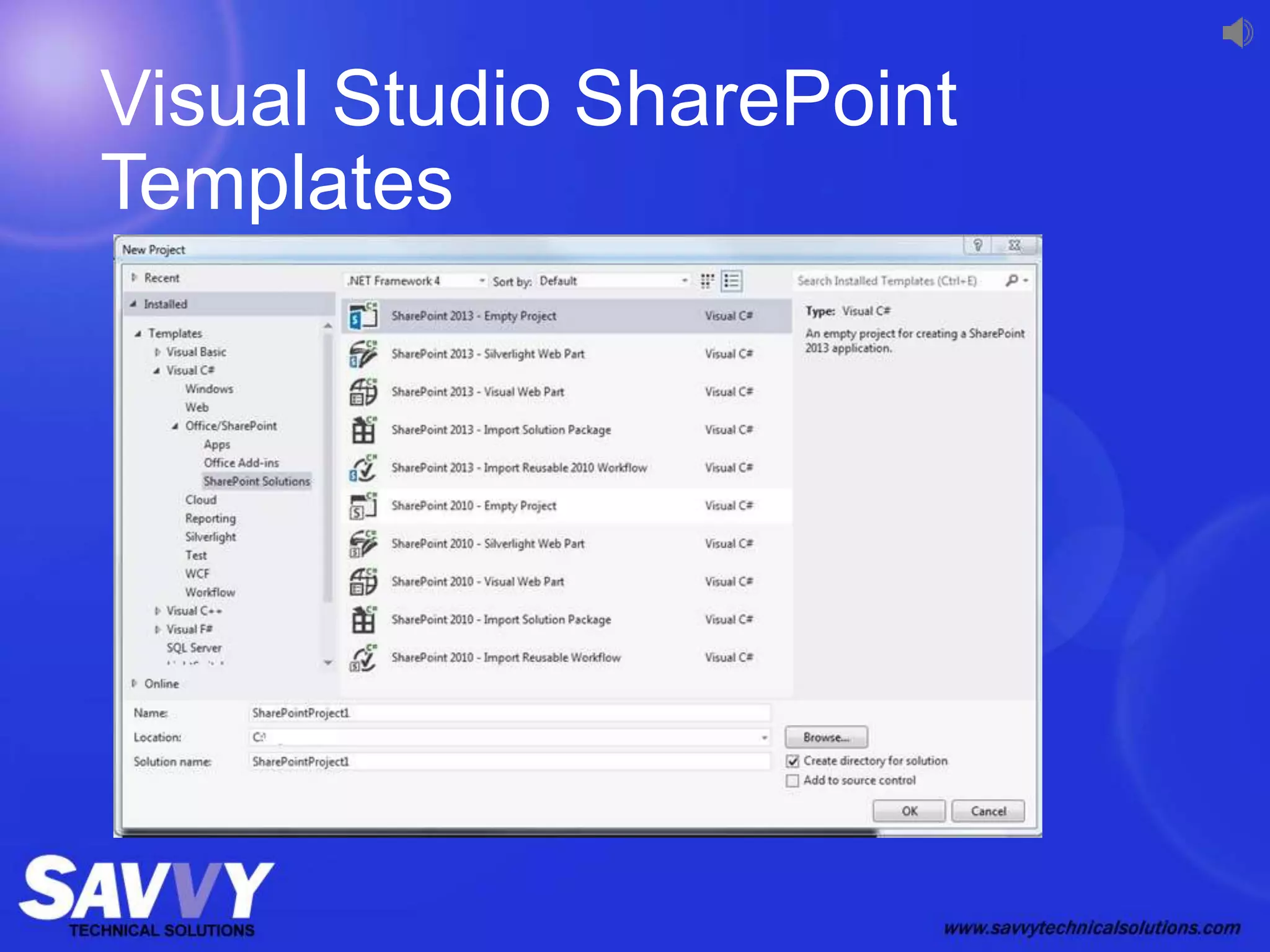
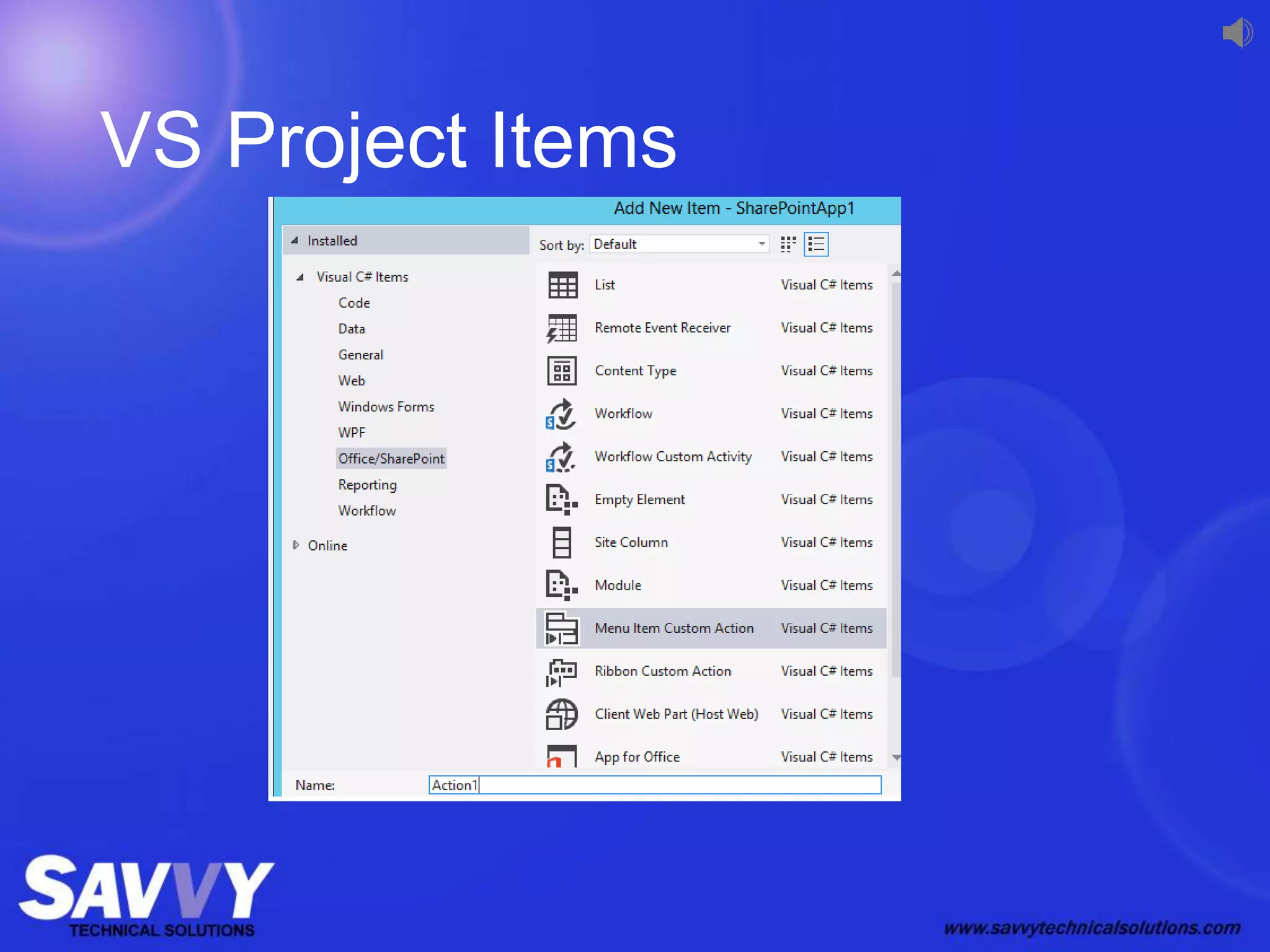
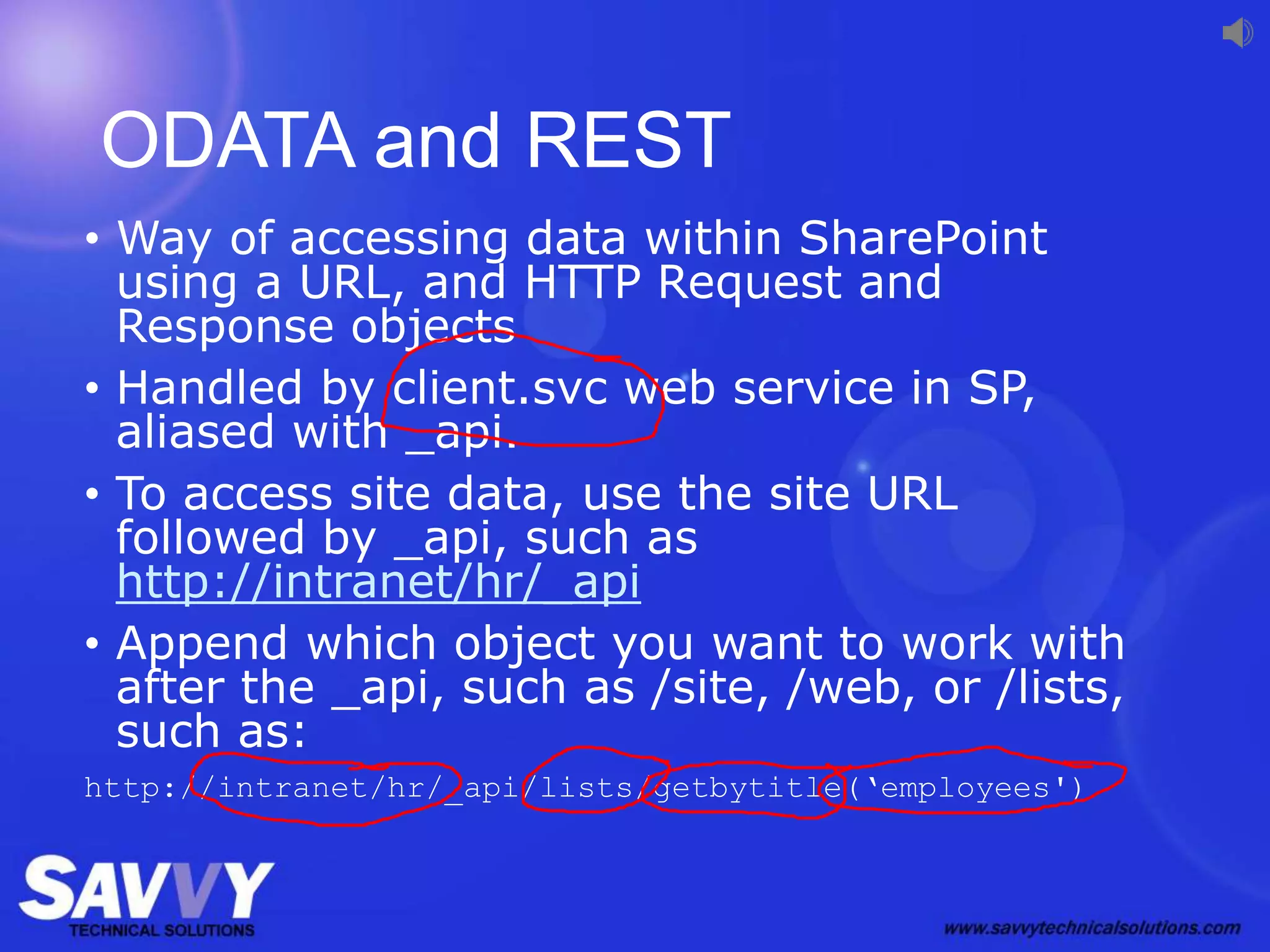
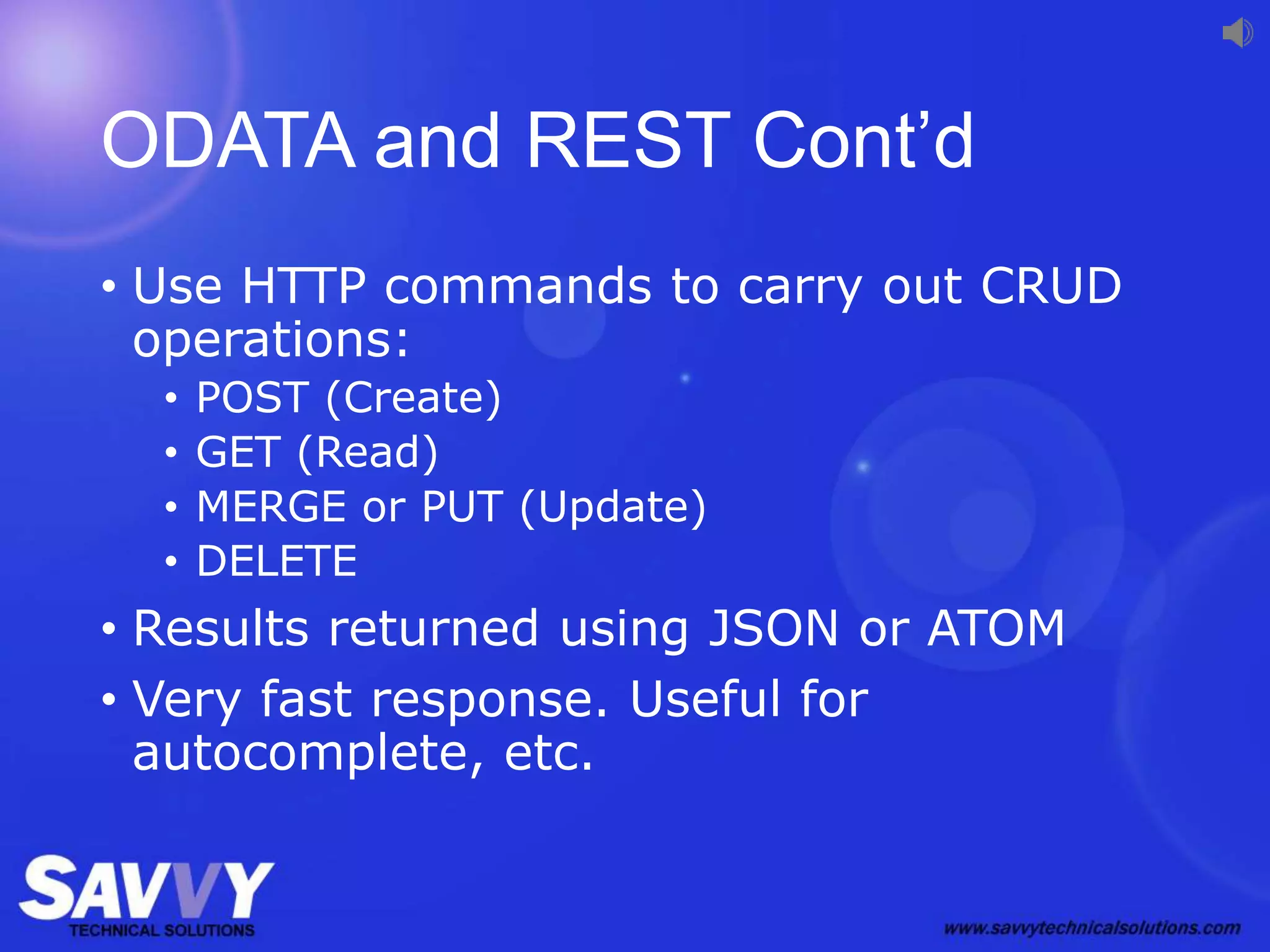
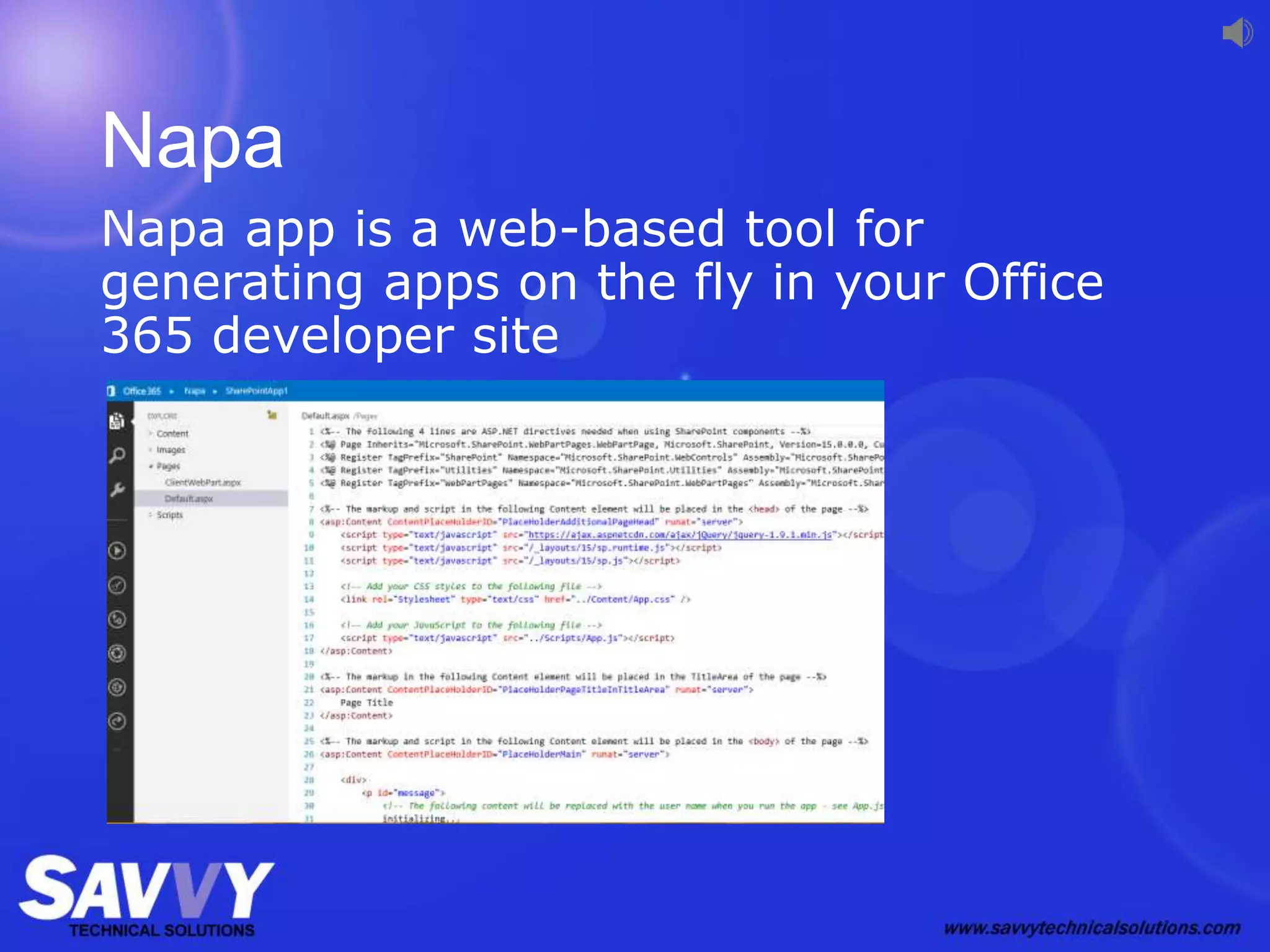
The document provides an overview of SharePoint development, including its various versions over time, what SharePoint is used for, and different approaches to customizing and developing for SharePoint. It discusses configuration vs customization vs development. It then covers key development approaches like using Visual Studio templates, solution packages, features, farm vs sandboxed solutions, and the server-side vs client-side object models. It also discusses the SharePoint app model and different app locations like host webs and app webs.