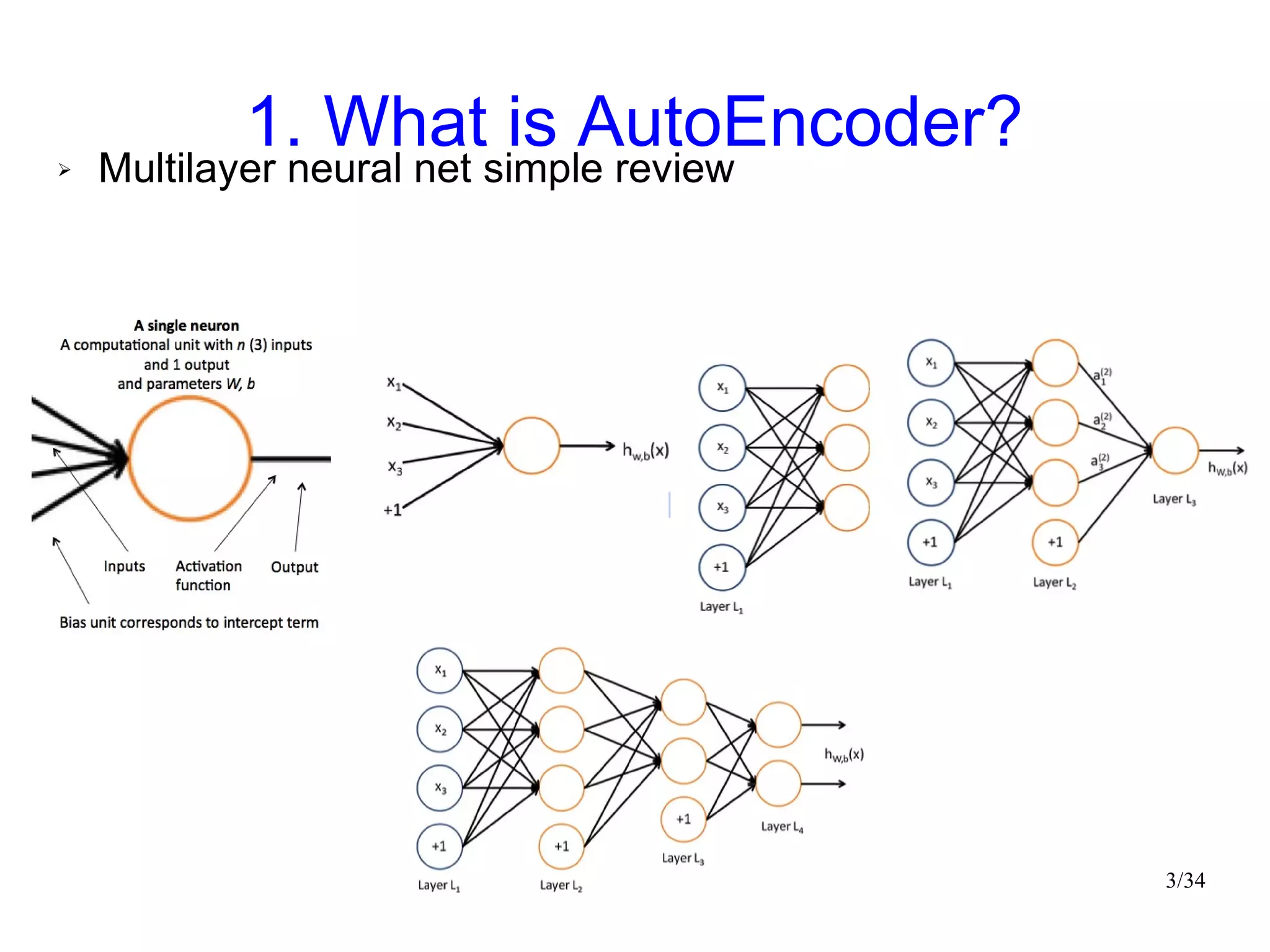
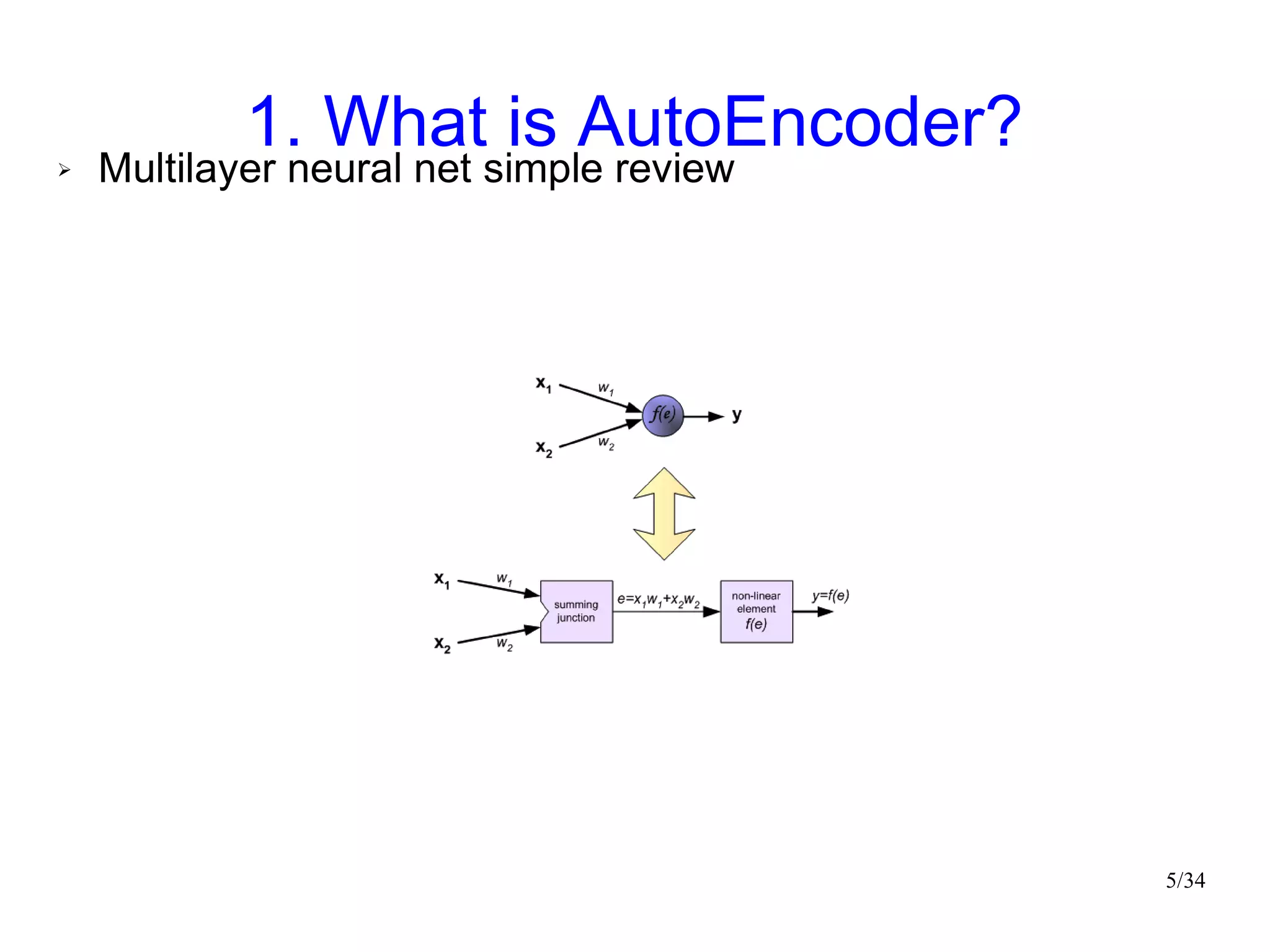
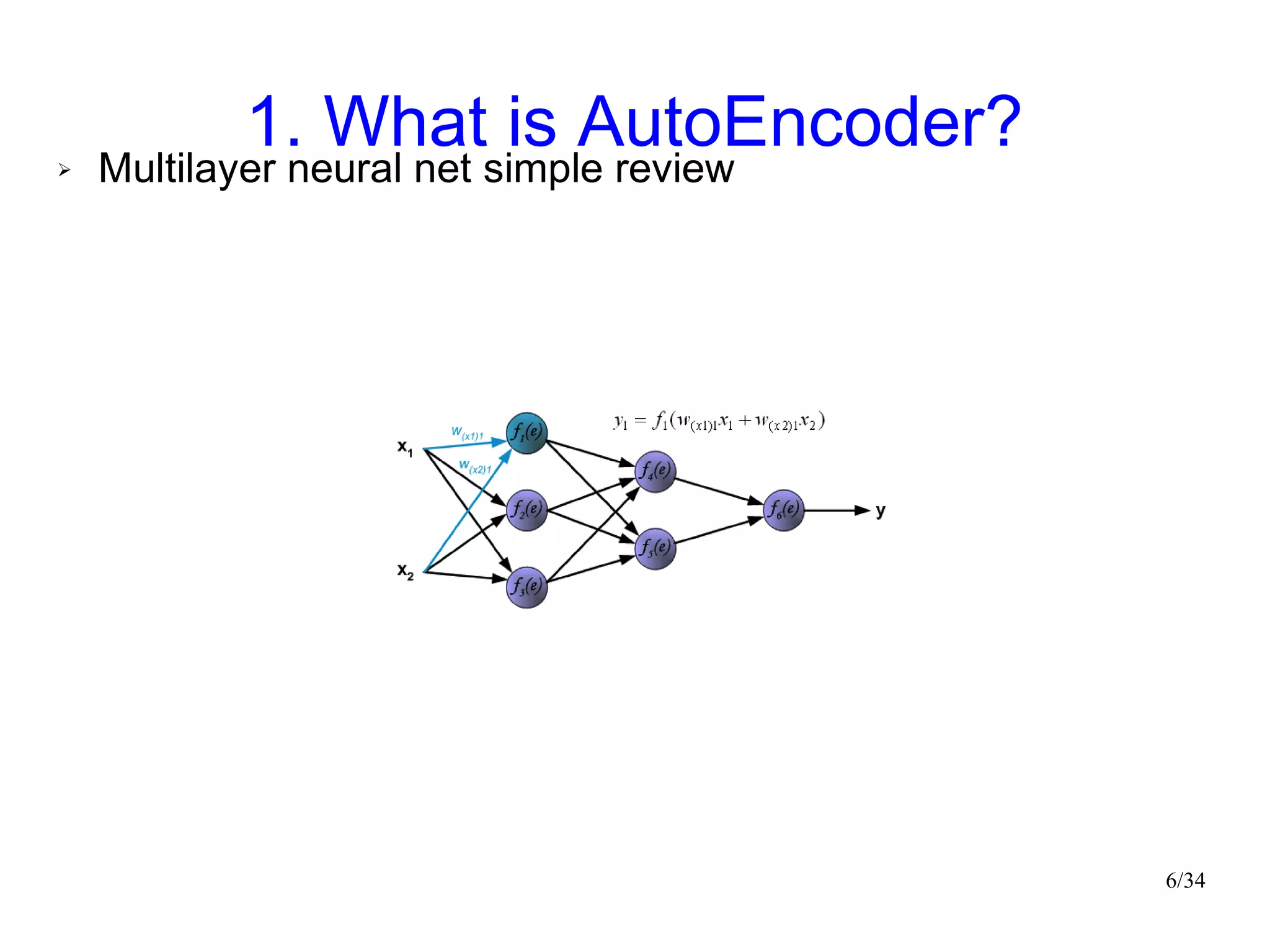
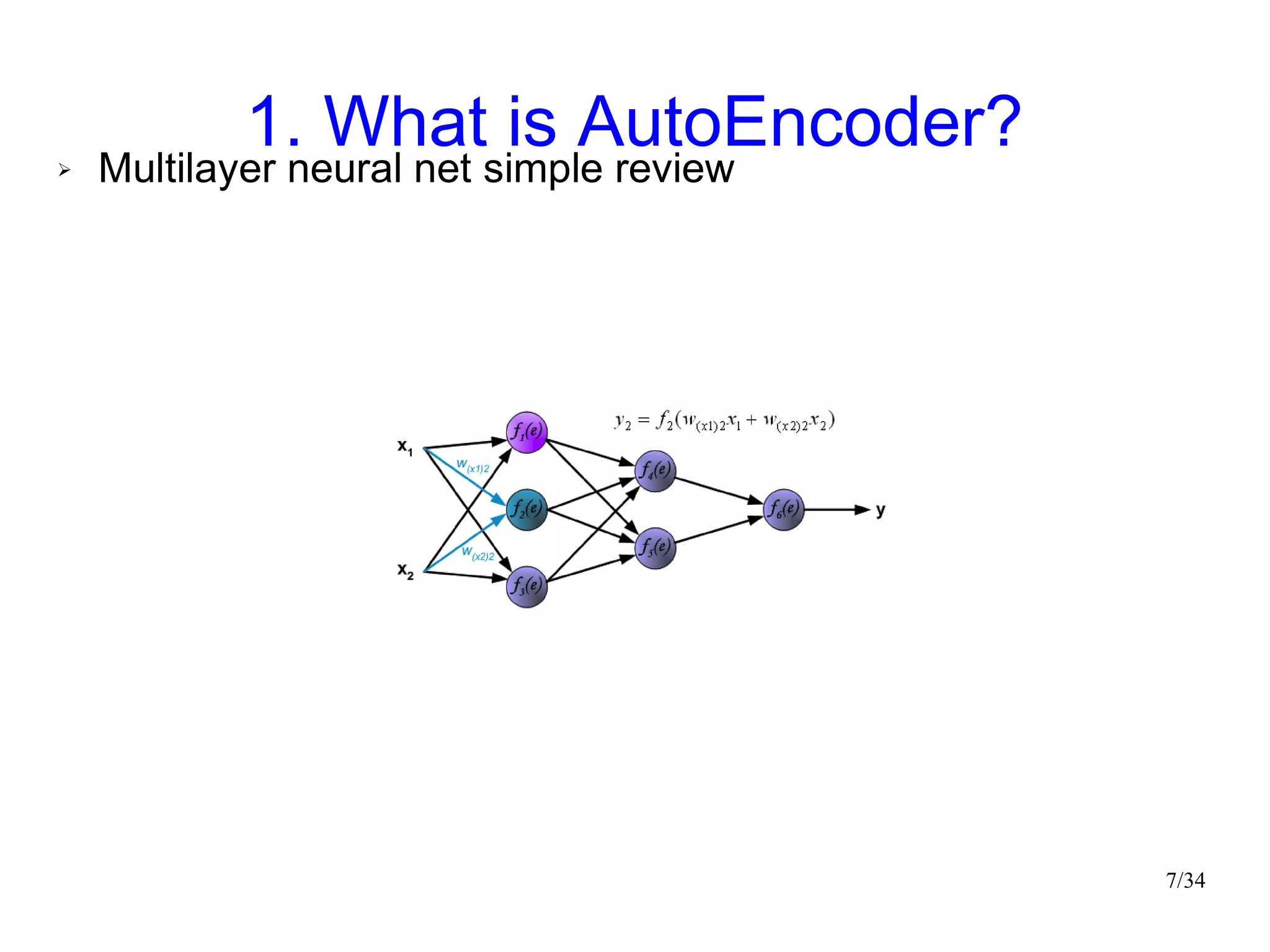
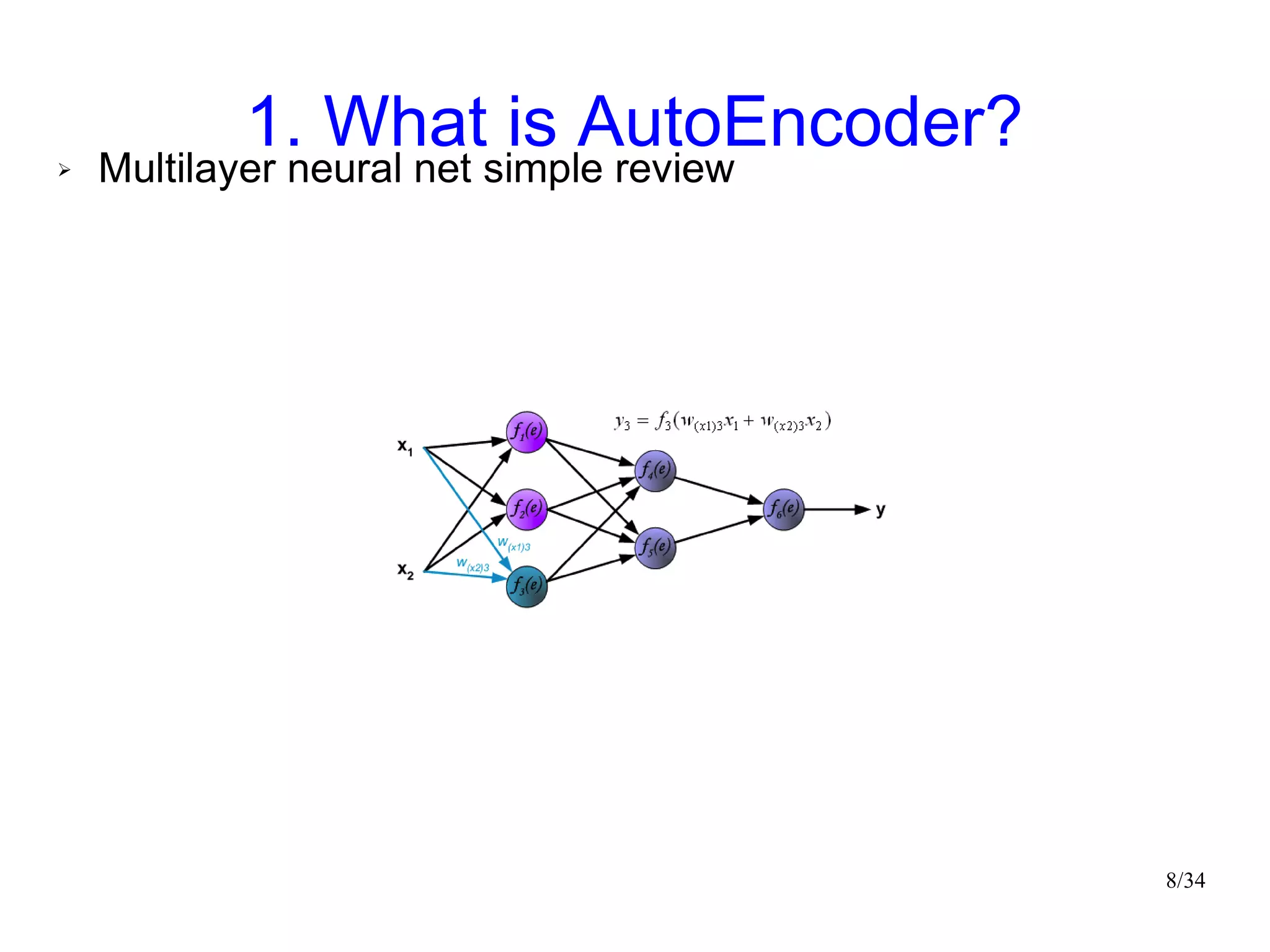
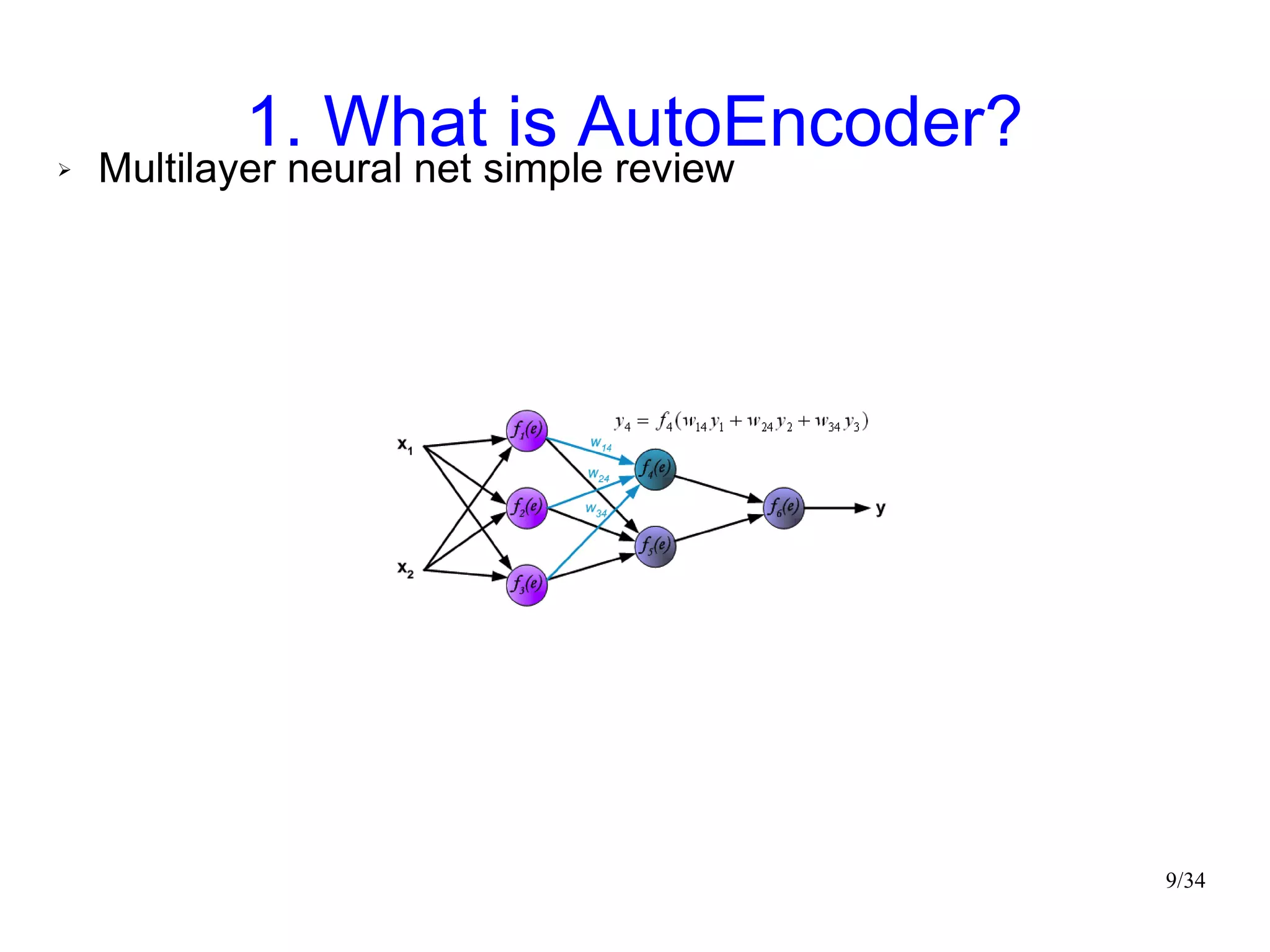
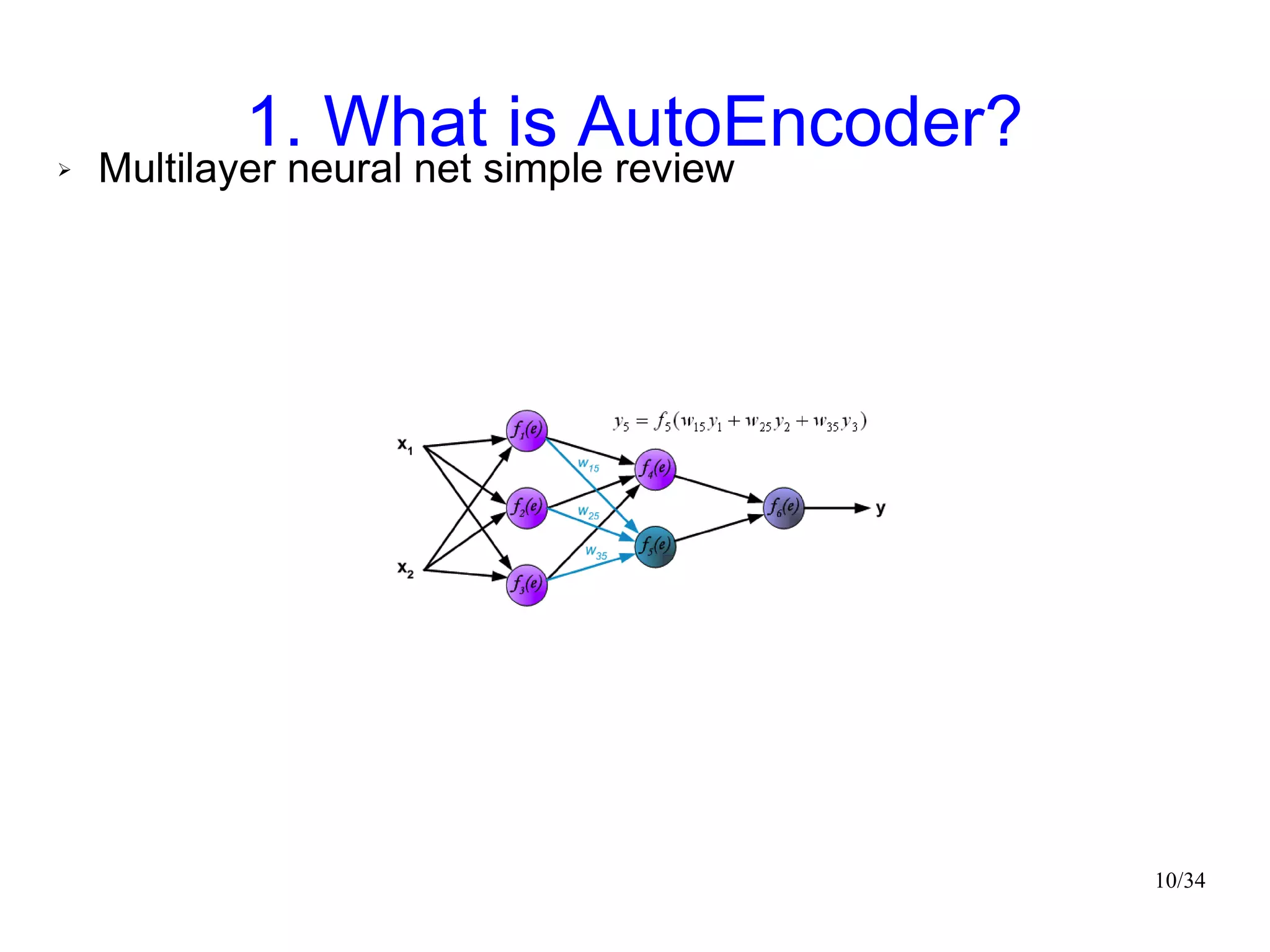
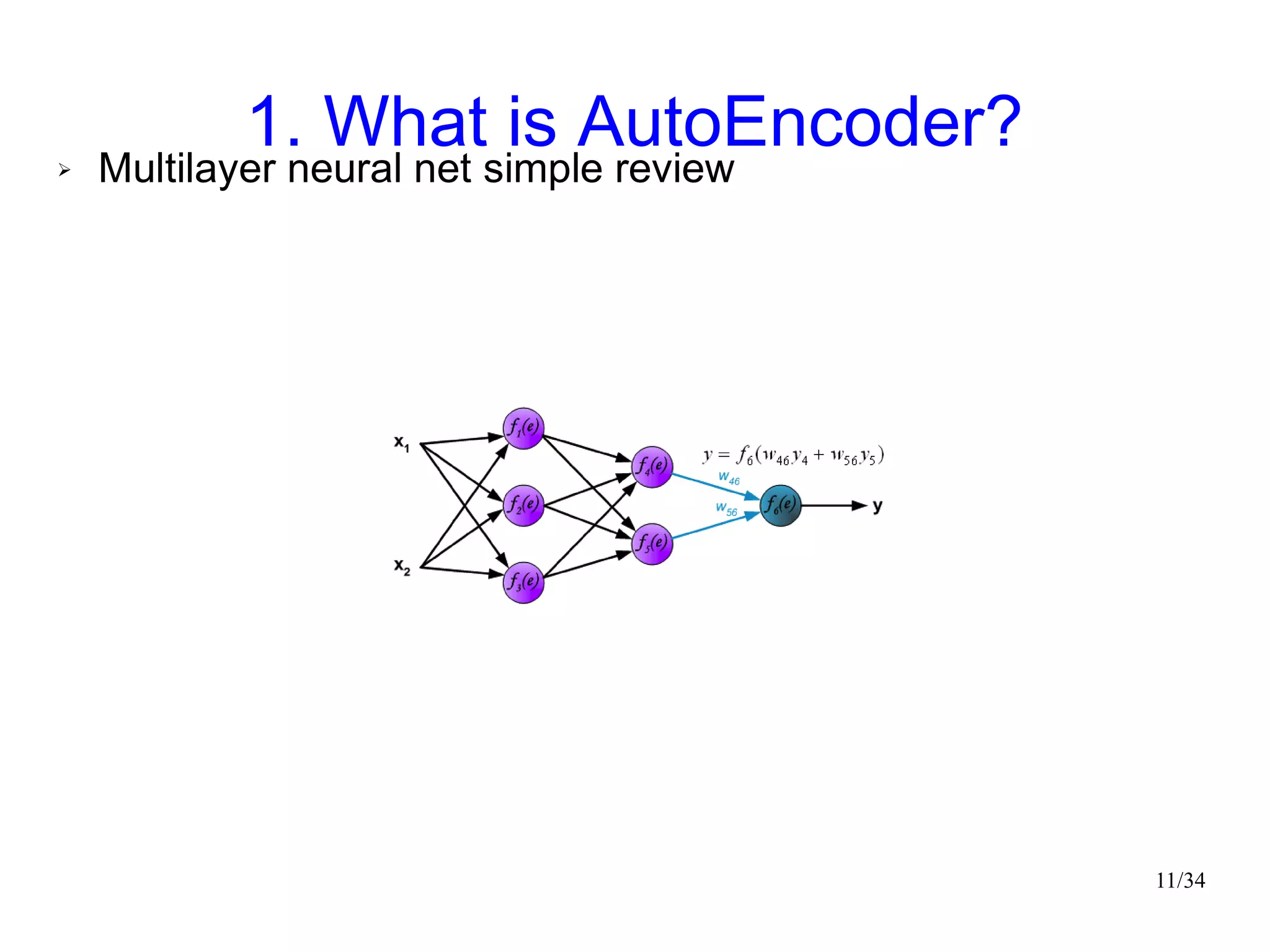
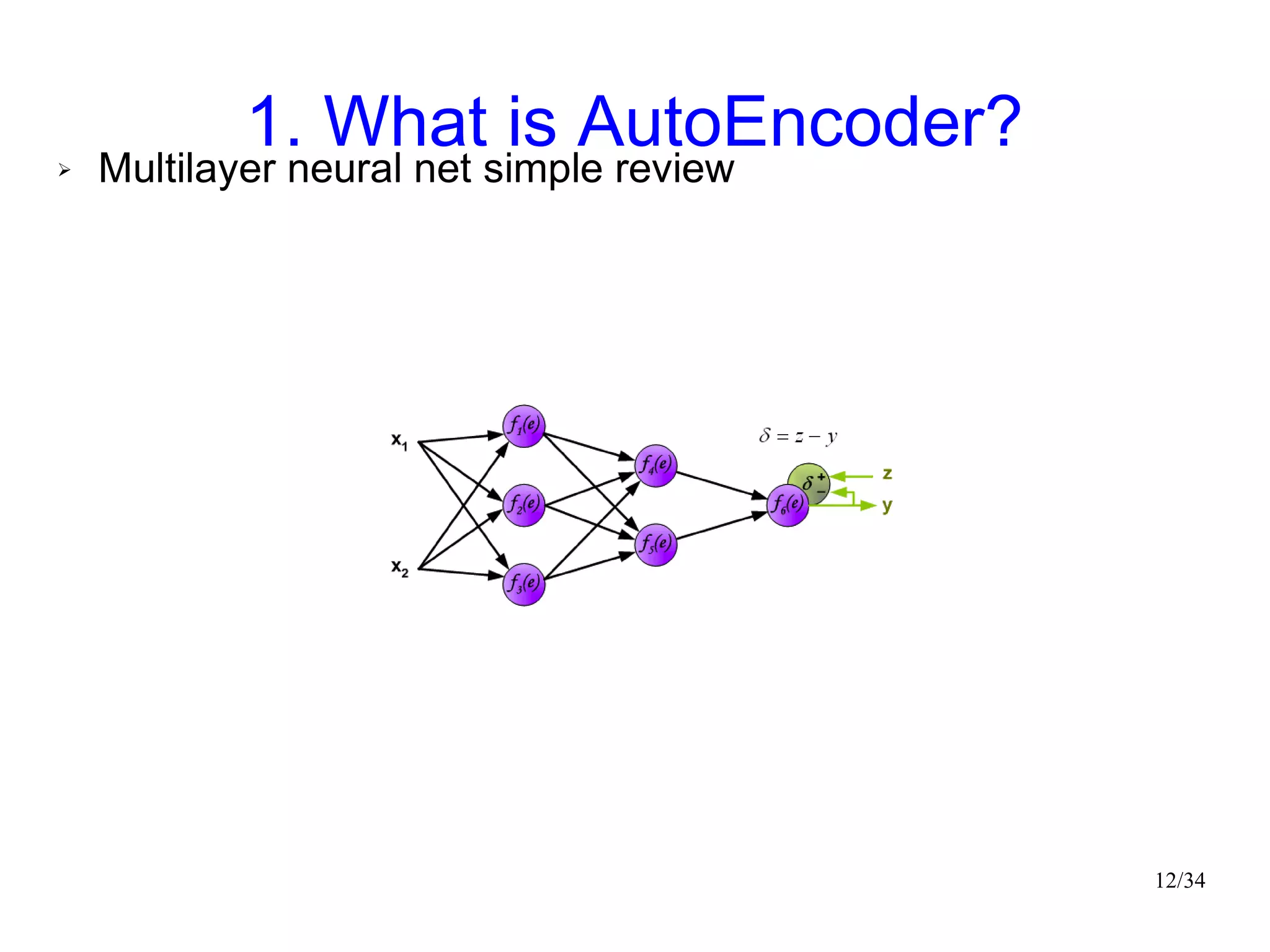
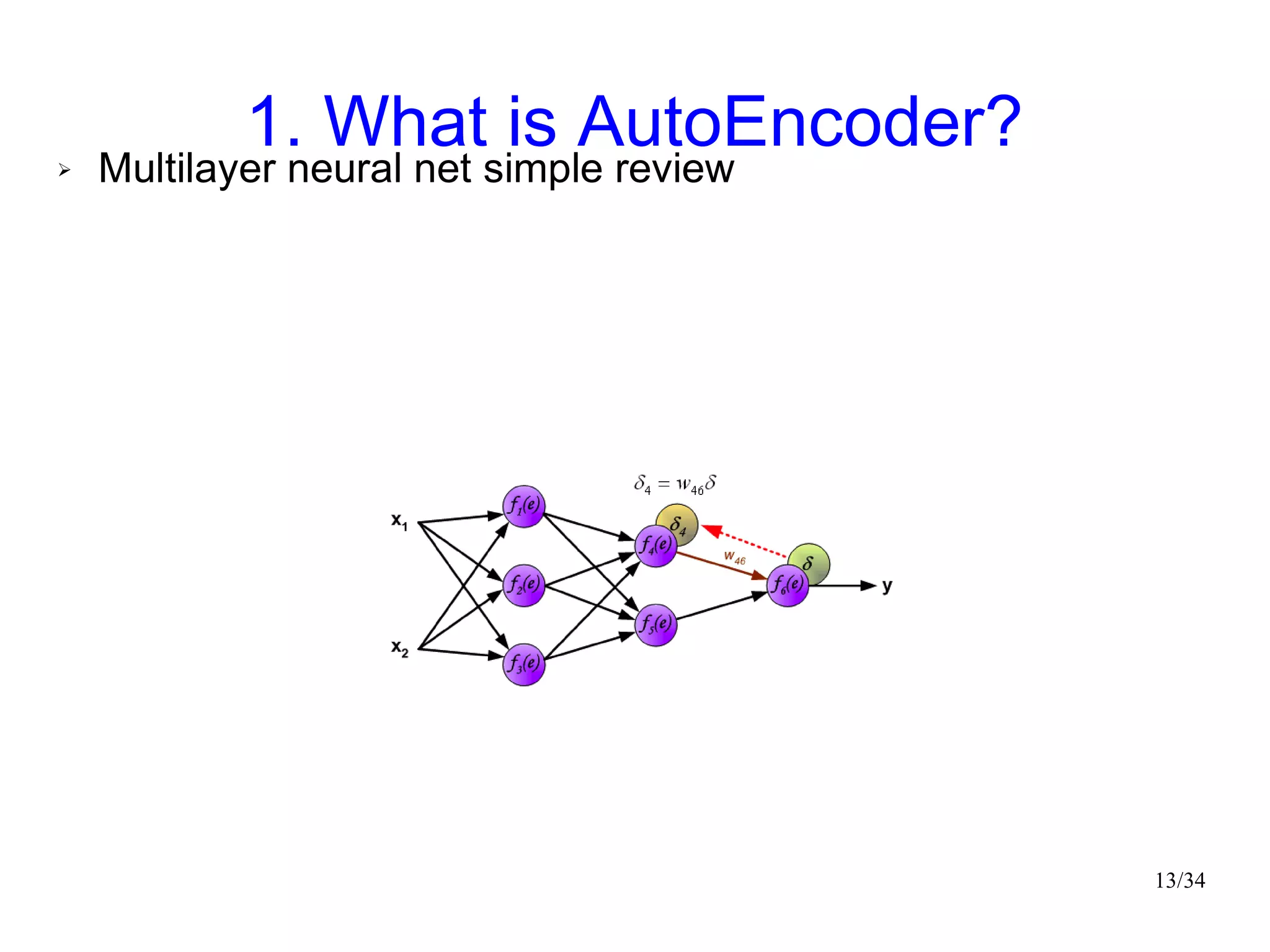
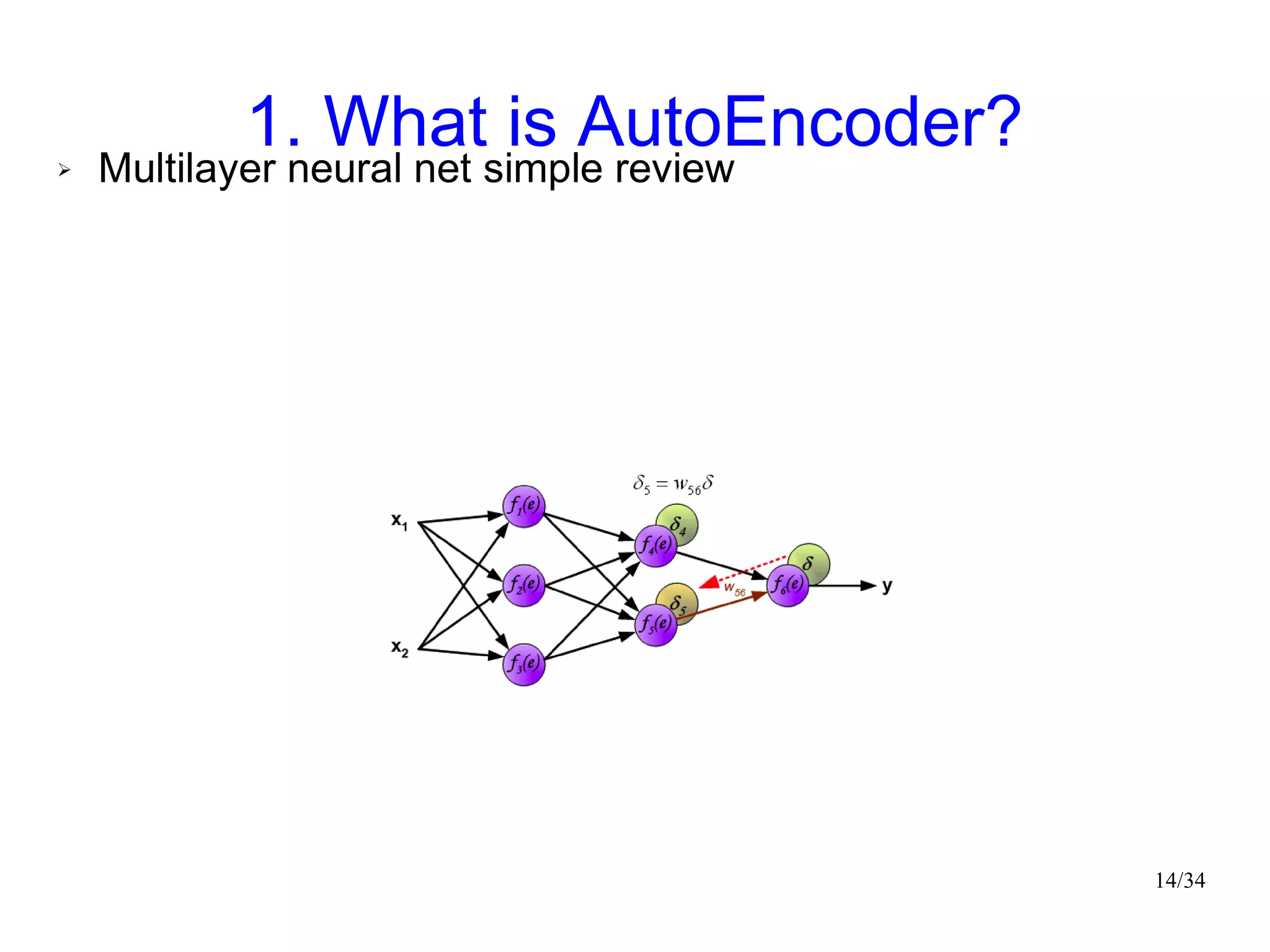
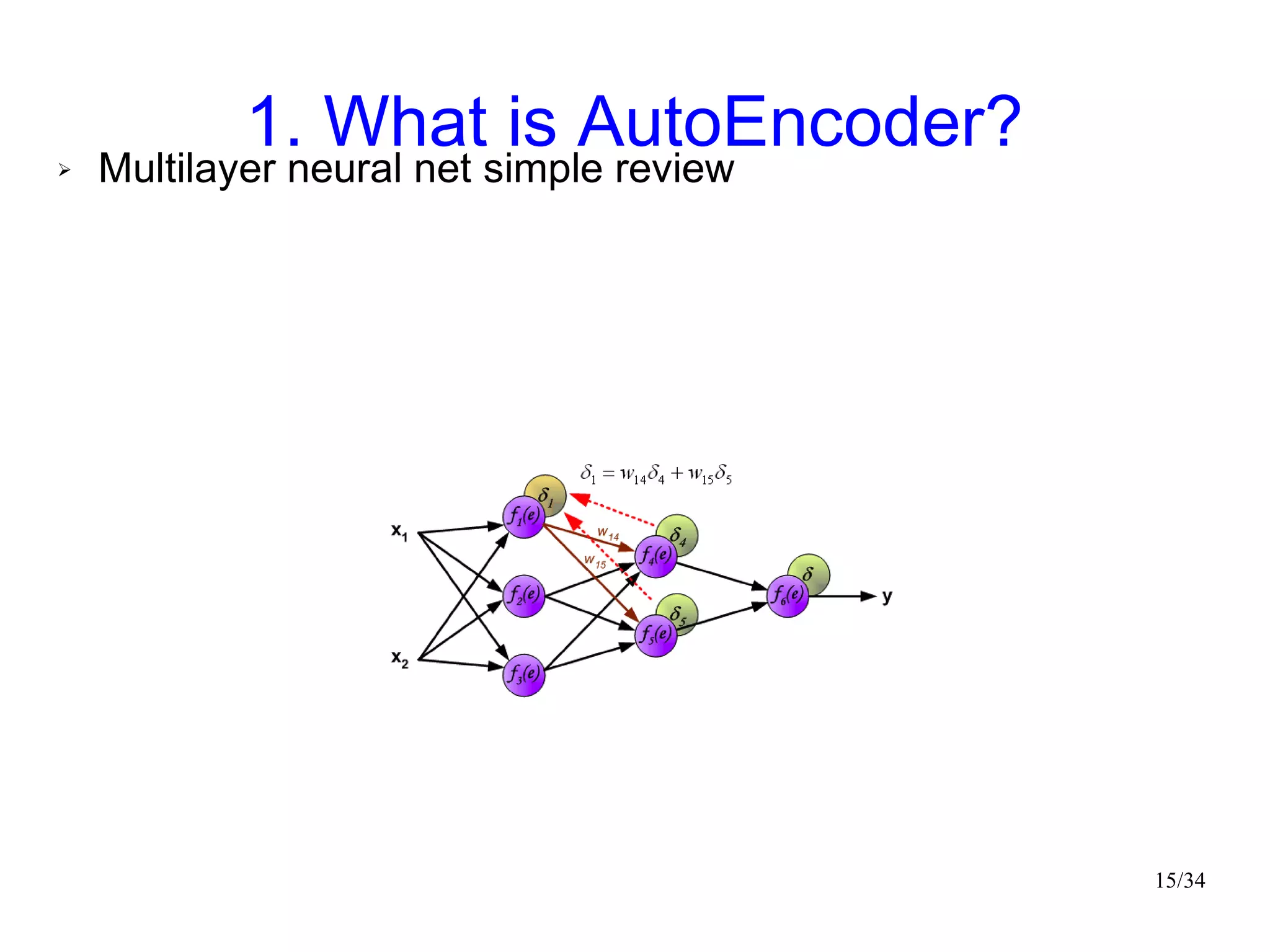
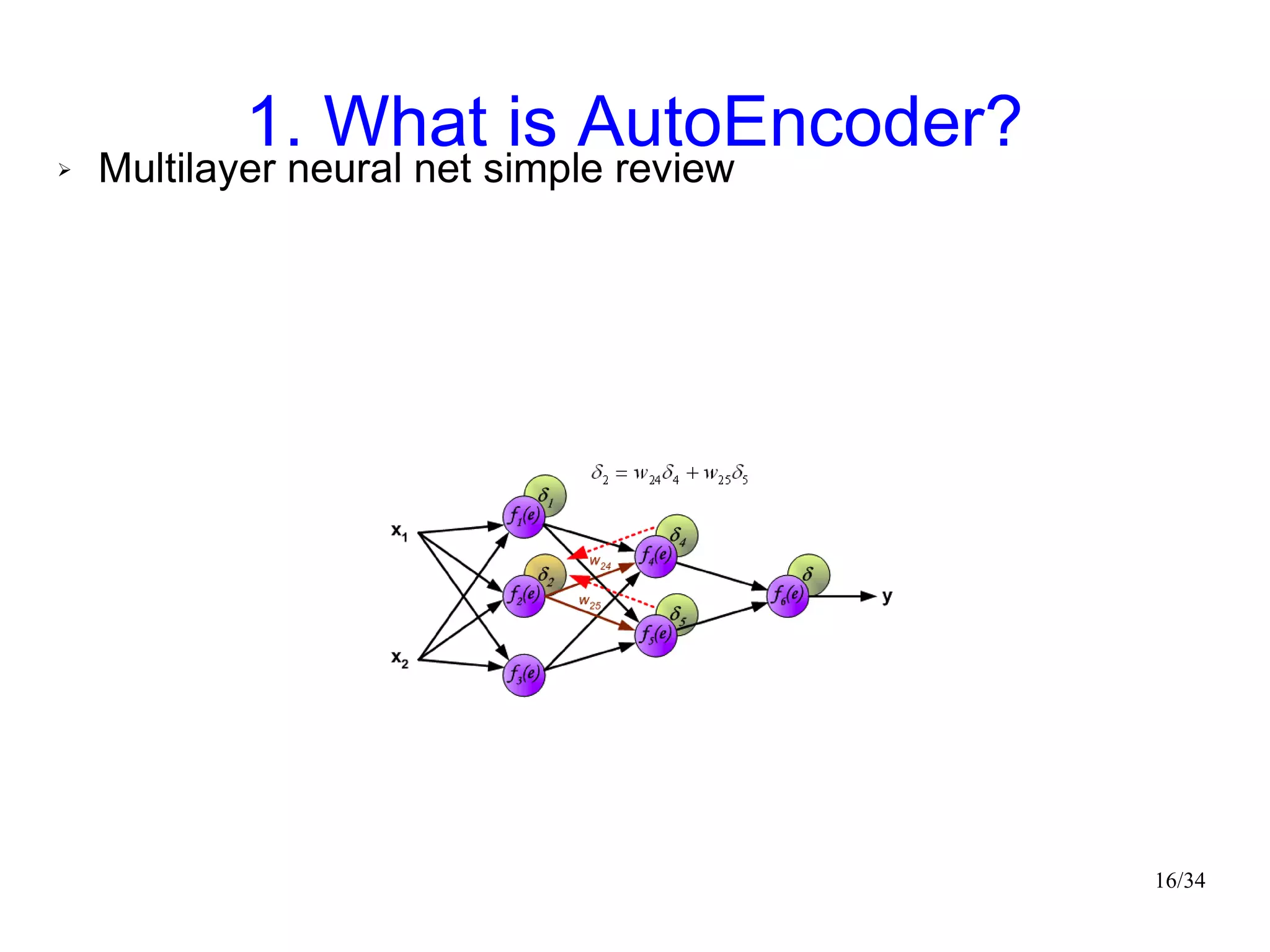
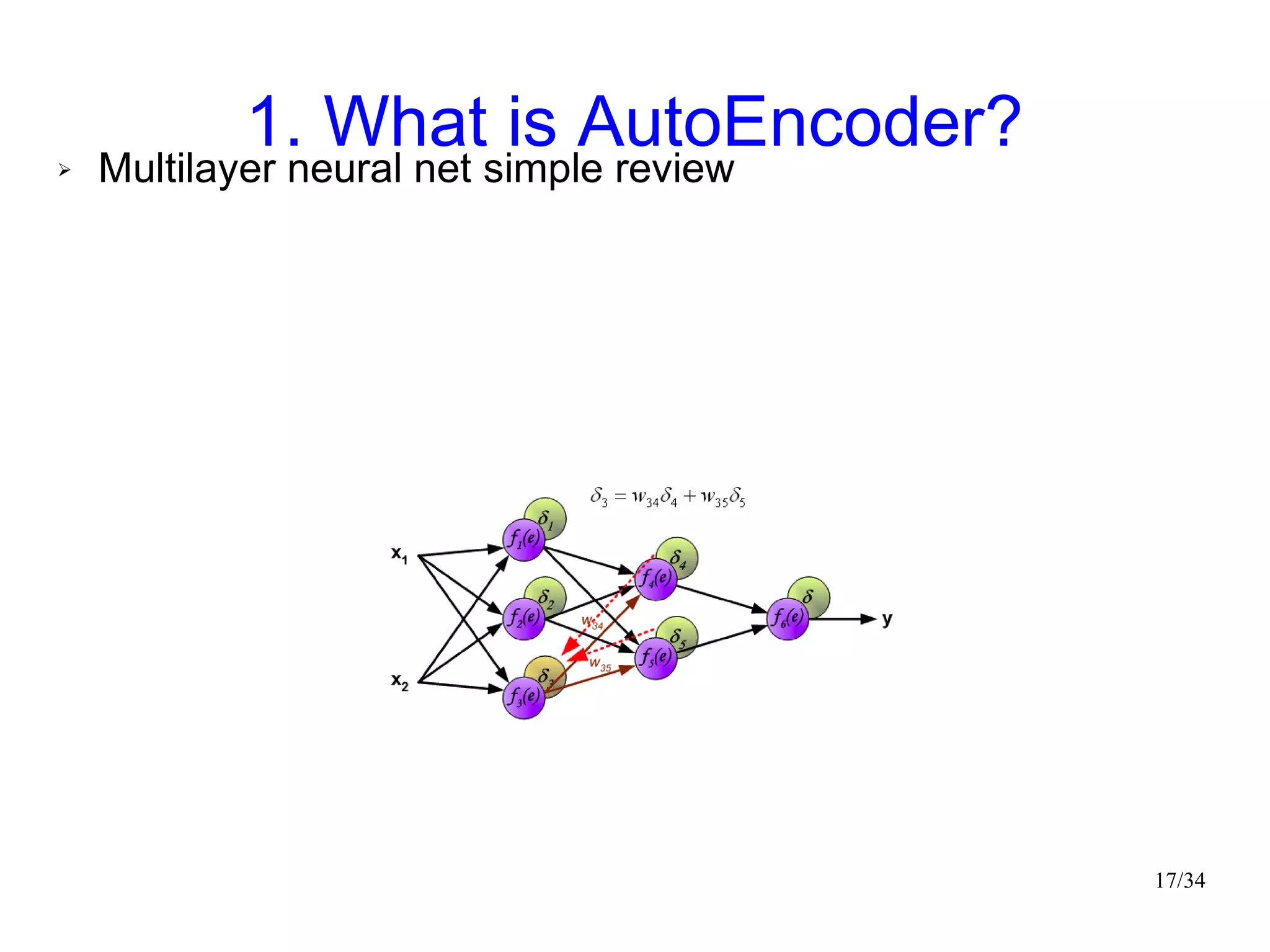
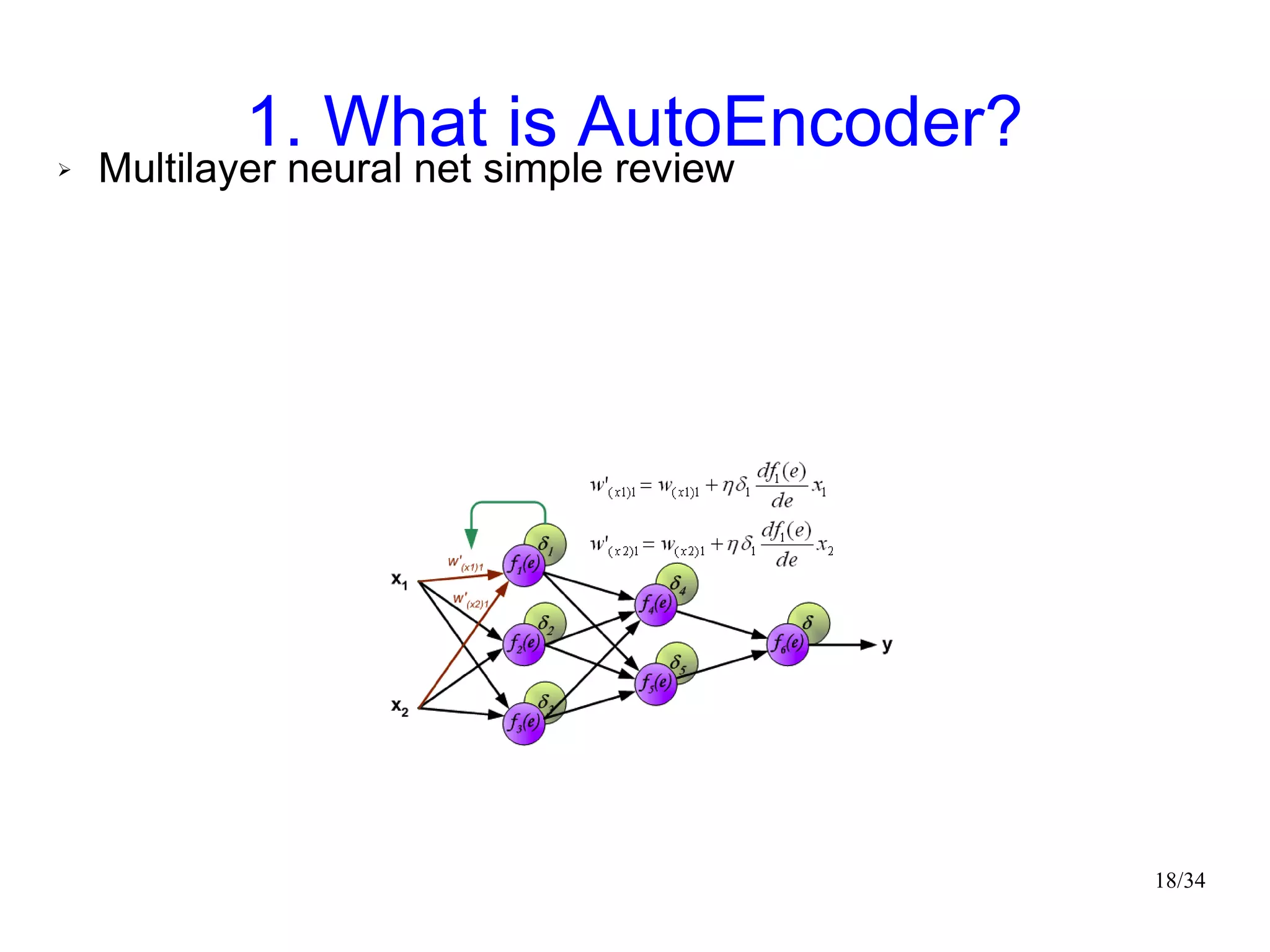
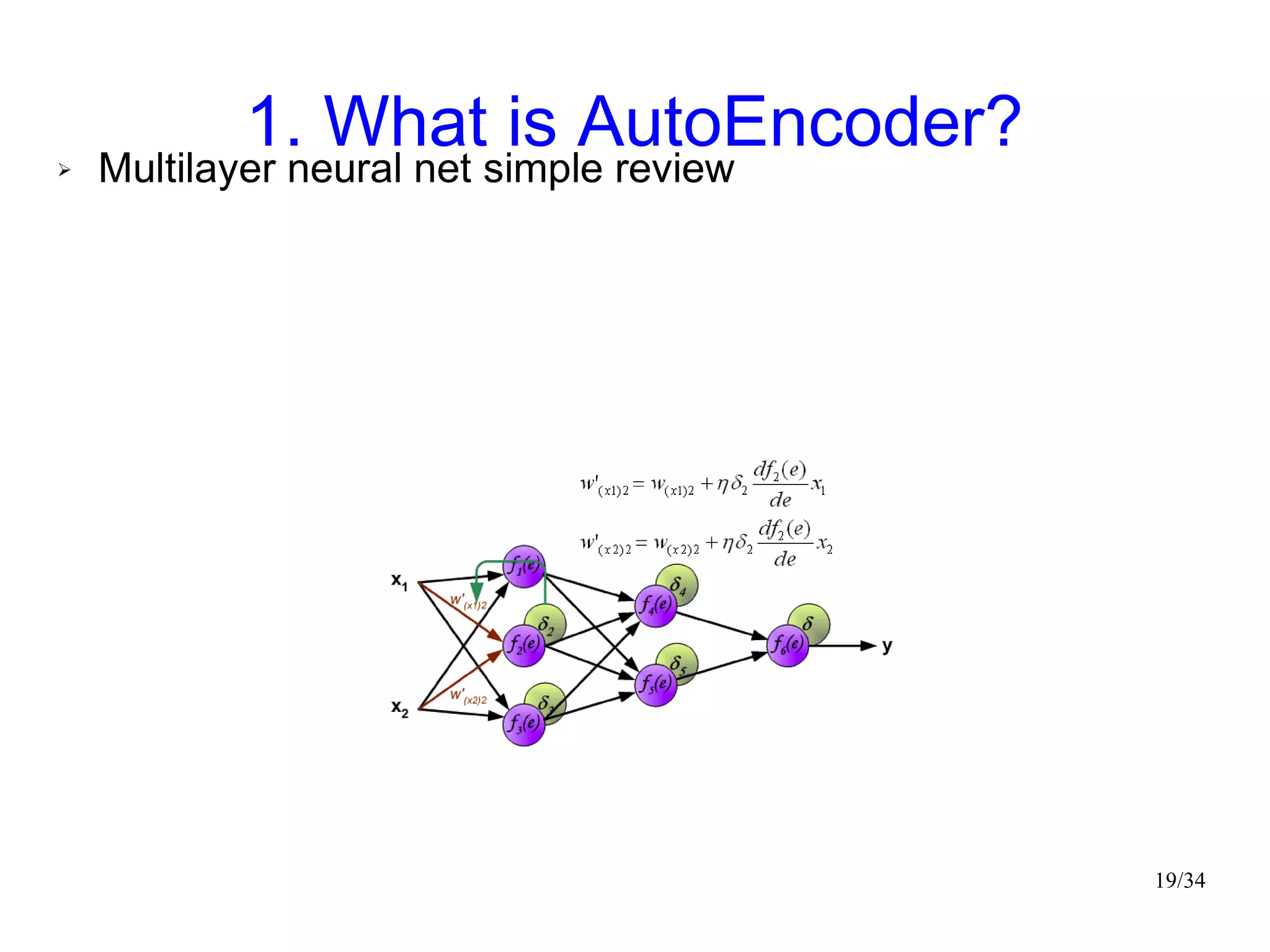
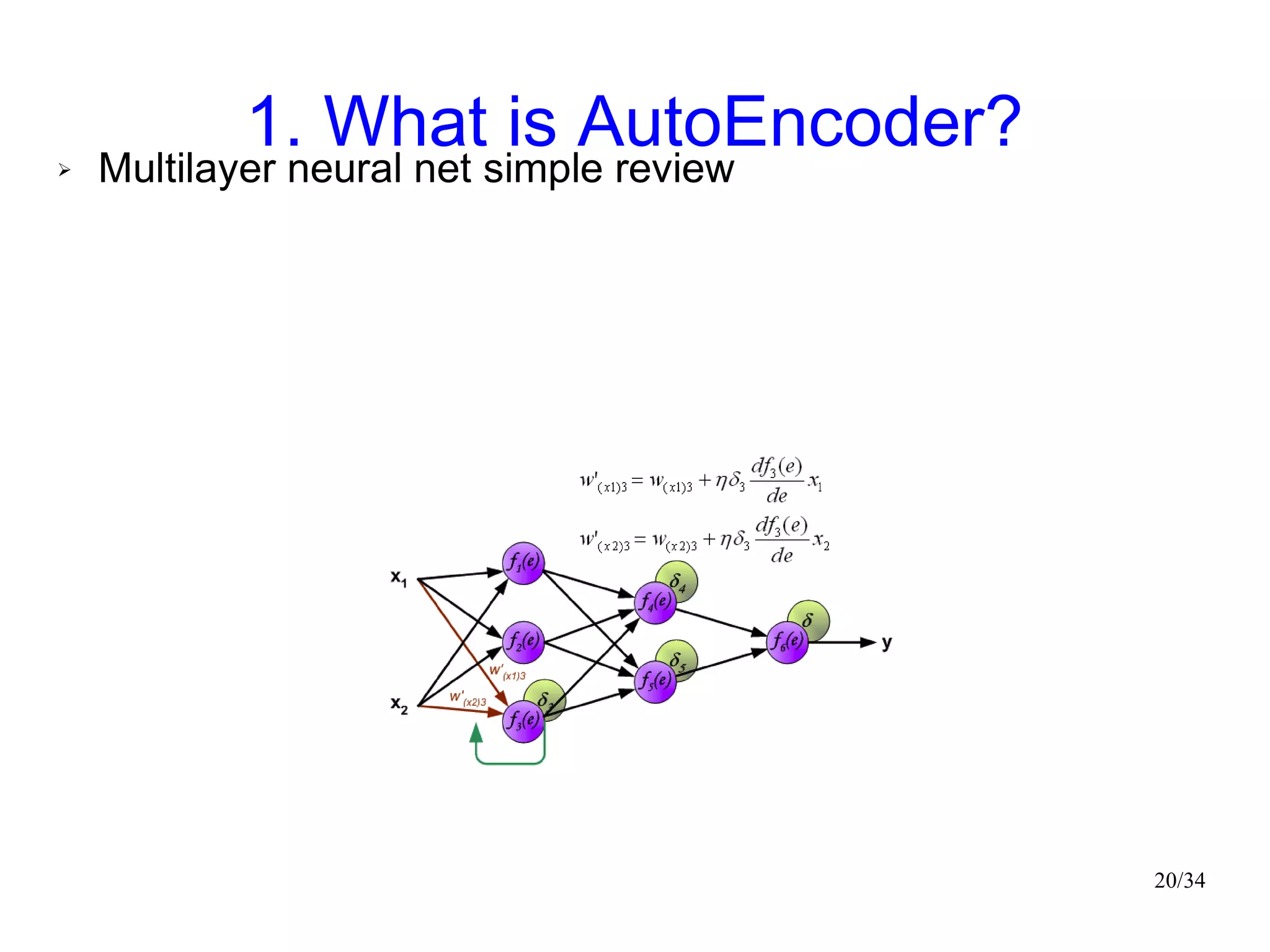
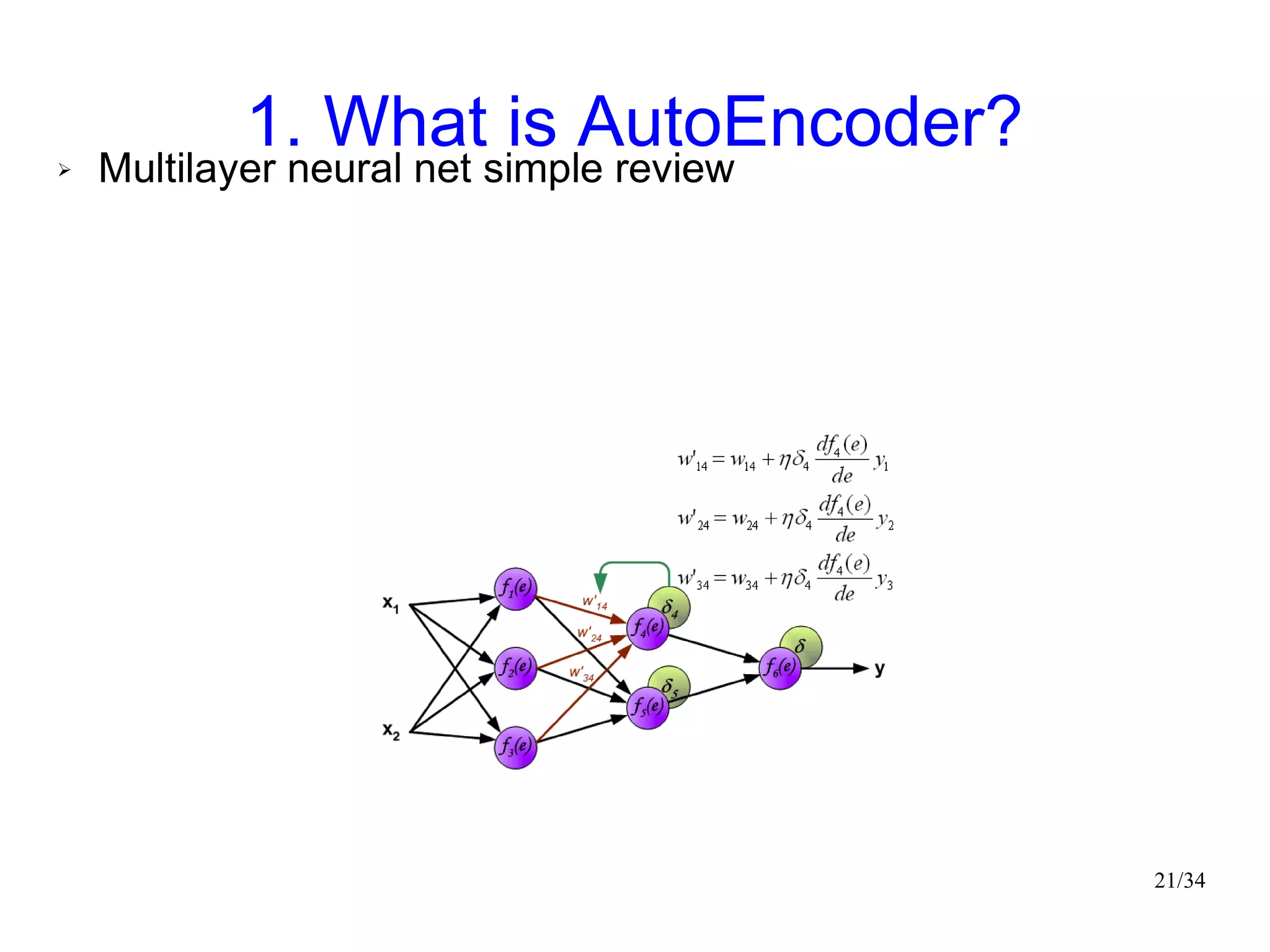
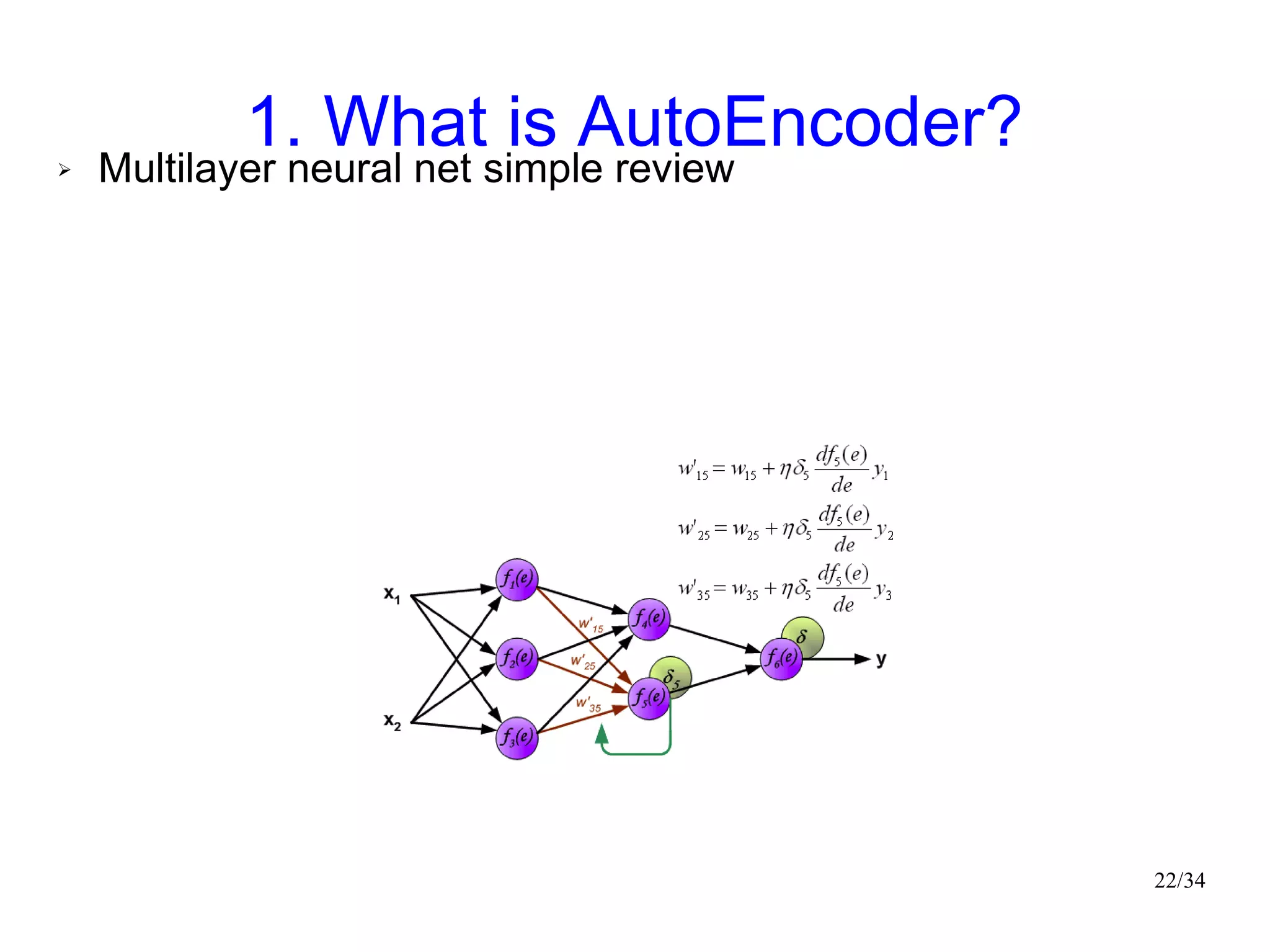
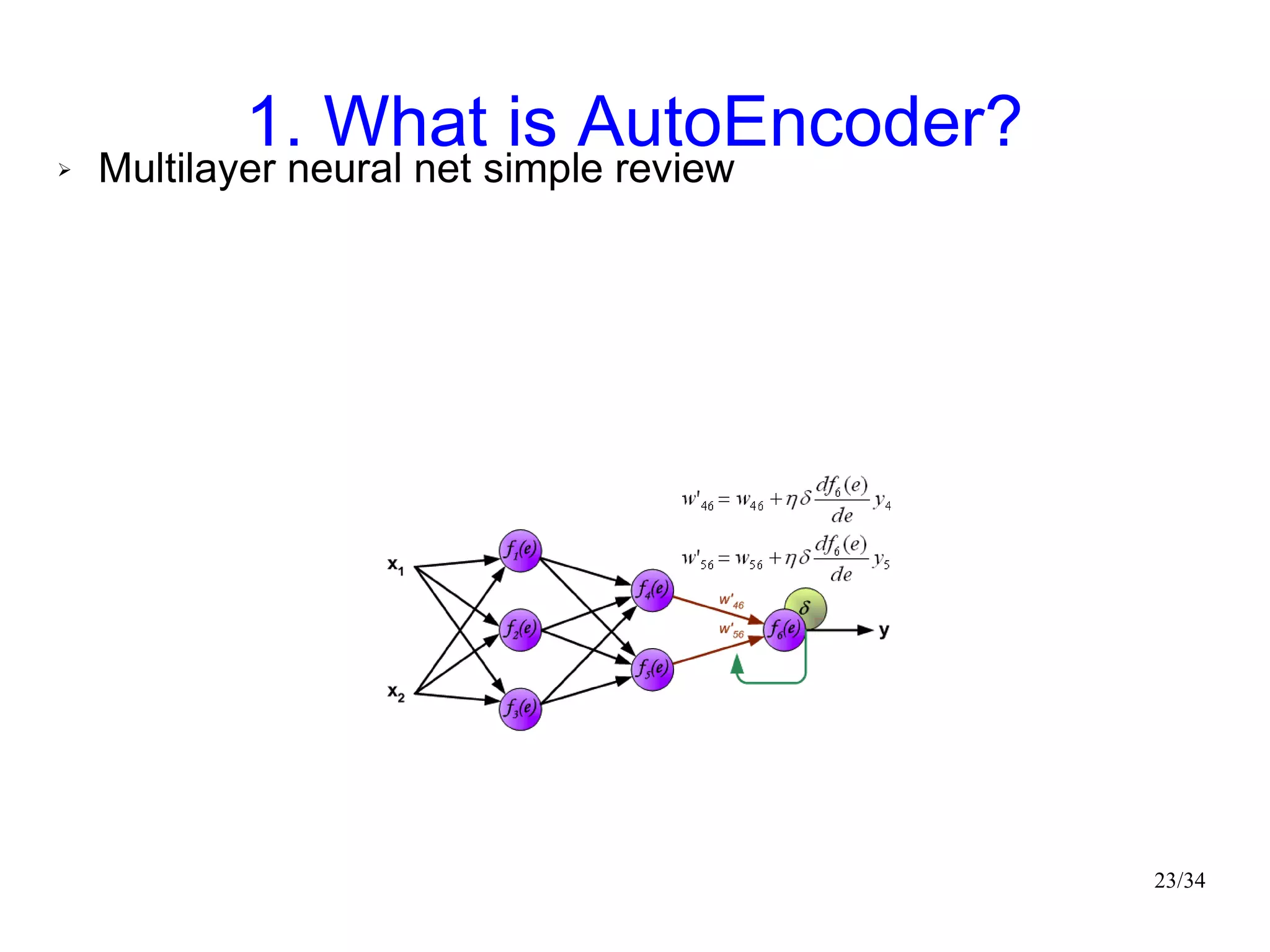
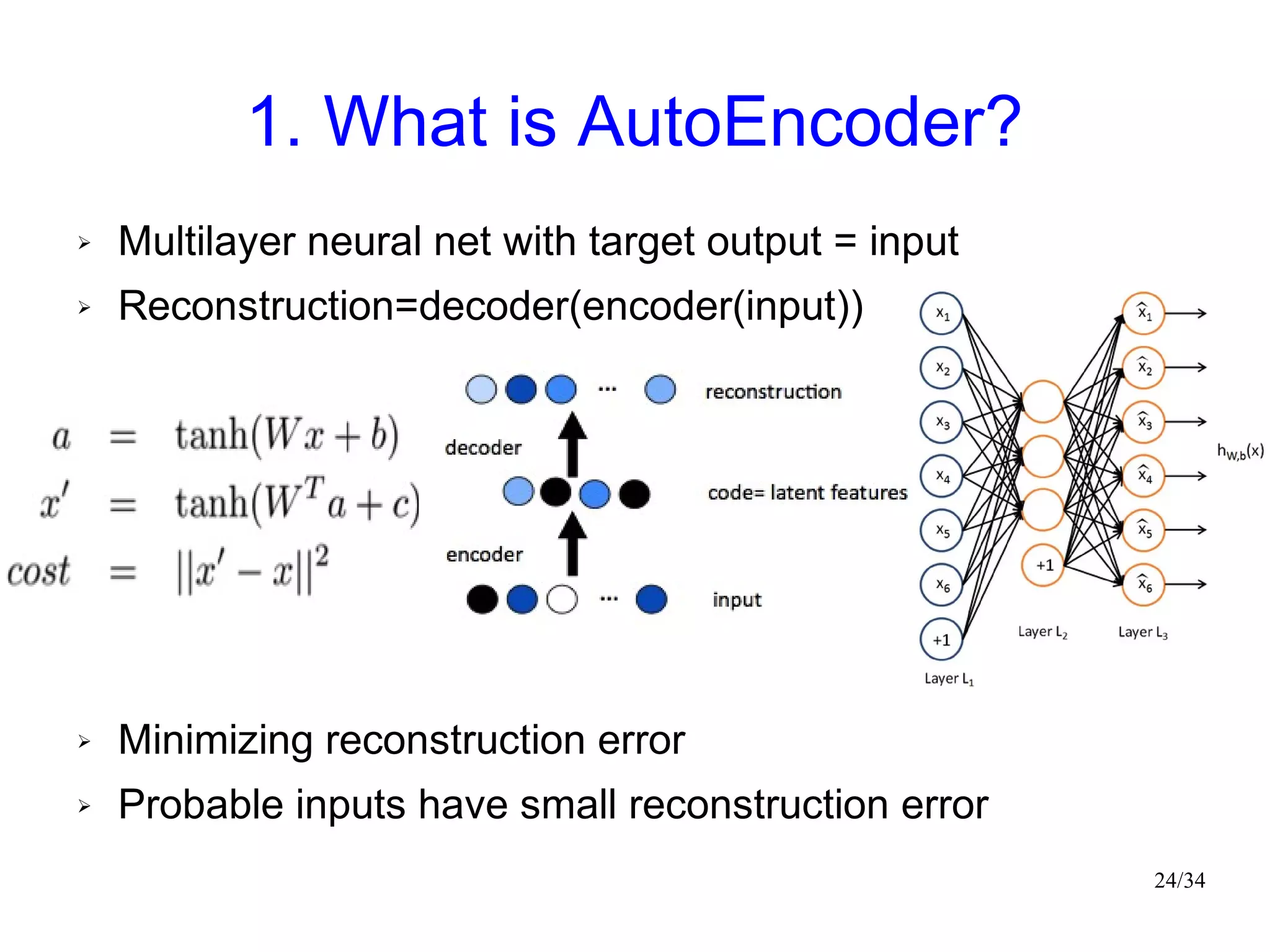
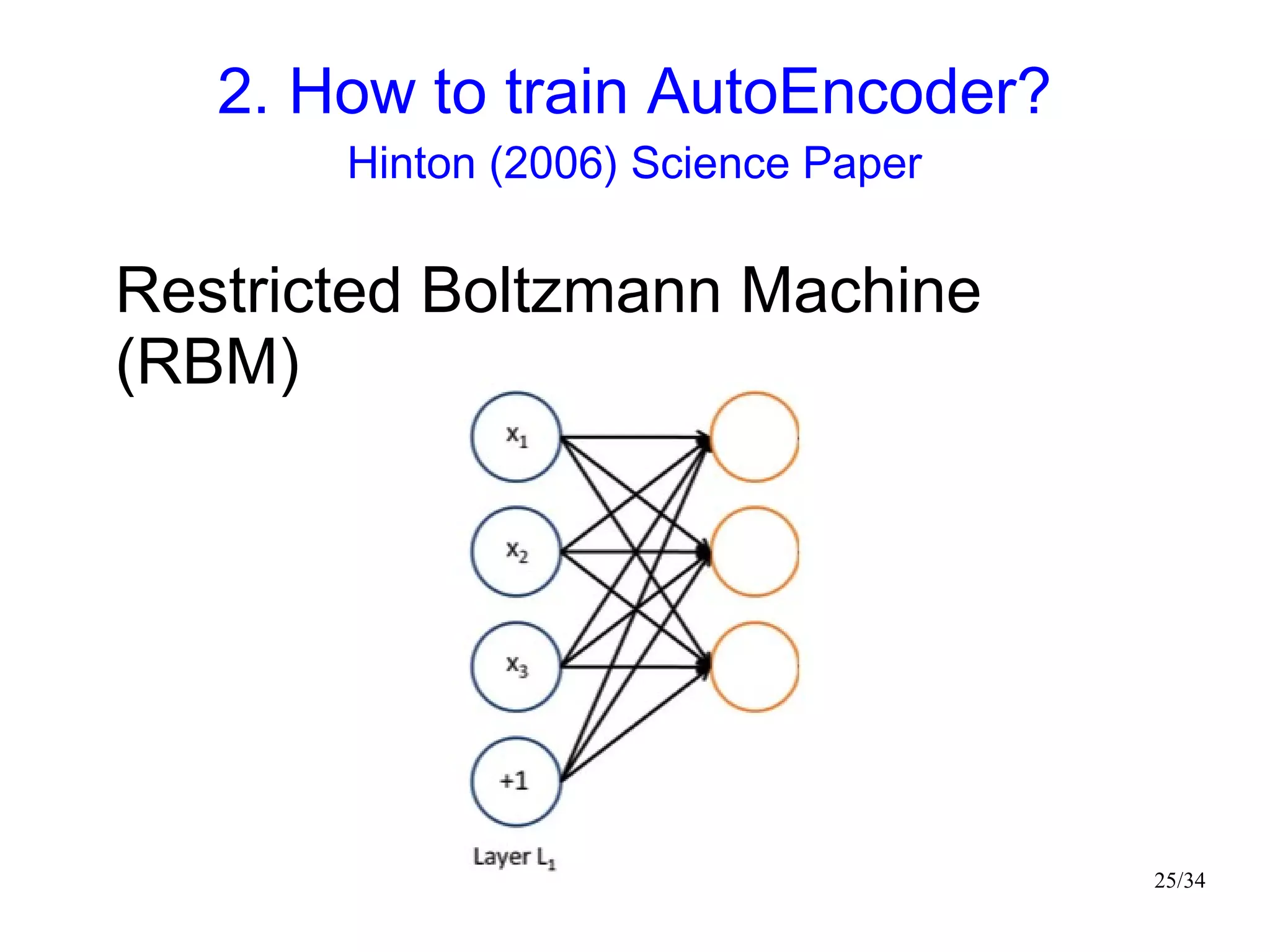
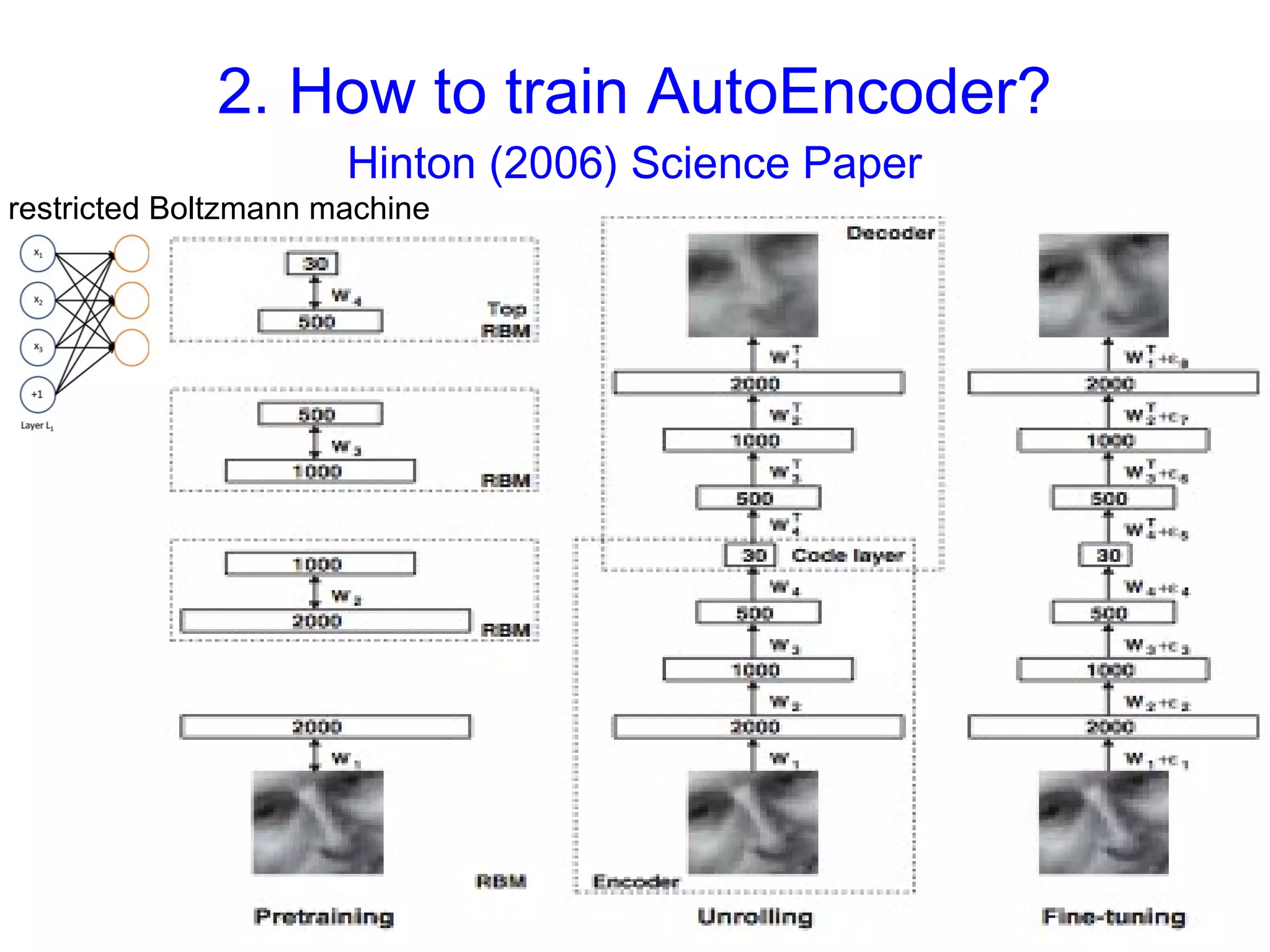
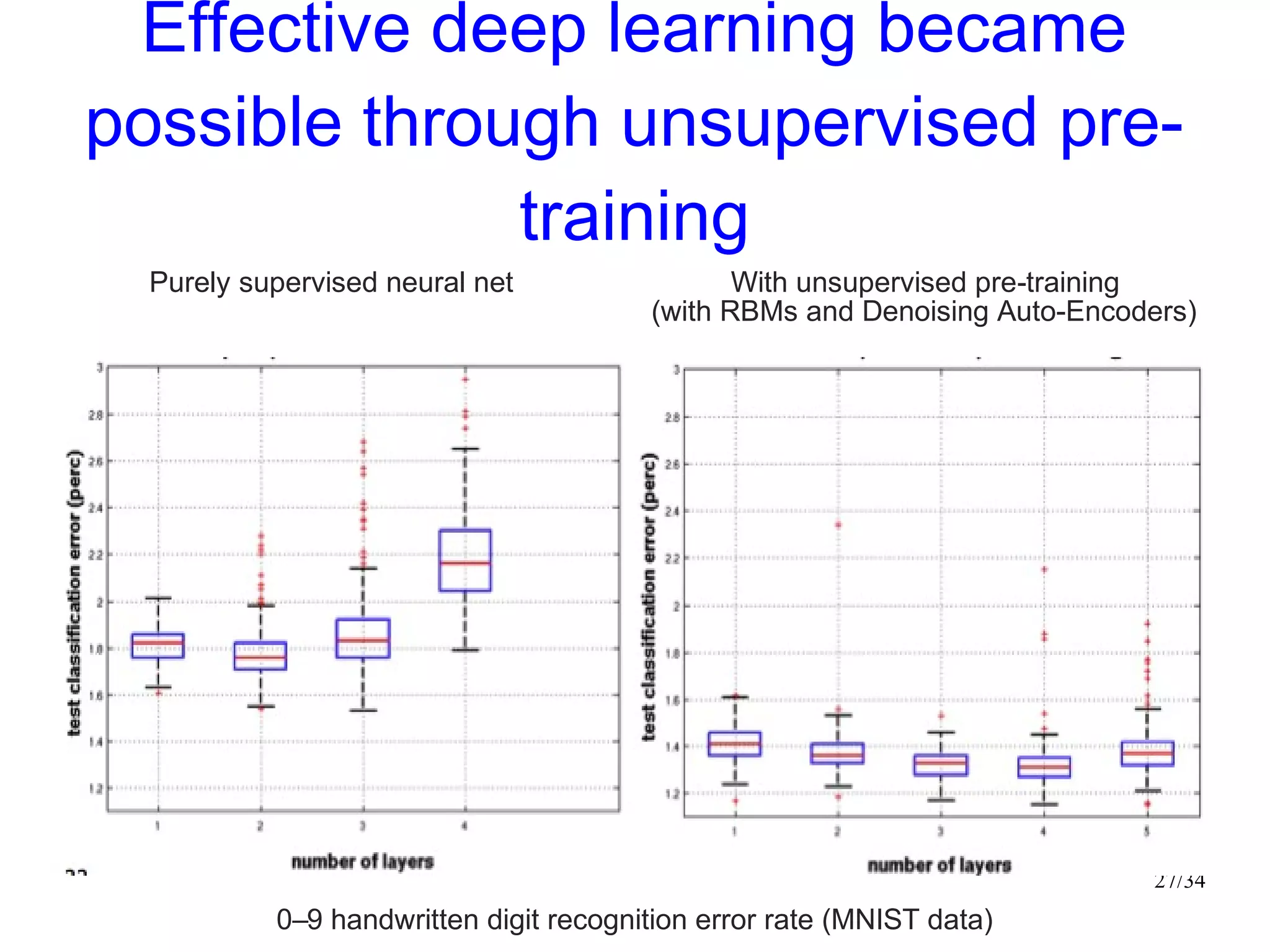
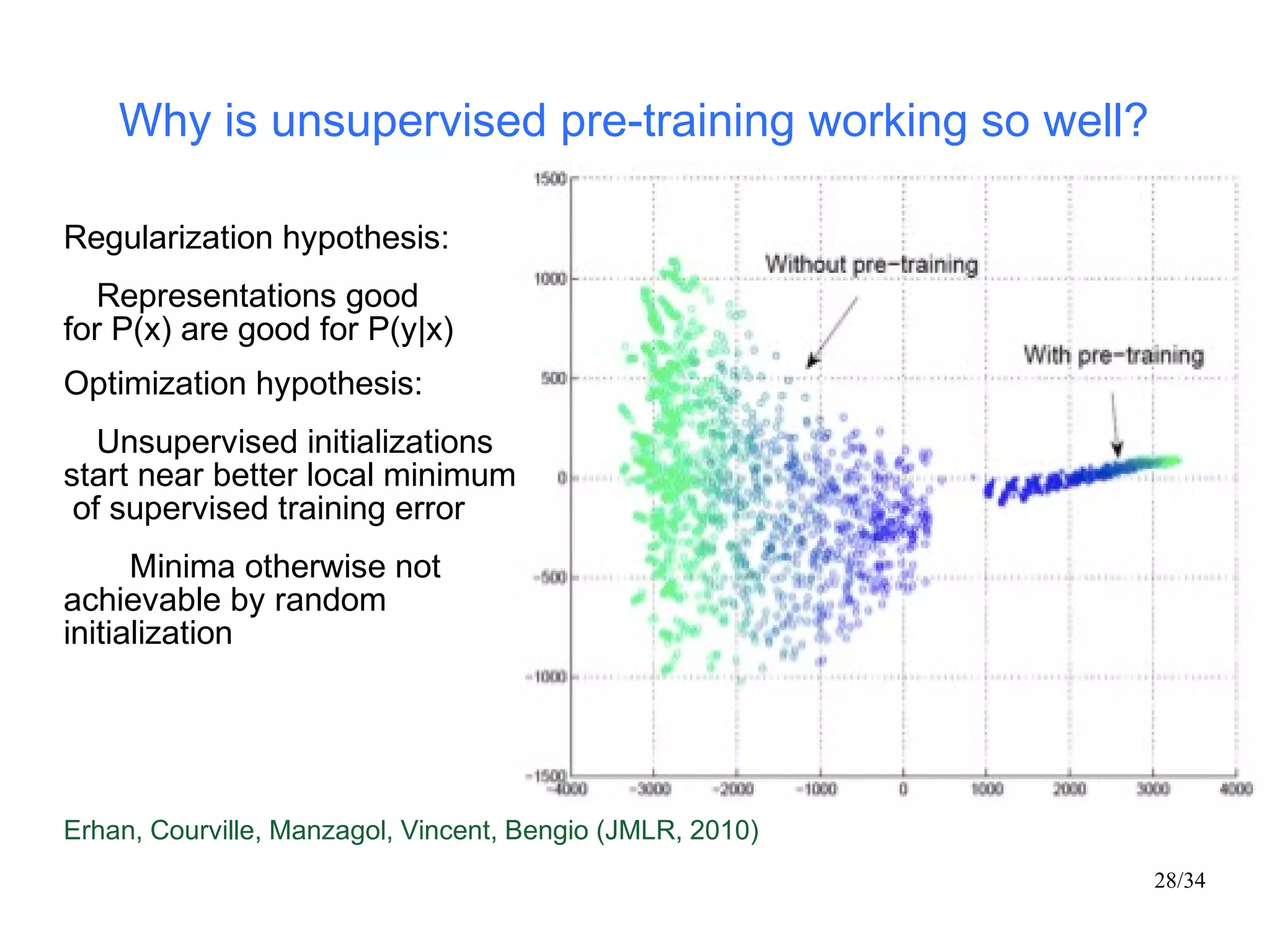
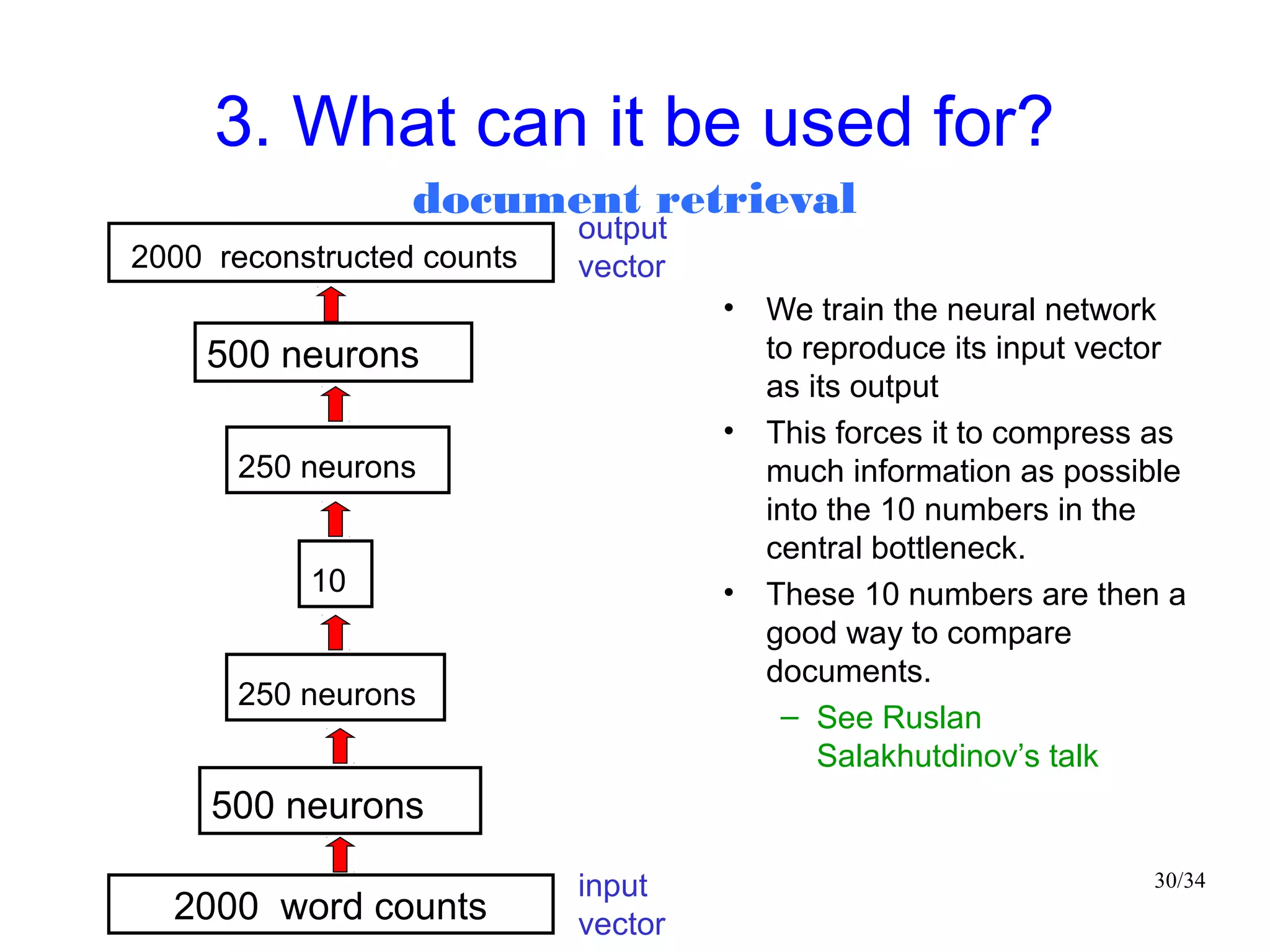
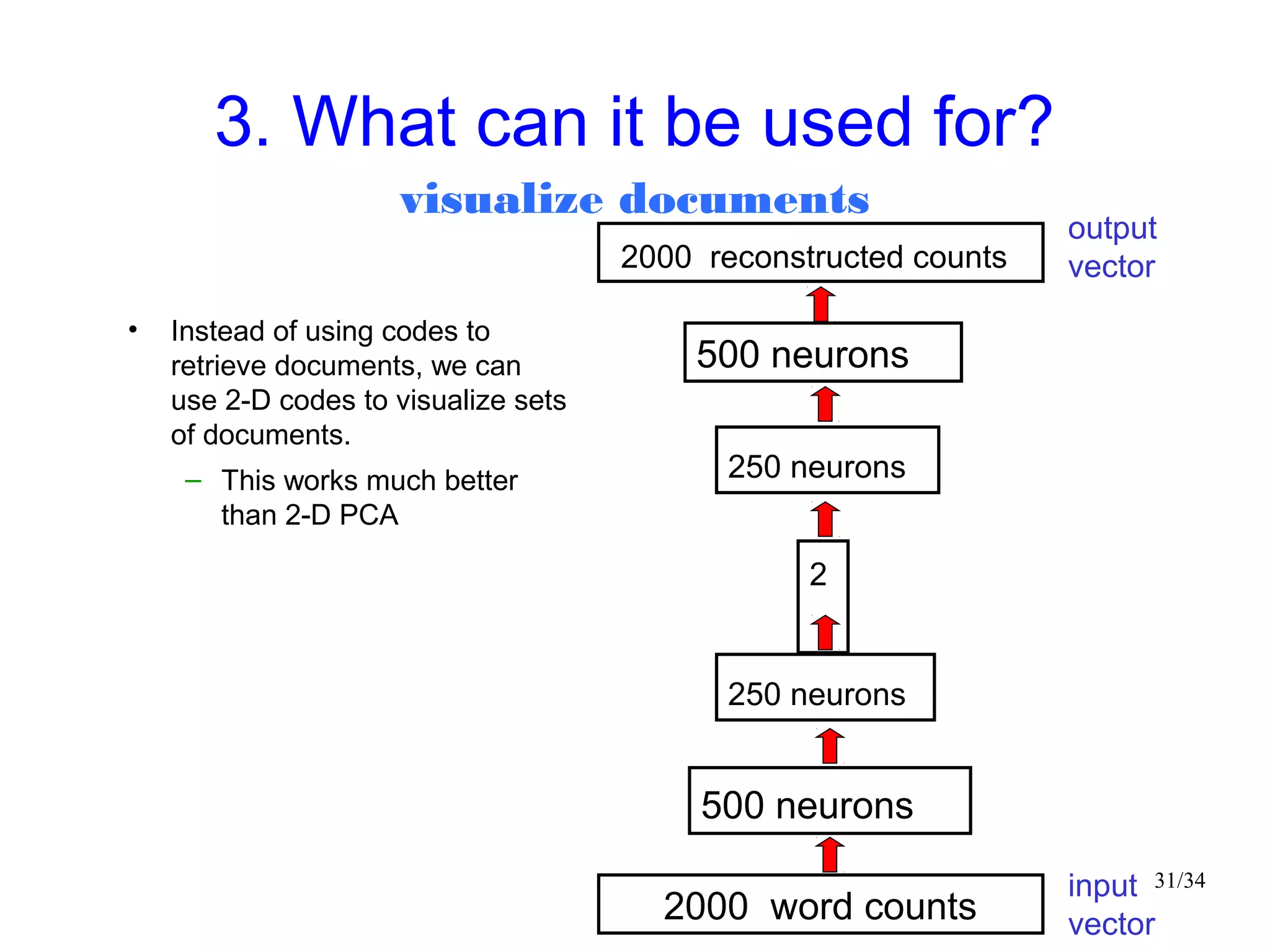
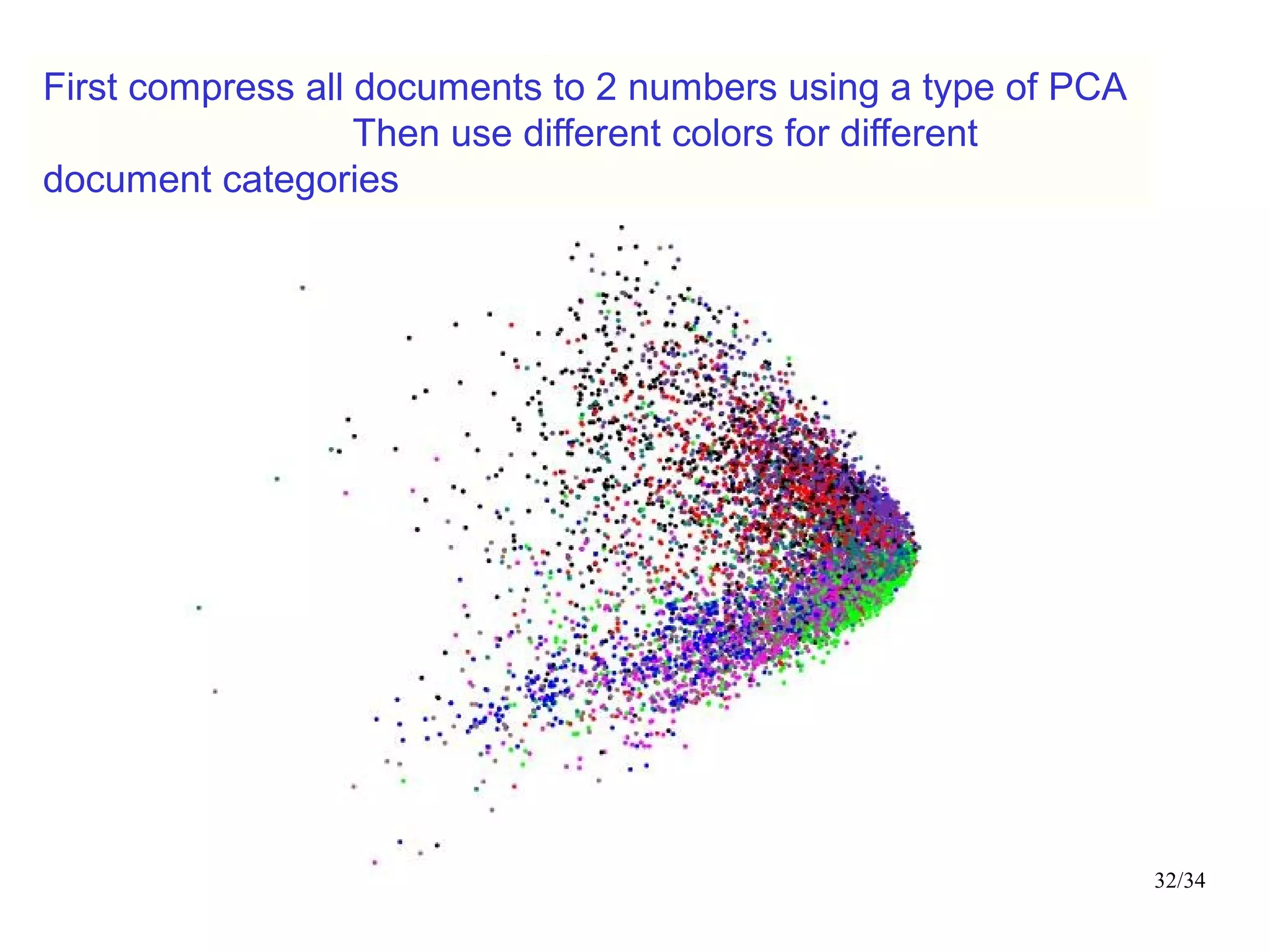
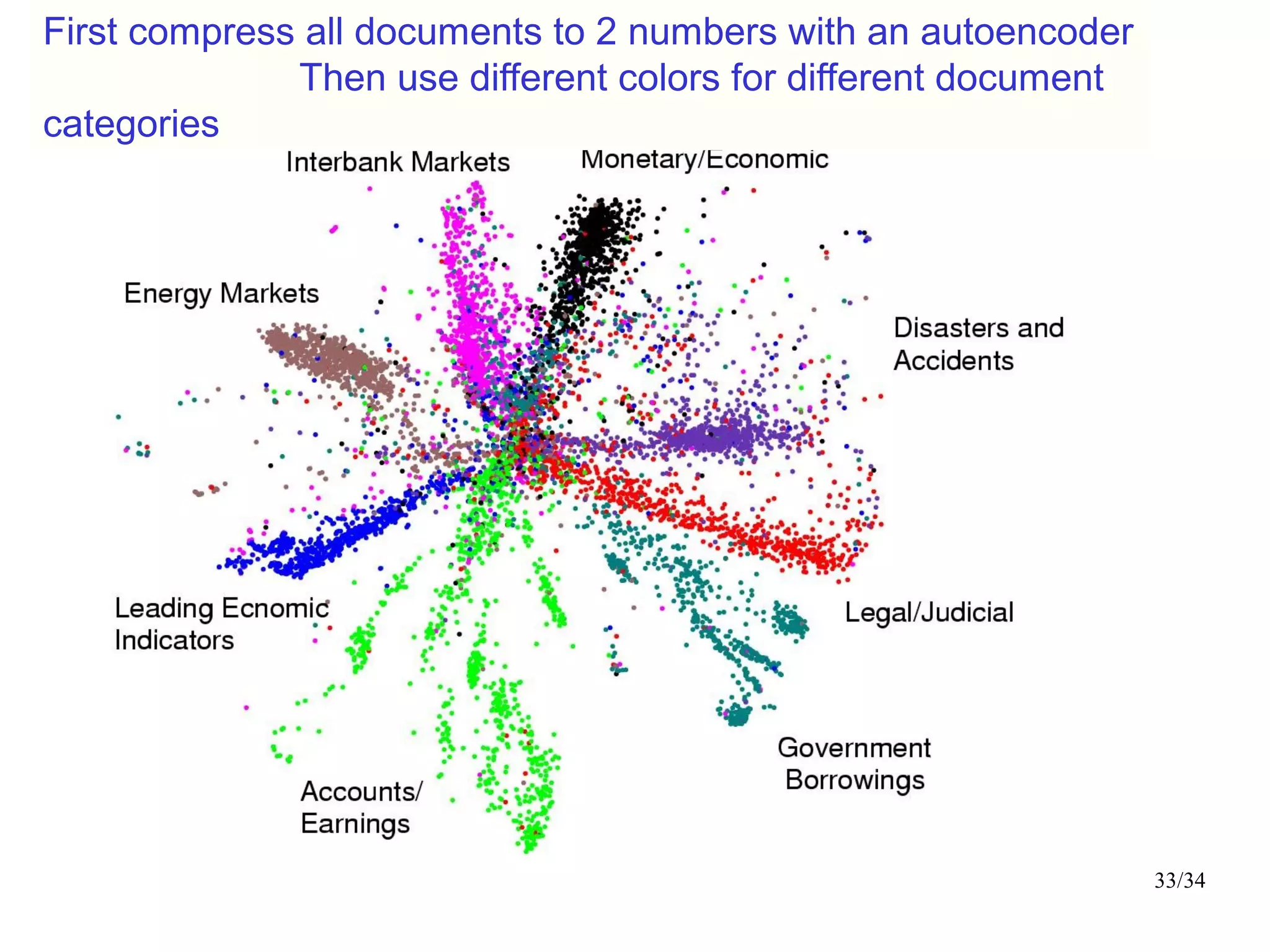
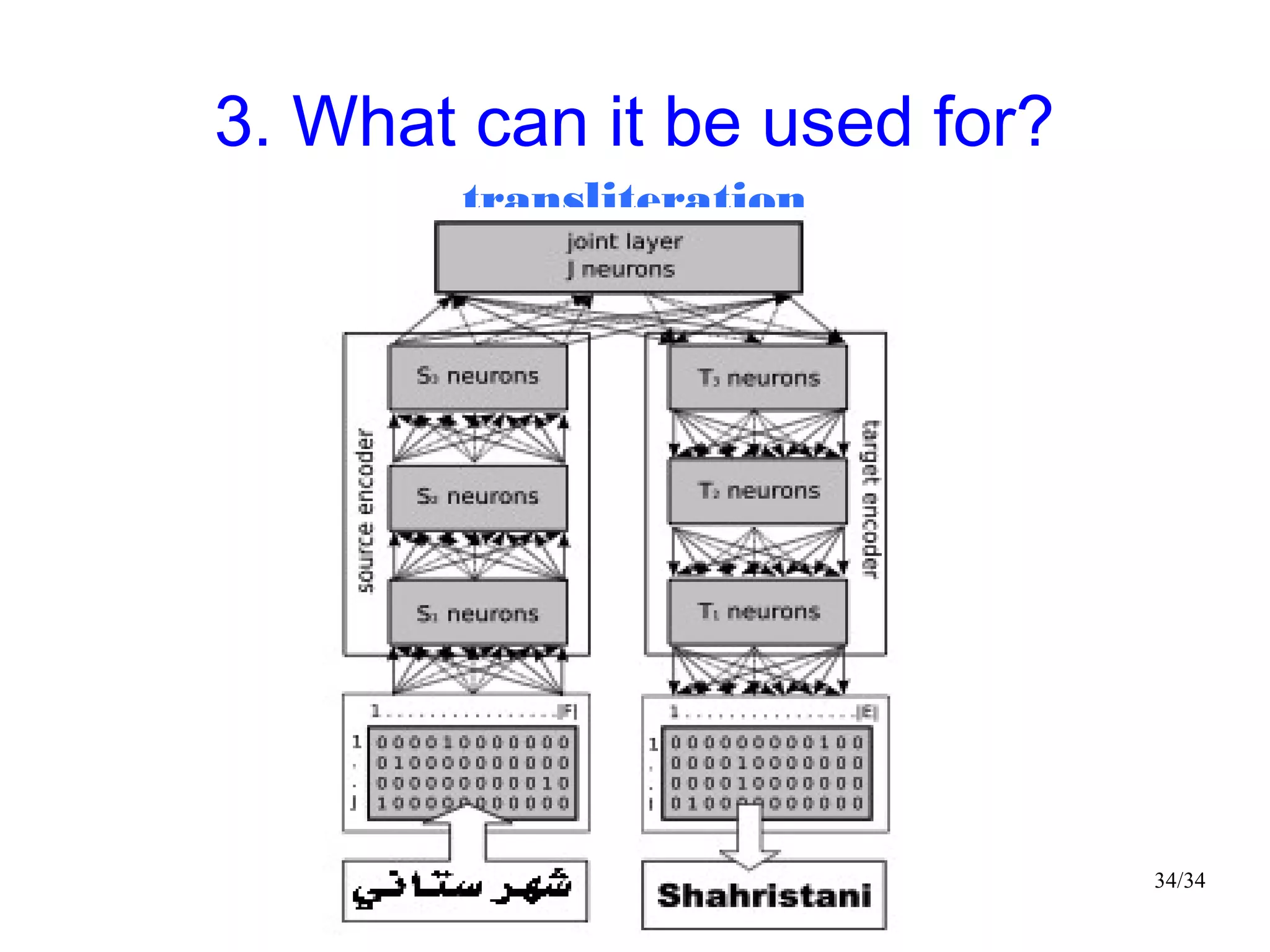
The document introduces autoencoders, which are neural networks that compress an input into a lower-dimensional code and then reconstruct the output from that code. It discusses that autoencoders can be trained using an unsupervised pre-training method called restricted Boltzmann machines to minimize the reconstruction error. Autoencoders can be used for dimensionality reduction, document retrieval by compressing documents into codes, and data visualization by compressing high-dimensional data points into 2D for plotting with different categories colored separately.