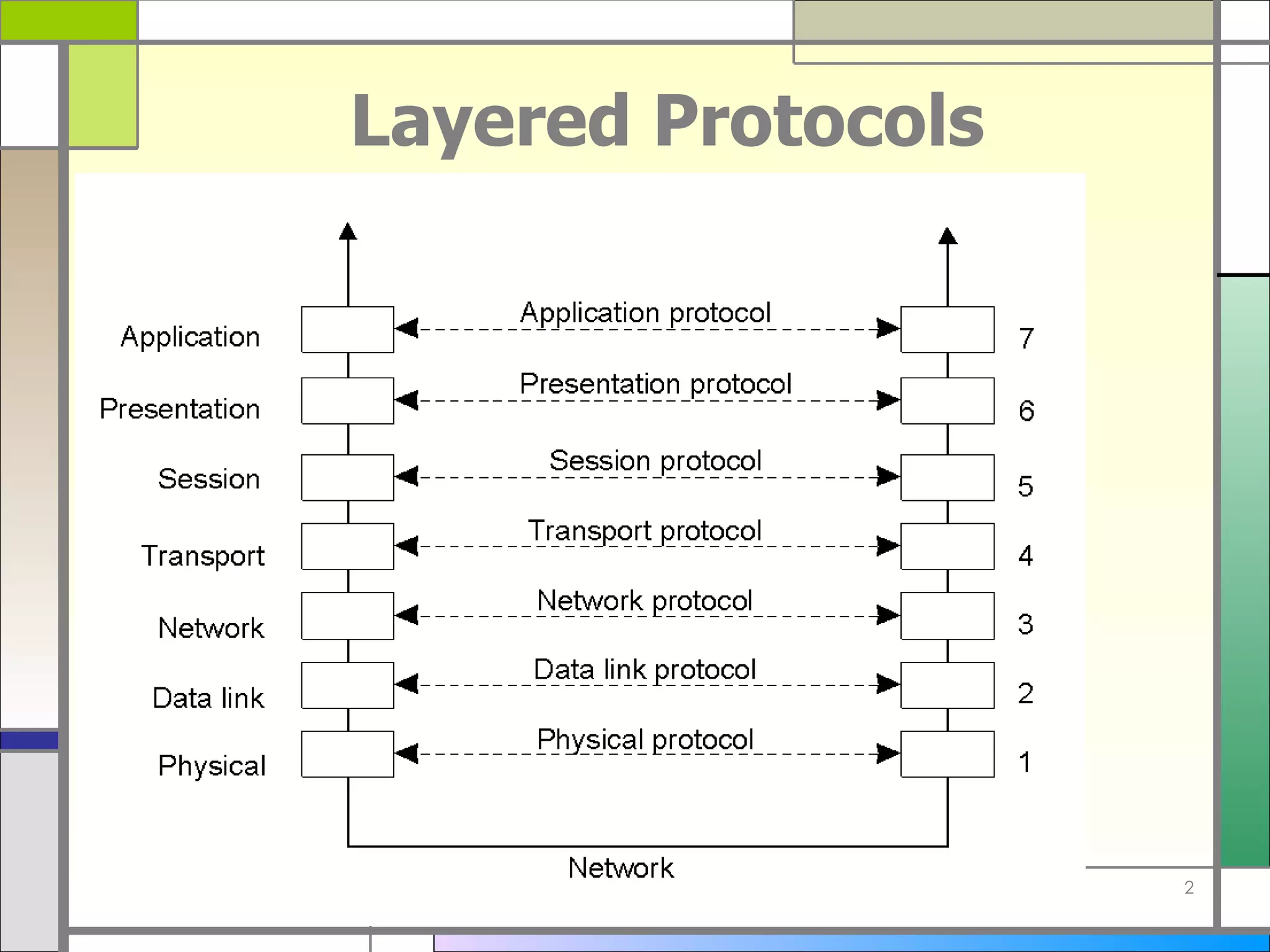
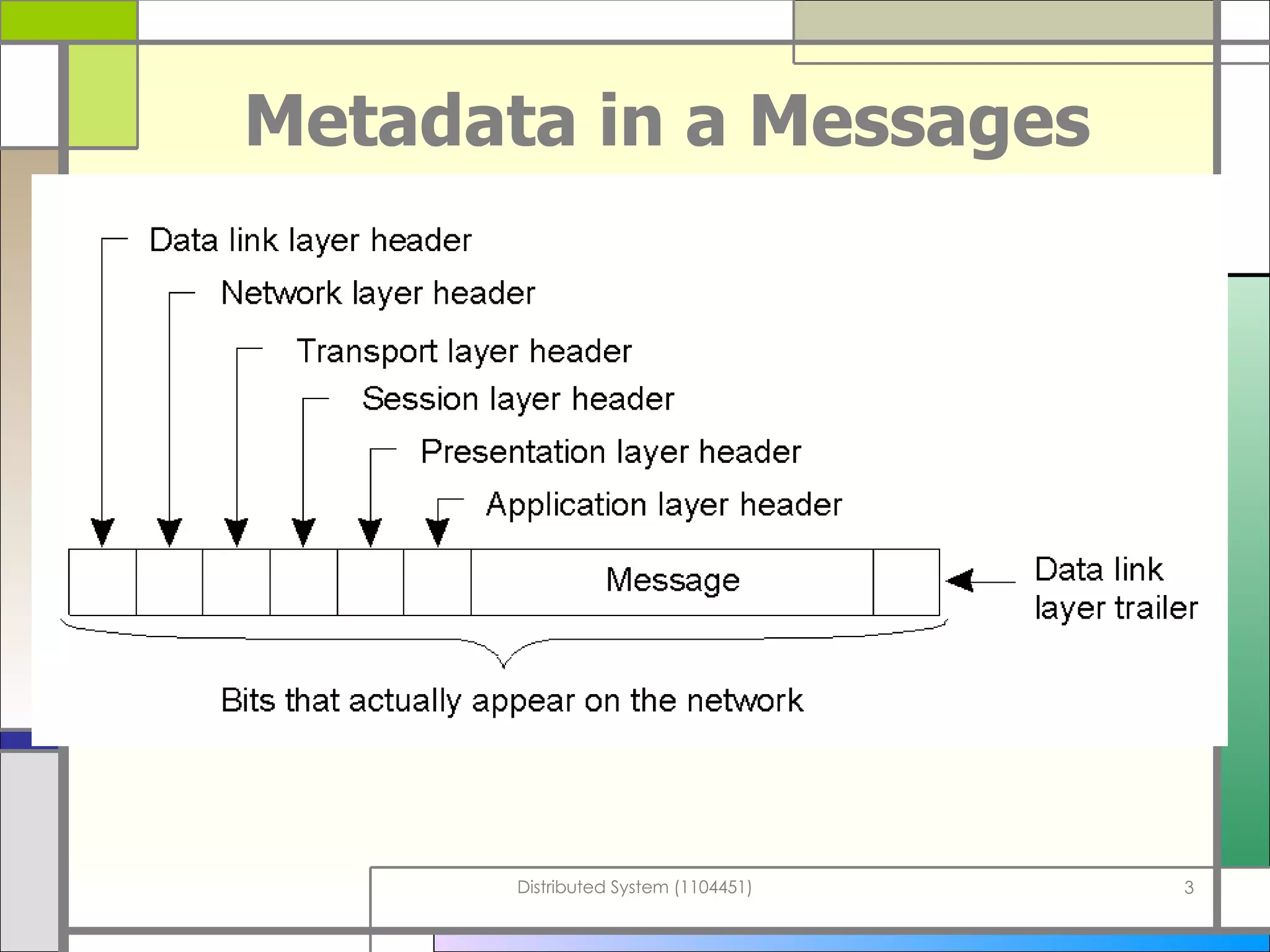
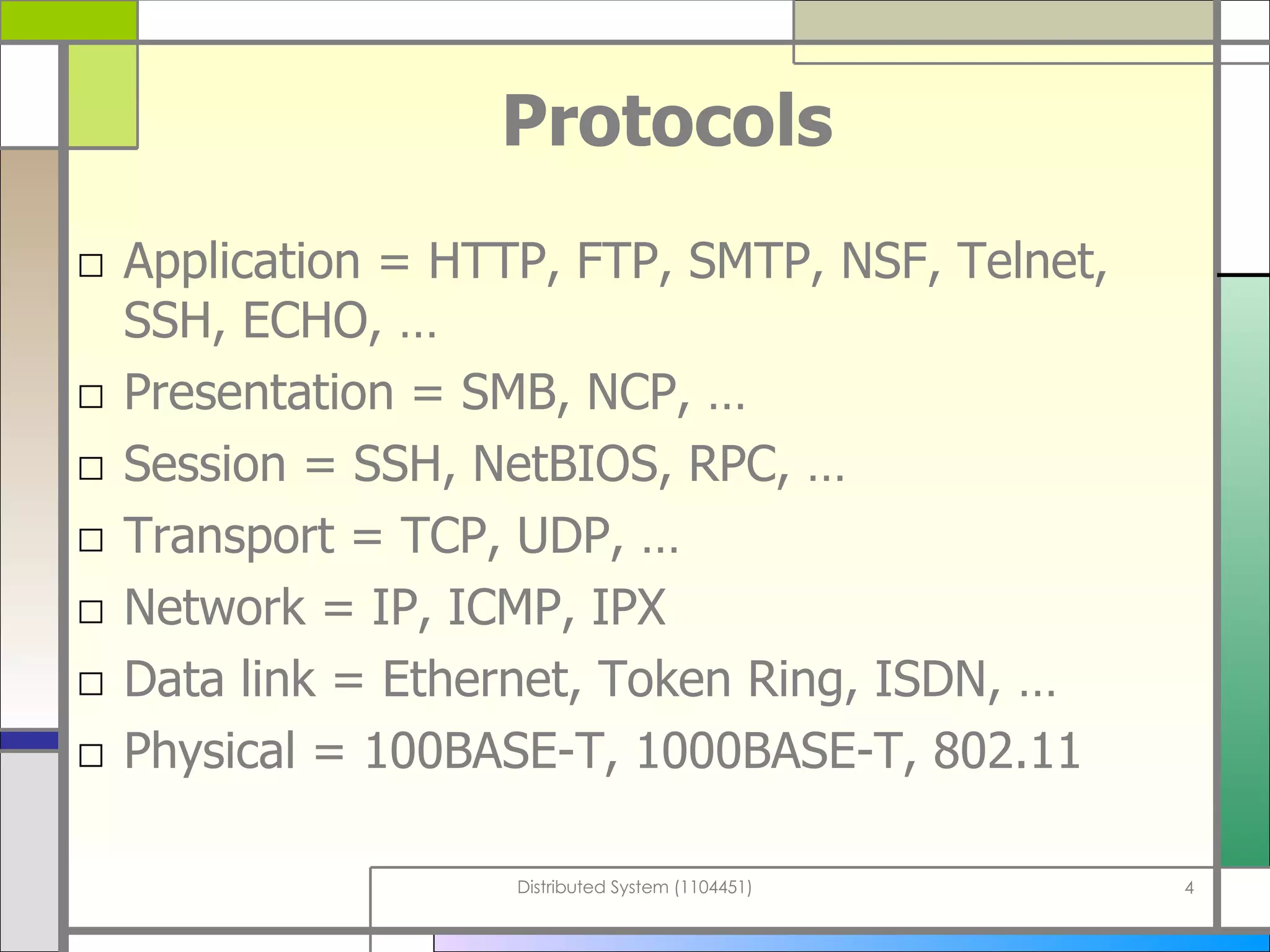
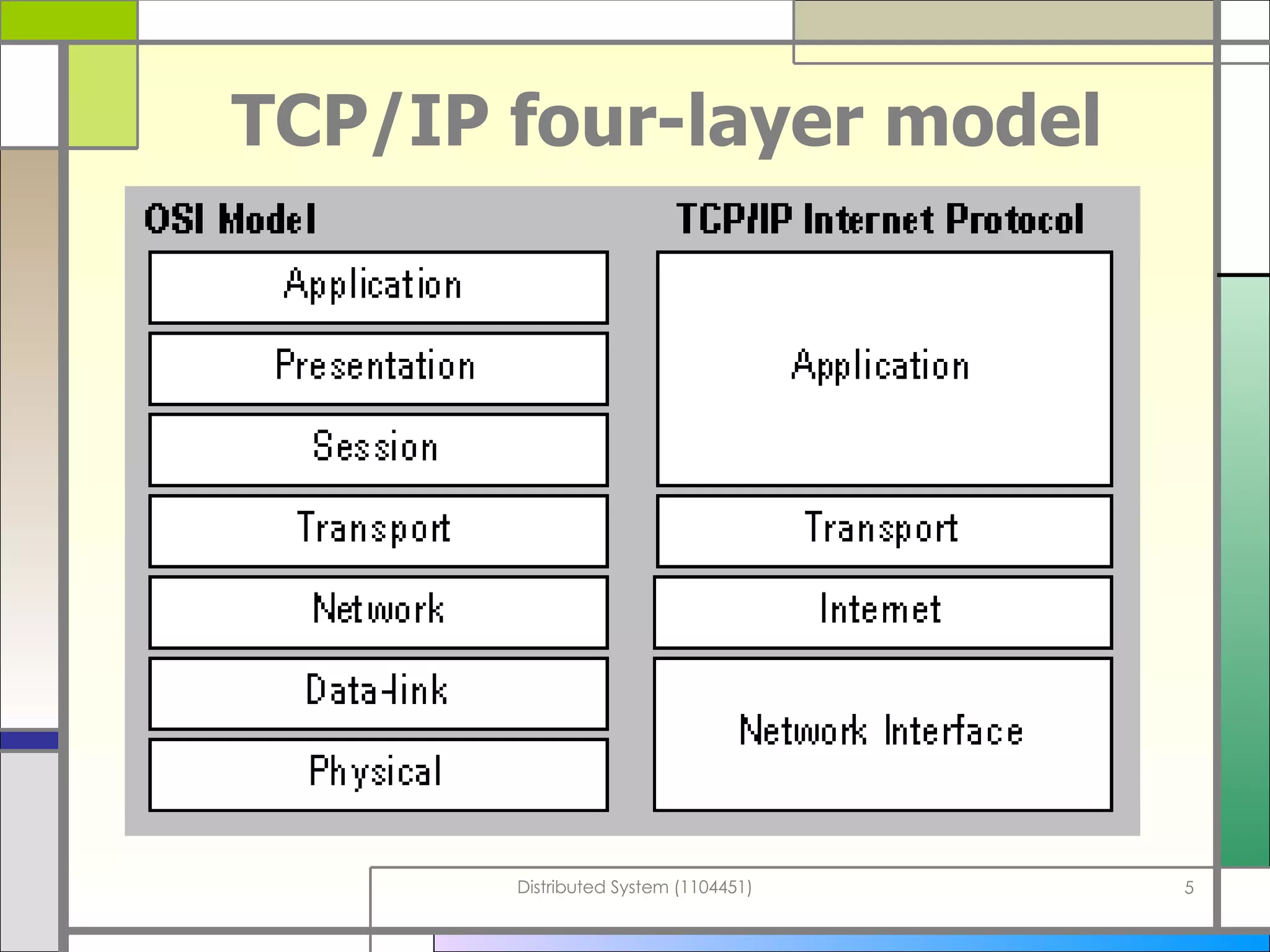
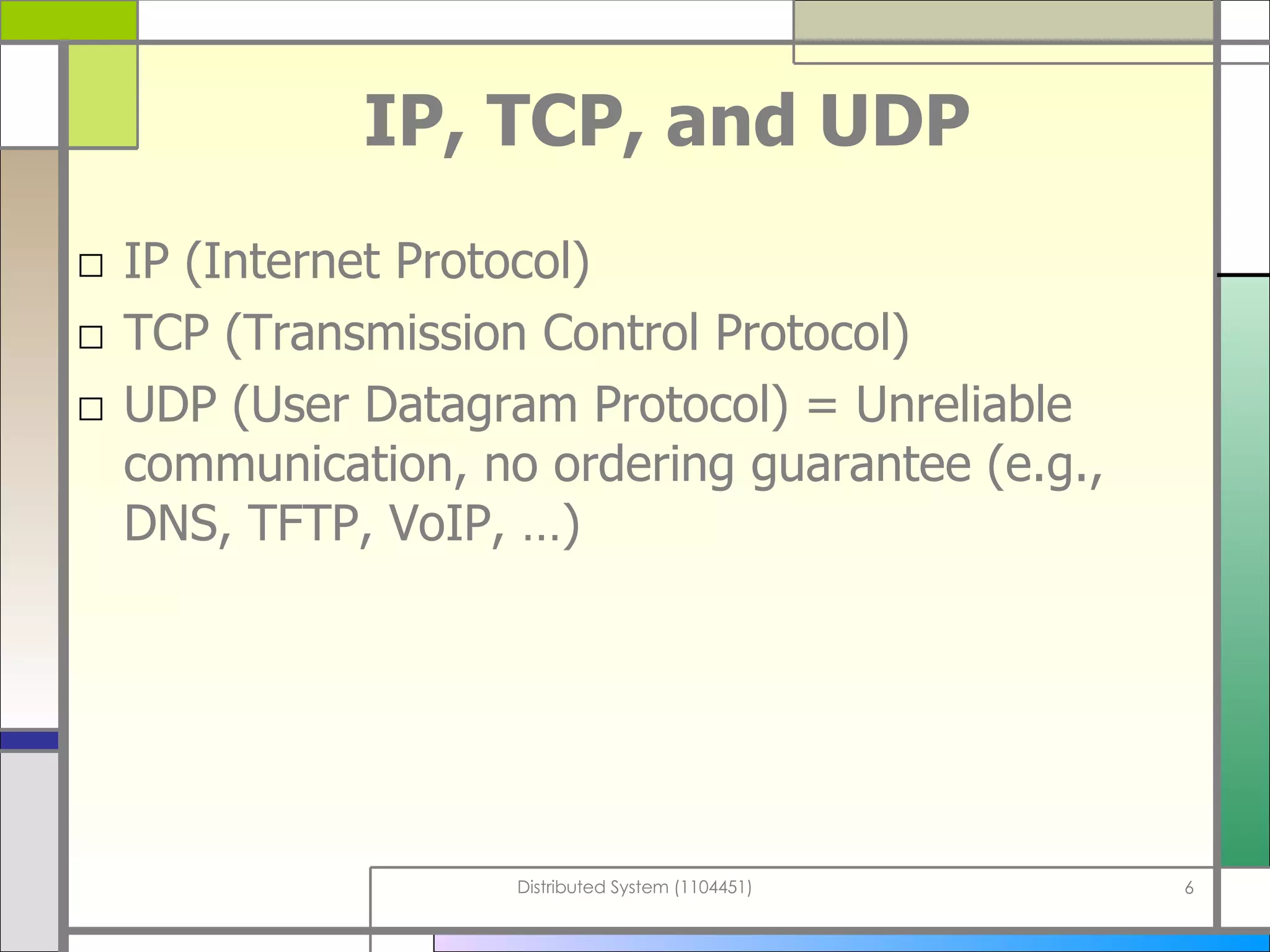
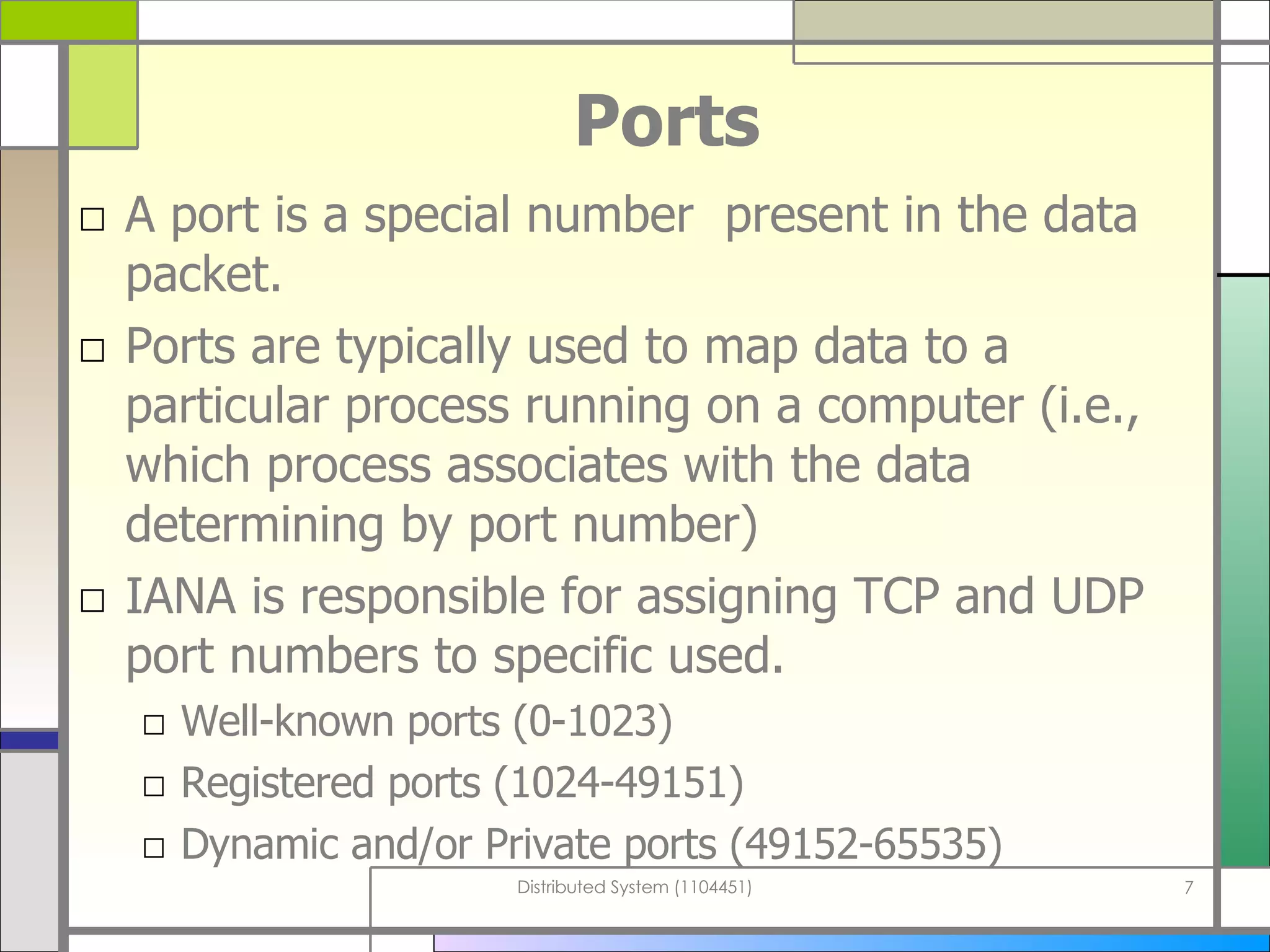
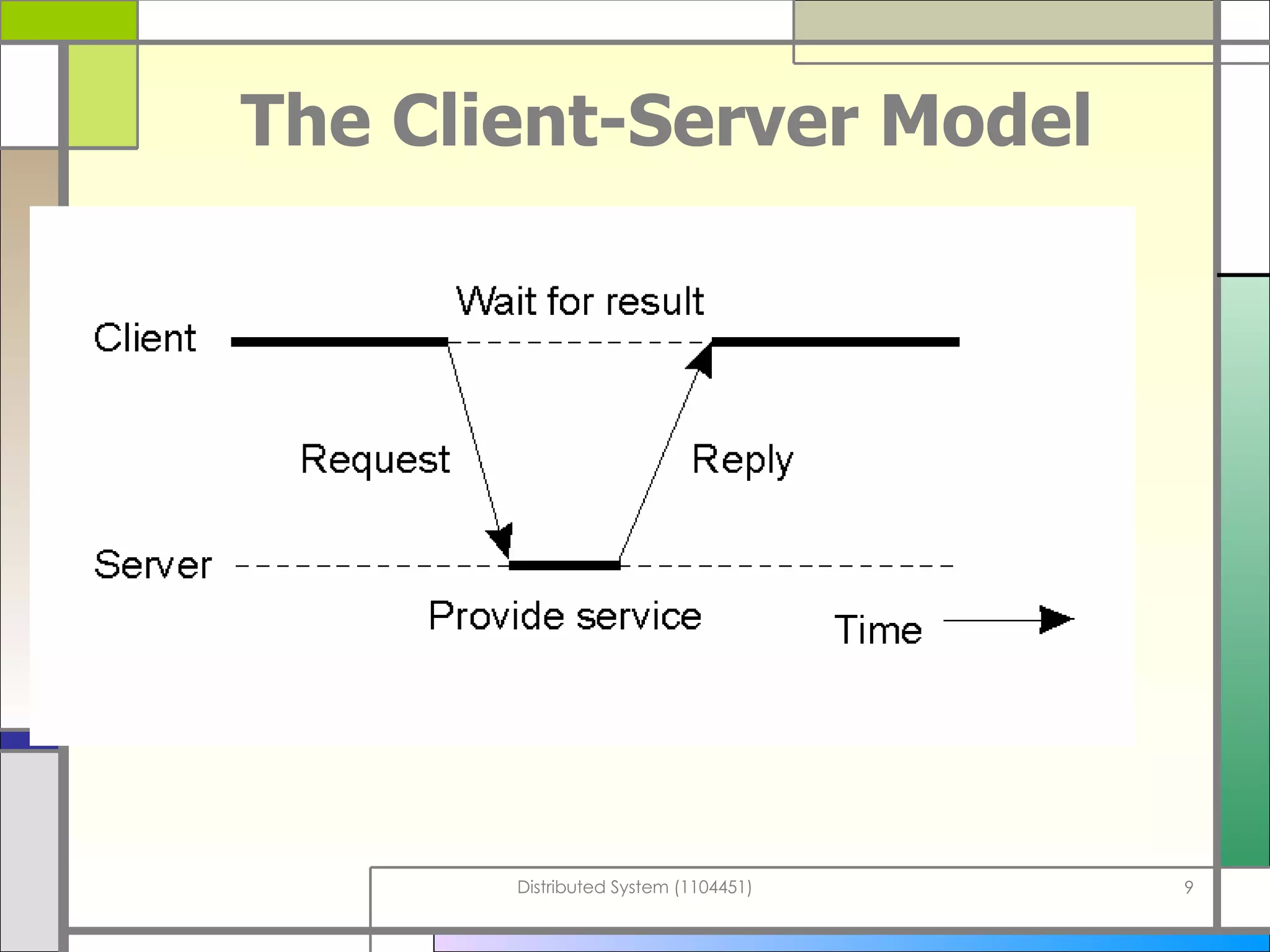
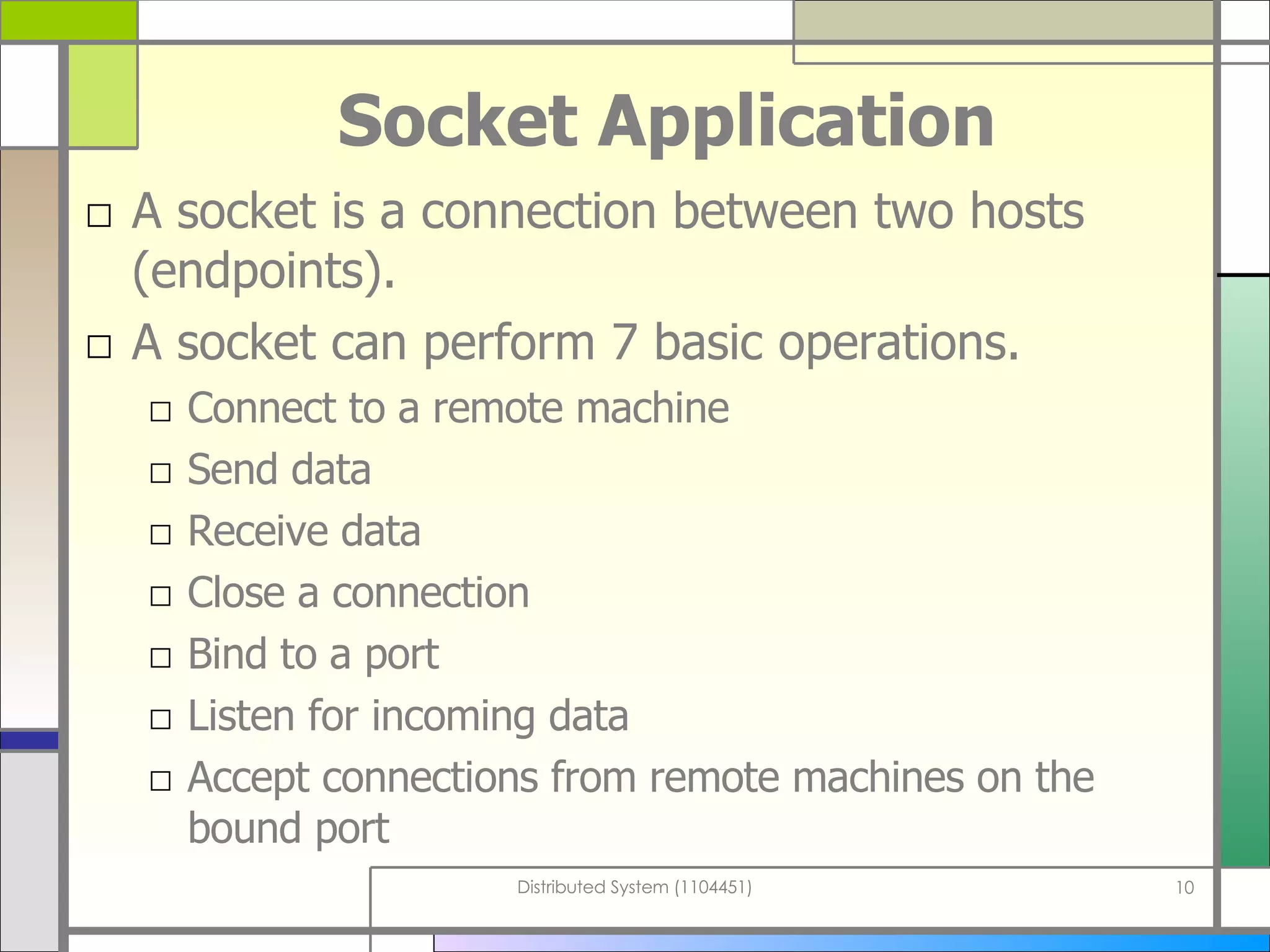
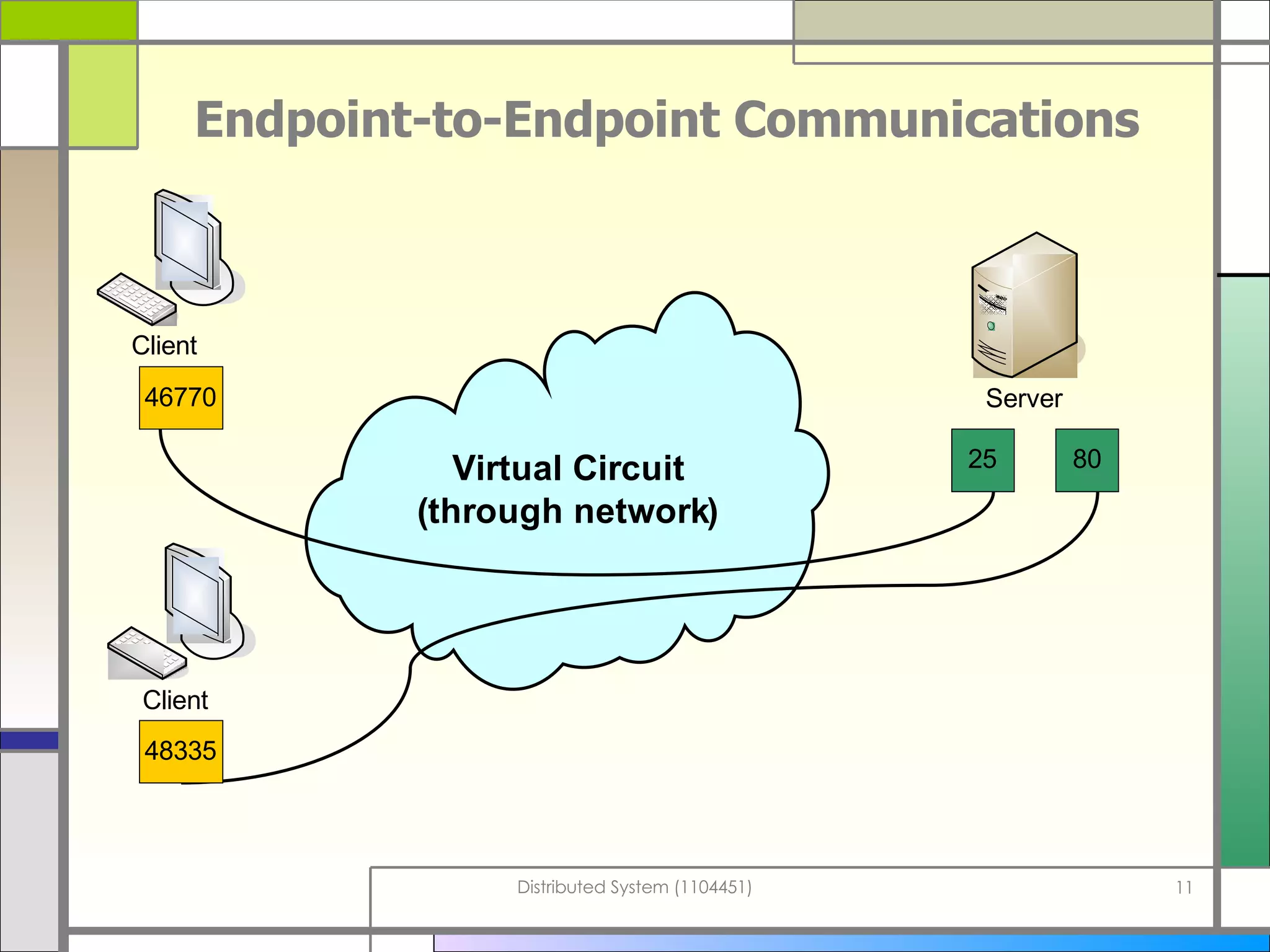
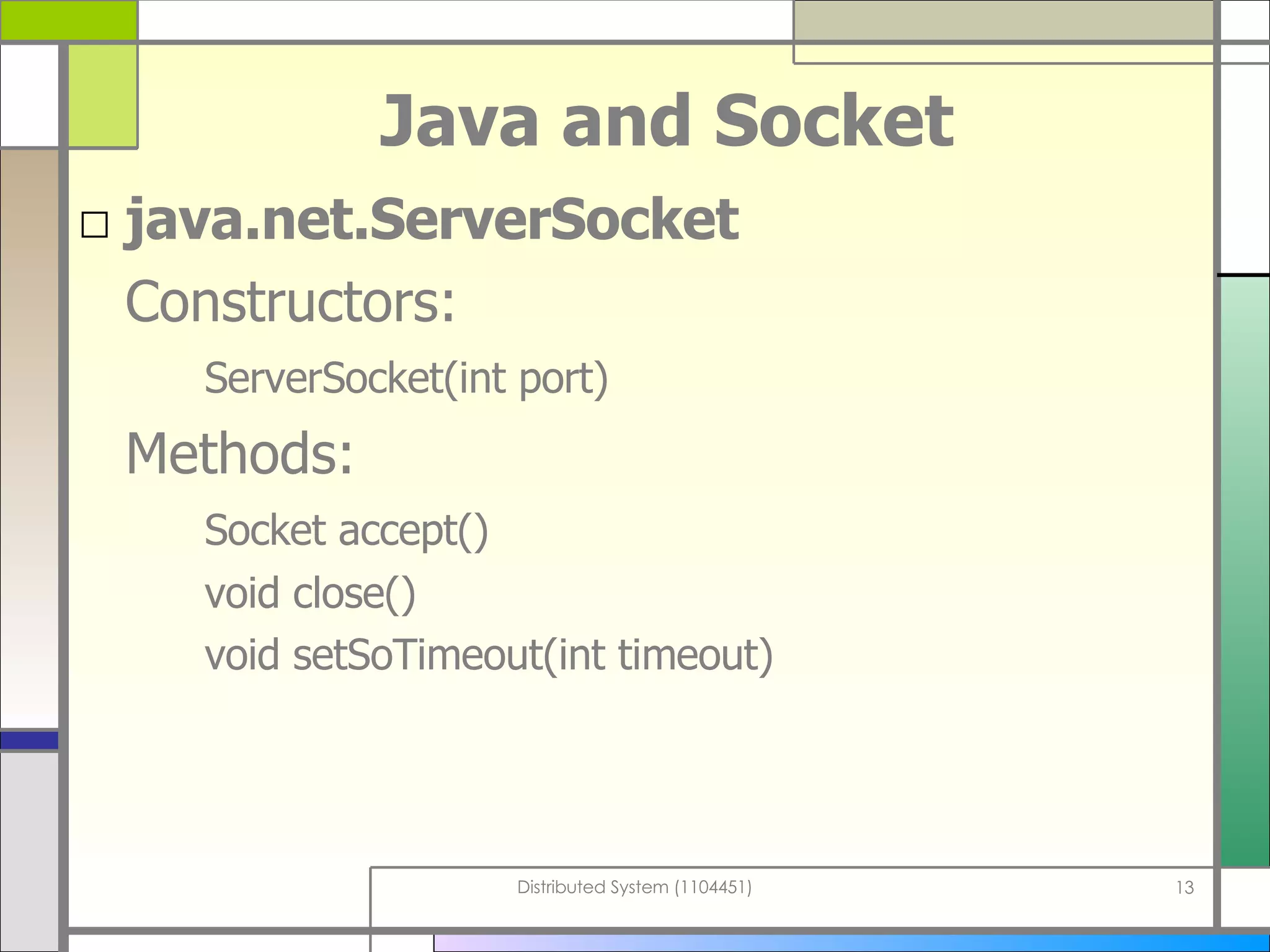
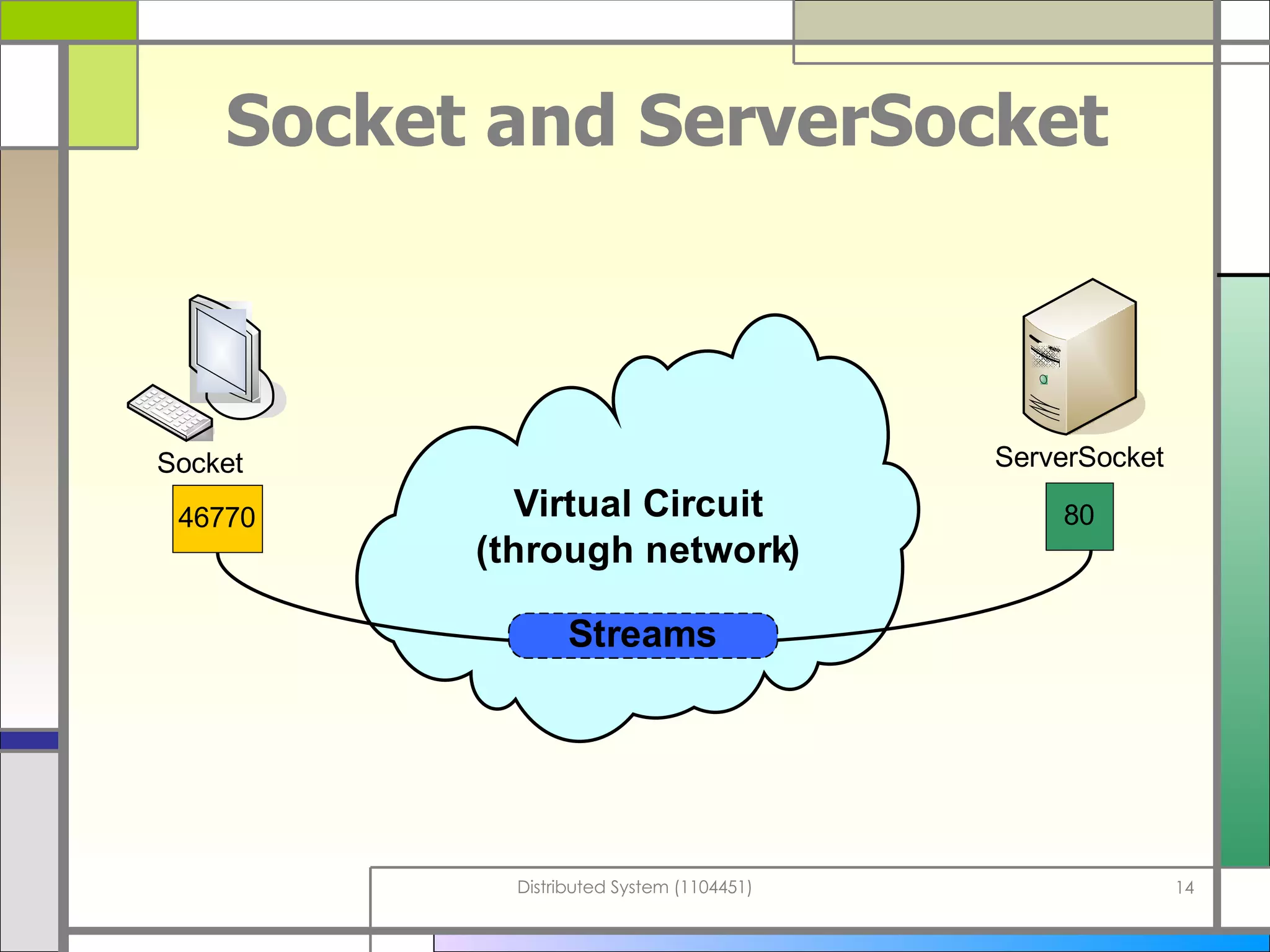
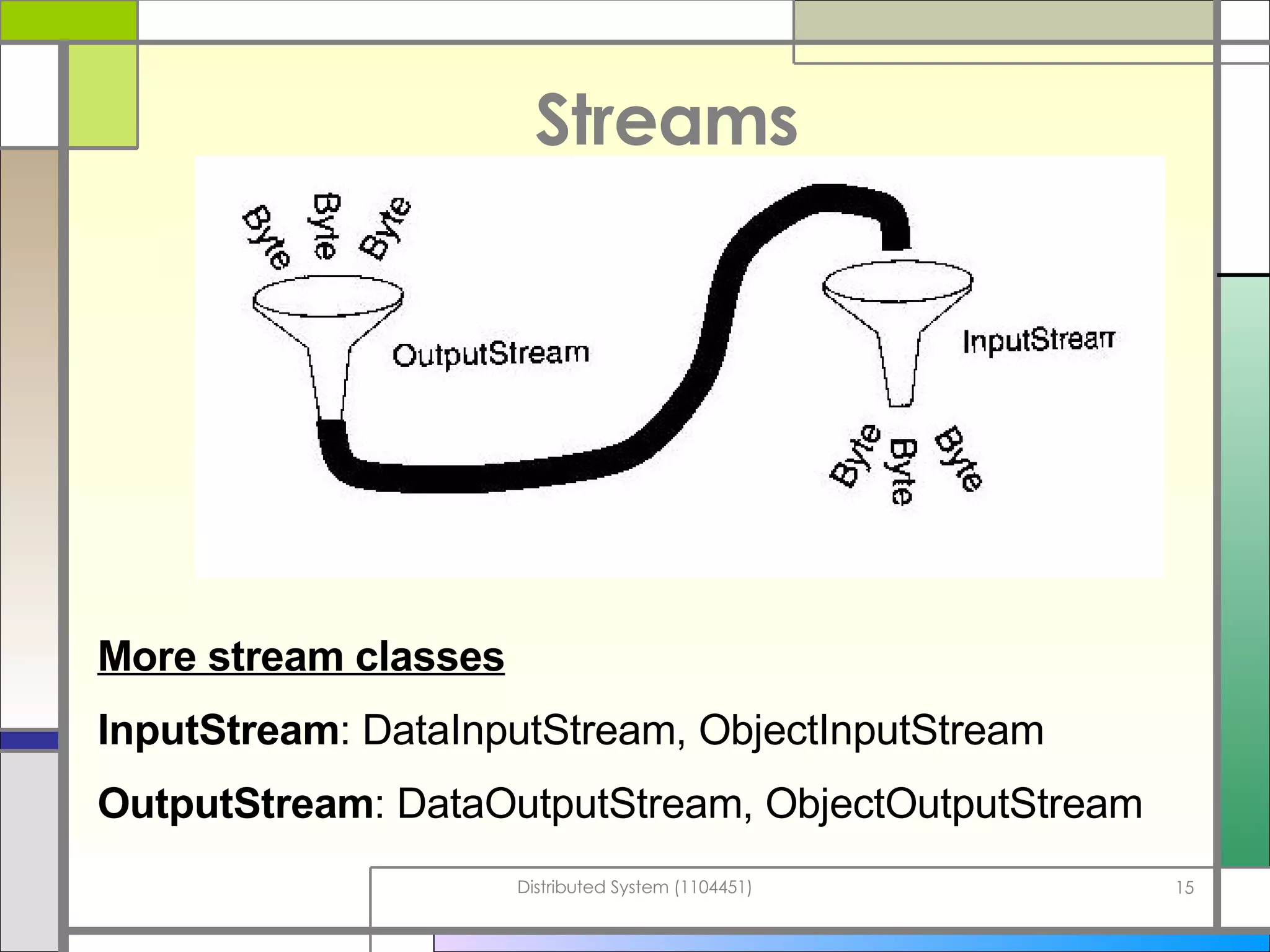
The document discusses socket programming in Java. It covers key concepts like layers of protocols, ports, the client-server model, and socket classes. Example code is provided to demonstrate how to create simple client and server applications using sockets to connect two processes and exchange data between them. The examples show how to bind sockets, send/receive data over input/output streams, and handle multiple concurrent connections by spawning new threads.




![Code: Socket Information import java . net . Socket; public class SocketInfo { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws Exception { Socket socket = new Socket (" www . sanook . com " , 80 ) ; System . out . println (" Connected to " + socket . getInetAddress () + " on port " + socket . getPort () + " from port " + socket . getLocalPort () + " of " + socket . getLocalAddress ()) ; } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter03-1216733257635944-8/75/Socket-Programming-17-2048.jpg)
![Steps to develop a socket app Client-Side Bind Socket object with a specified host&port then connect to the host&port [option] Send data via stream (from getOutputStream) Wait for a response of the host via getInputStream Server-Side Bind ServerSocket object with a specified port Listening for the incoming requesting Accept connection while listened to an incoming contact and get its Socket reference Send/Receive data via streams of the Socket Object](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter03-1216733257635944-8/75/Socket-Programming-18-2048.jpg)
![Code: Time Server import java . io . DataOutputStream; import java . net . *; import java . util . Date; public class TimeServer { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws Exception { ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket ( 7000 ) ; System . out . println (" Server is started ") ; while ( true ) { Socket socket = server . accept () ; DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream ( socket . getOutputStream ()) ; String time = new Date (). toString () ; dos . writeUTF ( time ) ; socket . close () ; } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter03-1216733257635944-8/75/Socket-Programming-19-2048.jpg)
![Code: Time Client import java . io . DataInputStream; import java . io . DataOutputStream; import java . net . Socket; public class TimeClient { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws Exception { Socket socket = new Socket (" localhost " , 7000 ) ; DataInputStream din = new DataInputStream ( socket . getInputStream ()) ; String time = din . readUTF () ; System . out . println ( time ) ; } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter03-1216733257635944-8/75/Socket-Programming-20-2048.jpg)
![Code: Hello Server import java . io . *; import java . net . *; public class HelloServer { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws Exception { ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket ( 12345 ) ; System . out . println (" Server is started ") ; while ( true ) { Socket socket = server . accept () ; DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream ( socket . getInputStream ()) ; DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream ( socket . getOutputStream ()) ; String name = dis . readUTF () ; System . out . println (" I see " + name ) ; dos . writeUTF (" Hello " + name ) ; socket . close () ; } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter03-1216733257635944-8/75/Socket-Programming-21-2048.jpg)
![Code: Hello Client import java . io*; import java . net . *; public class HelloClient { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws Exception { Socket socket = new Socket (" localhost " , 12345 ) ; DataInputStream din = new DataInputStream ( socket . getInputStream ()) ; DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream ( socket . getOutputStream ()) ; String name = " World " ; if ( args . length > 0 ) name = args [ 0 ] ; dos . writeUTF ( name ) ; String message = din . readUTF () ; System . out . println ( message ) ; } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter03-1216733257635944-8/75/Socket-Programming-22-2048.jpg)
![Code: Busy Hello Server import java . io . *; import java . net . *; public class BusyHelloServer { public static void main ( String [] args ) throws Exception { ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket ( 12345 ) ; while ( true ) { Socket socket = server . accept () ; DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream ( socket . getInputStream ()) ; DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream ( socket . getOutputStream ()) ; String name = dis . readUTF () ; System . out . println (" I see " + name ) ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++) { Thread . sleep ( 1000 ) ; System . out . println (" Delay for " + name + " # " + i ) ; } dos . writeUTF (" Hello " + name ) ; socket . close () ; } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter03-1216733257635944-8/75/Socket-Programming-23-2048.jpg)
![Code: Multithread Hello Server import java . io . *; import java . net . *; public class ThreadingHelloServer extends Thread { Socket soc; public ThreadingHelloServer ( Socket soc ) { this . soc = soc; } public void run () { try { DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream ( soc . getInputStream ()) ; DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream ( soc . getOutputStream ()) ; String name = dis . readUTF () ; System . out . println (" I see " + name ) ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++) { Thread . sleep ( 1000 ) ; System . out . println (" Delay for " + name + " # " + i ) ; } dos . writeUTF (" Hello " + name ) ; soc . close () ; } catch ( Exception ex ) {ex . printStackTrace () ;} } public static void main ( String [] args ) throws Exception { ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket ( 12345 ) ; while ( true ) { Socket socket = server . accept () ; new ThreadingHelloServer ( socket ) .start () ; } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter03-1216733257635944-8/75/Socket-Programming-24-2048.jpg)
![Code: Multithread Hello Server (Short Form) import java.io.*; import java.net.*; public class ThreadingHelloServer2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(12345); System.out.println("Server is started"); while(true) { final Socket socket = server.accept(); Thread t = new Thread() { public void run() { try { DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream()); DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream()); String name = dis.readUTF(); System.out.println("I see " + name); for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("Delay for " + name + " #" + i); } dos.writeUTF("Hello " + name); socket.close(); } catch(Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } }}; t.start(); }}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter03-1216733257635944-8/75/Socket-Programming-25-2048.jpg)
