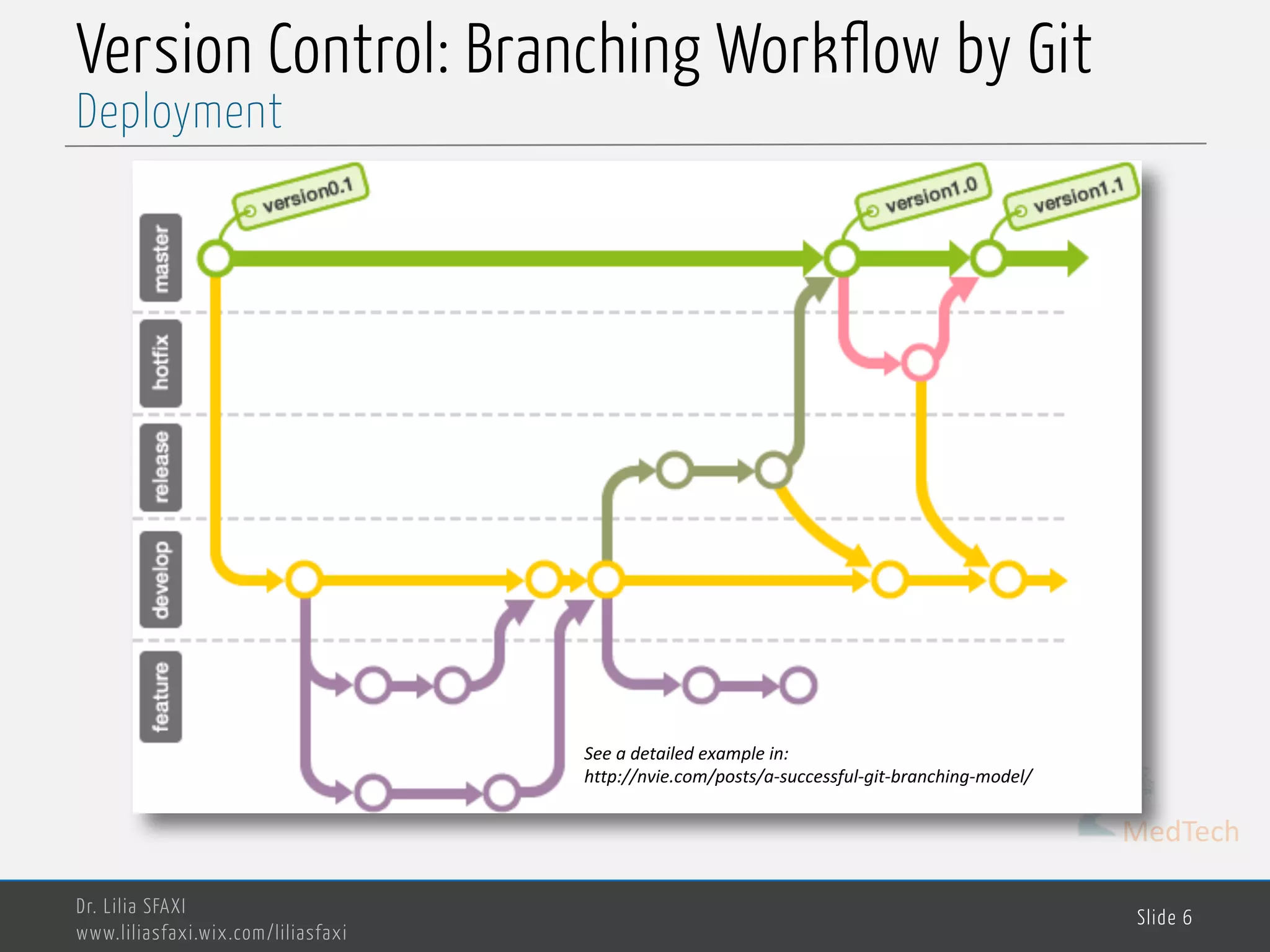
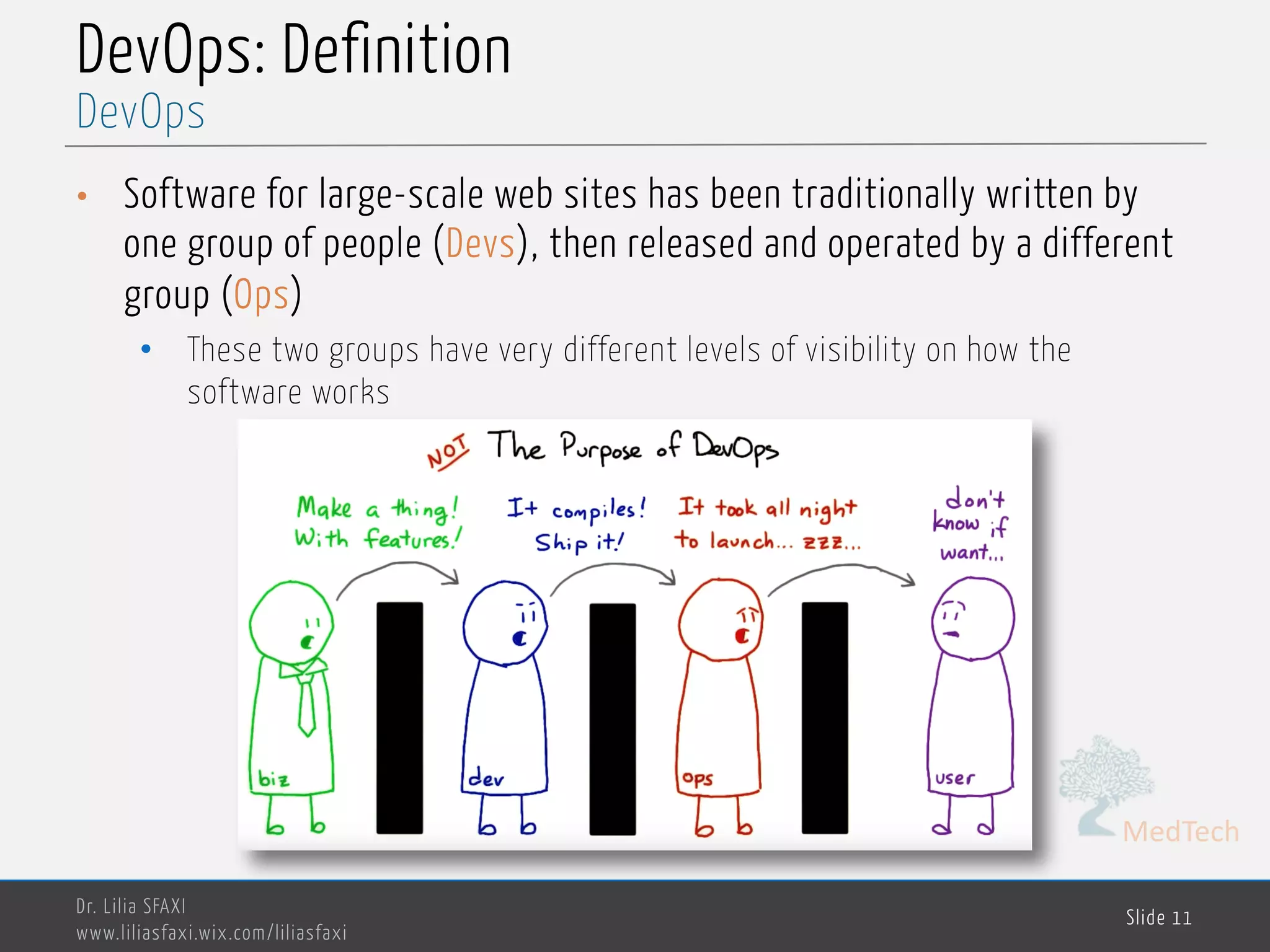
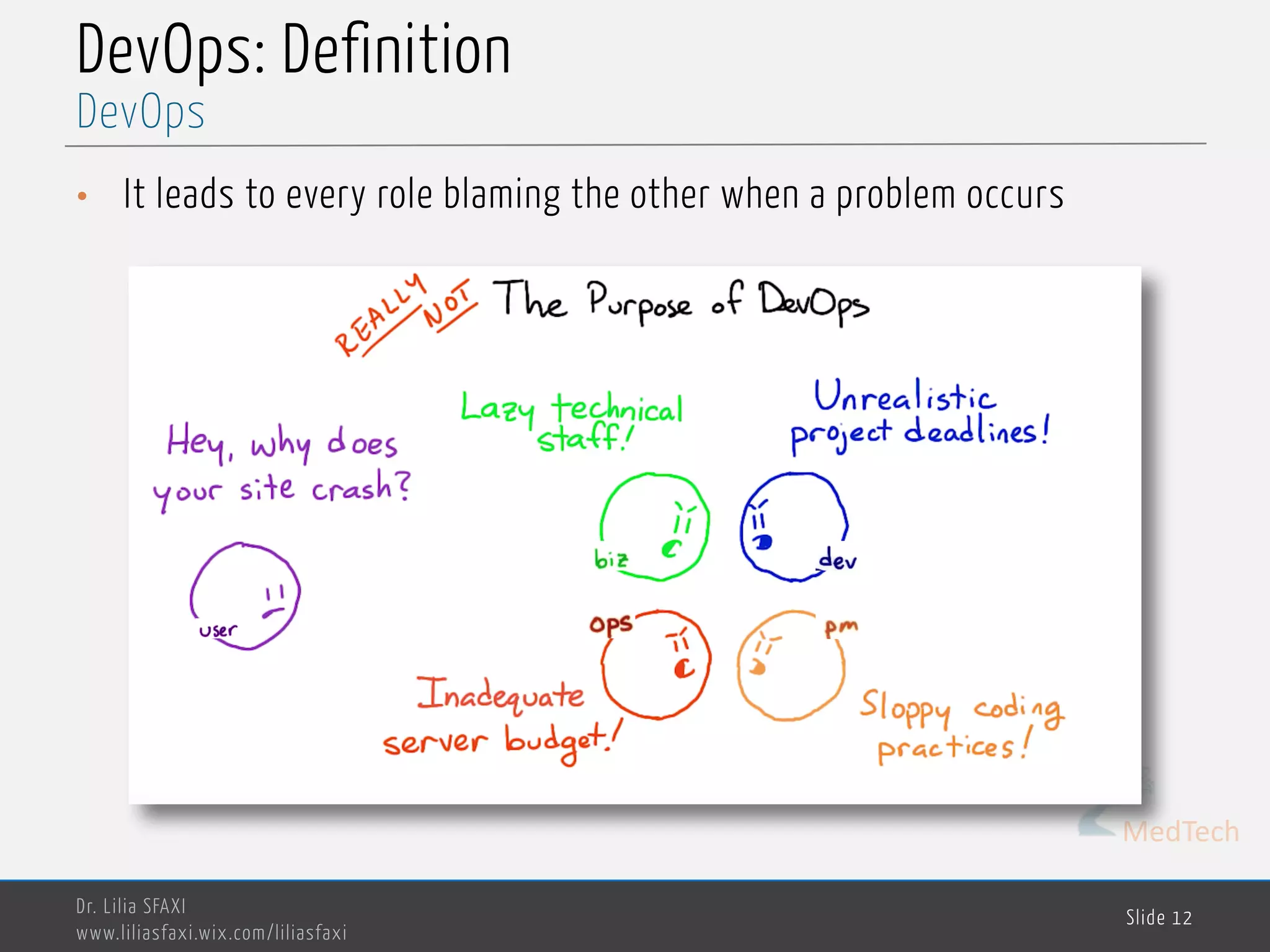
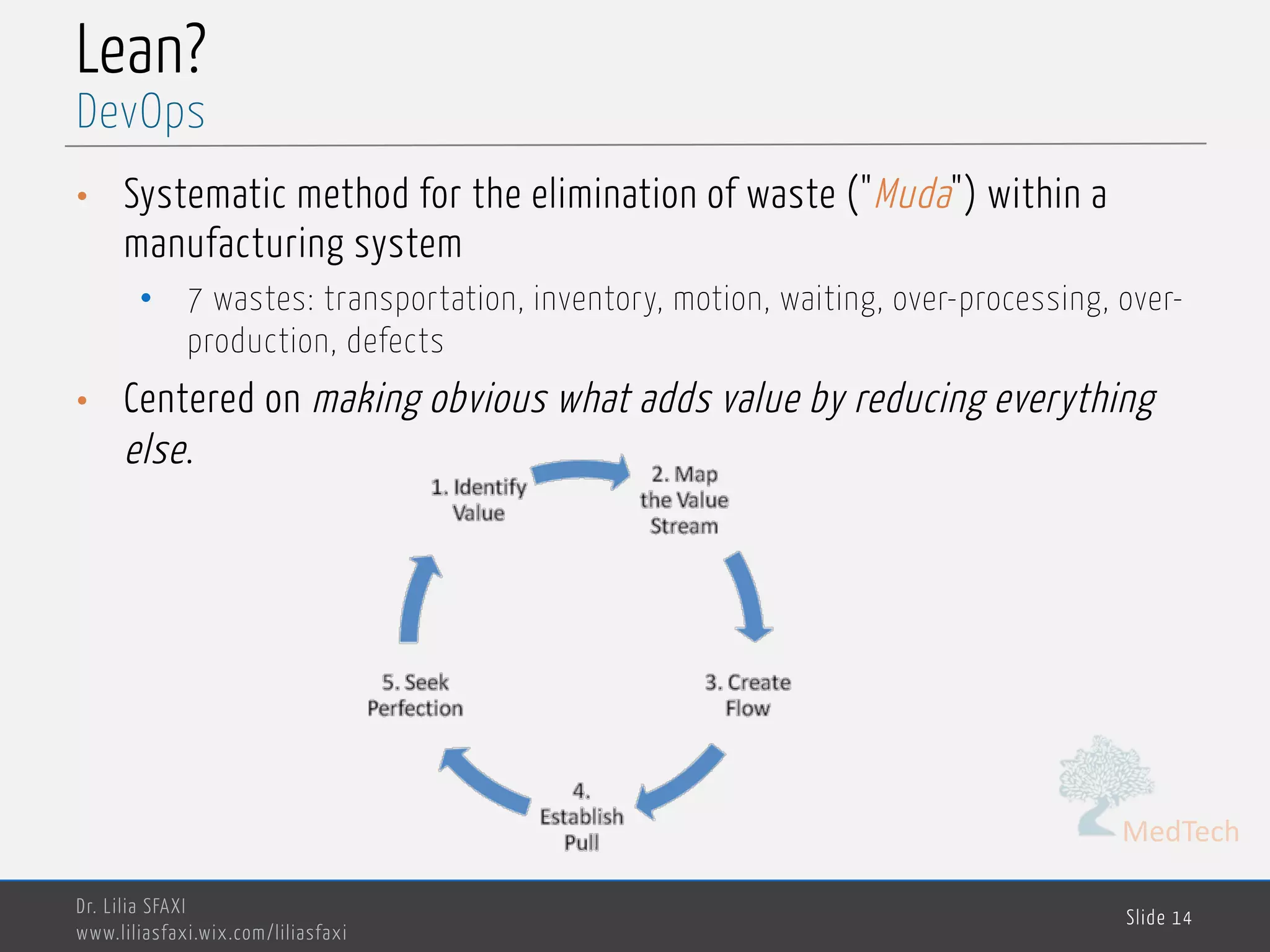
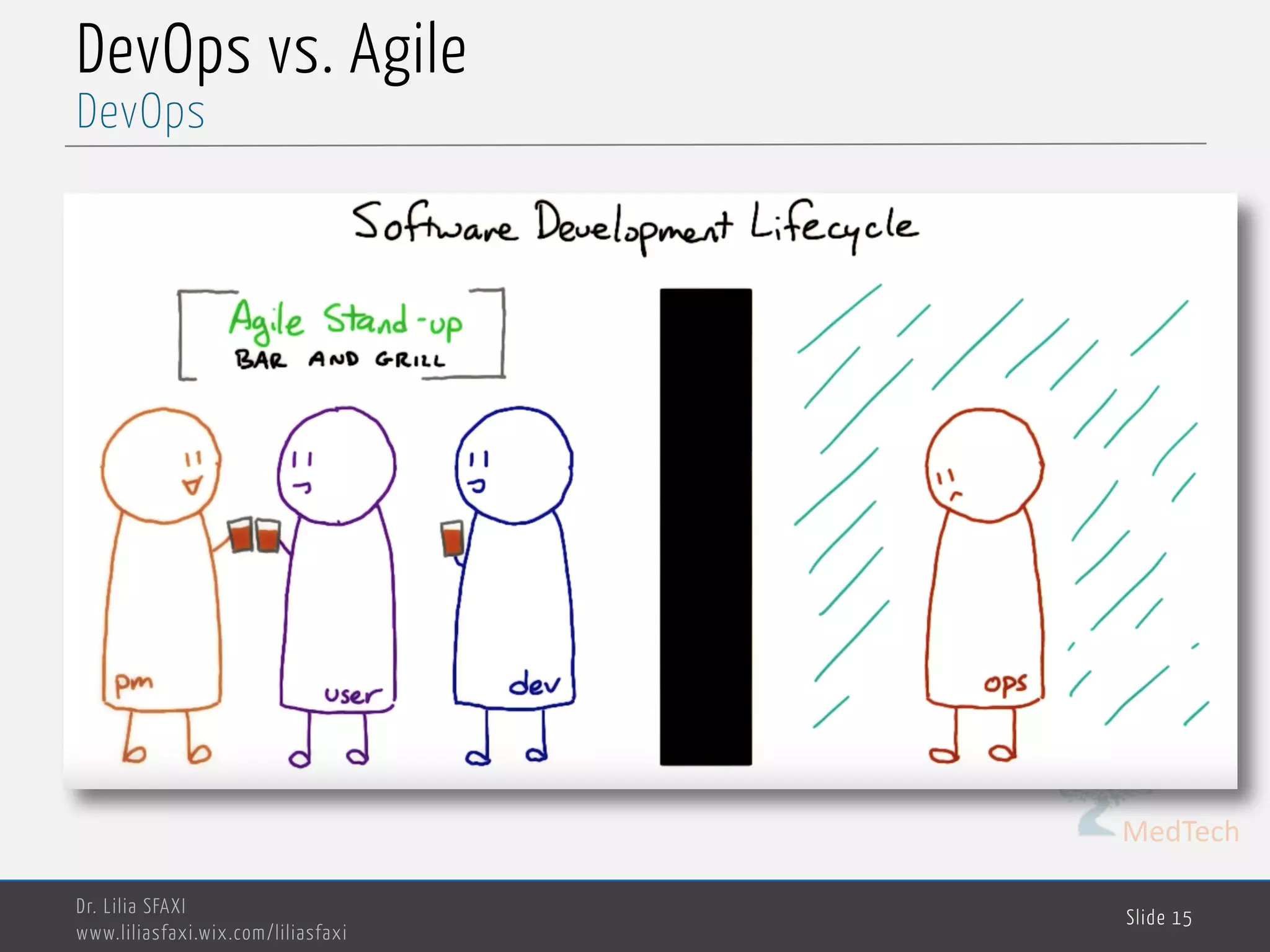
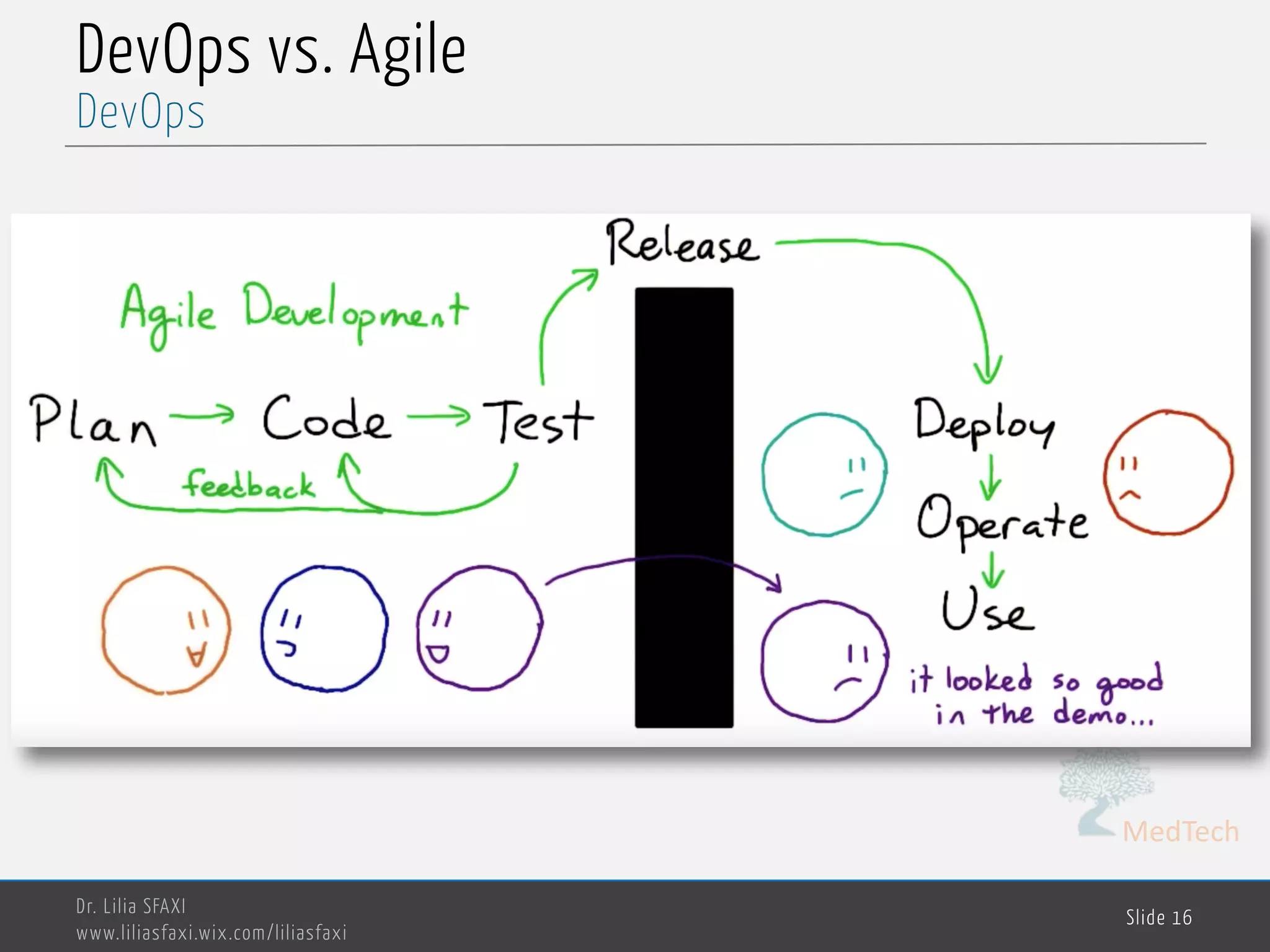
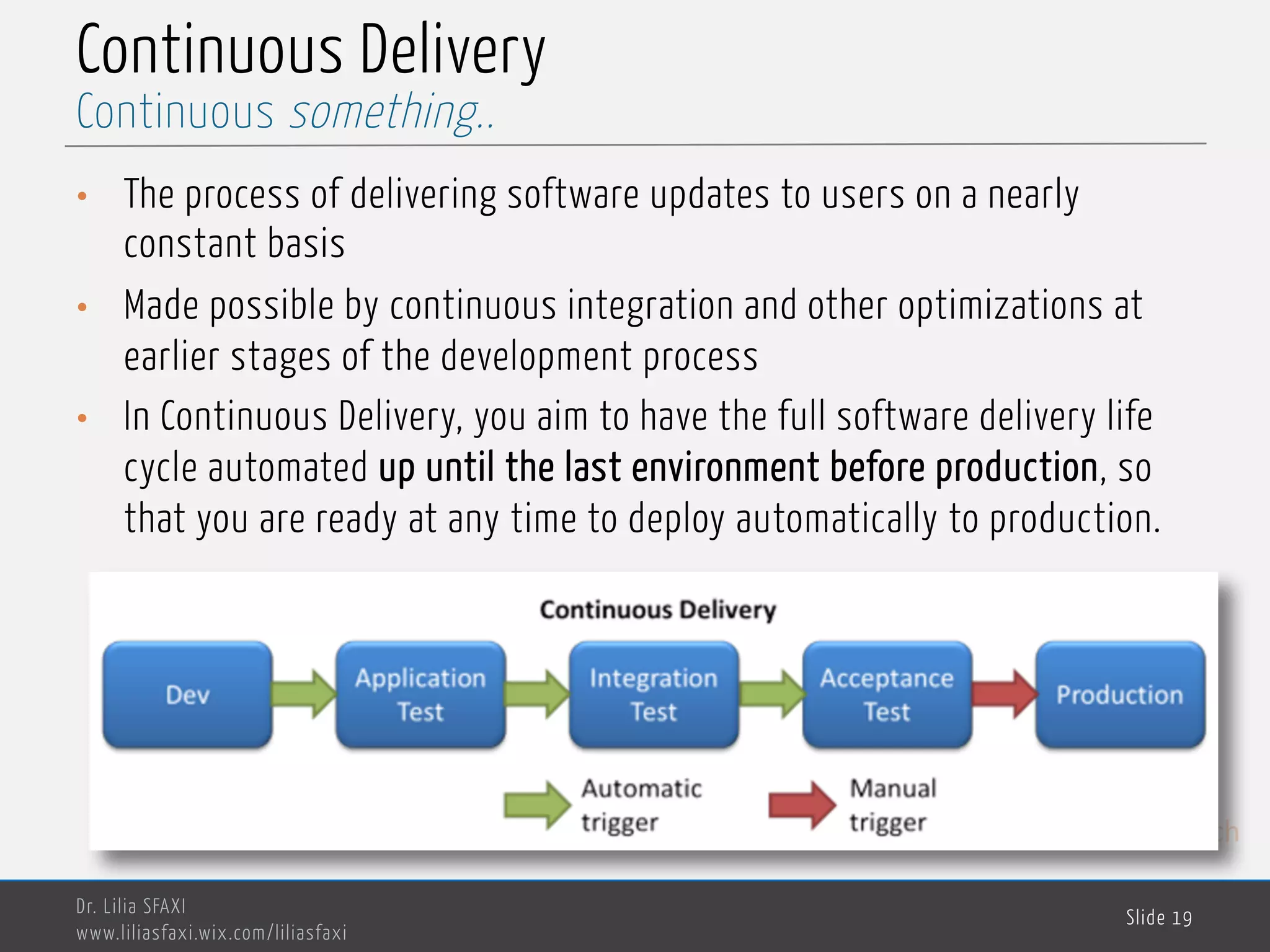
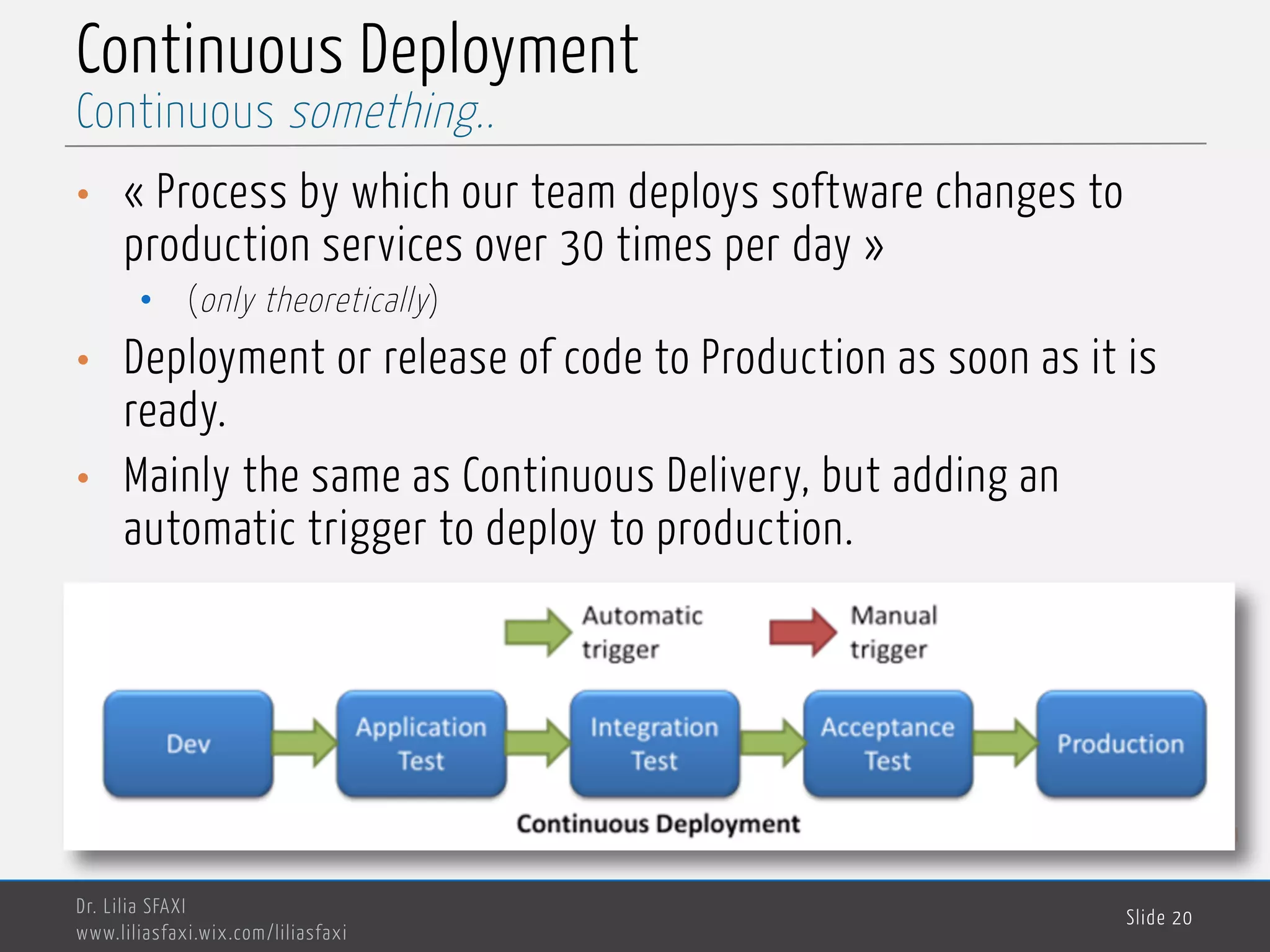
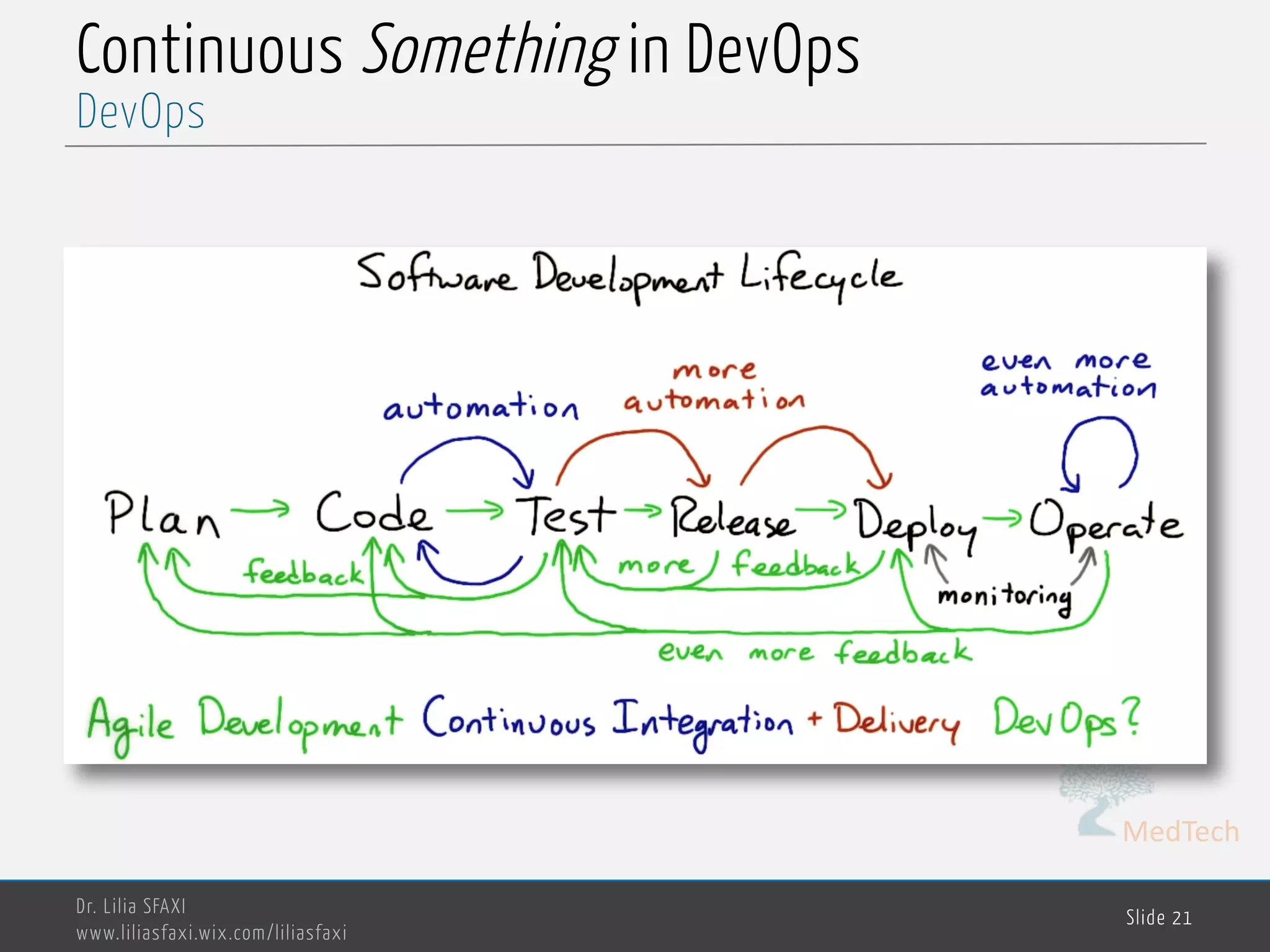
This document discusses deployment processes and best practices. It defines deployment as the activities that make a software system available for use and involve moving approved releases to test and production environments. The document outlines deployment workflows involving development, staging, and production environments. It also discusses concepts like continuous integration, continuous delivery, continuous deployment, and DevOps practices for automating deployment processes.