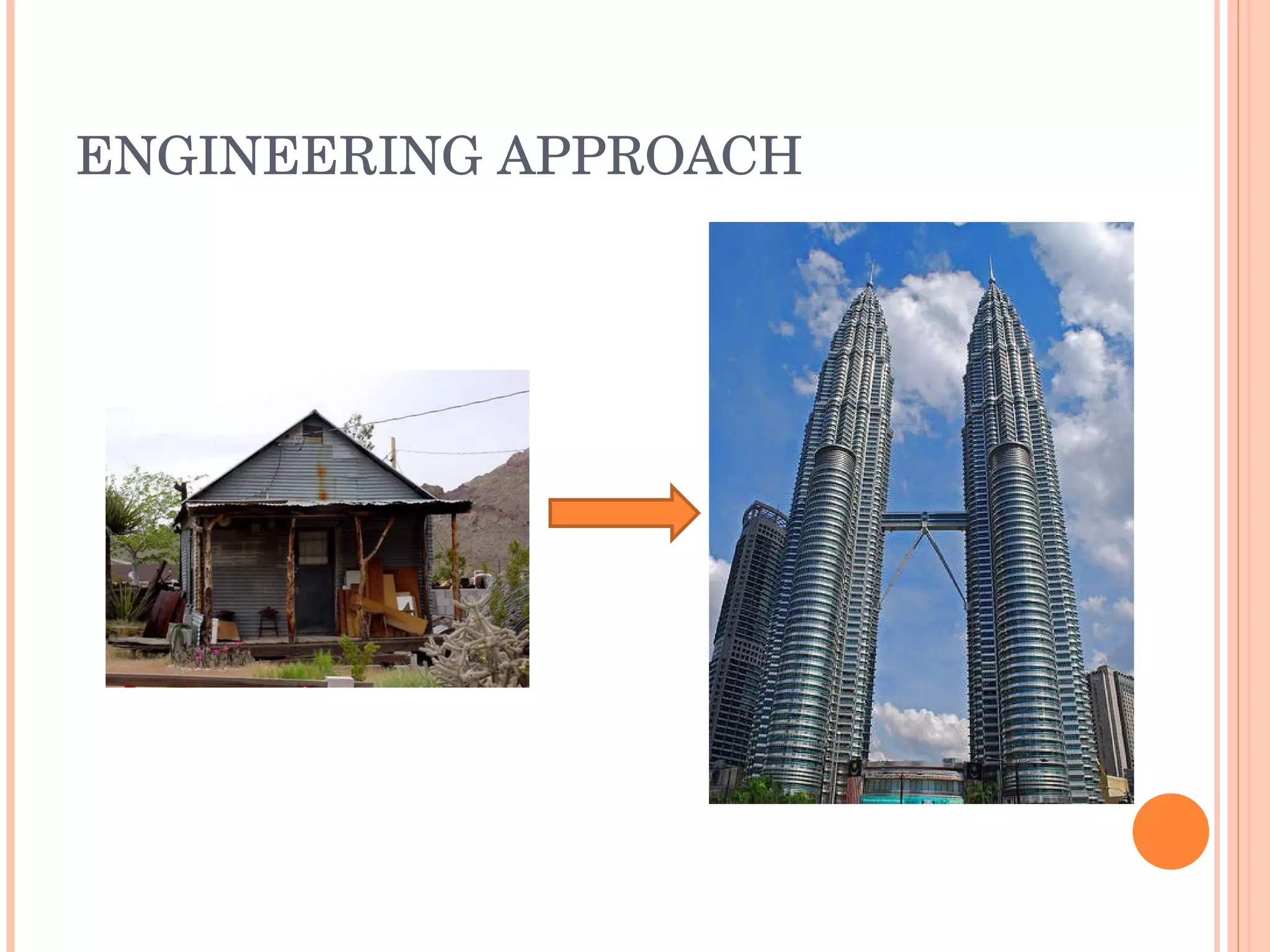
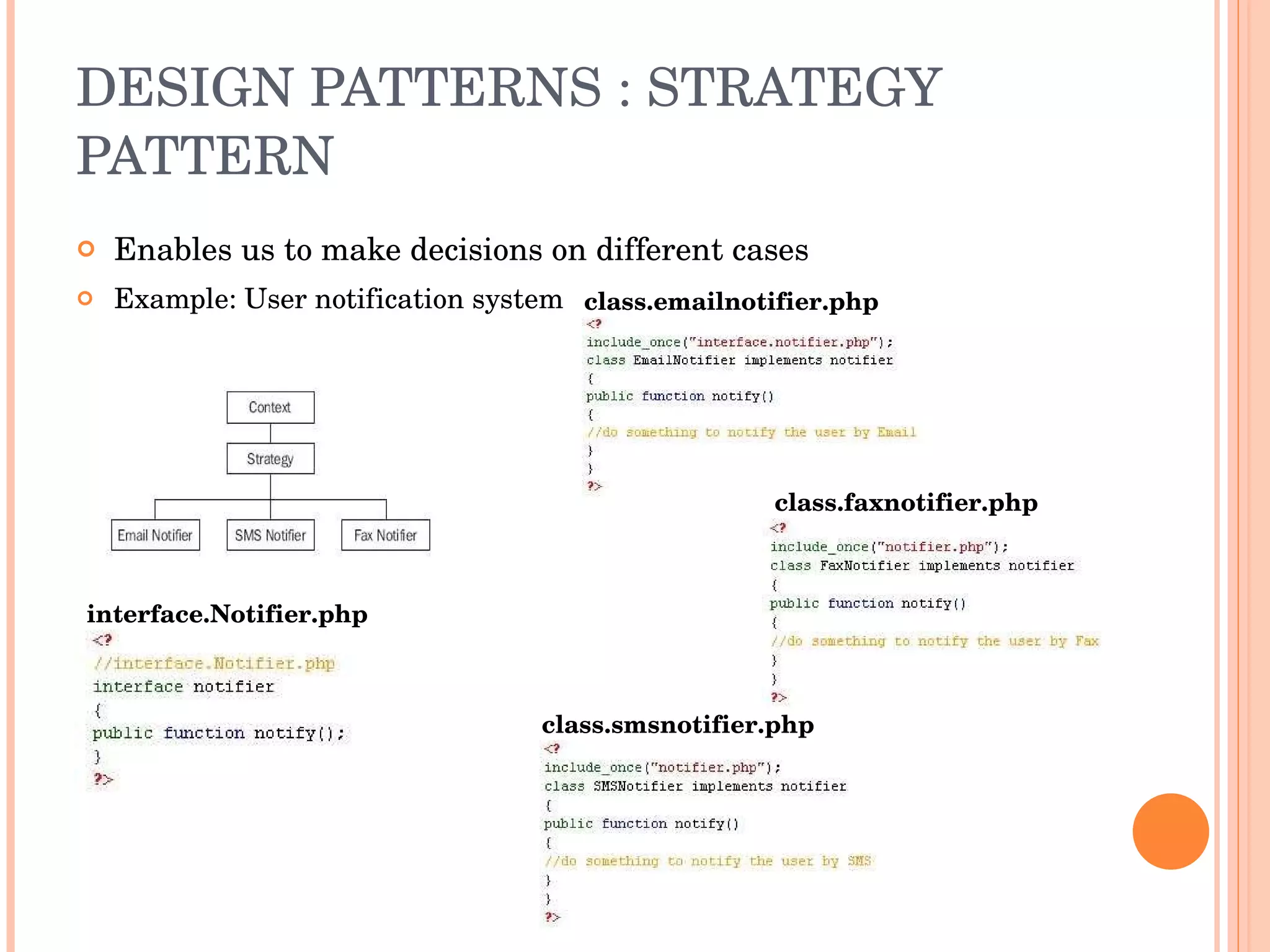
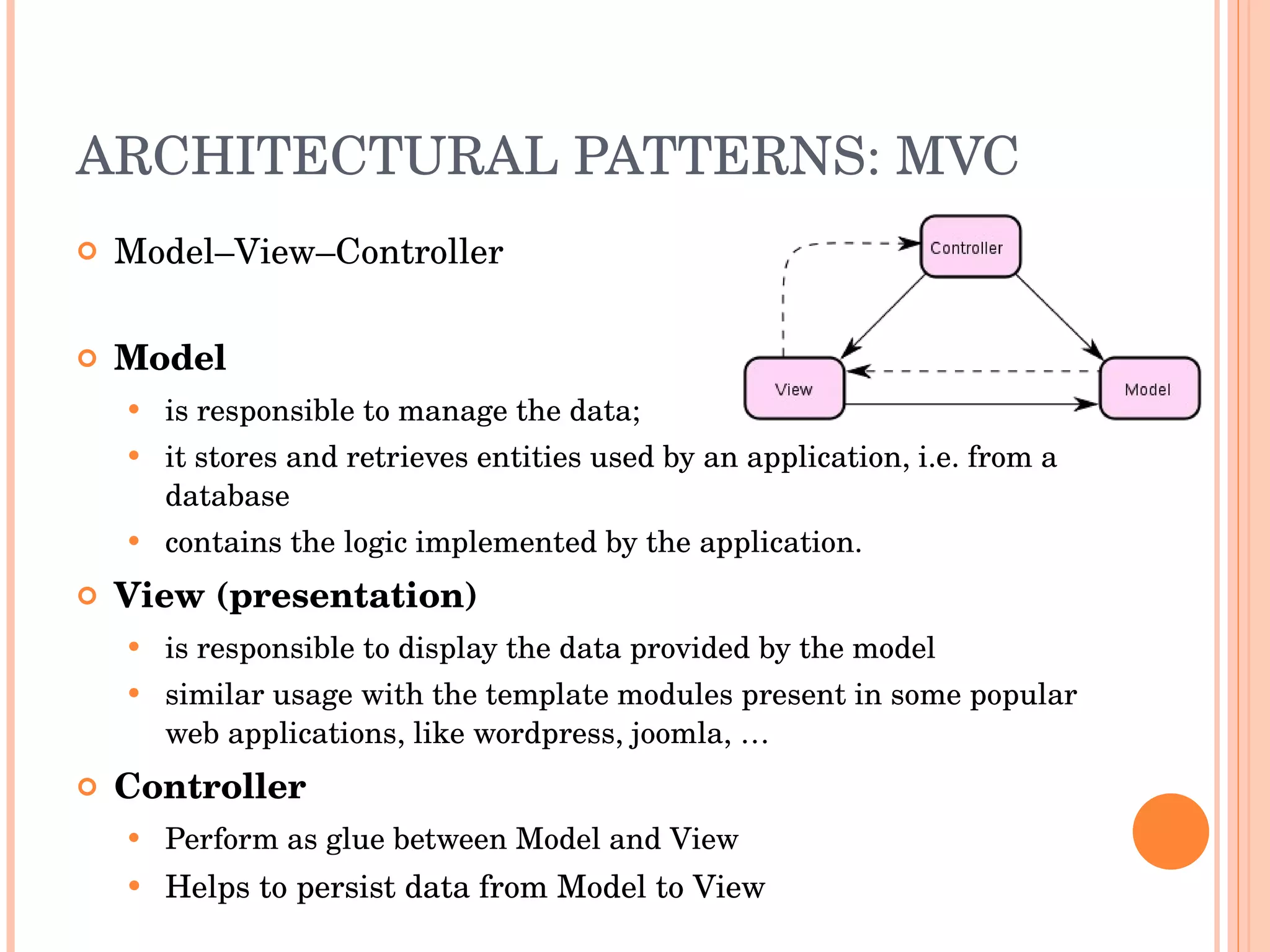
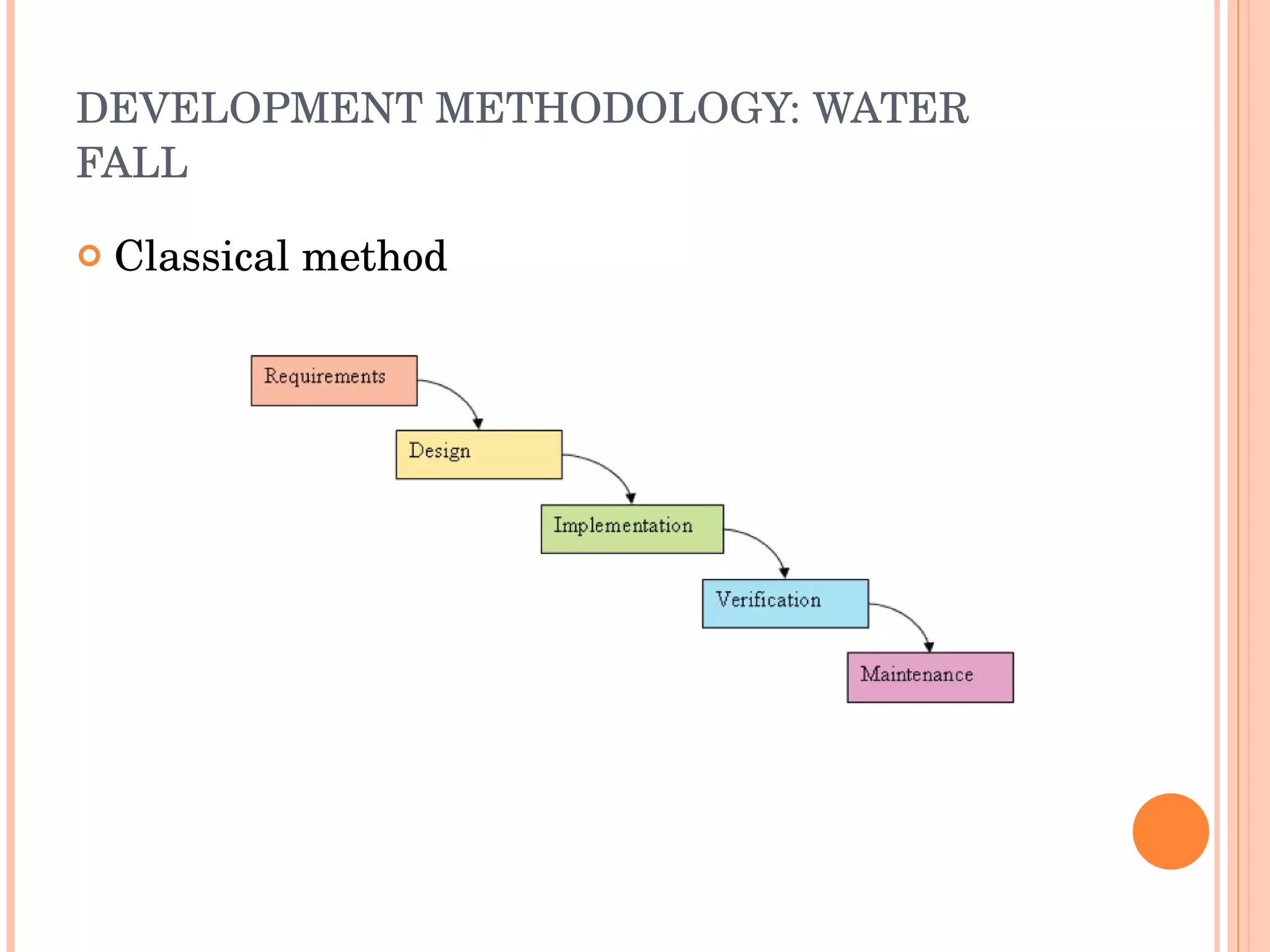
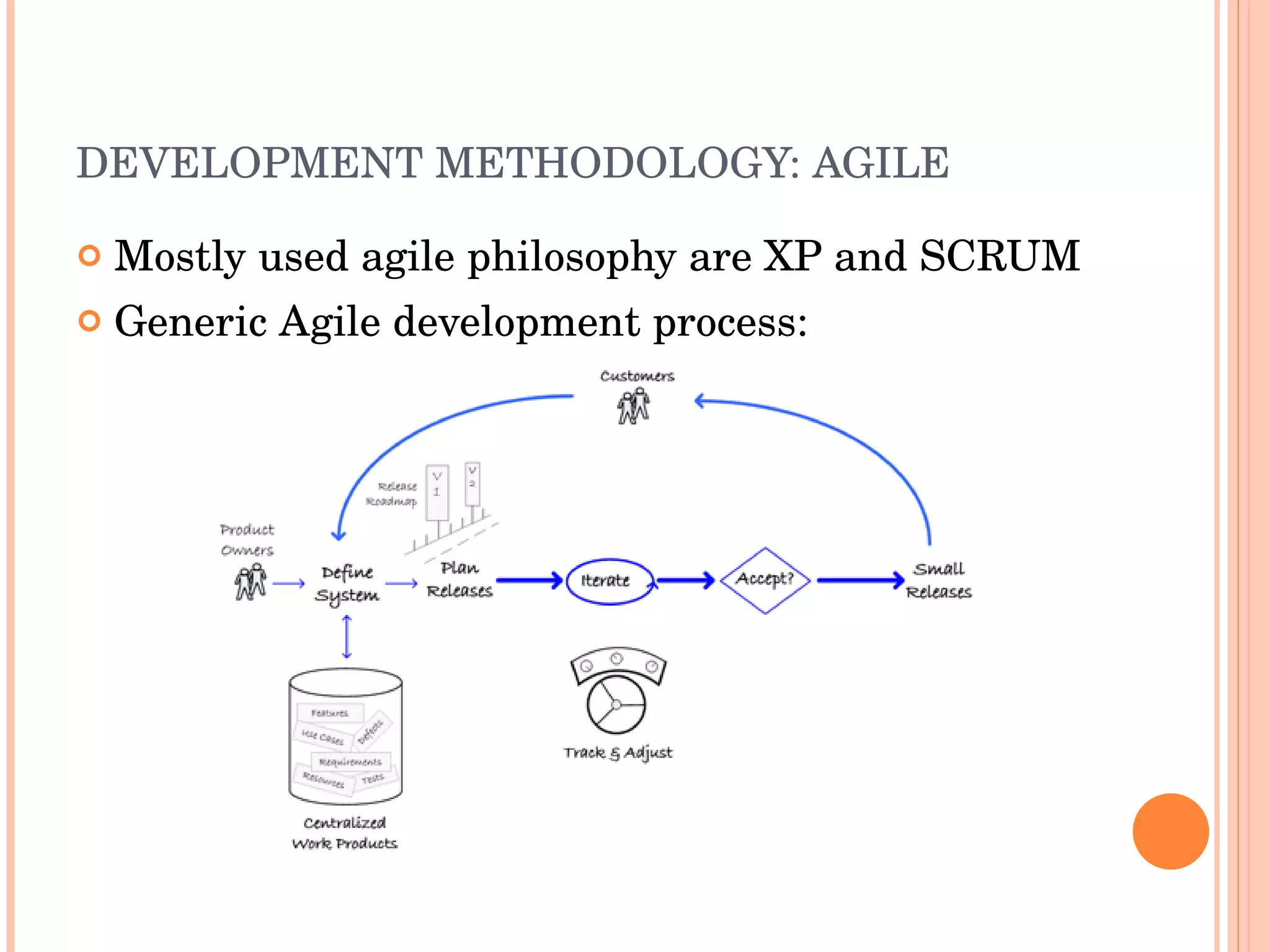
The document discusses engineering principles and best practices for PHP development. It covers design patterns like strategy and singleton patterns, architectural patterns like MVC, development methodologies like waterfall and agile, processes like using frameworks, foundations, security testing, debugging and optimization. It also discusses deployment, performance, refactoring, open source models, documentation and commercial support.