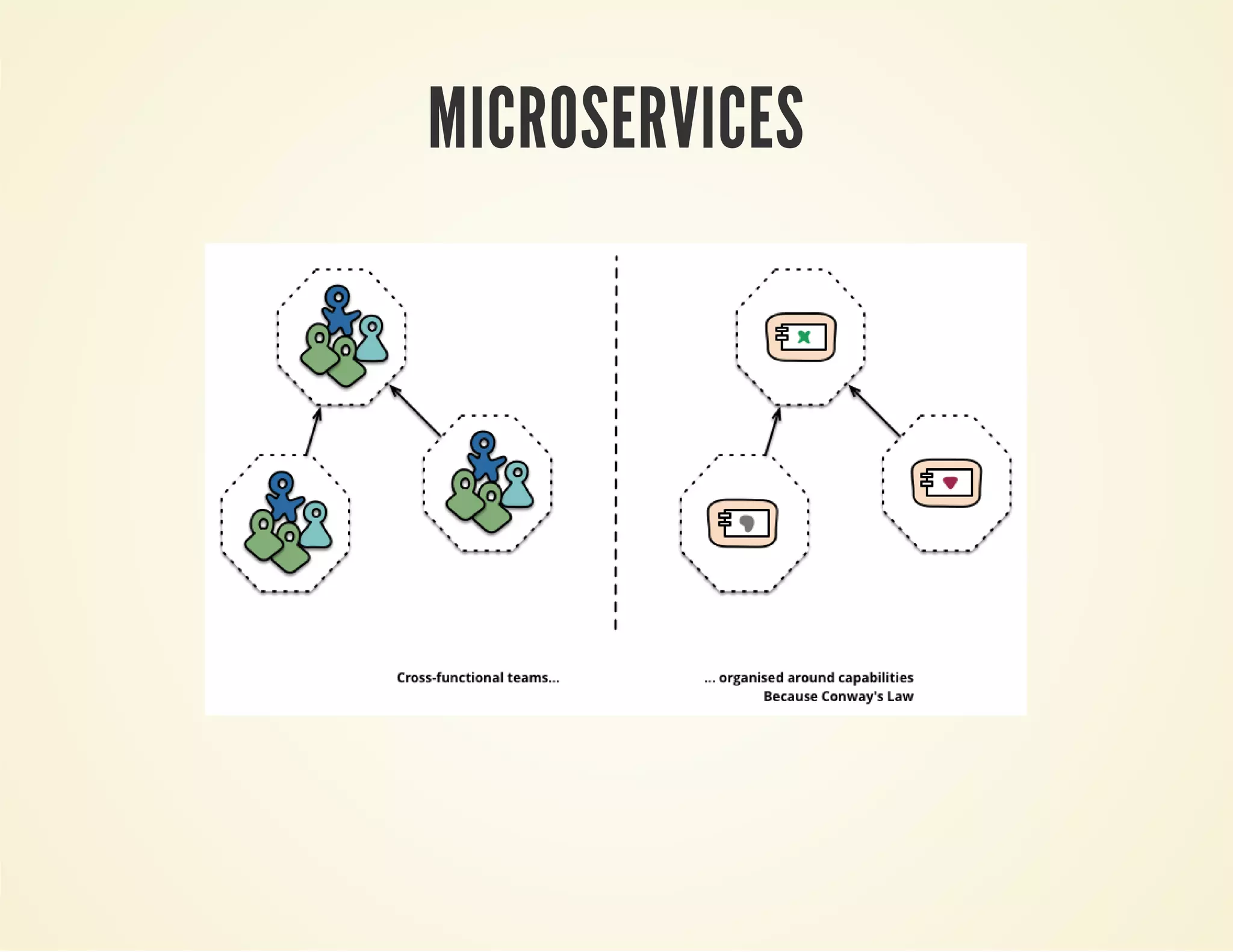
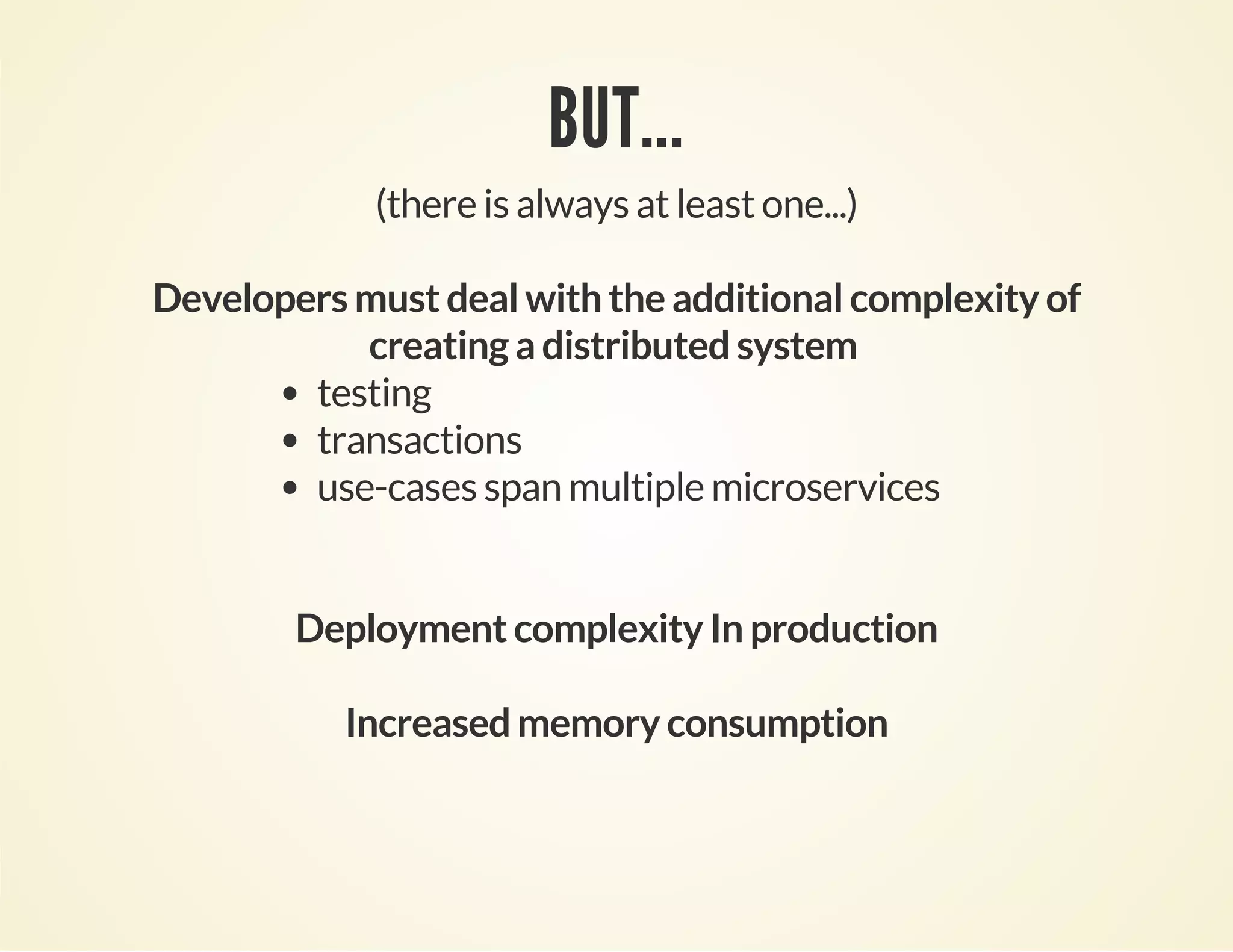
The document discusses microservices architecture and how Spring Boot can be used to develop microservices. Some key points include:
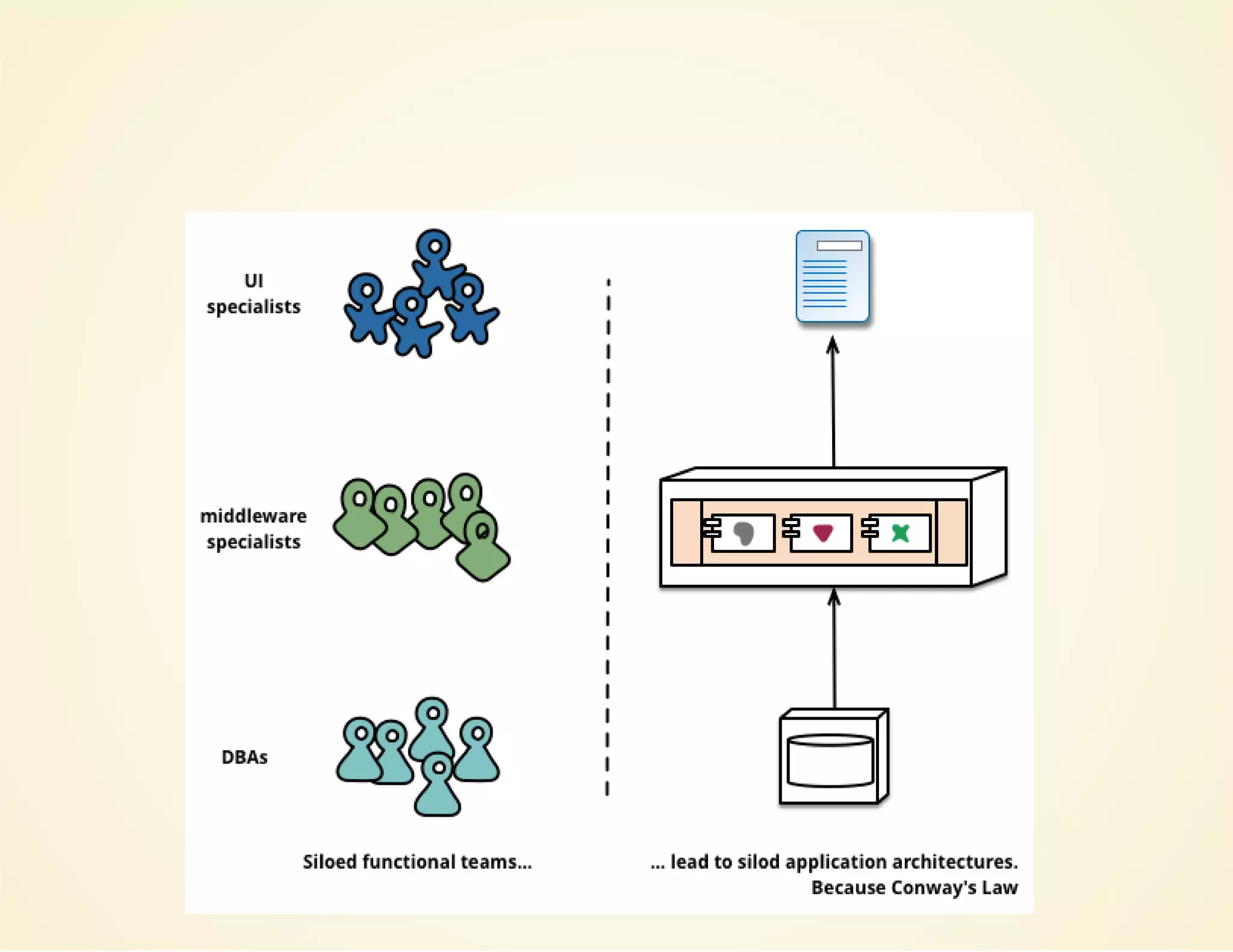
- Microservices architecture decomposes an application into small, independent services that communicate over the network, improving fault isolation and scalability compared to a monolithic architecture.
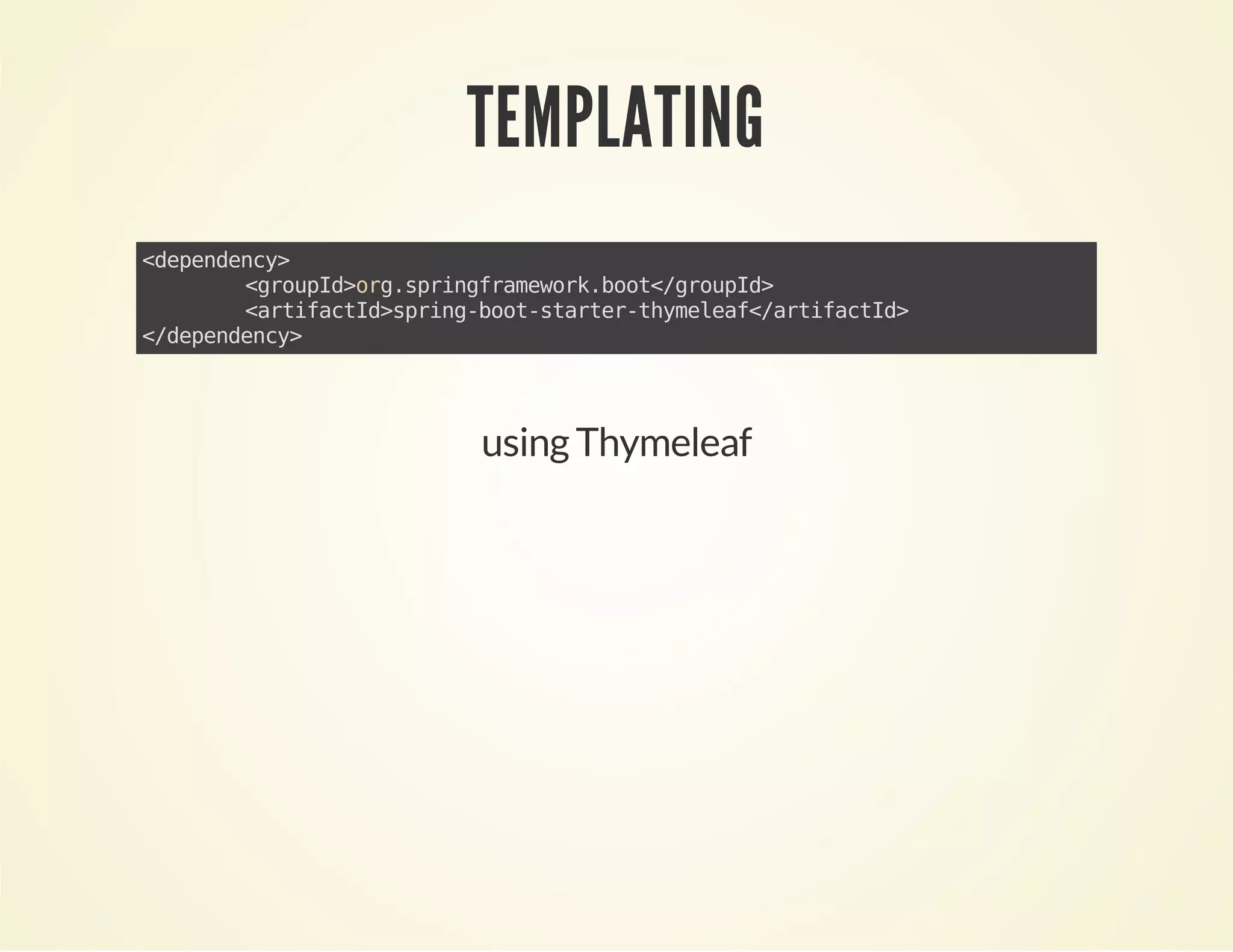
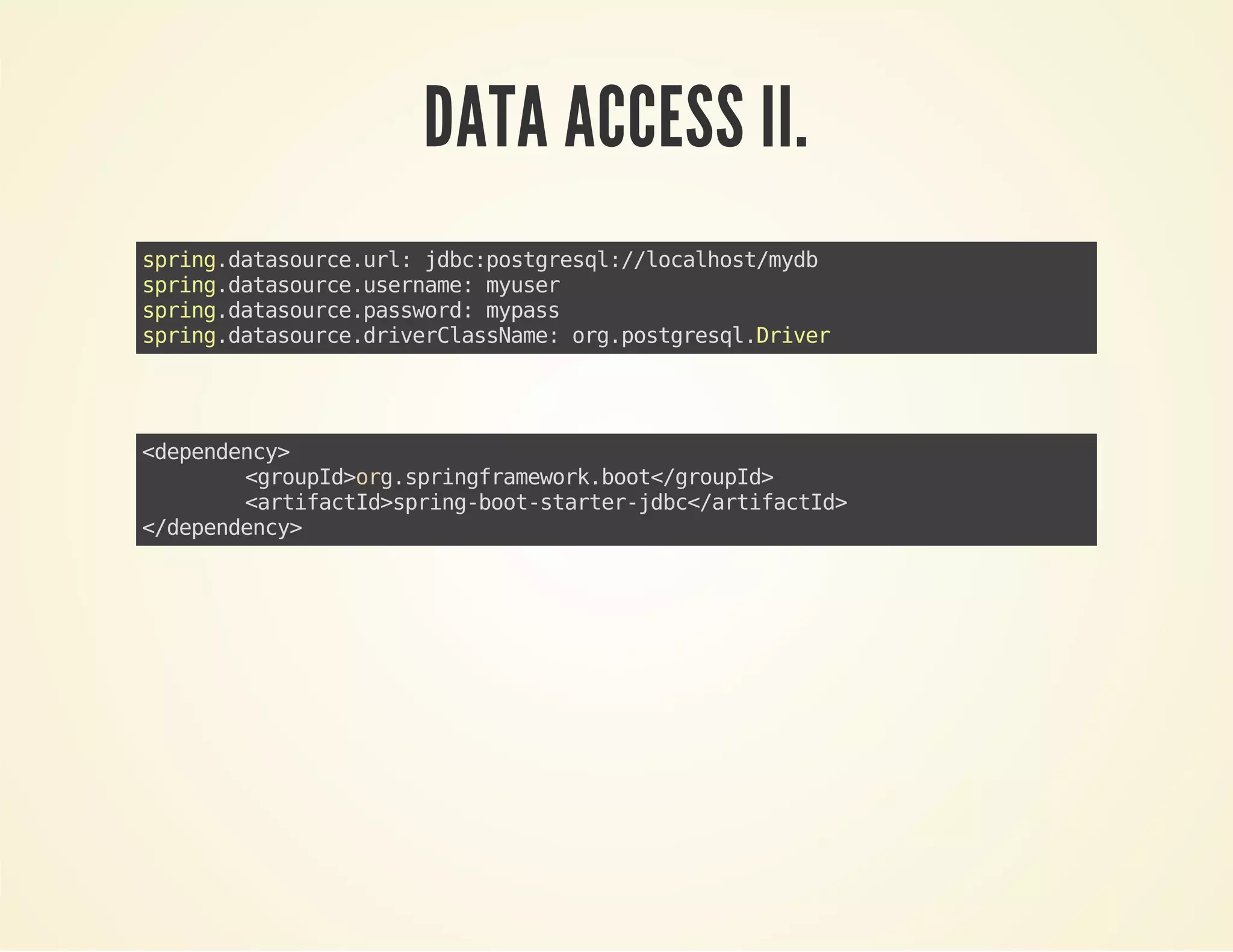
- Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone Spring-based applications and services. It includes useful starter dependencies and auto-configuration options.
- Developing microservices with Spring Boot offers benefits like rapid development cycles, easy scaling, and leveraging the Spring ecosystem of Java libraries and tools.










![APP CODE
package hello;
import org.springframework.boot.*;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.*;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@Controller
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class SampleController {
@RequestMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
String home() {
return "Hello World!";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(SampleController.class, args);
... the beauty of autoconfiguration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spring-boot-and-microservices-141031024942-conversion-gate02/75/Spring-Boot-and-Microservices-14-2048.jpg)