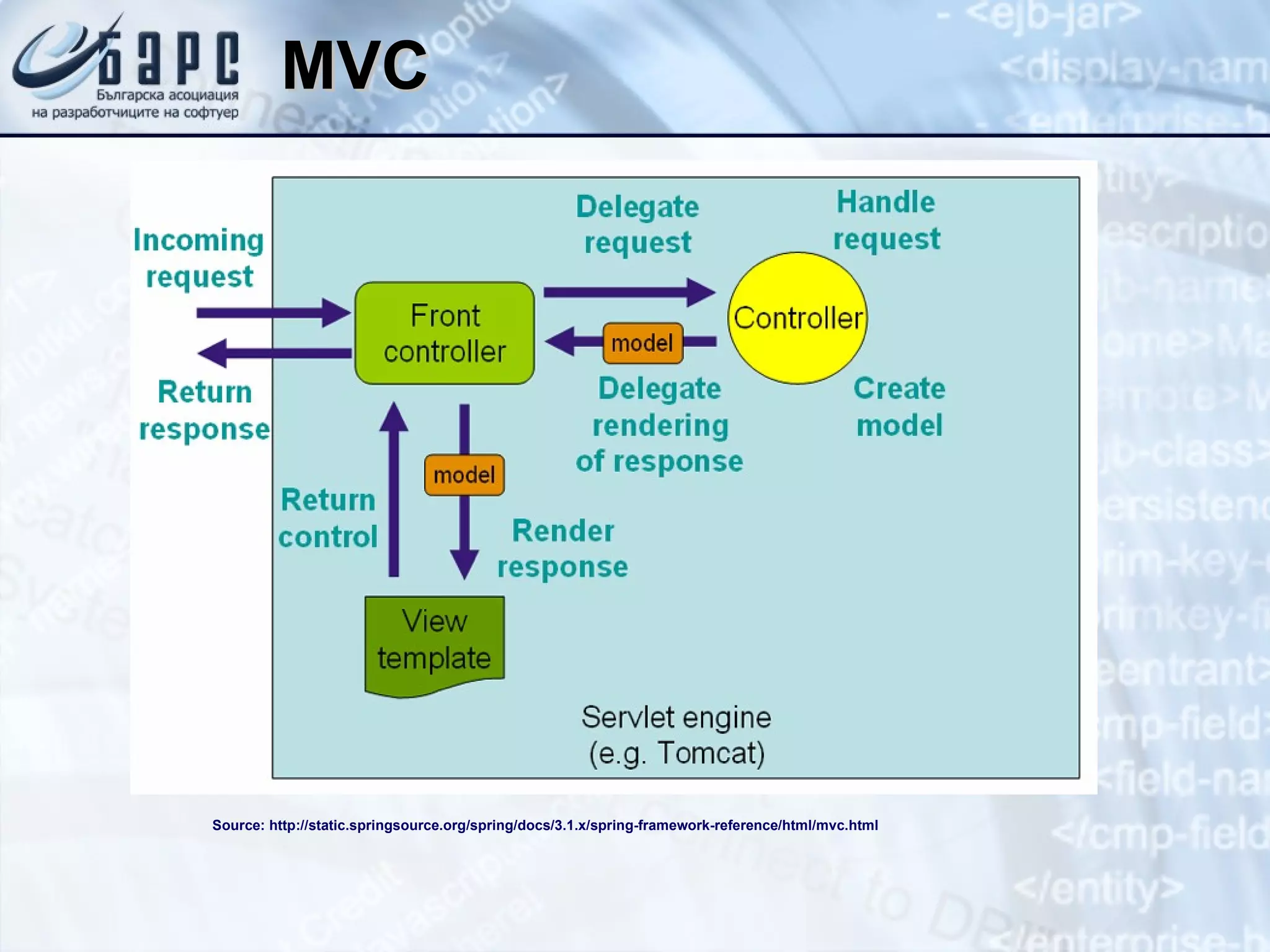
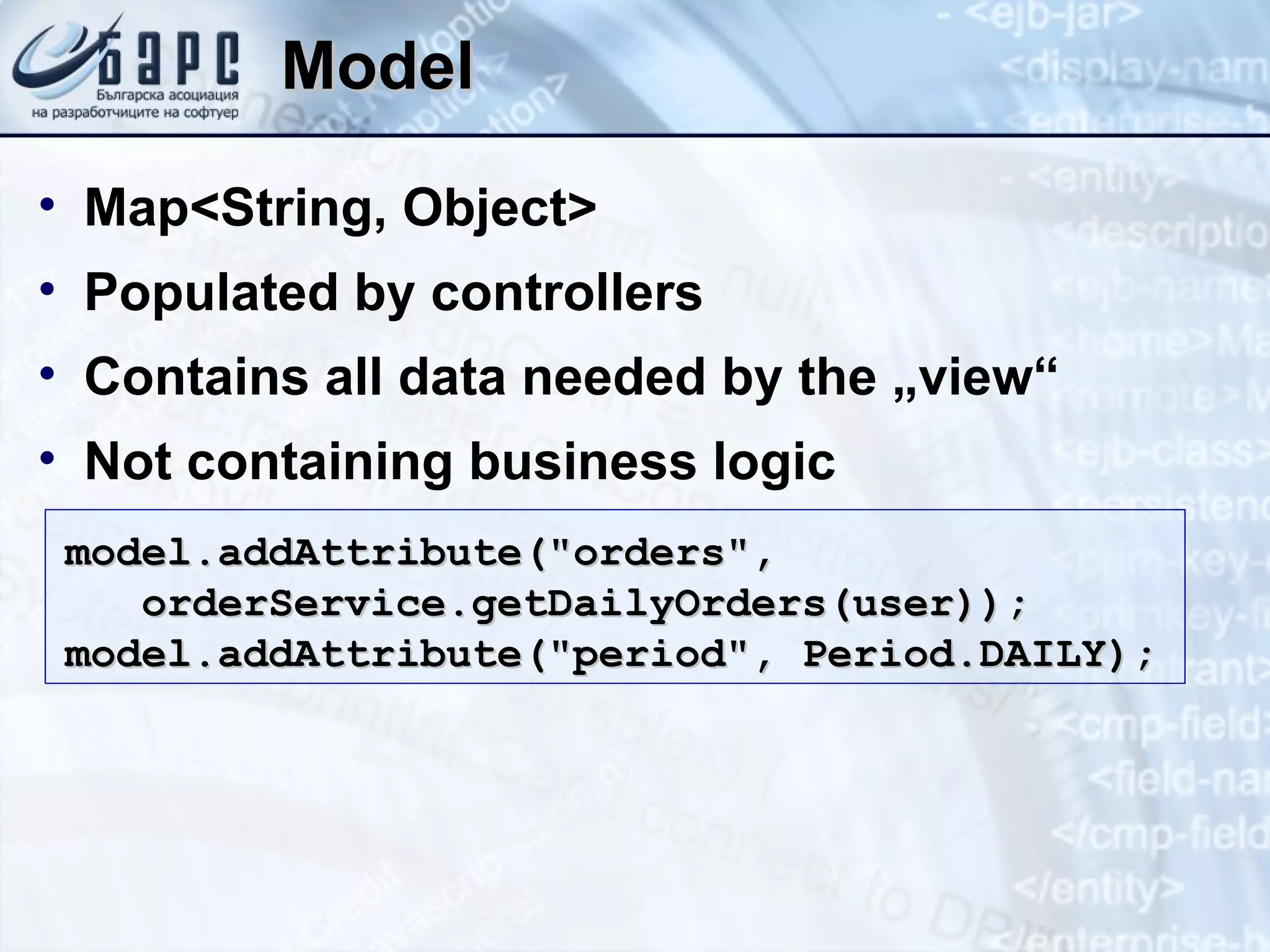
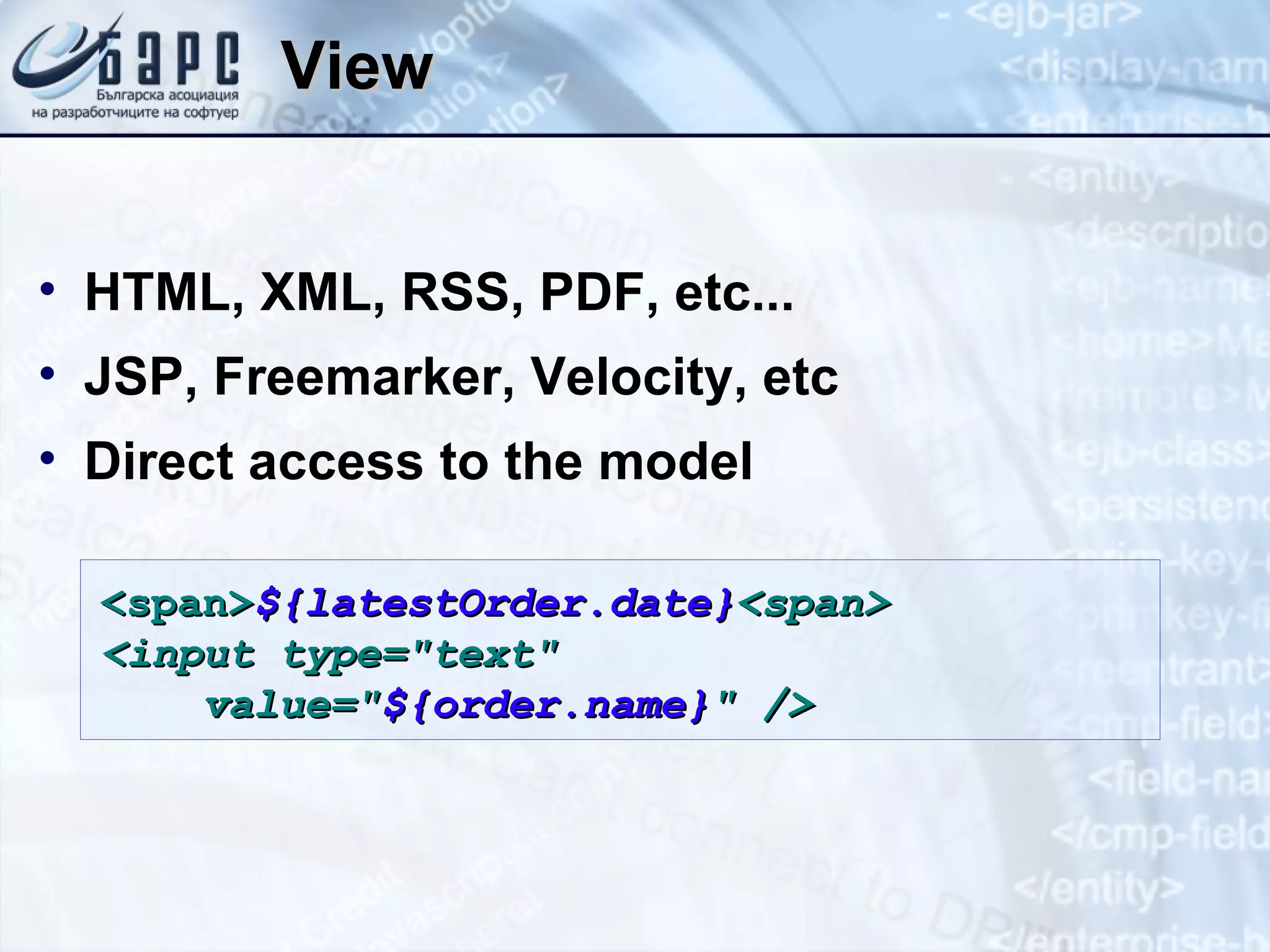
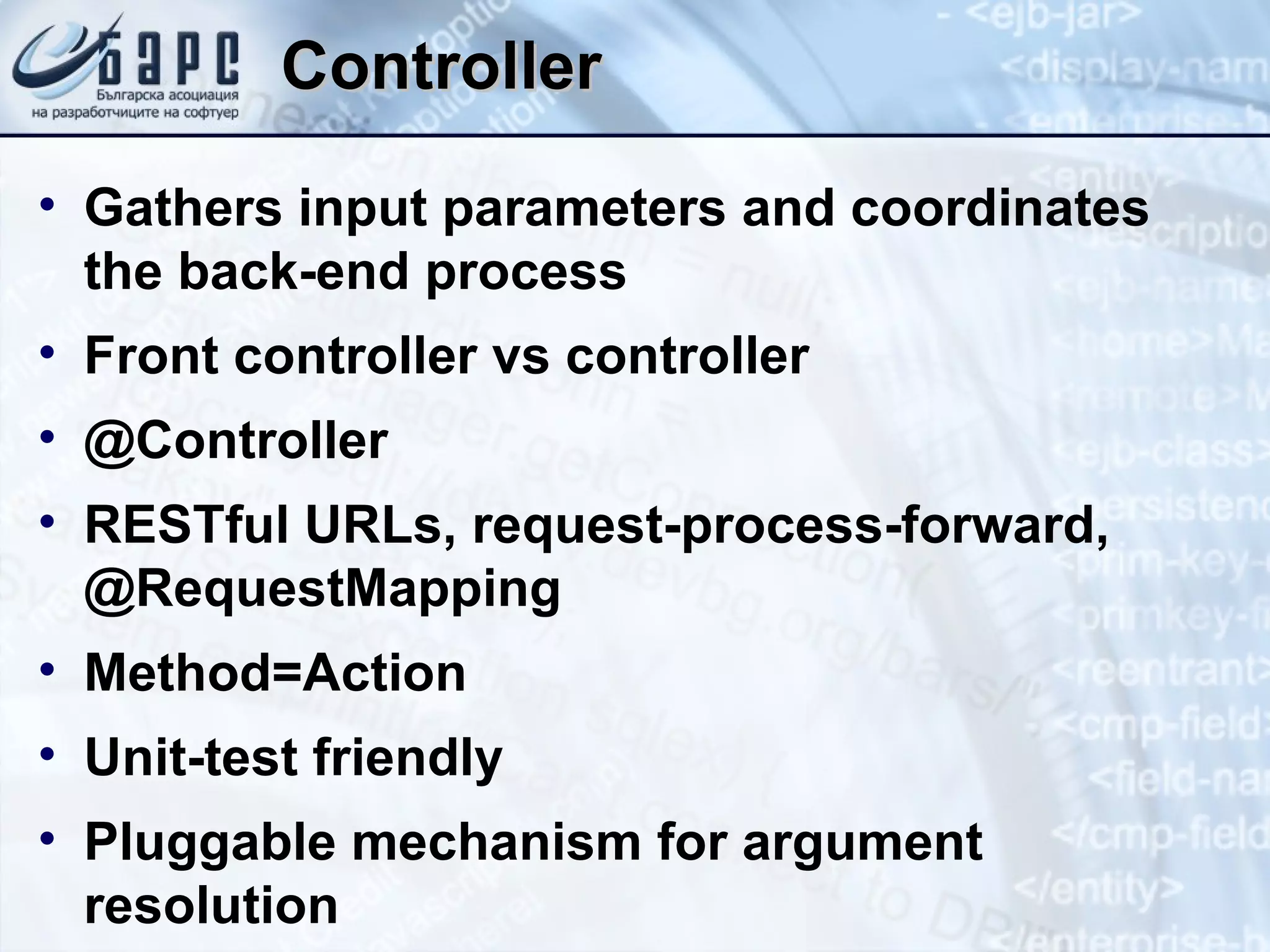
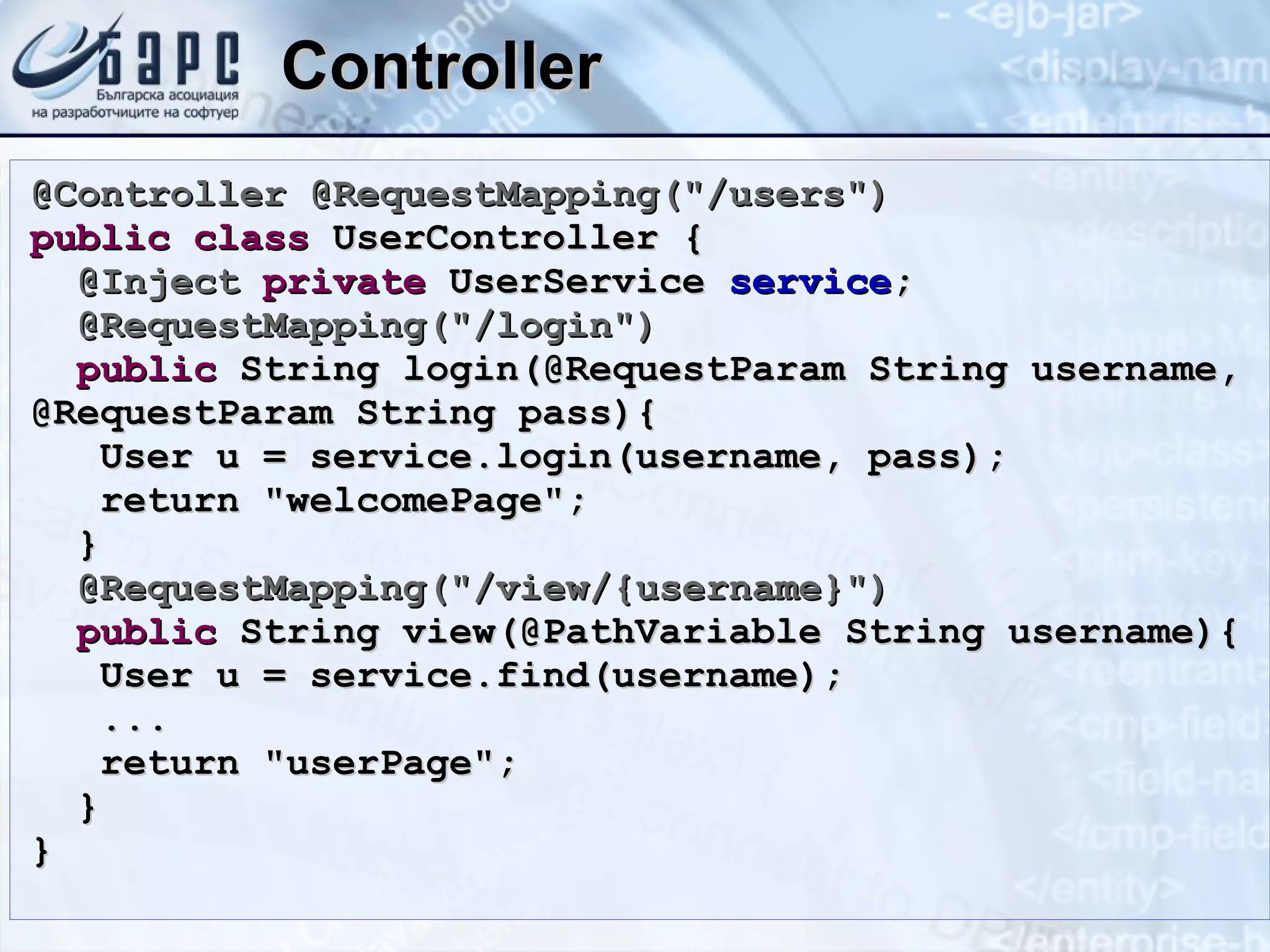
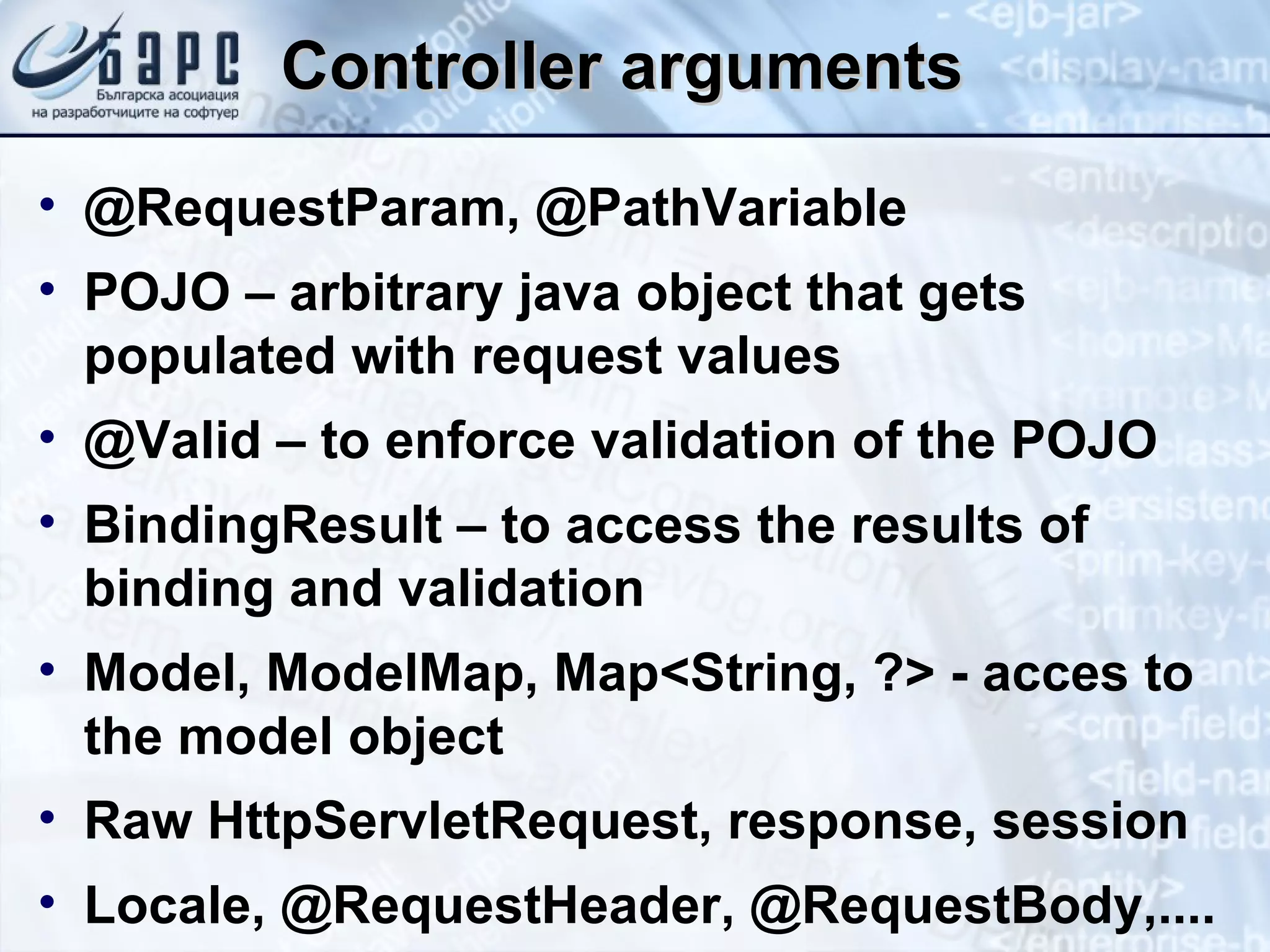
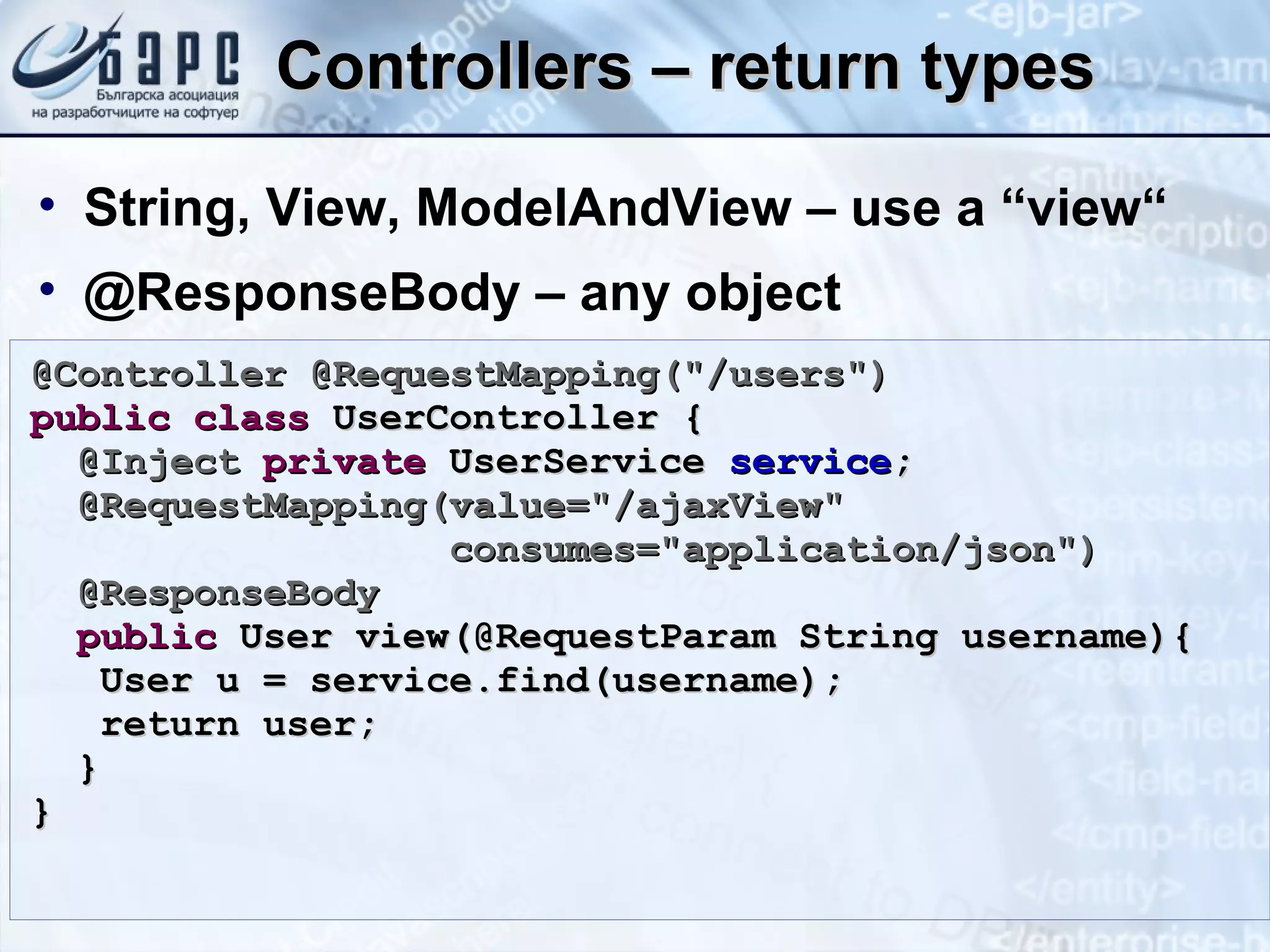
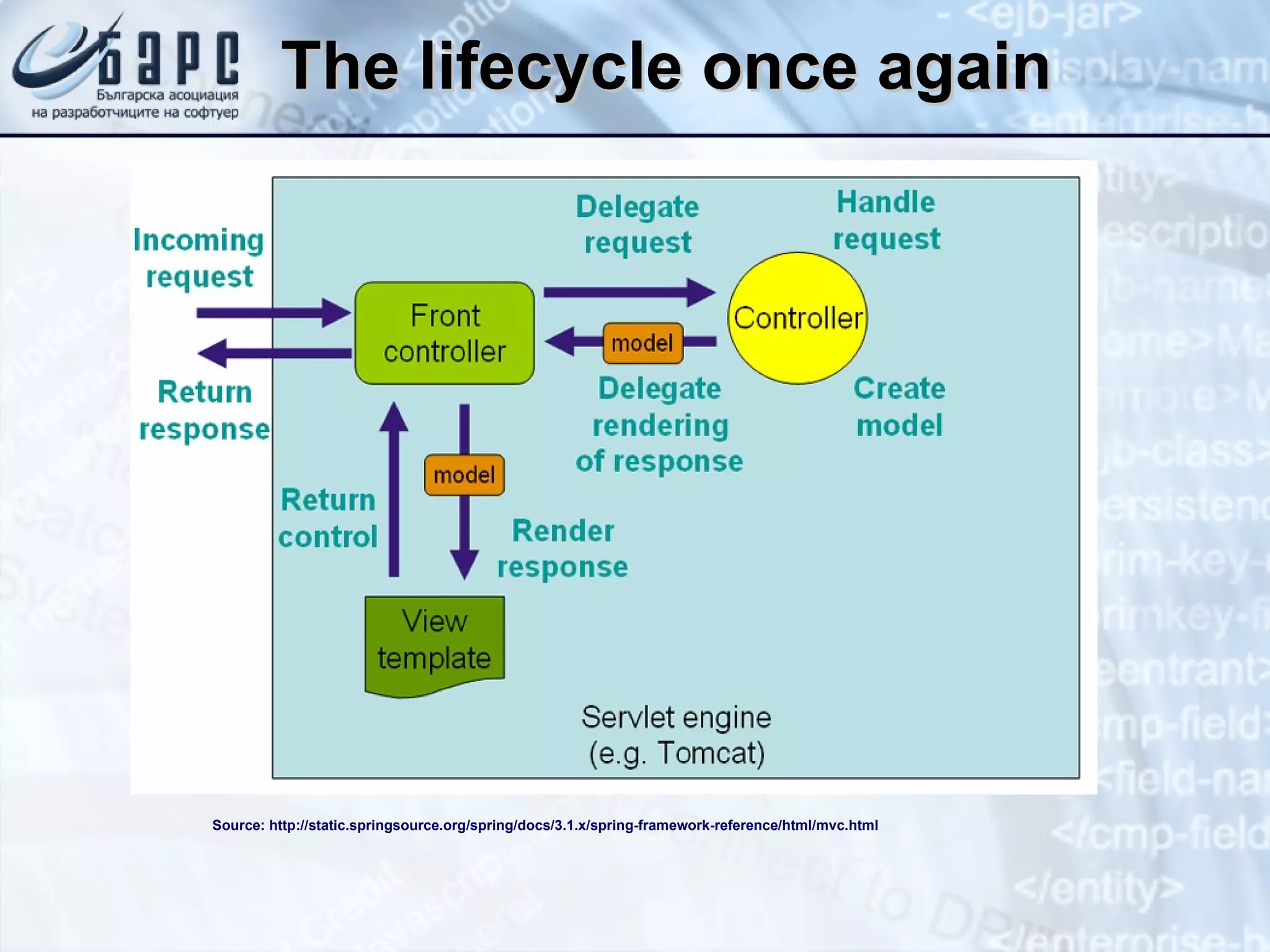
This document summarizes the basics of Spring MVC, including the model-view-controller (MVC) pattern it uses. It describes the main components - the model which contains application data, the view which displays data to the user, and the controller which handles requests and coordinates the model and view. It provides examples of how controllers work using annotations like @RequestMapping and how they can return different types of responses. It also briefly mentions other related concepts like interceptors, exceptions, and static resources.