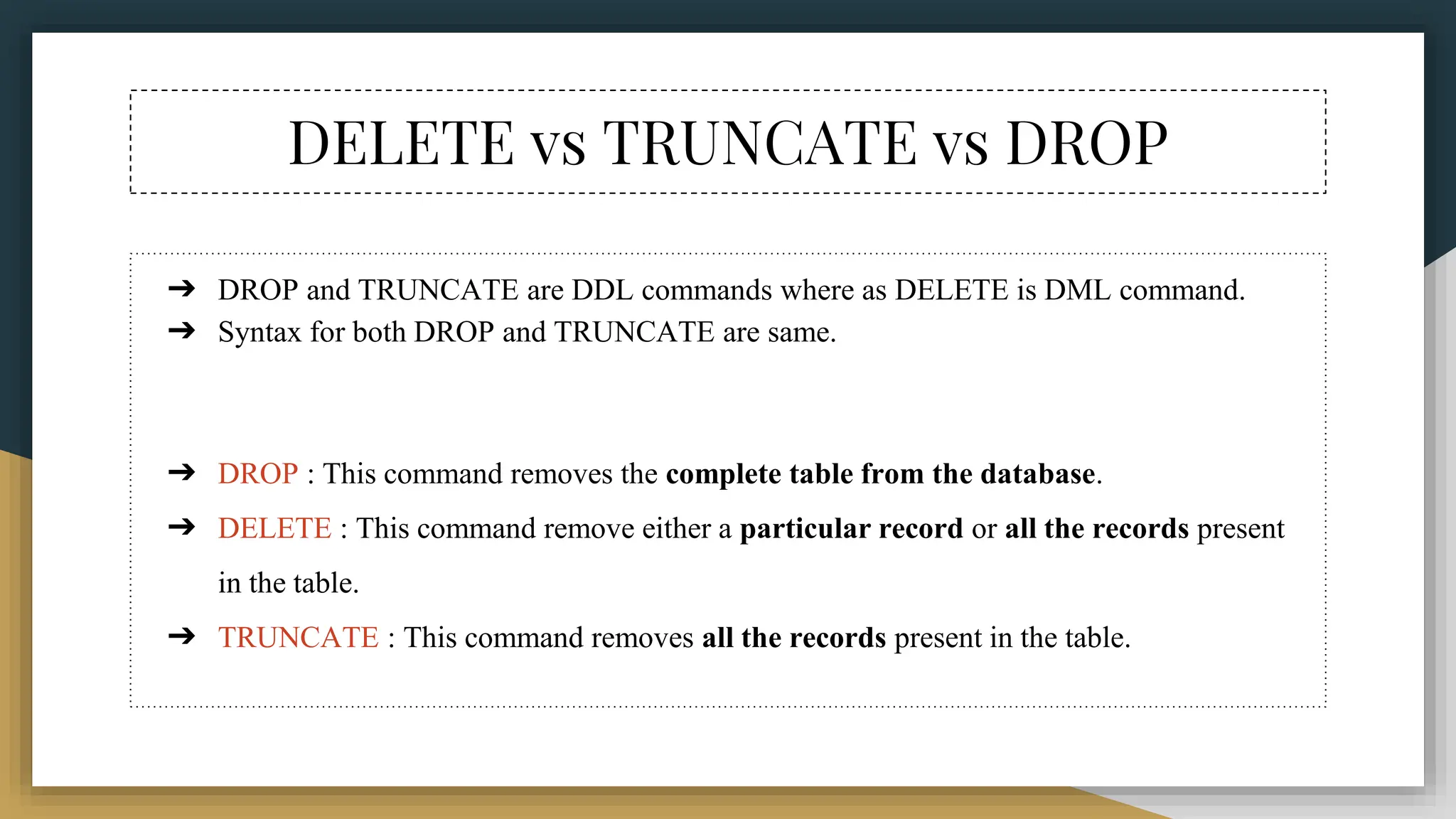
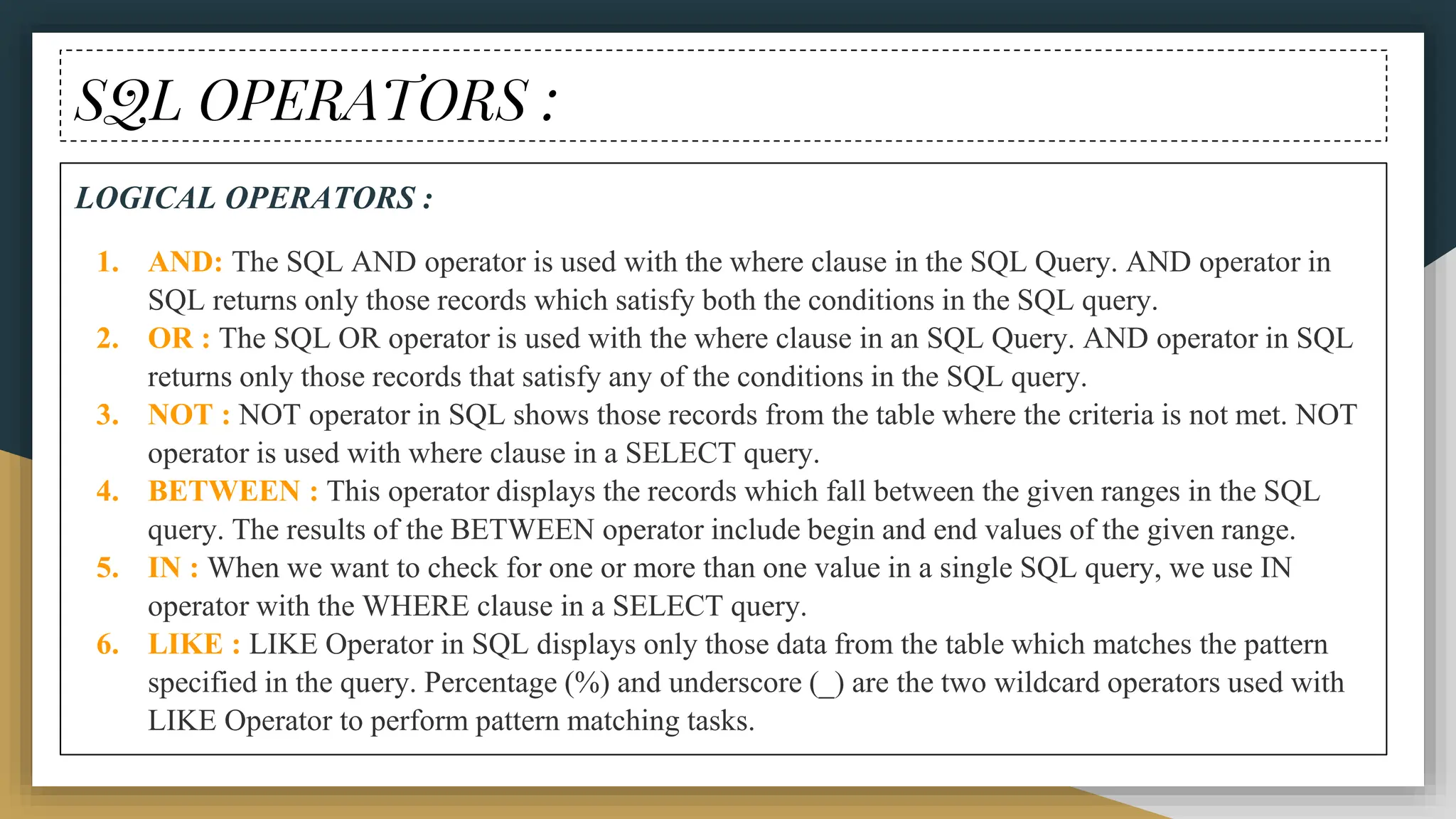
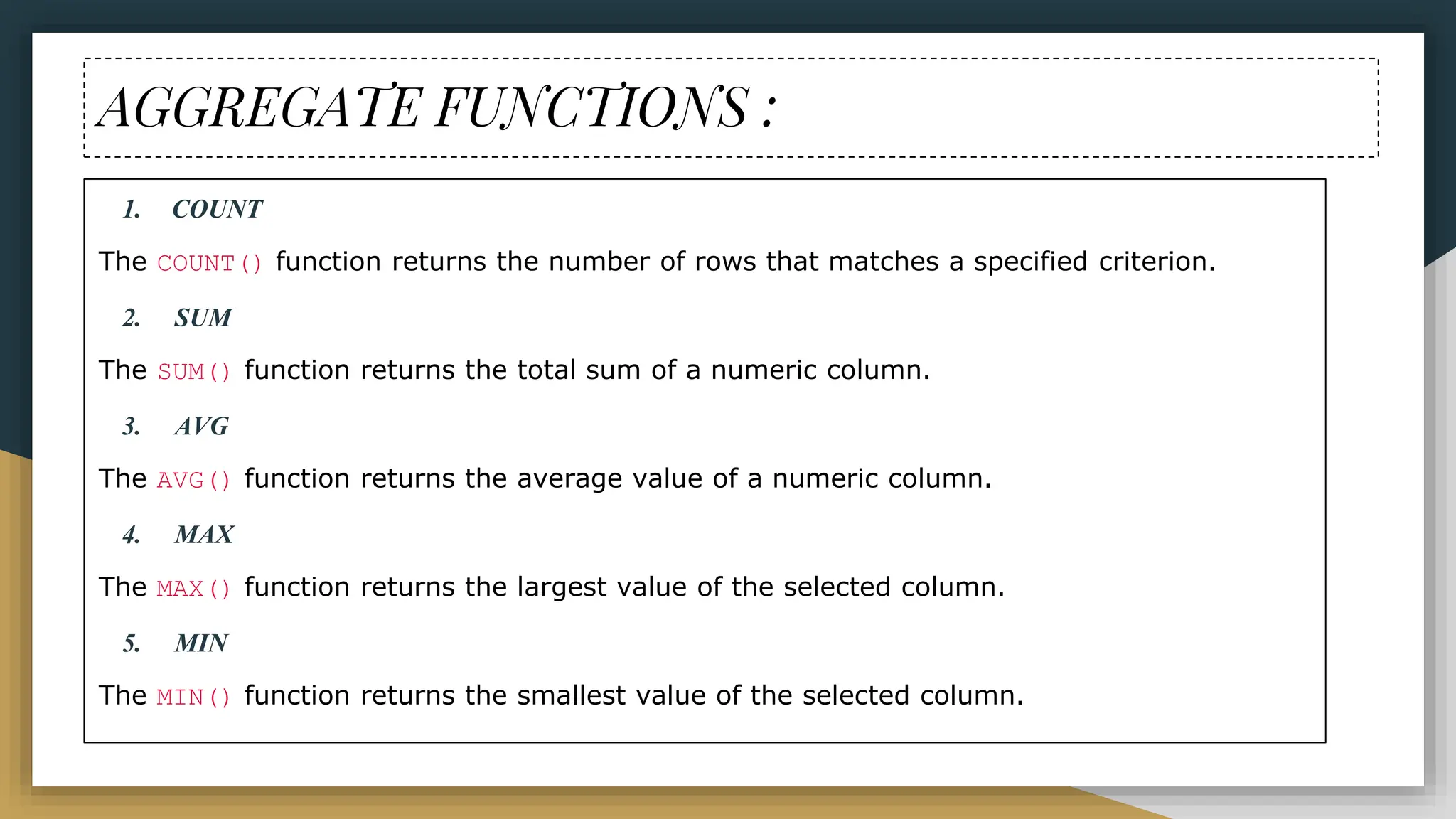
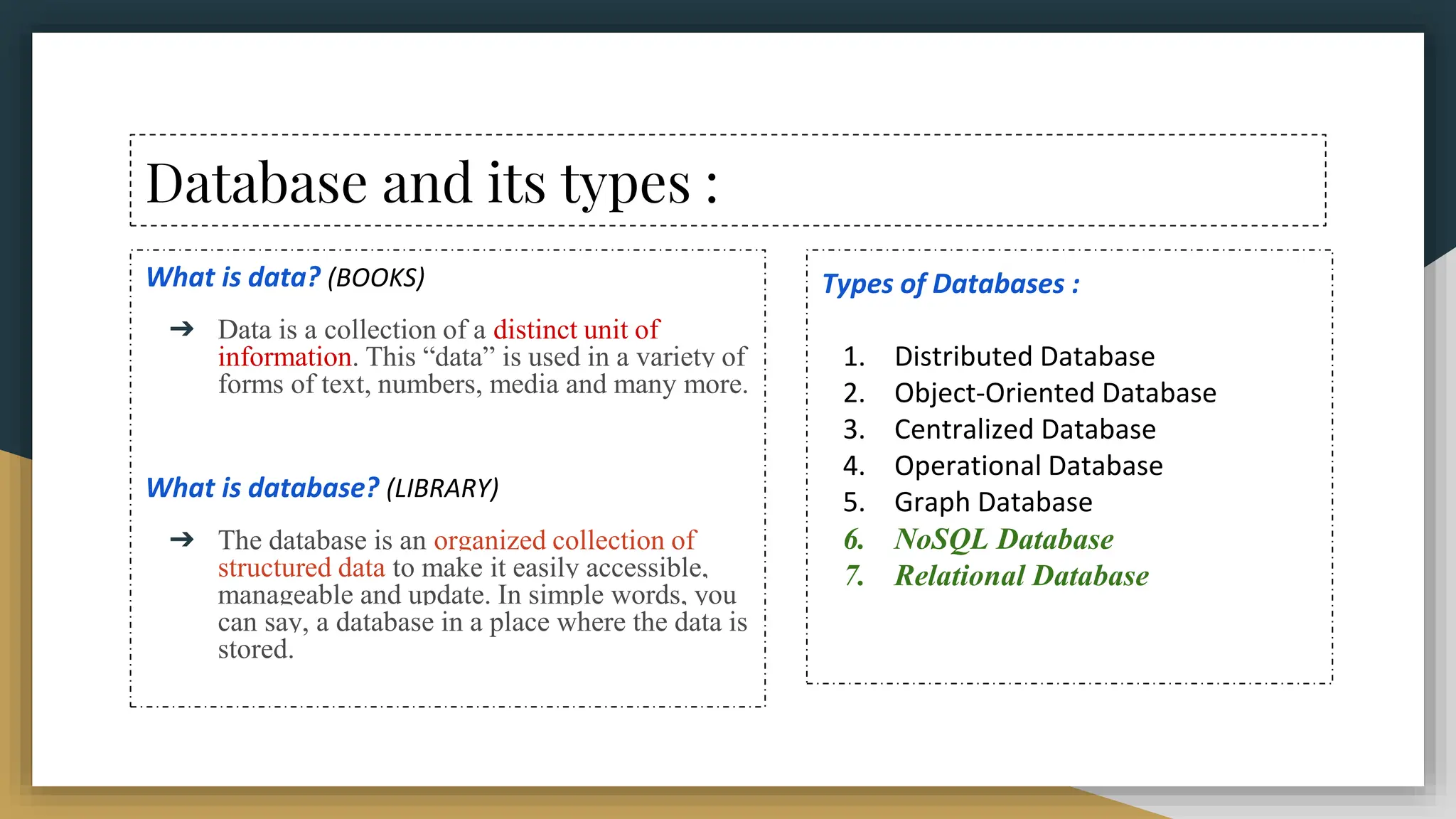
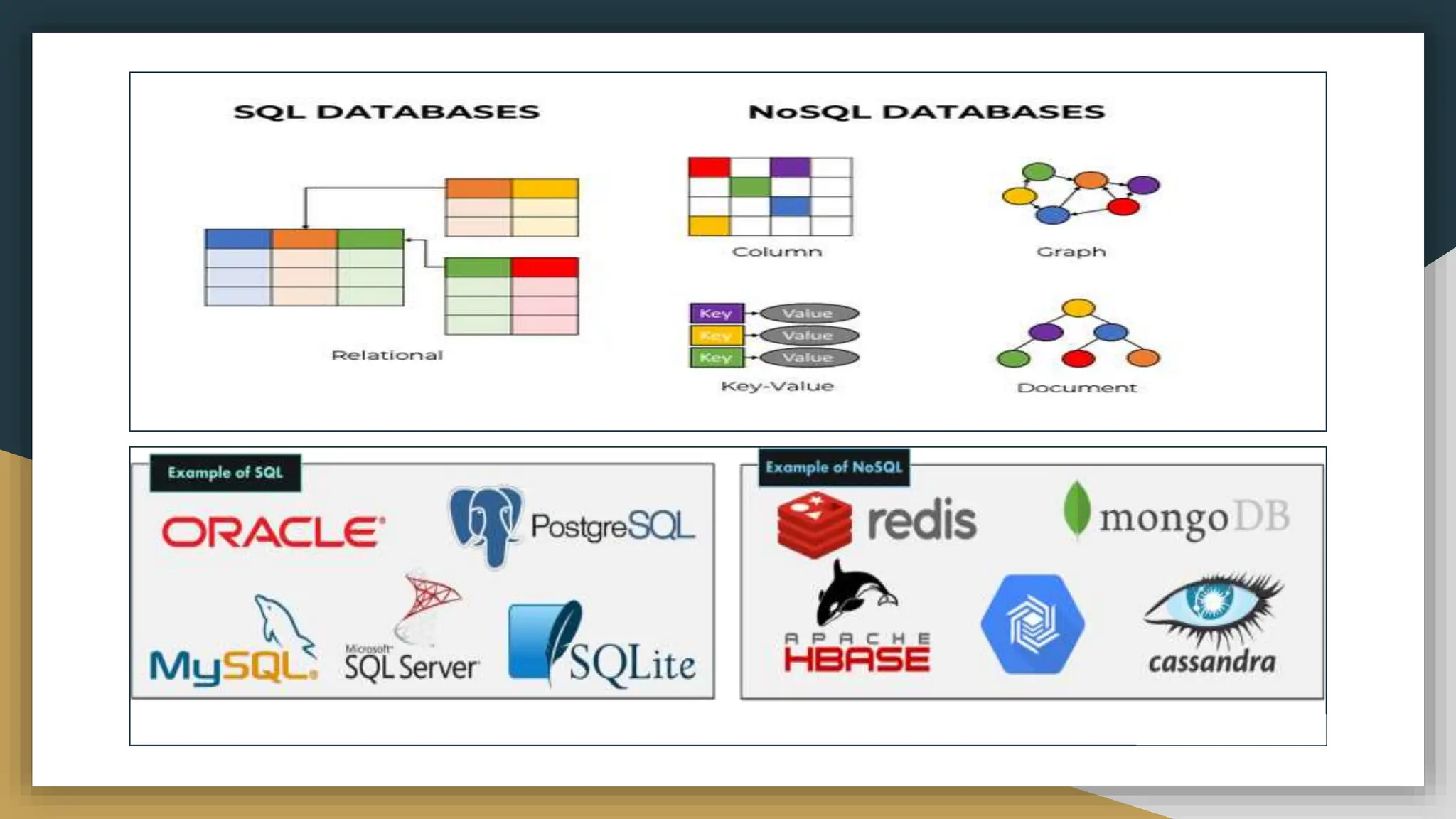
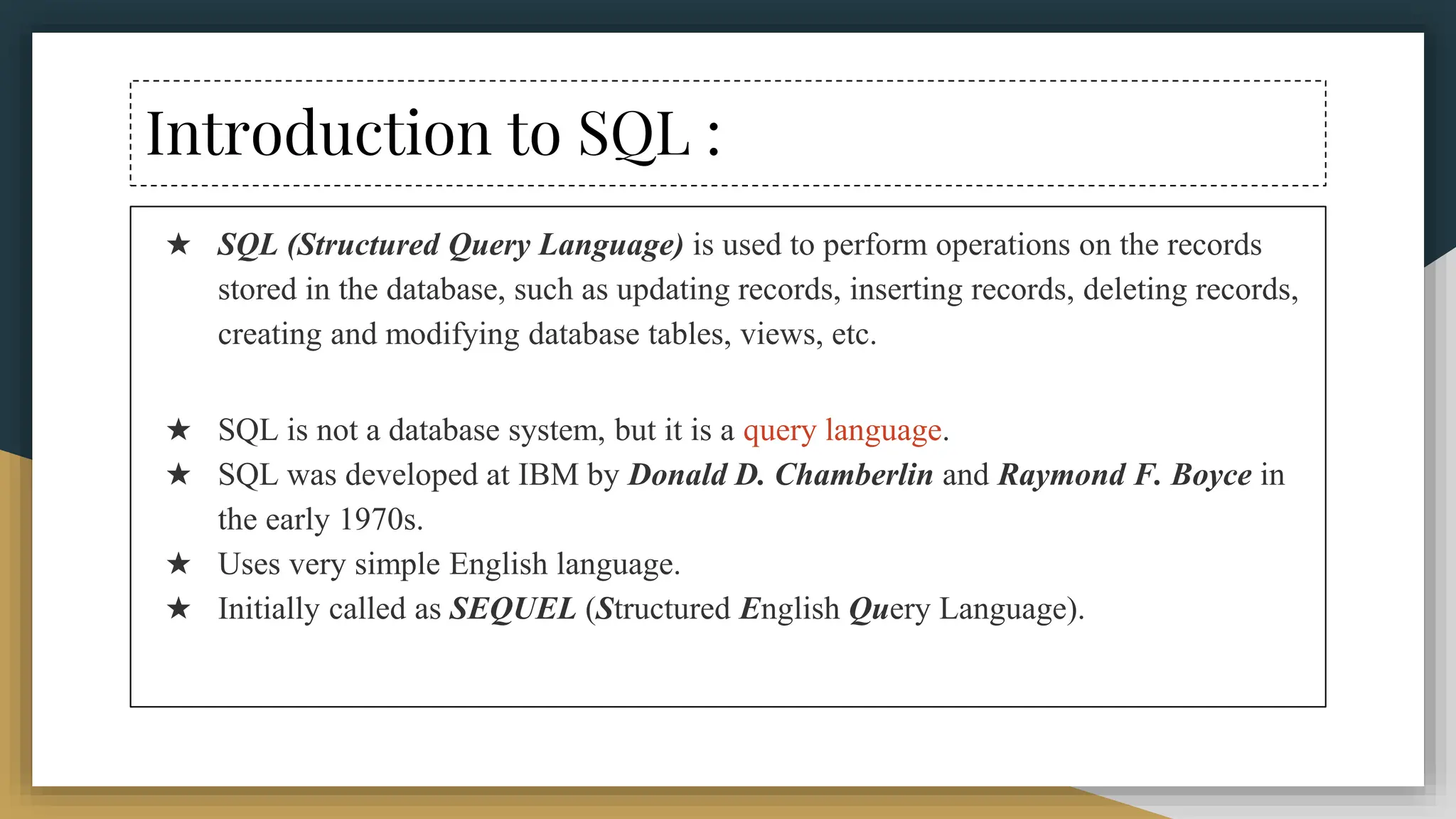
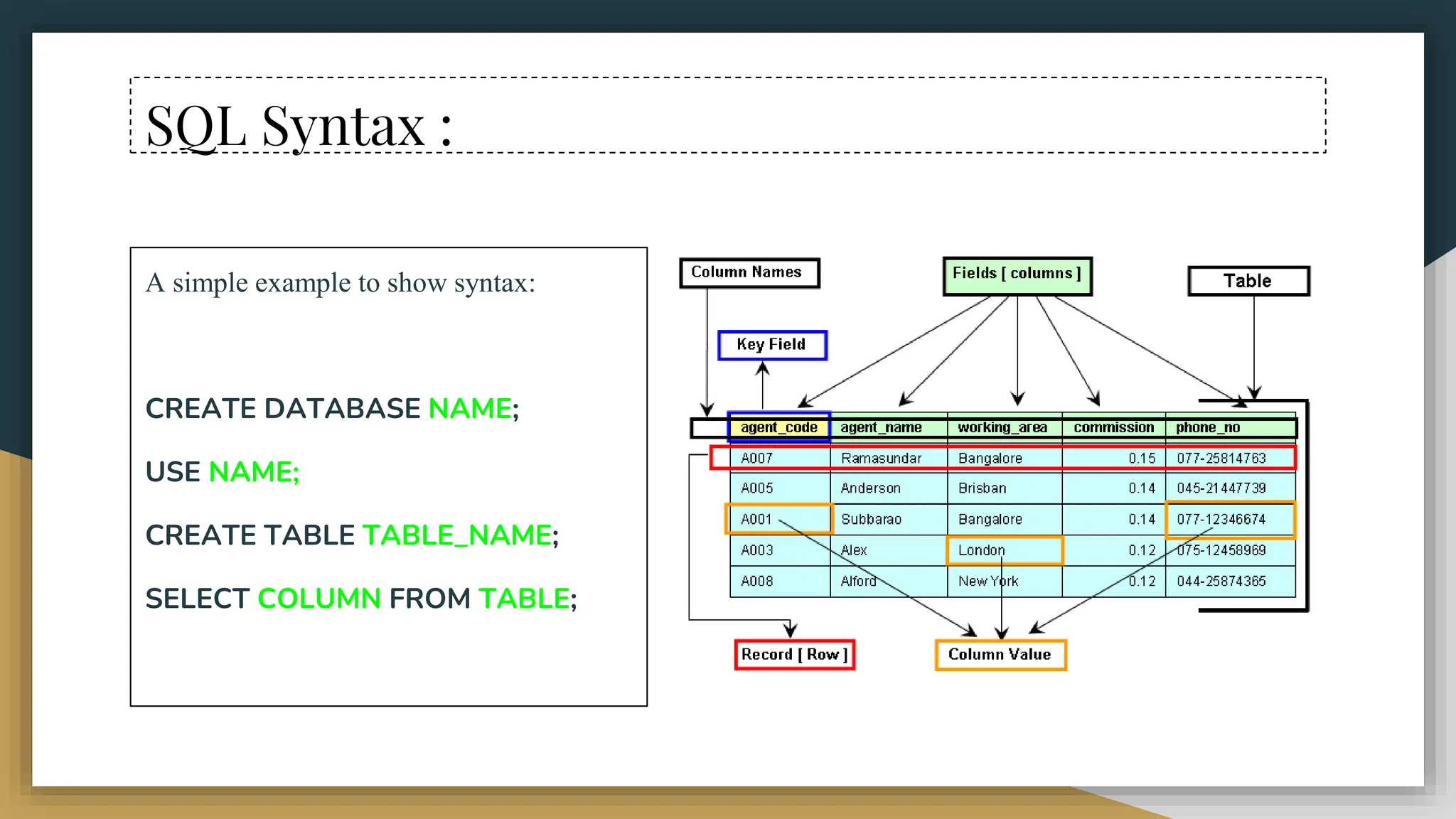
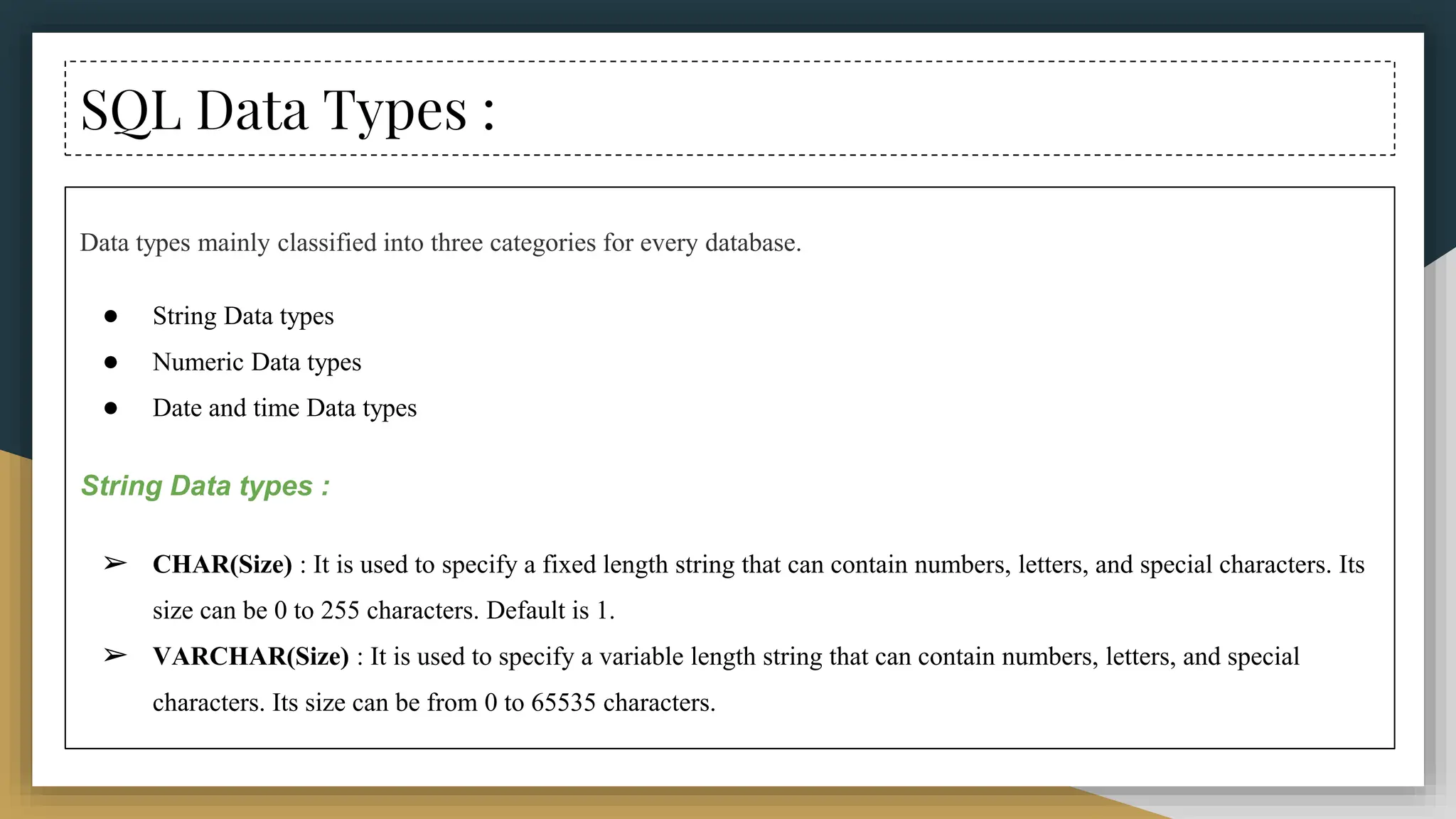
The document provides a comprehensive overview of SQL (Structured Query Language), covering its definition, syntax, data types, commands, and operators used for database management. It details various database types, SQL commands including DDL and DML, and explains aggregate functions alongside their usage examples. The document also highlights the differences between commands such as delete, truncate, and drop, along with the functionalities of logical operators and wildcards.




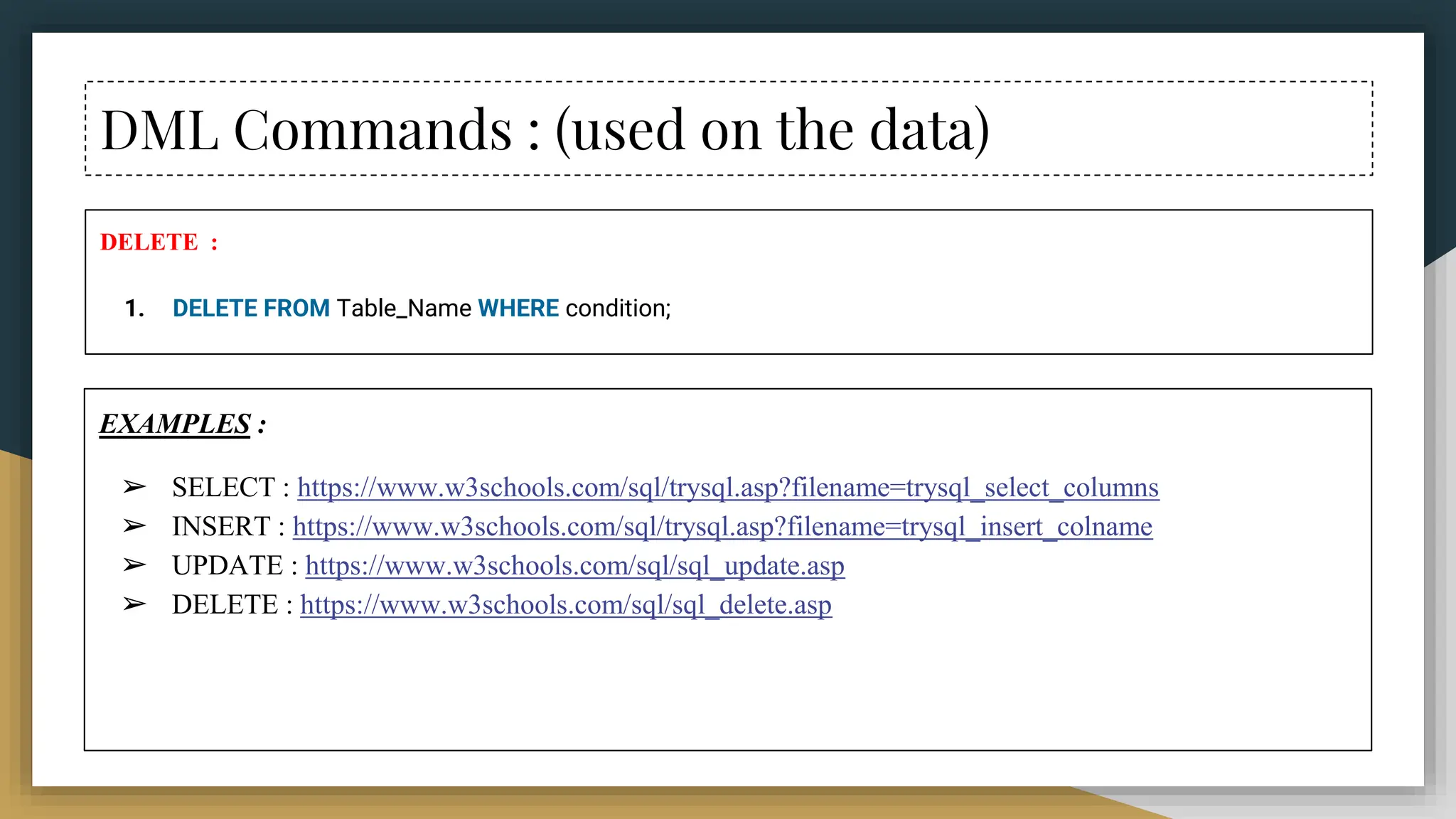
![DML Commands : (used on the data)
SELECT :
1. SELECT column_Name_1, column_Name_2, ….., column_Name_N FROM Name_of_table;
INSERT :
1. INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME ( column_Name1 , column_Name2 , column_Name3 , .... column_NameN )
VALUES (value_1, value_2, value_3, .... value_N ) ;
UPDATE :
1. UPDATE Table_name SET [column_name1= value_1, ….., column_nameN = value_N] WHERE CONDITION;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql-240722070503-b5428df0/75/SQL_all_commnads_aggregate_functions-pptx-12-2048.jpg)