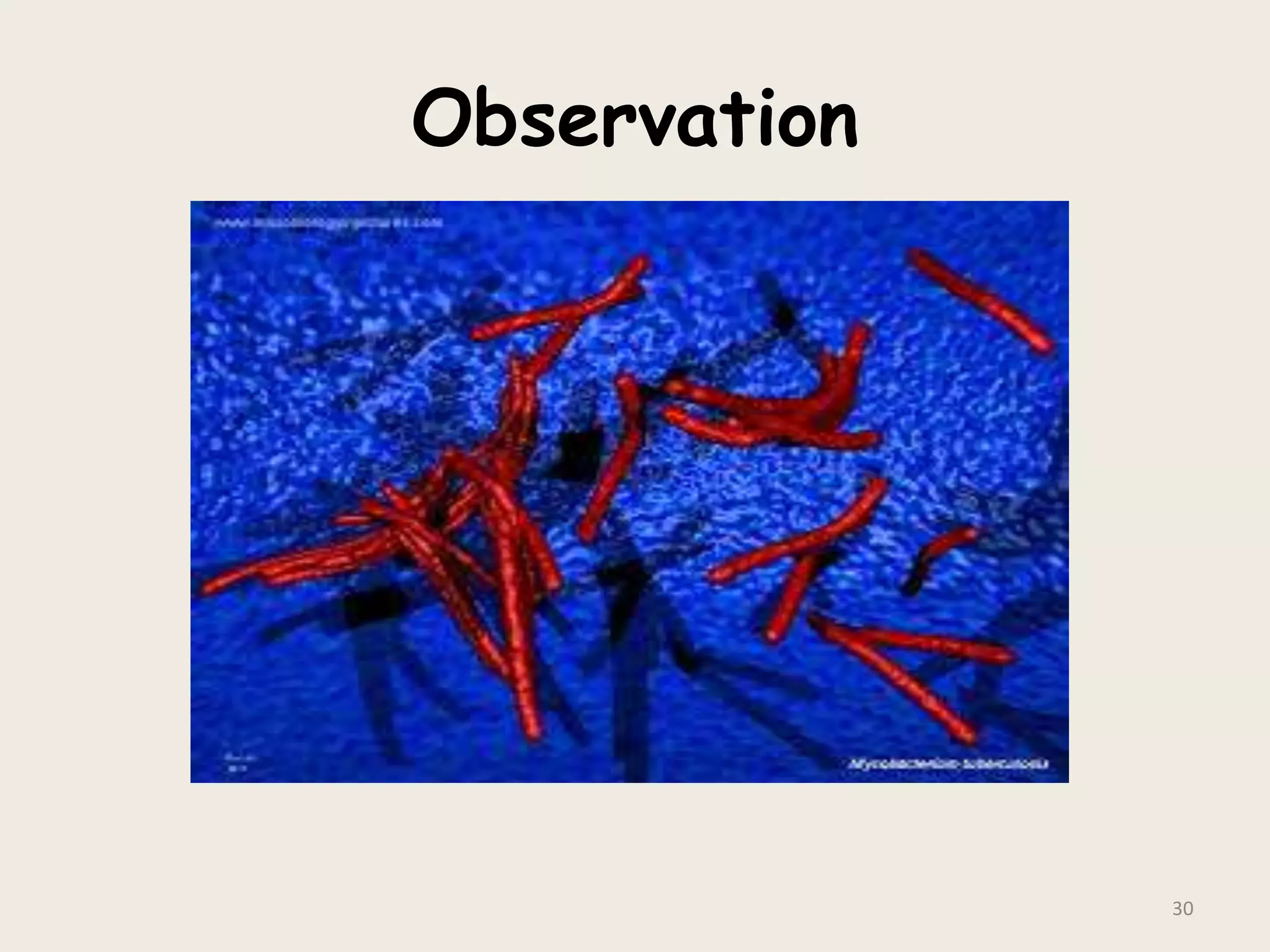
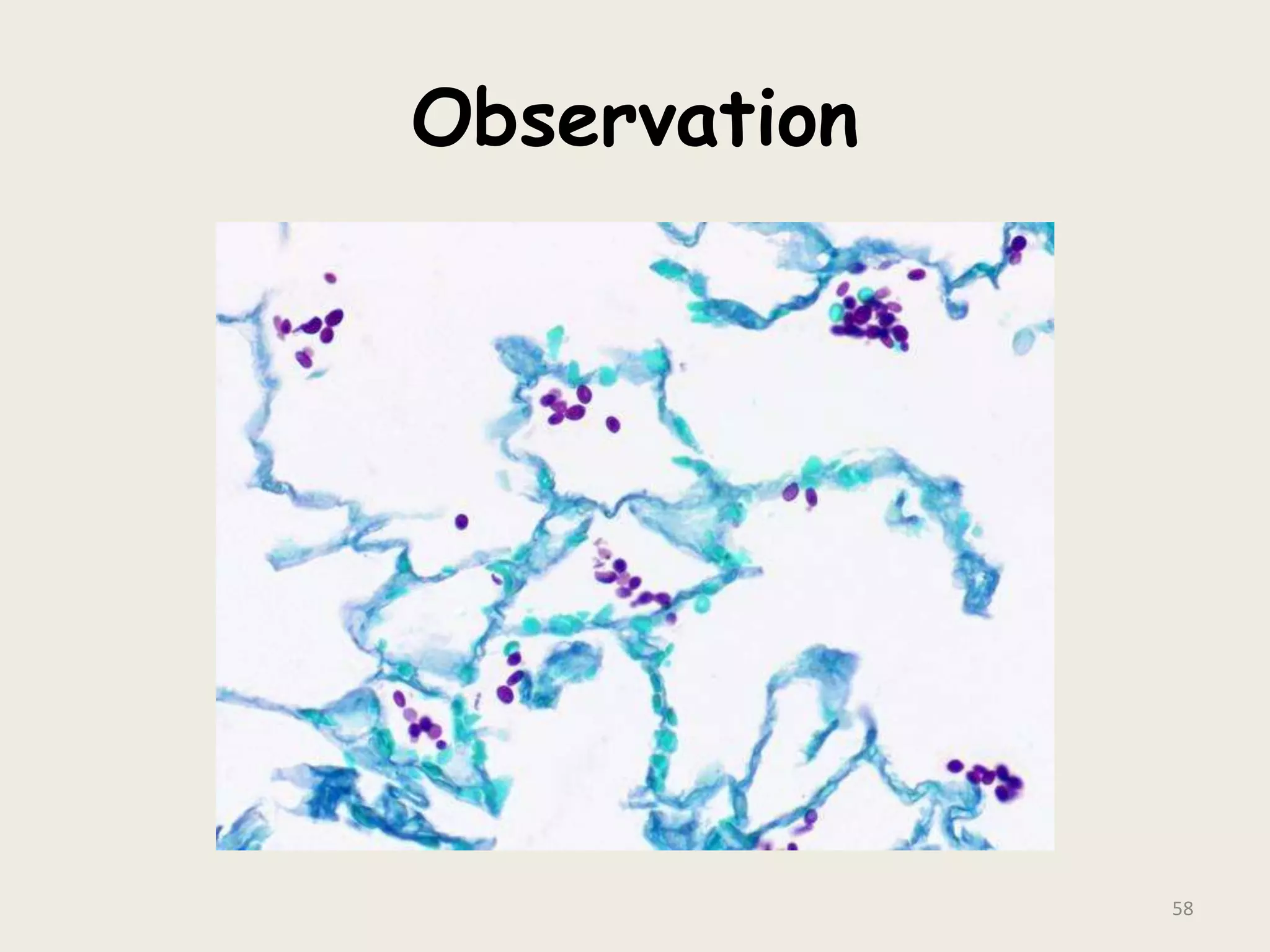
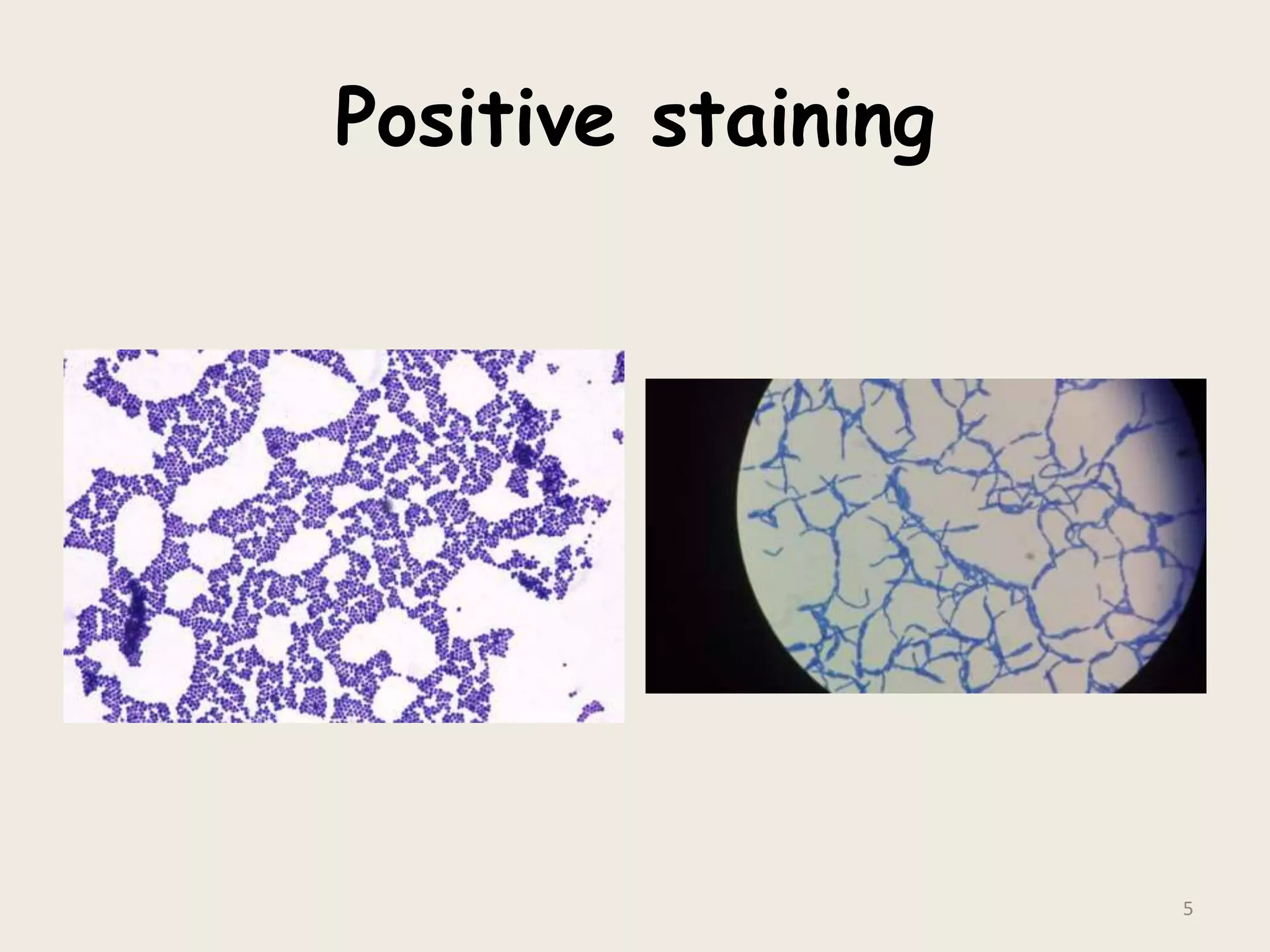
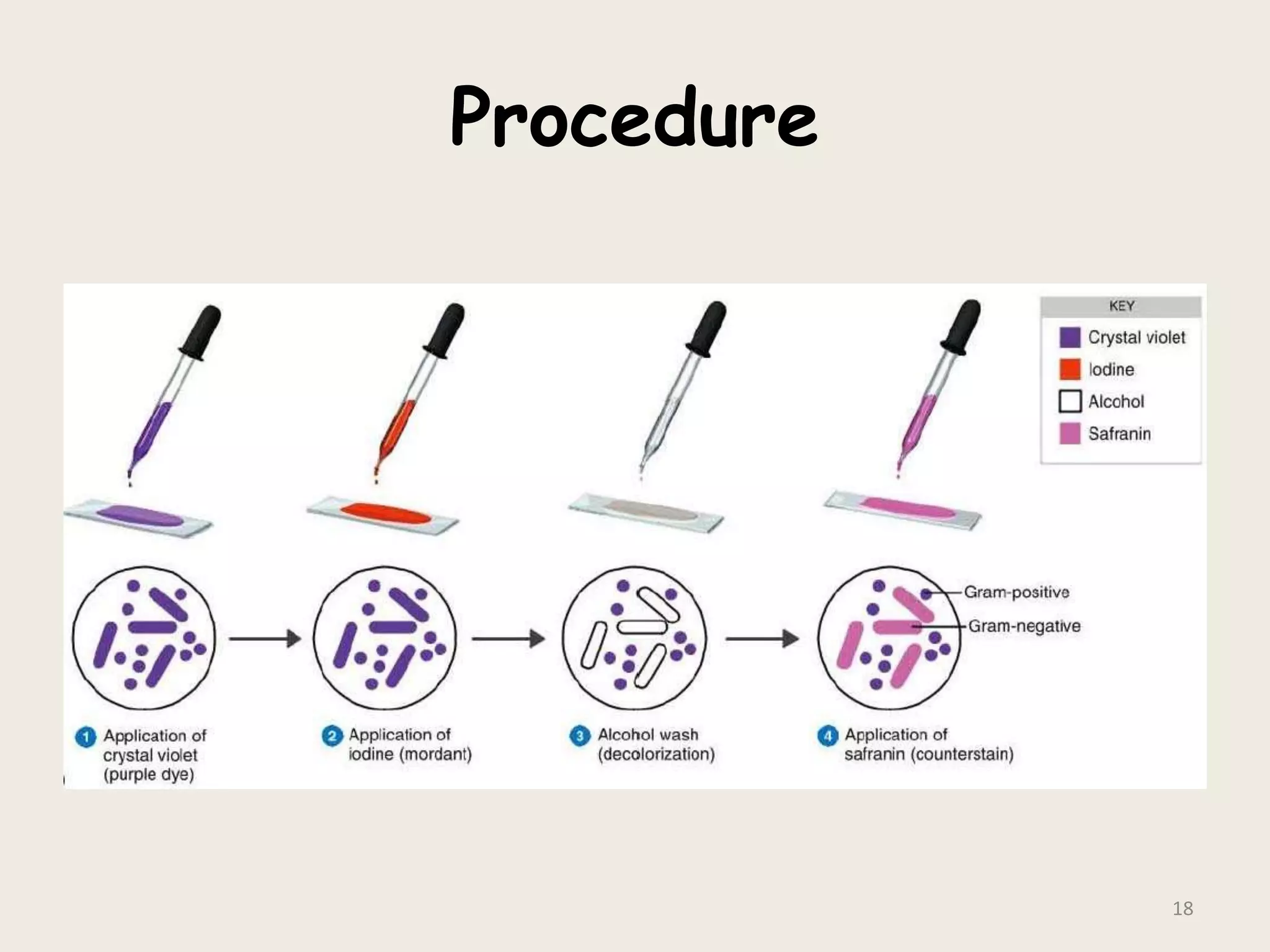
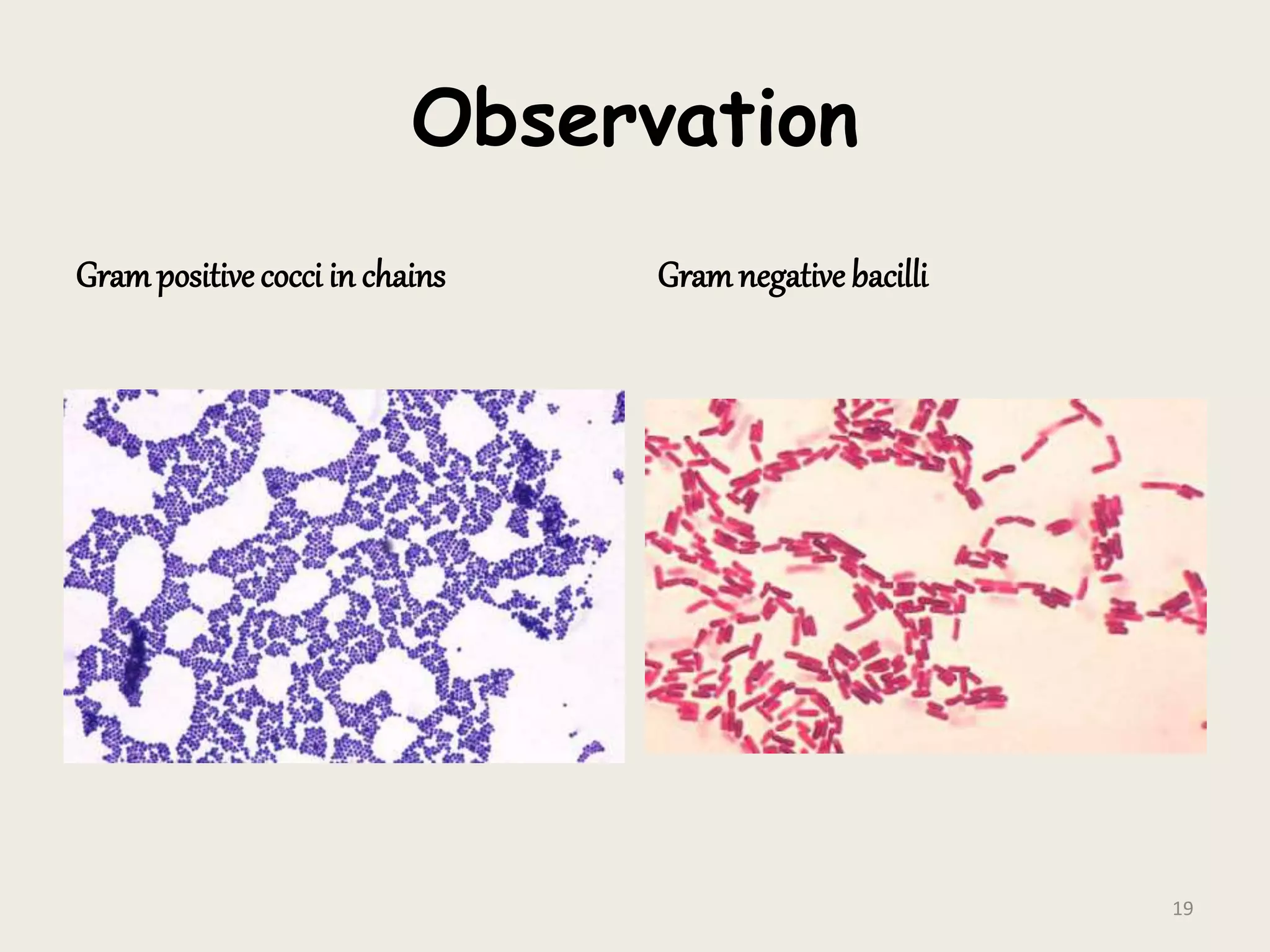
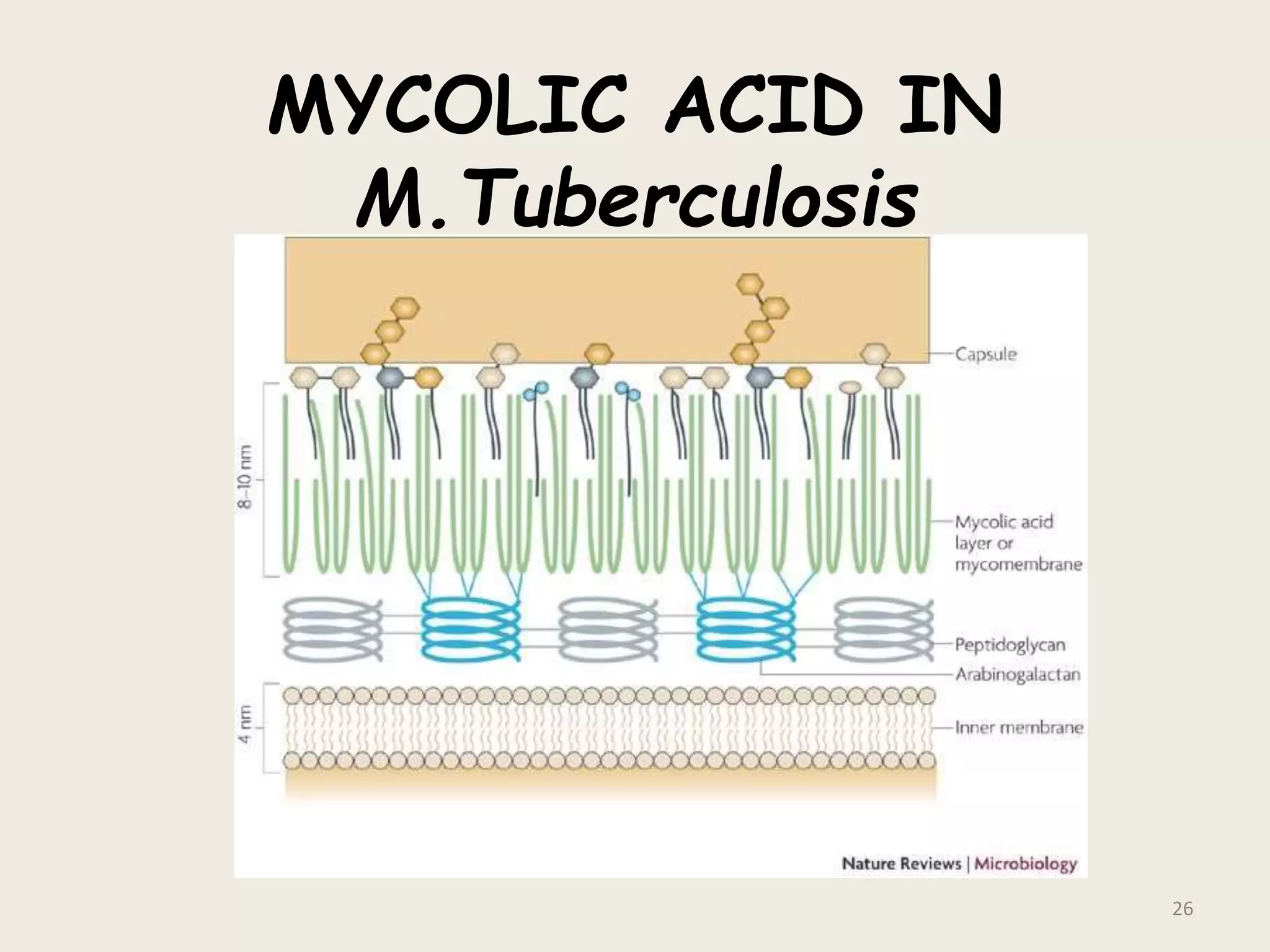
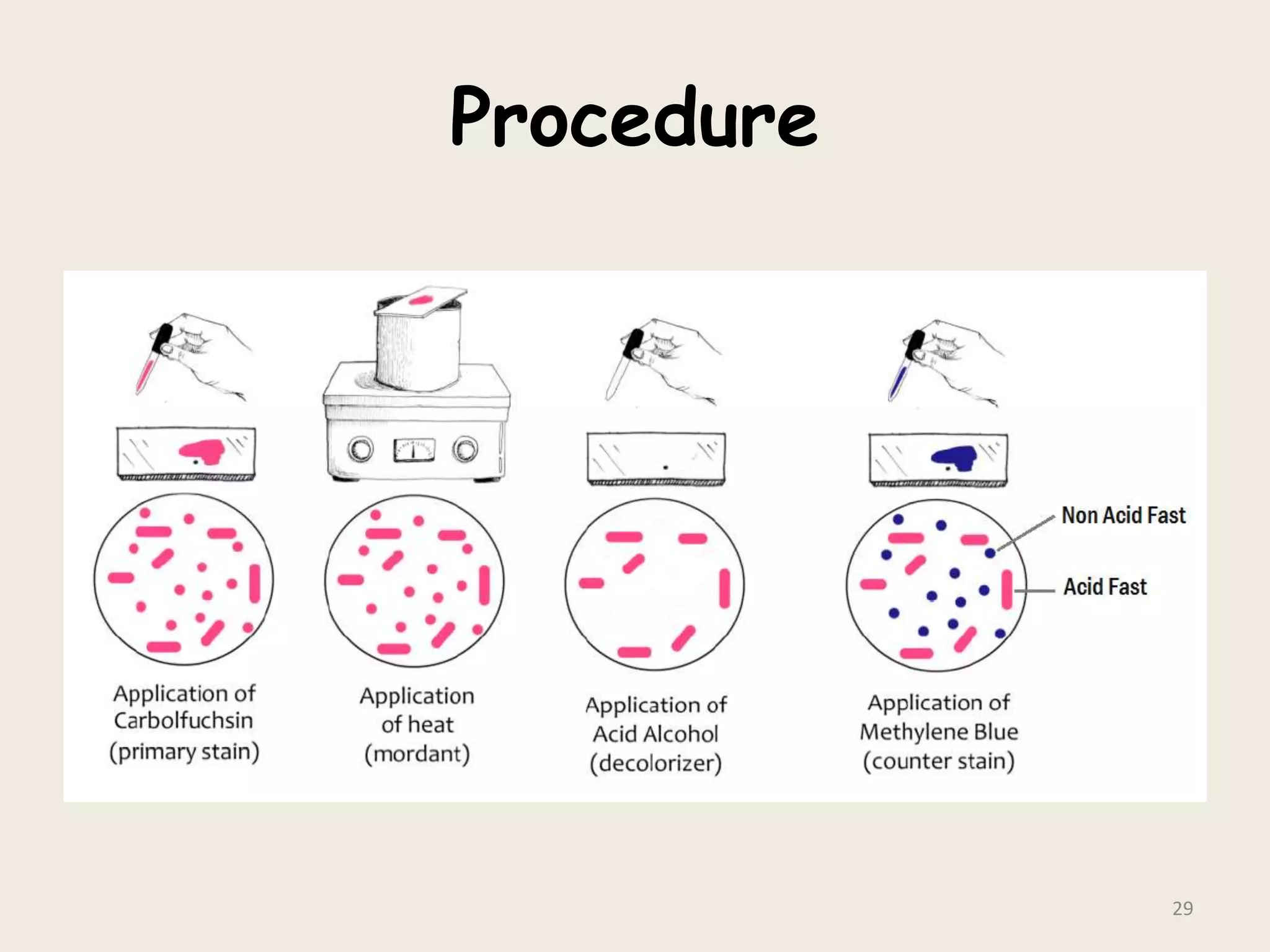
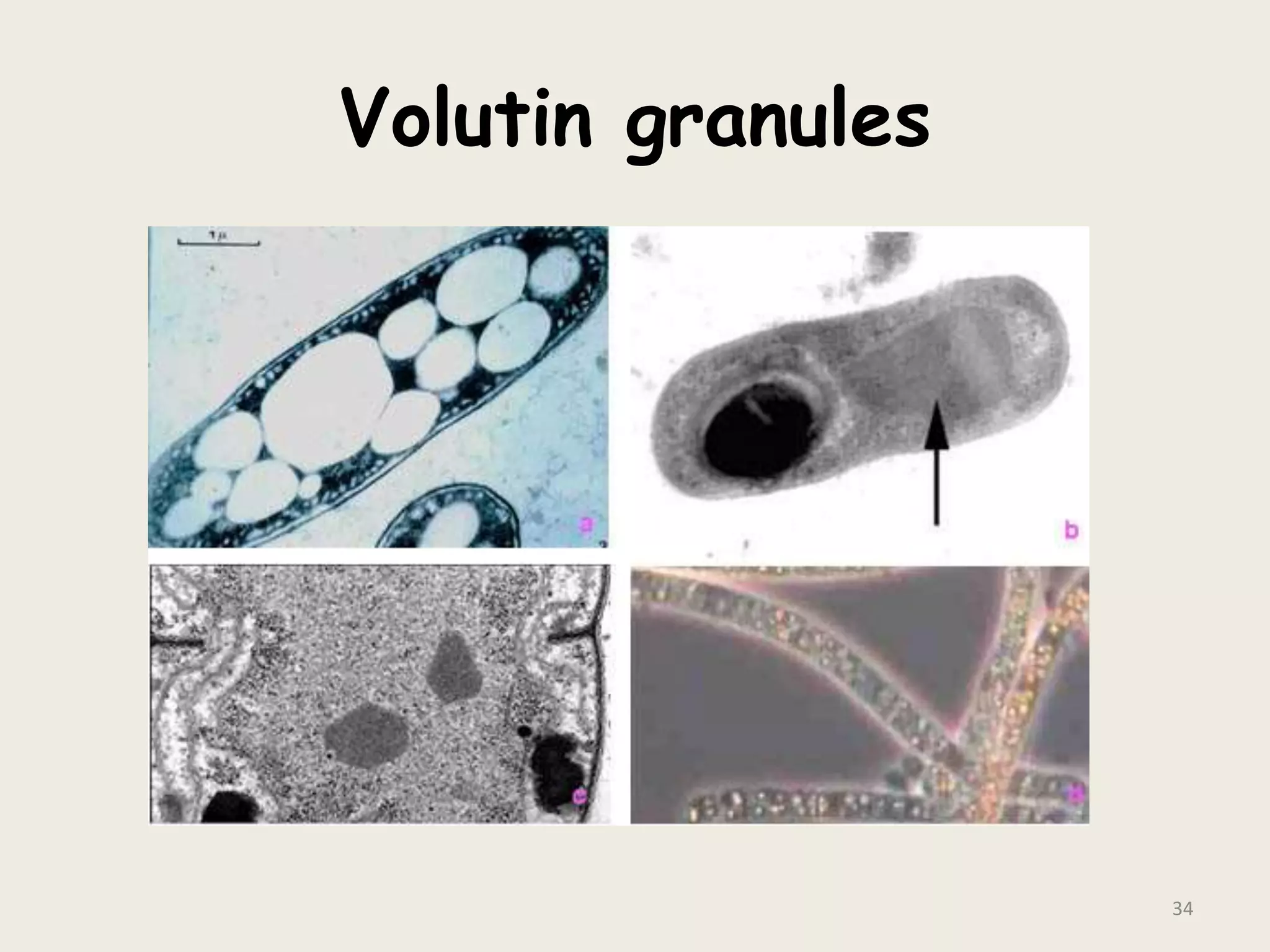
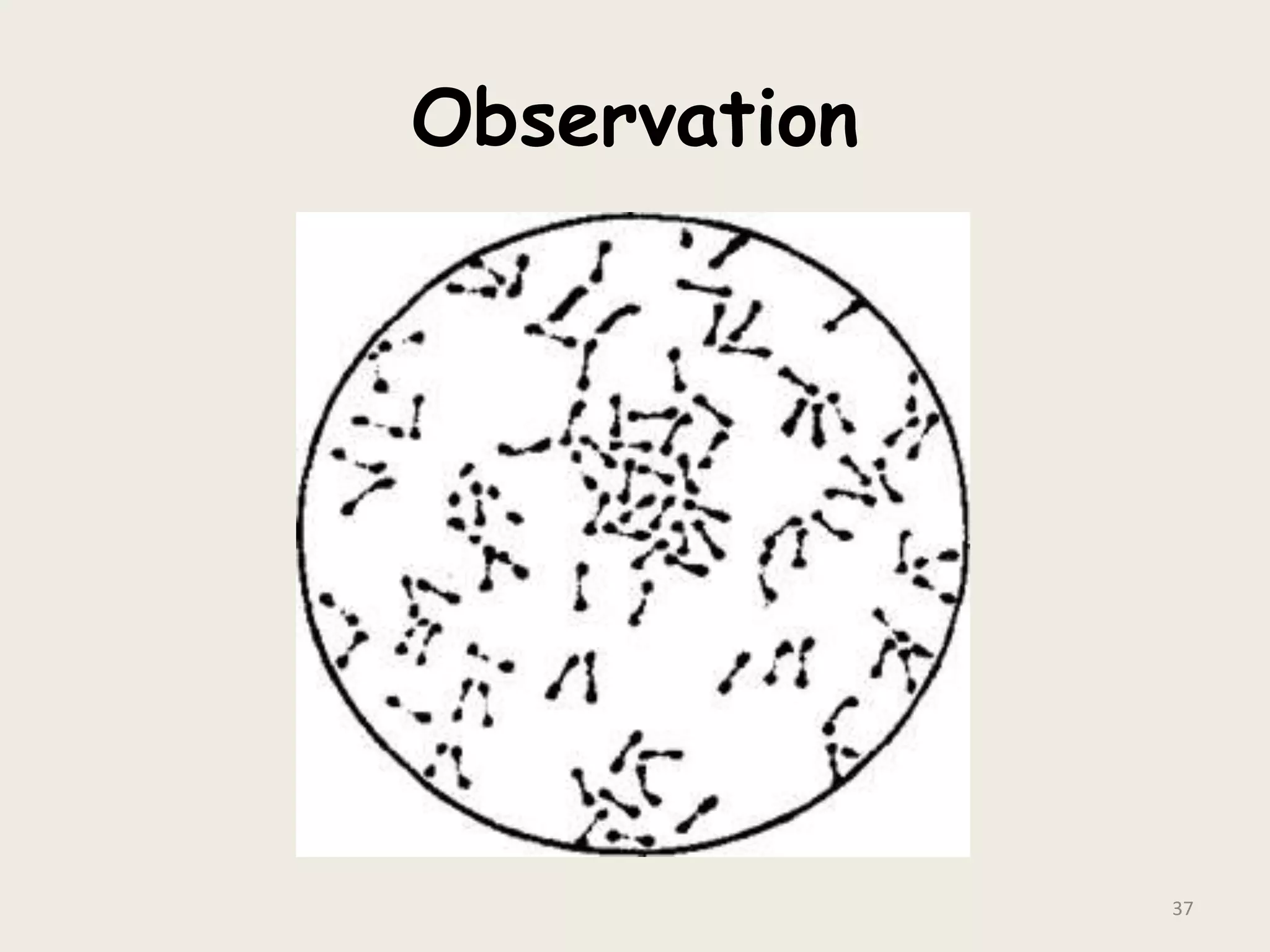
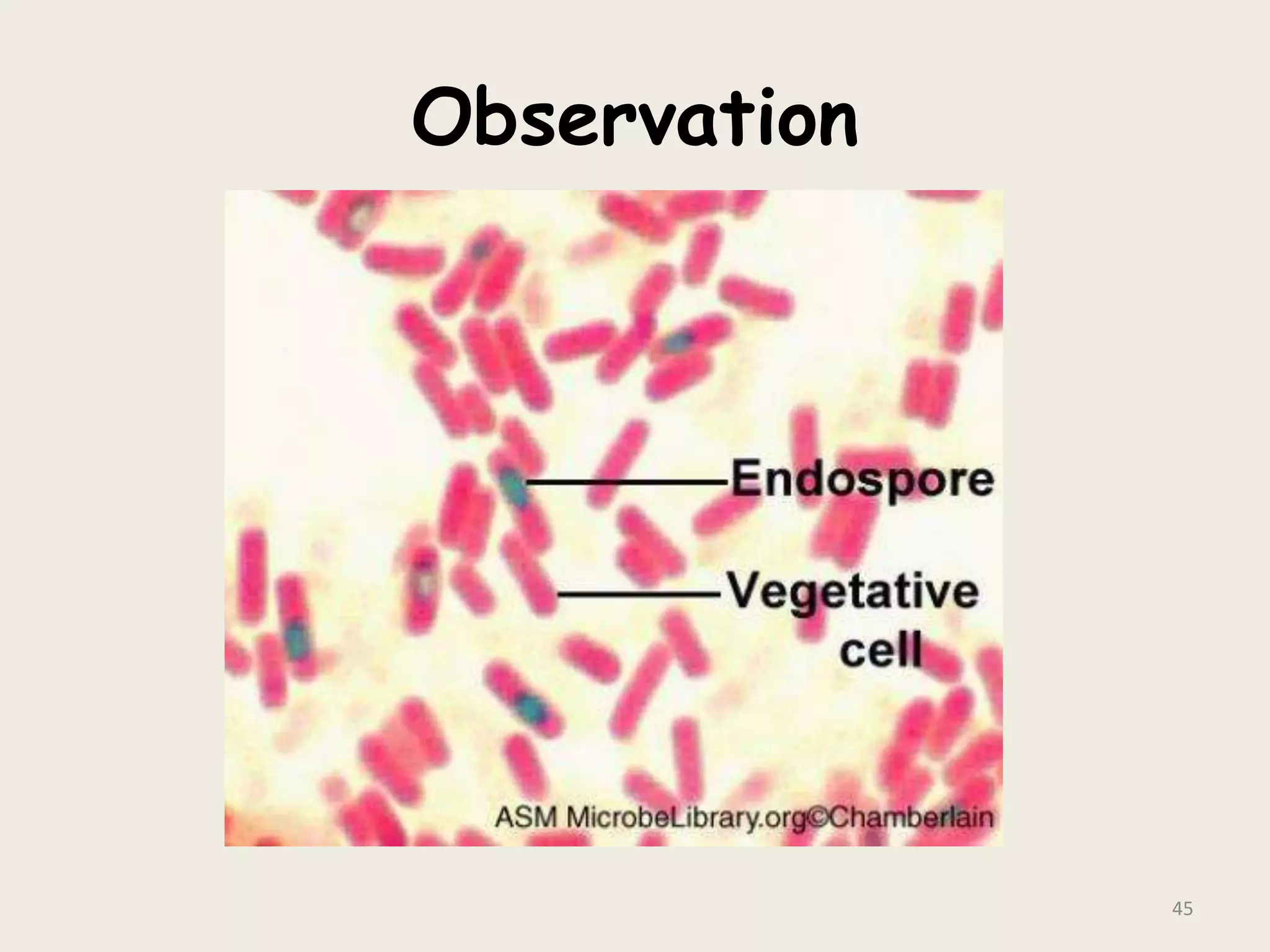
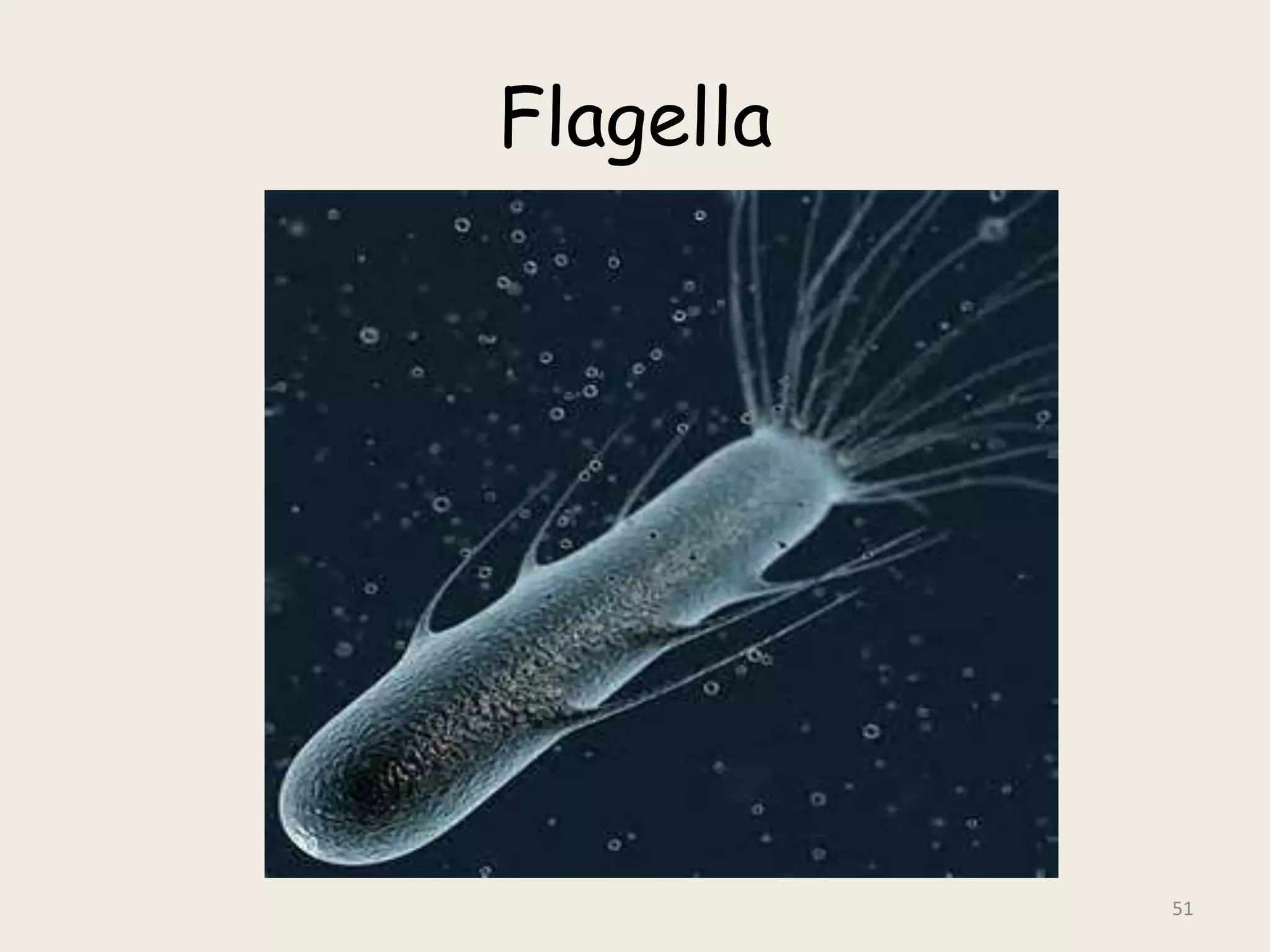
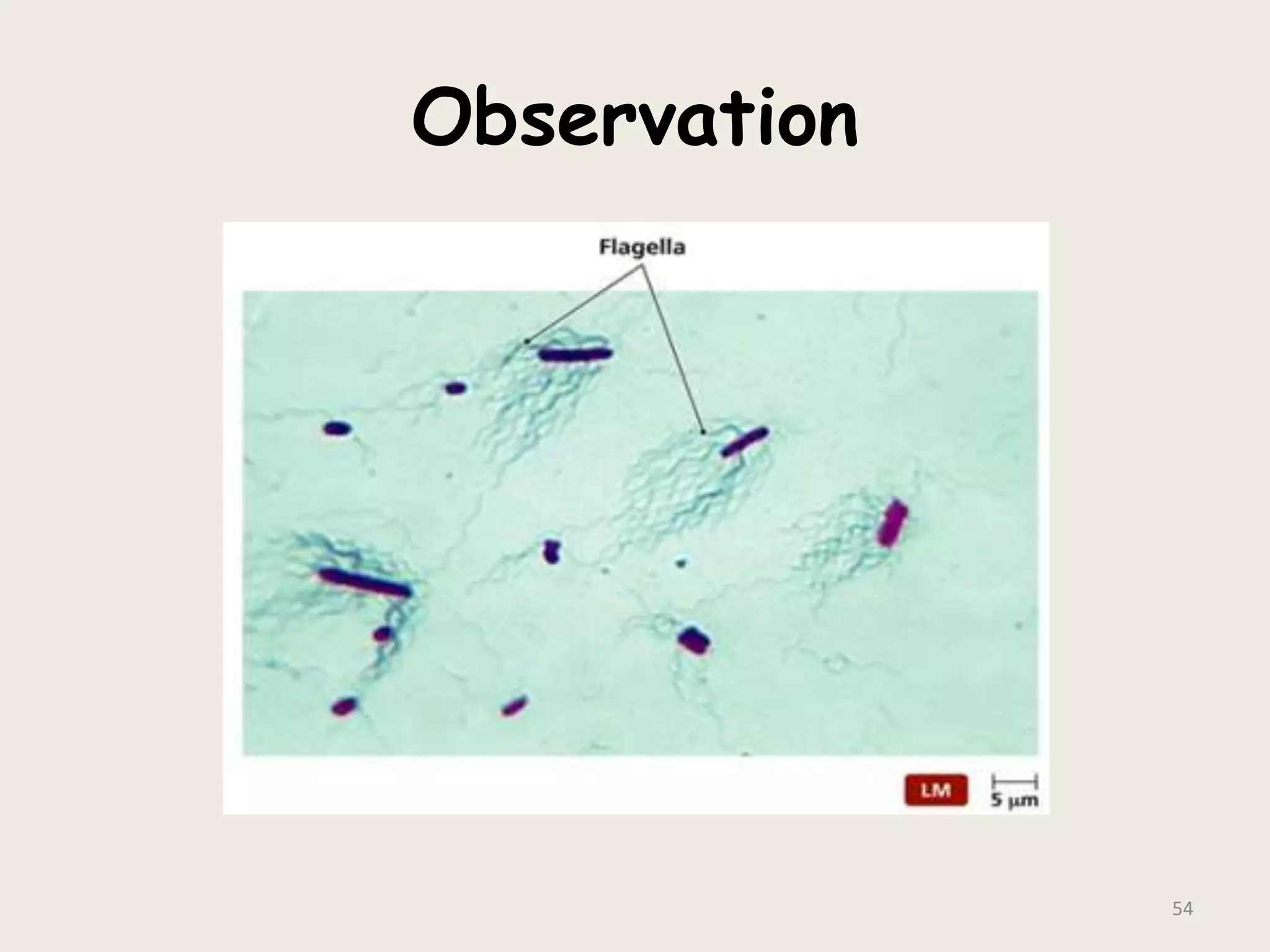
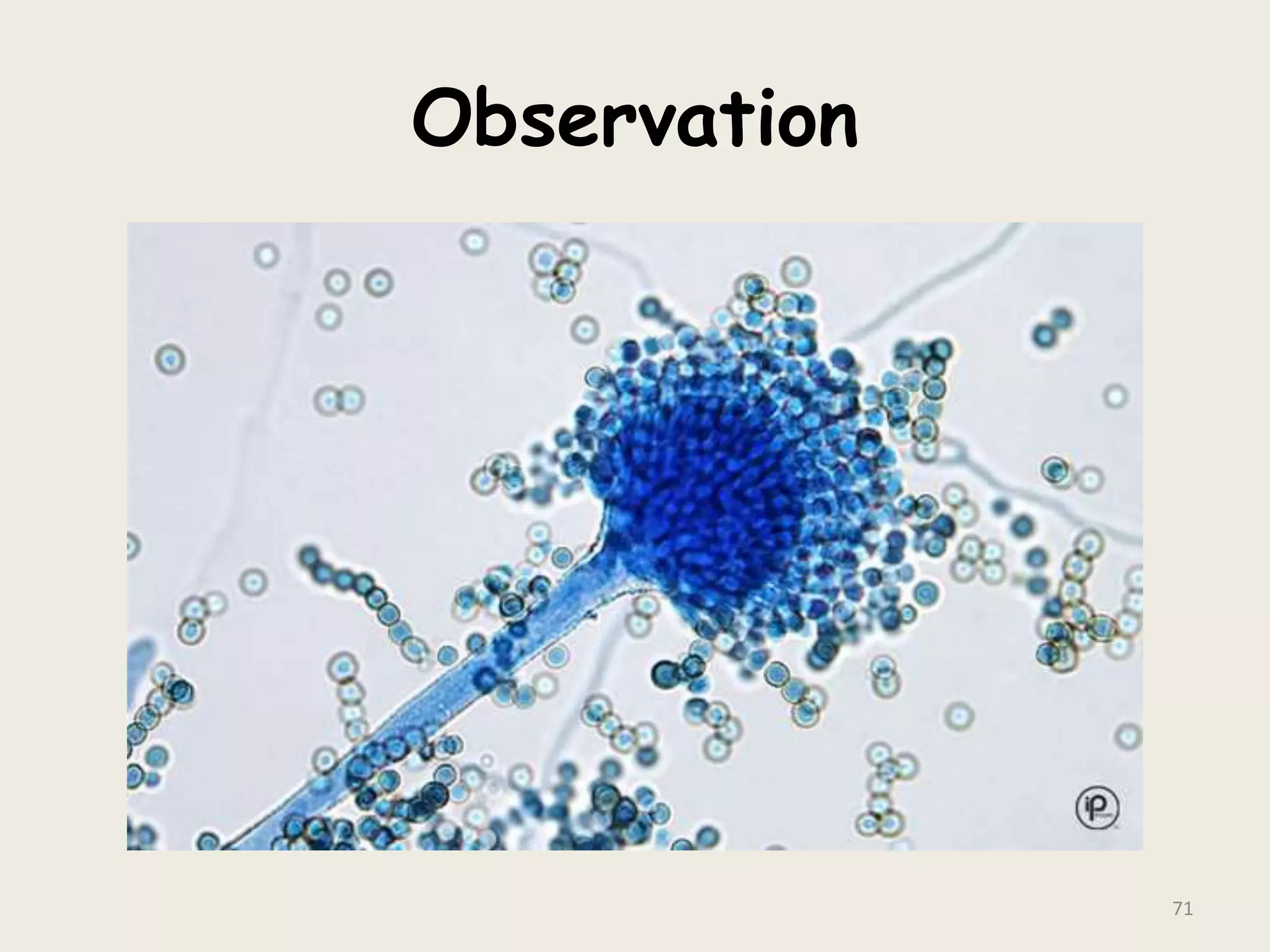
This document discusses various staining techniques used to visualize bacteria under a microscope. It covers simple staining techniques like Gram staining and acid-fast staining, as well as methods to identify specific structures like volutin granules and bacterial spores. Gram staining uses dyes to differentiate between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria based on their cell wall composition. Acid-fast staining targets bacteria with thick lipid cell walls like Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Specialized techniques employ unique dyes and fixation steps to highlight intracellular inclusions and endospores. Proper staining is crucial for bacterial identification and clinical diagnosis.