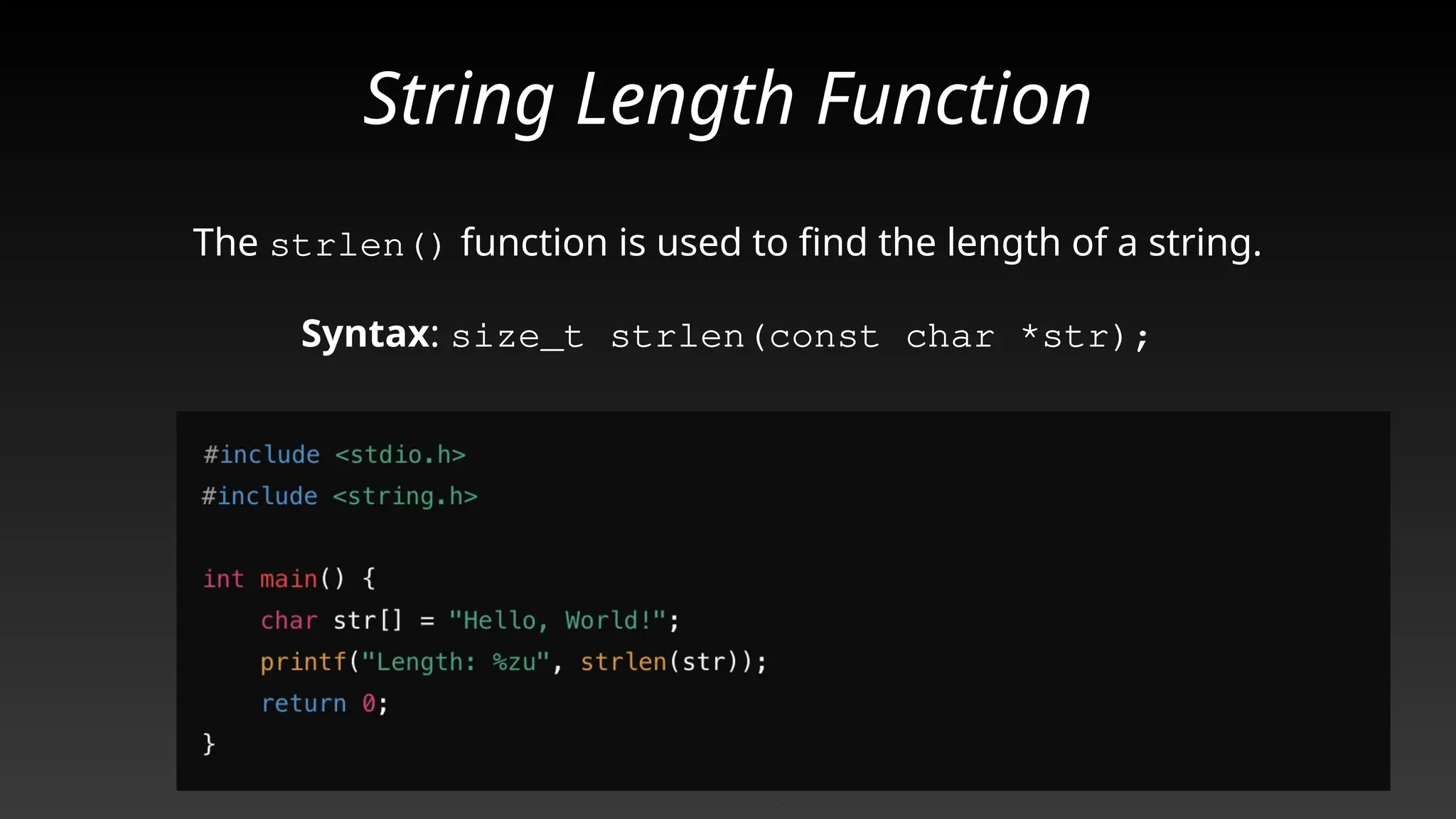
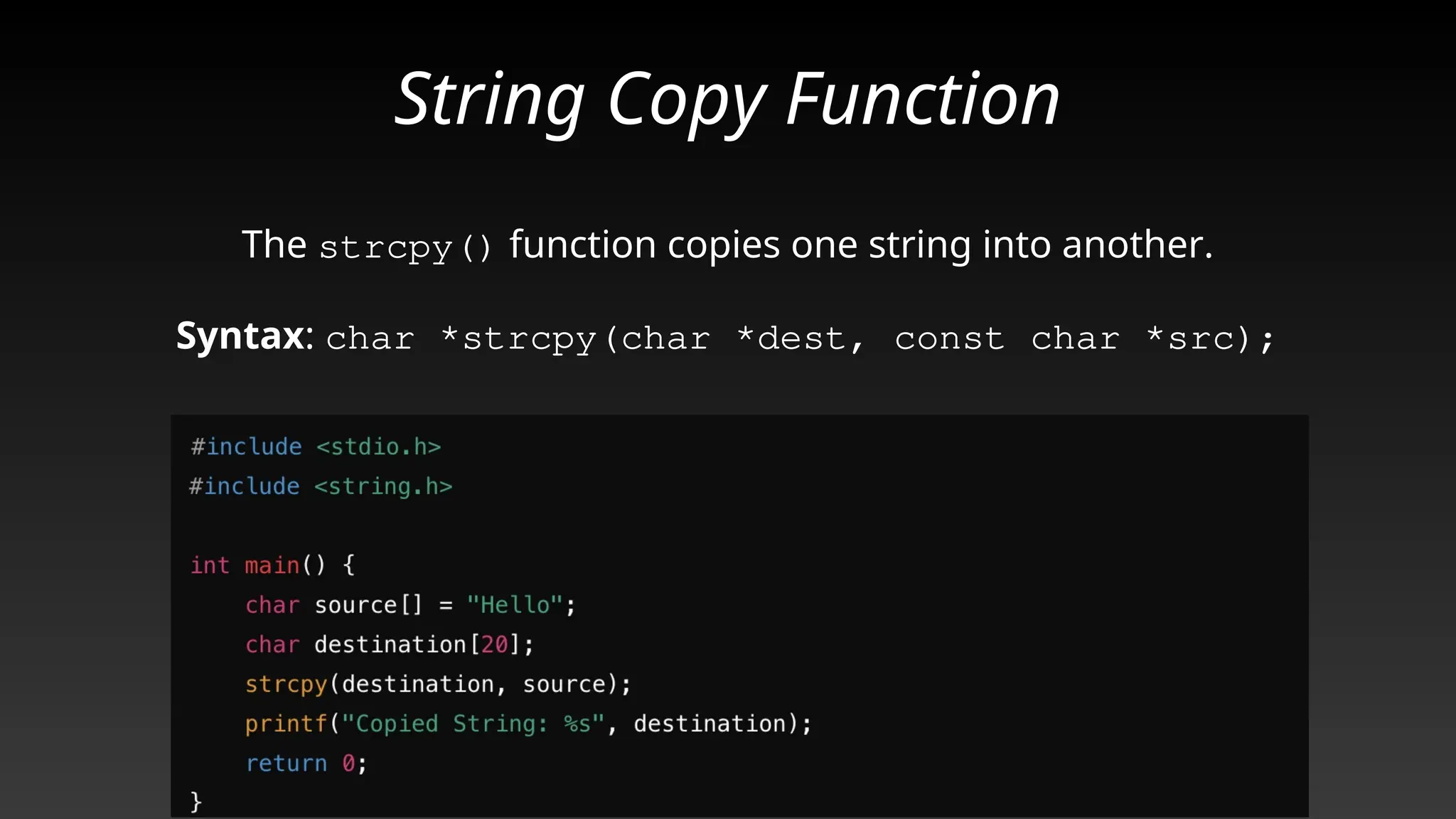
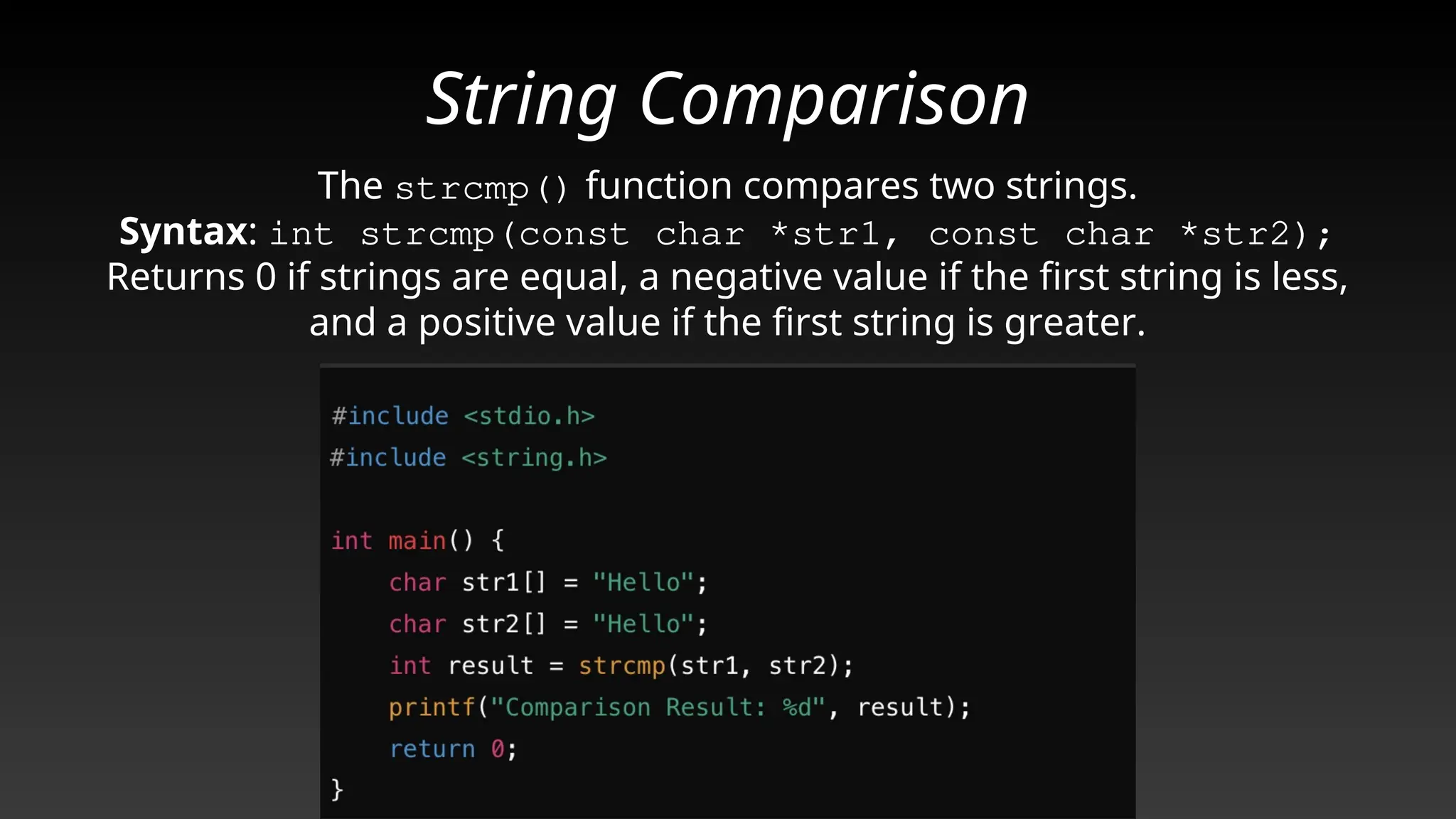
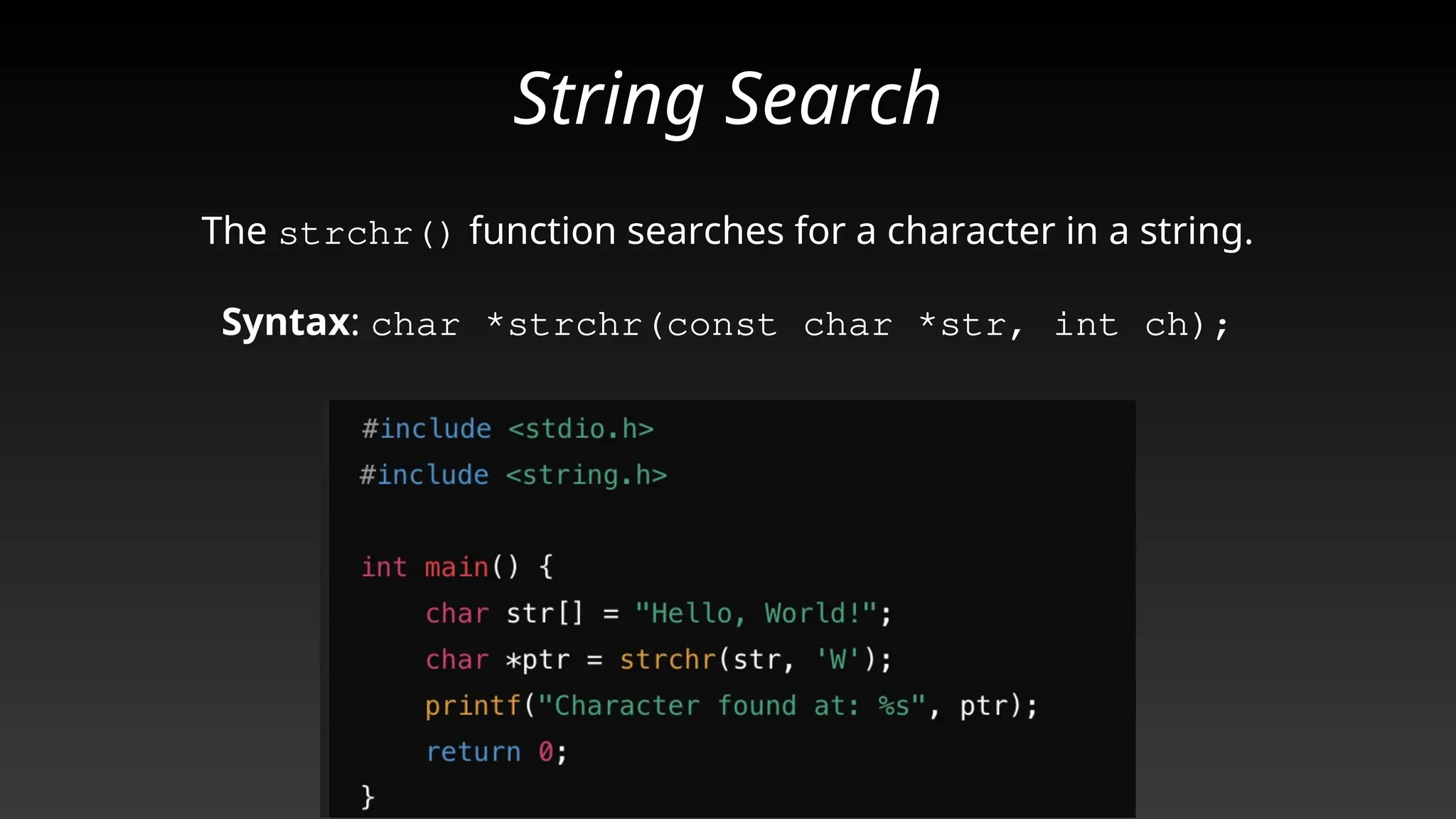
This document provides a comprehensive overview of strings and their implementation in C programming. It covers the representation of strings as arrays of characters, essential string operations such as length, concatenation, copying, and comparison, as well as common pitfalls and best practices. The document emphasizes the importance of proper null termination and safe memory handling when working with strings.


![String Representation in C
A string in C is an array of characters: char str[] = “Hello";
Strings are stored in contiguous memory locations.
Example: char str[] = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ‘0'};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringsinc-250121073802-a70c74e1/75/Strings-In-C-and-its-syntax-and-uses-ppt-3-2048.jpg)
![Declaring Strings in C
Strings can be declared in two ways:
1. Array of characters: char str[20];
2.String literal: char str[] = “Hello";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringsinc-250121073802-a70c74e1/75/Strings-In-C-and-its-syntax-and-uses-ppt-4-2048.jpg)