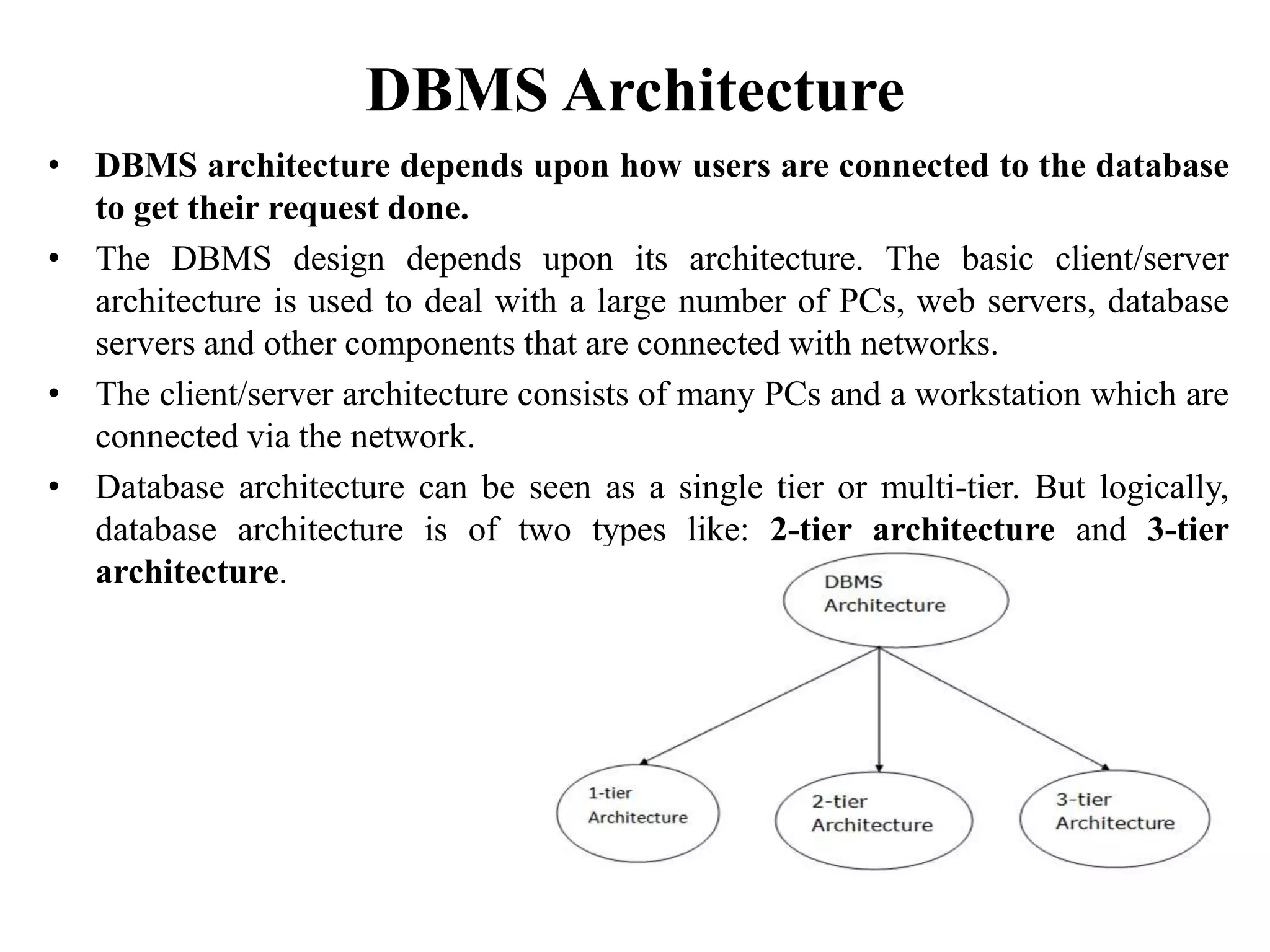
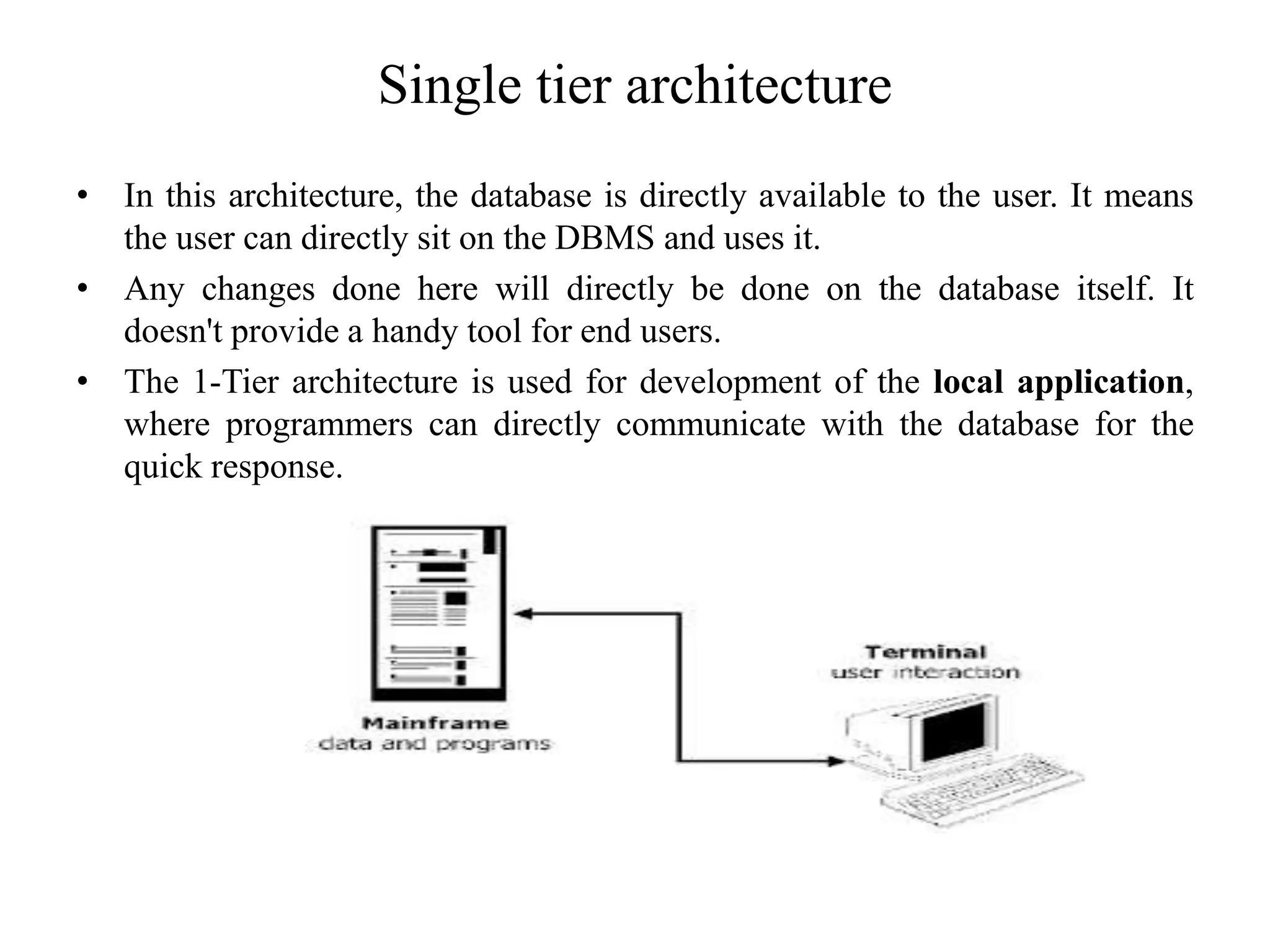
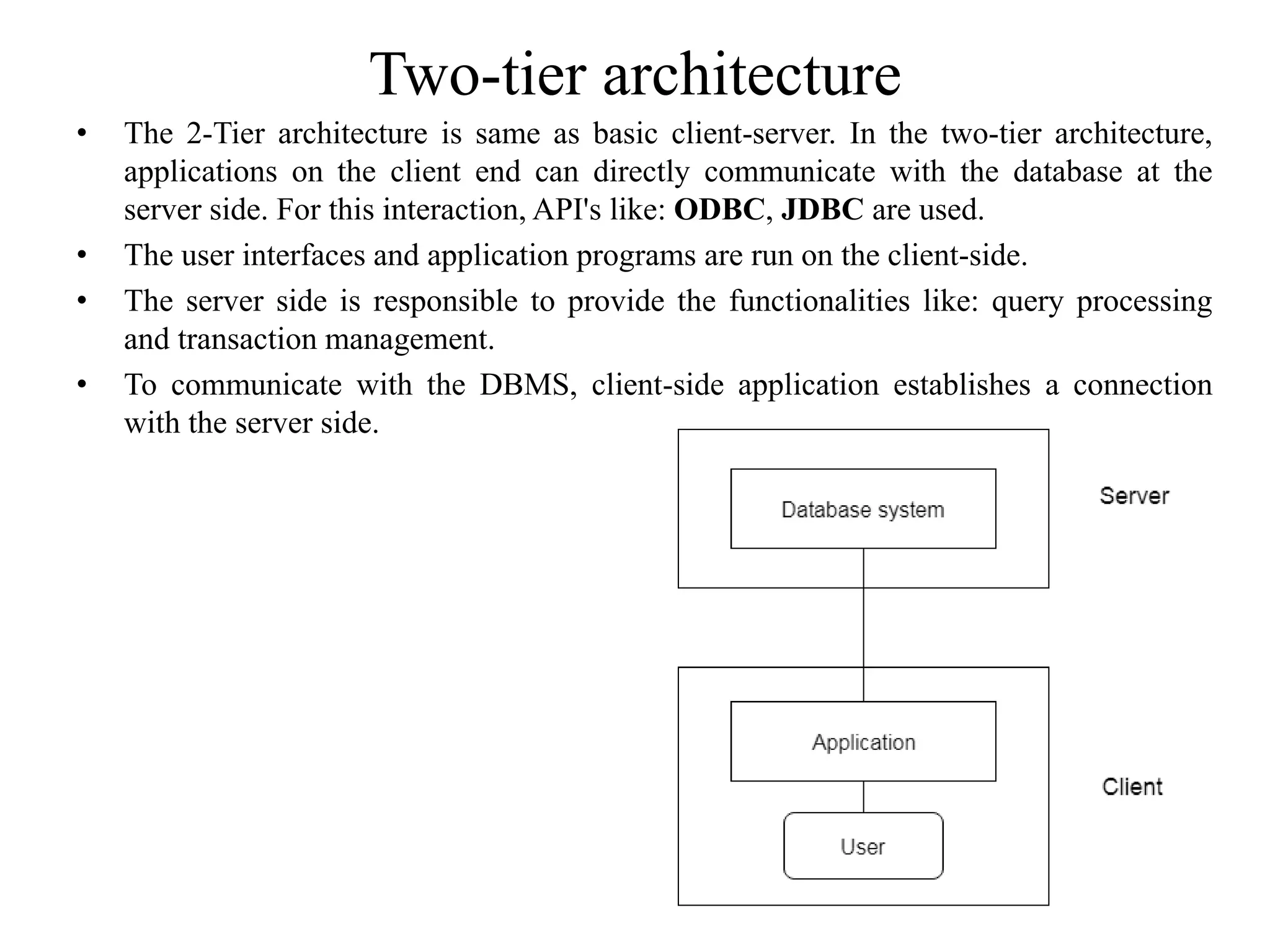
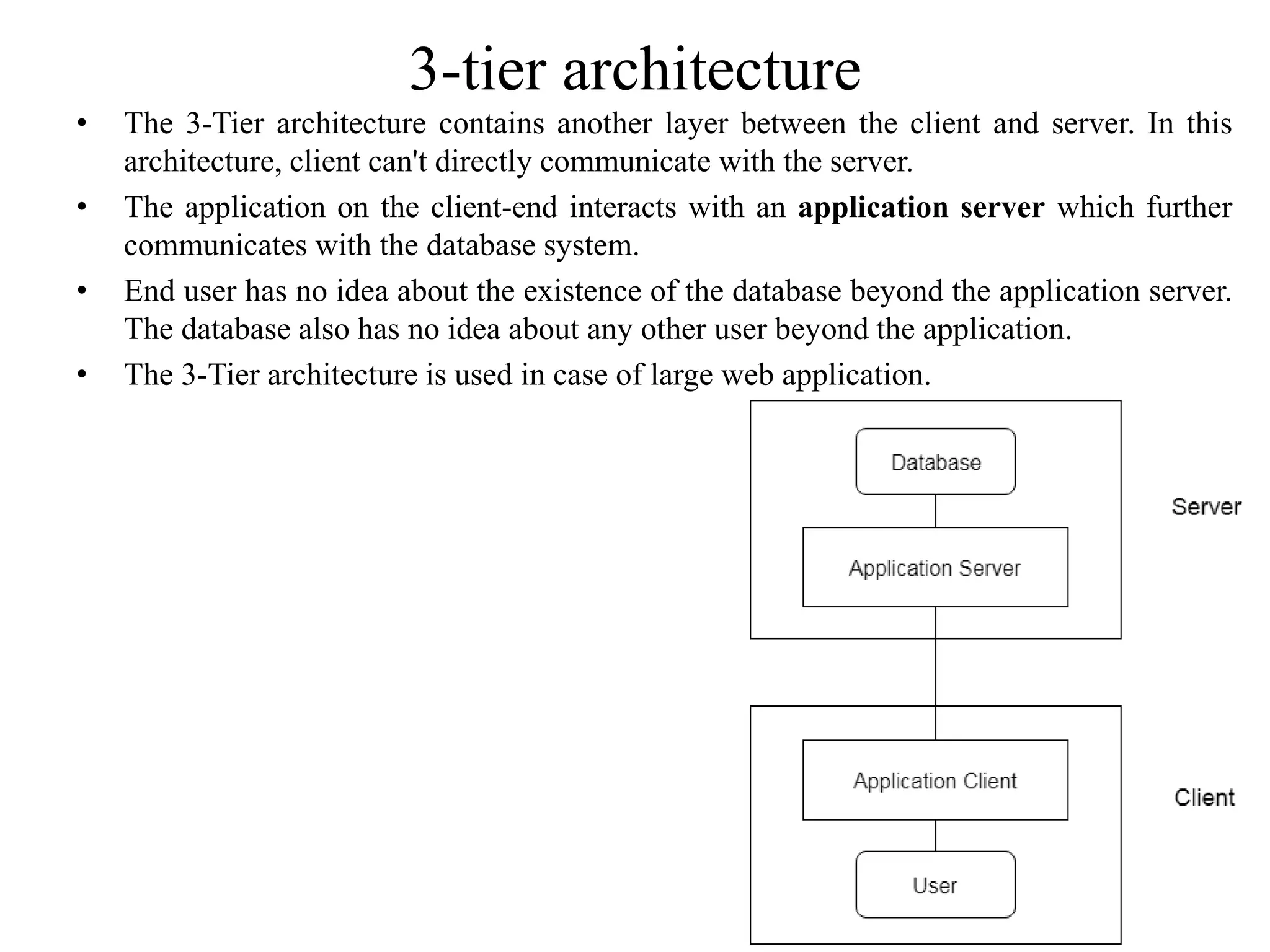
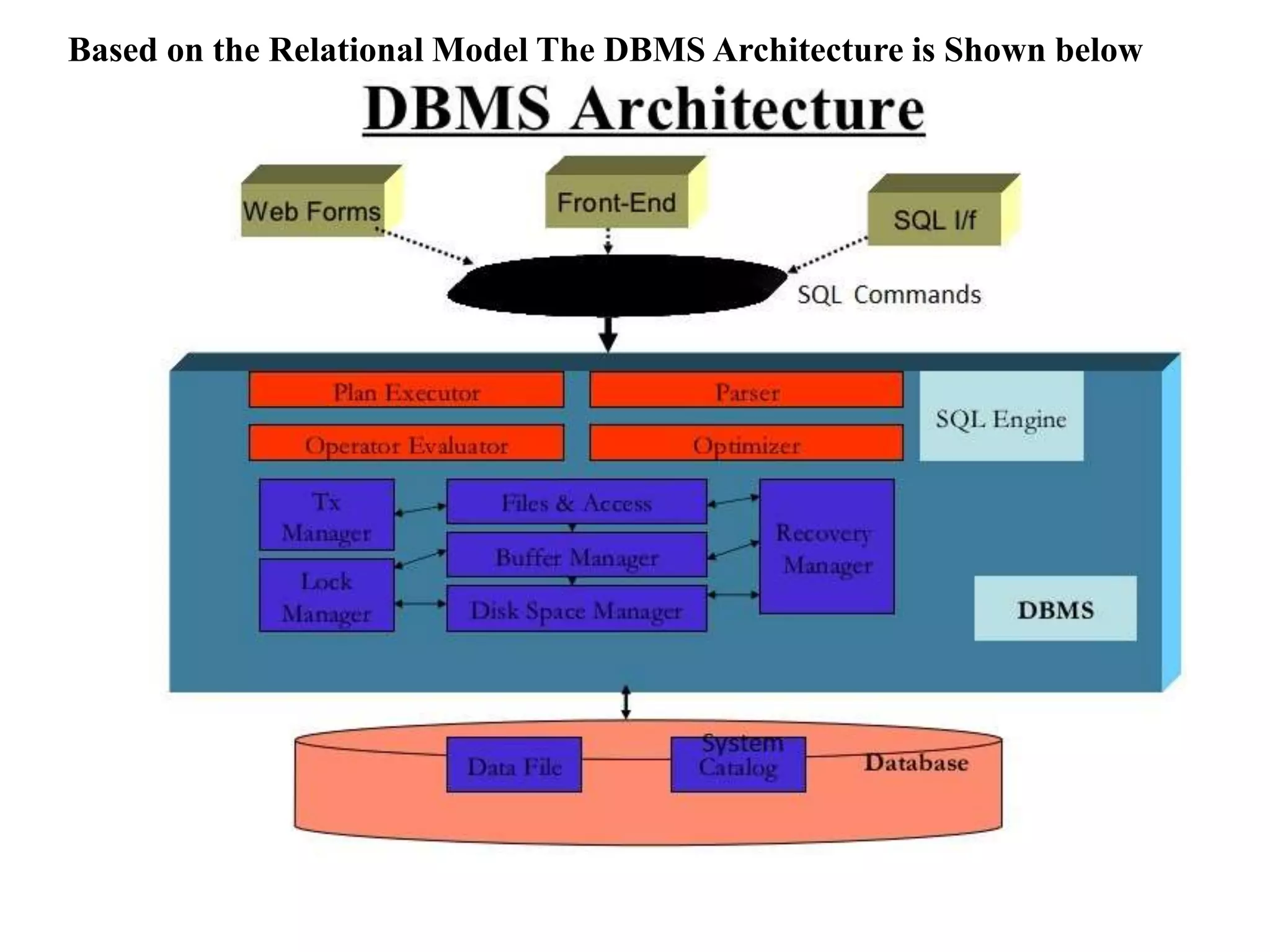
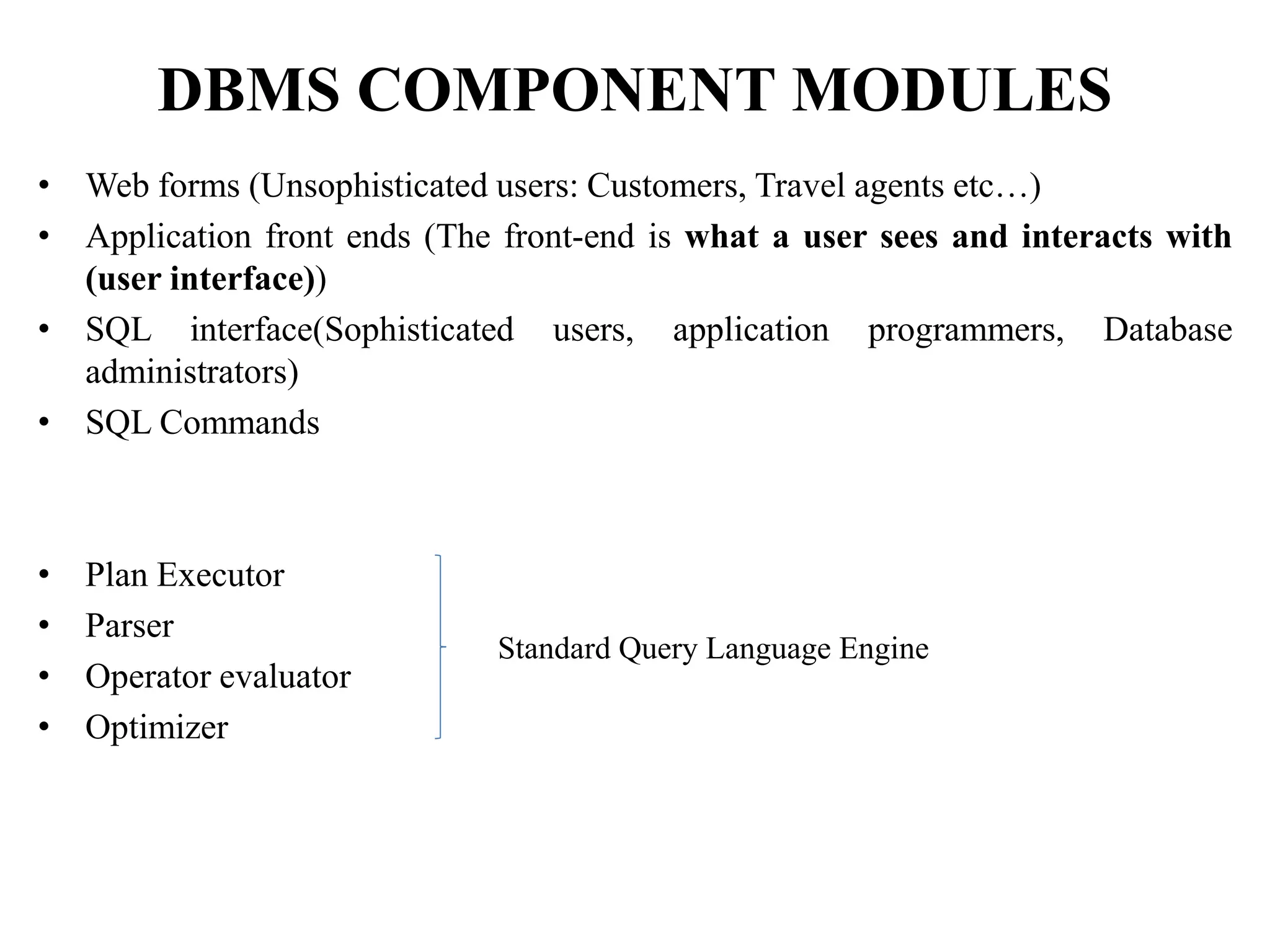
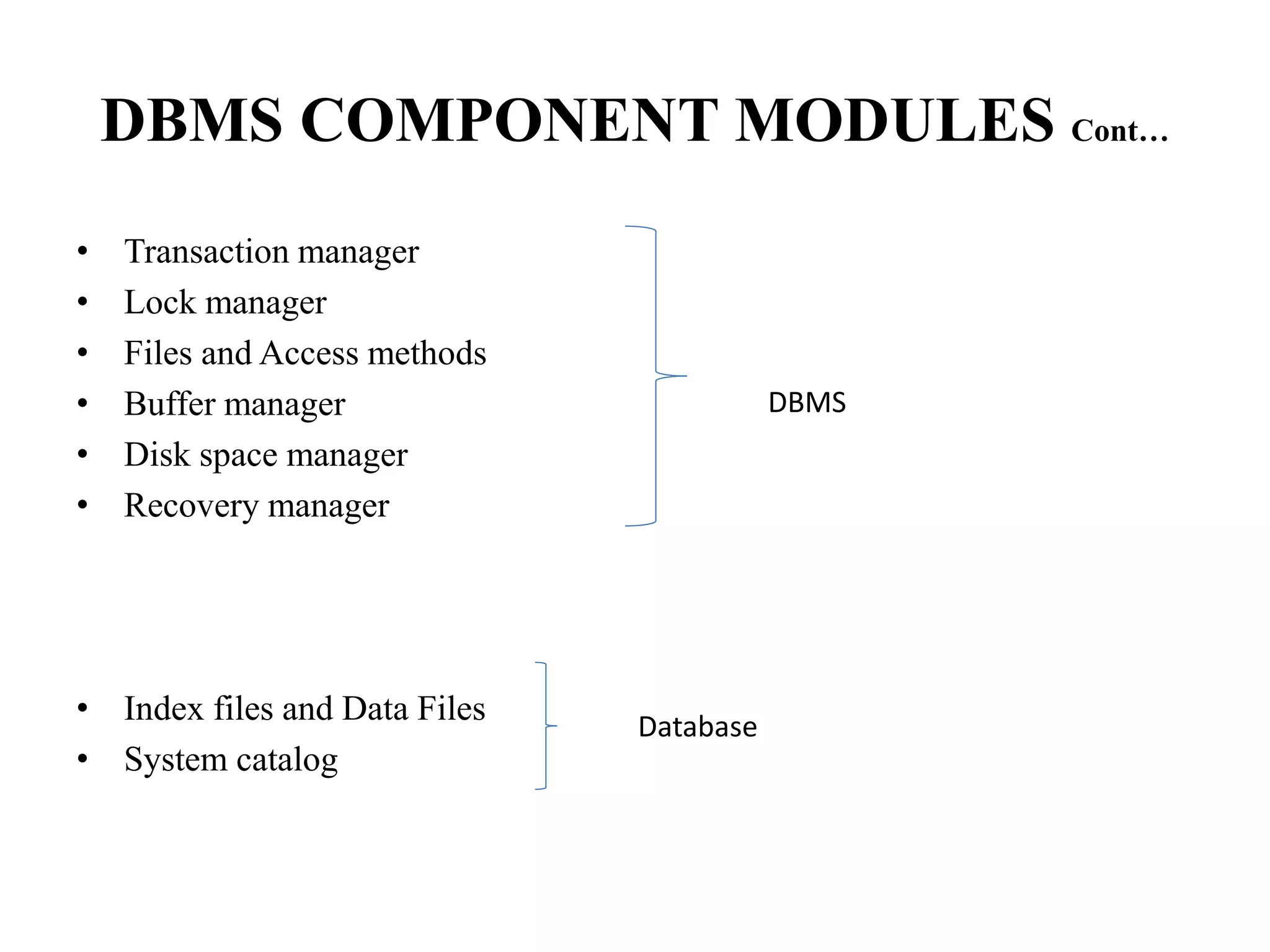
The document discusses the architecture of database management systems, including single-tier, two-tier, and three-tier architectures. It describes how the two-tier architecture allows applications to directly communicate with the database server, while the three-tier architecture inserts an application server layer between the client and database. The document also outlines the typical modules that make up a DBMS, such as the transaction manager, buffer manager, and system catalog.