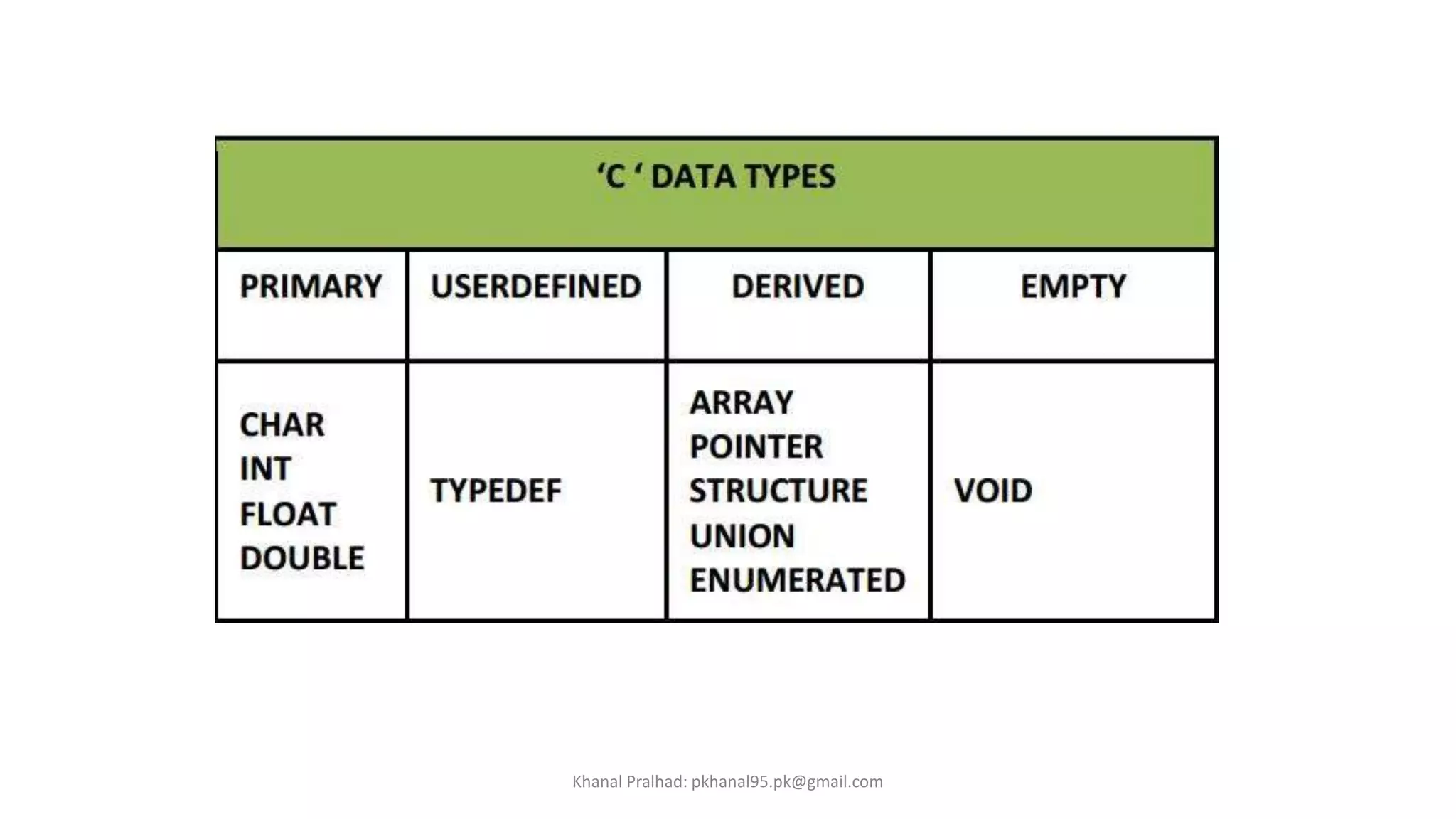
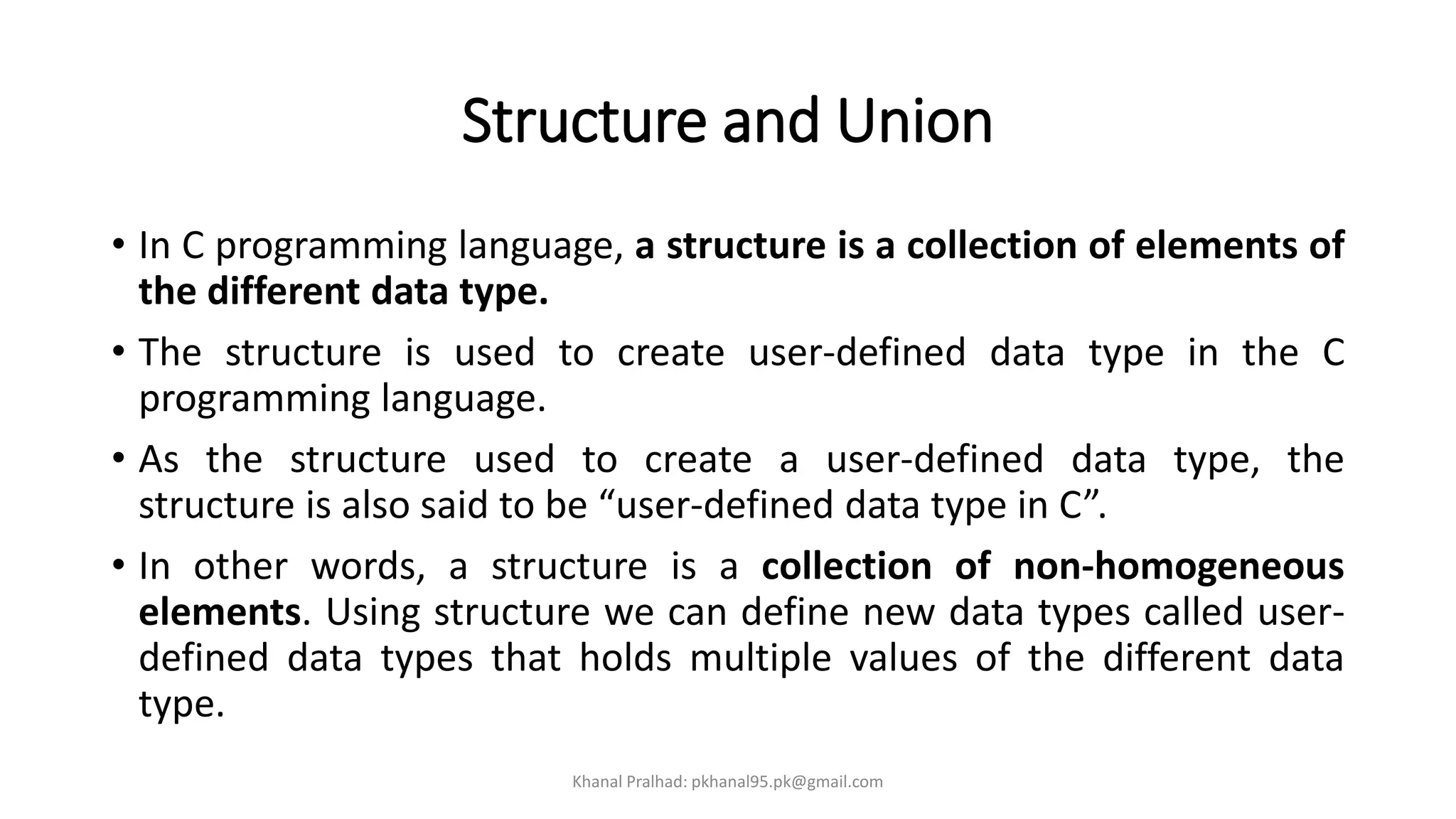
The document discusses structures in C programming. It defines a structure as a collection of variables of different data types grouped under a single name. Structures allow grouping of related data and can contain variables of similar or dissimilar types. The key points are:
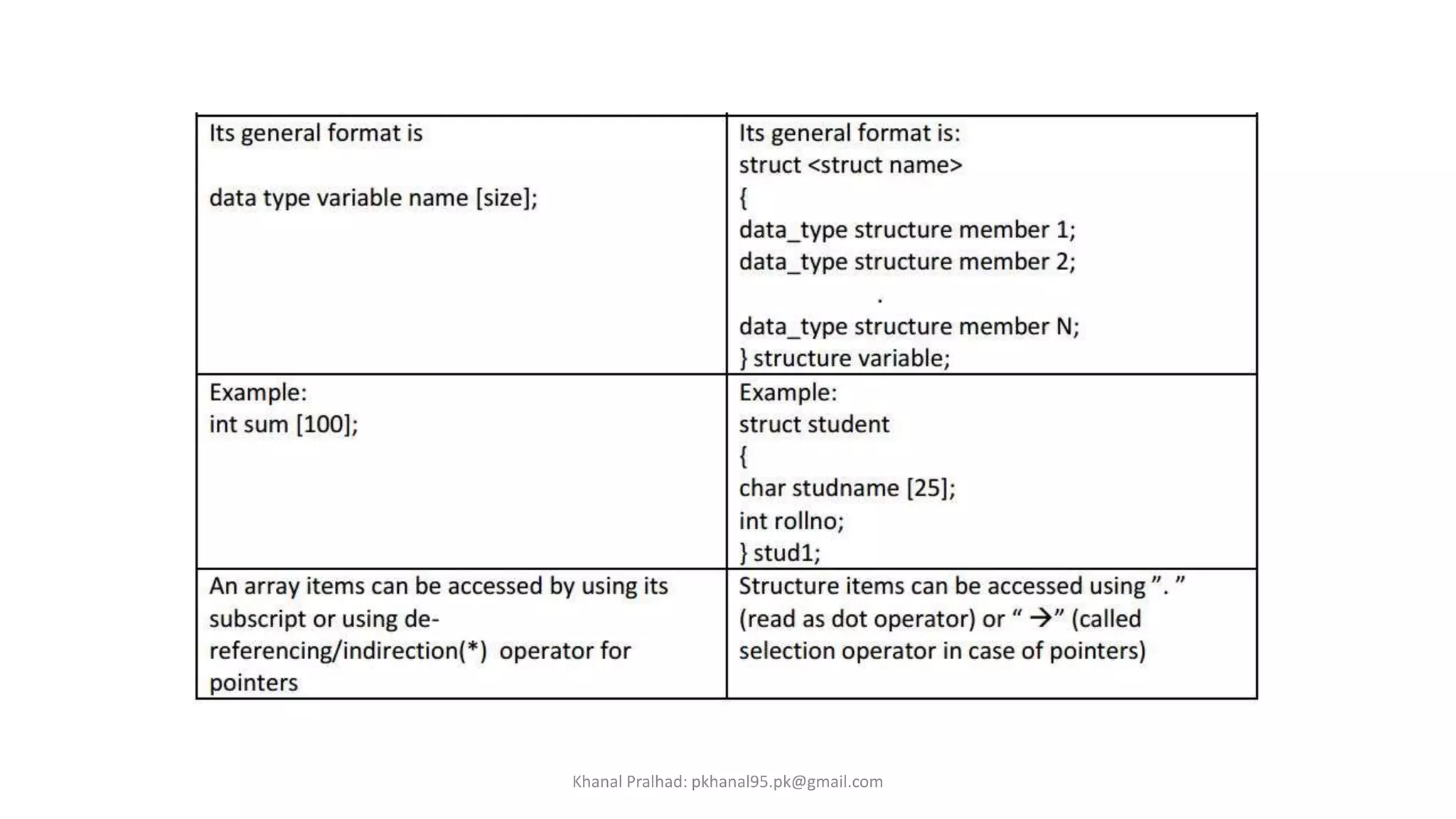
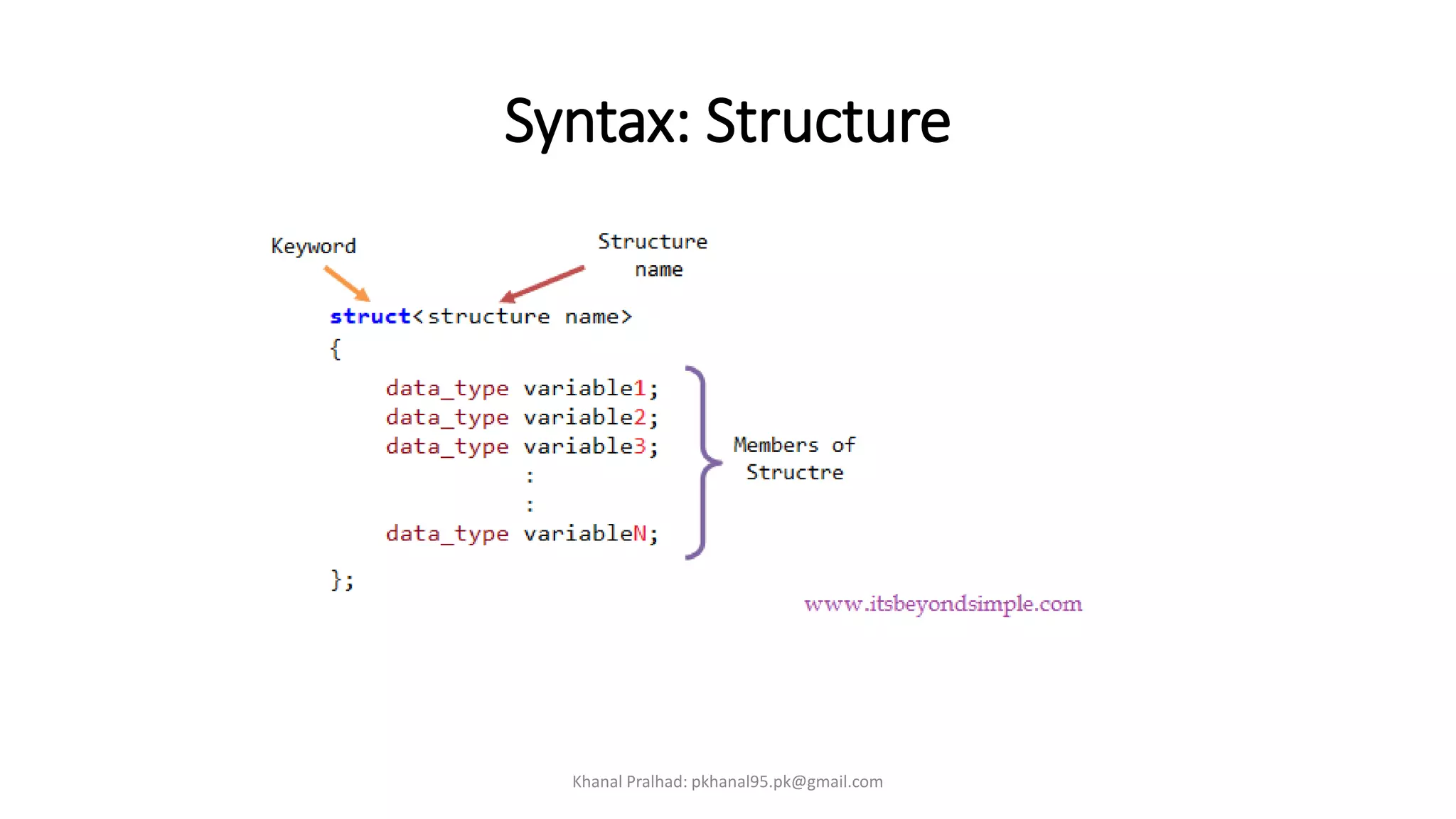
1. Structures are defined using the "struct" keyword followed by a tag name and variables.
2. Structure variables are declared and accessed using the structure tag and dot operator.
3. Structures allow organizing related data like student name, roll number and marks together rather than separate variables.
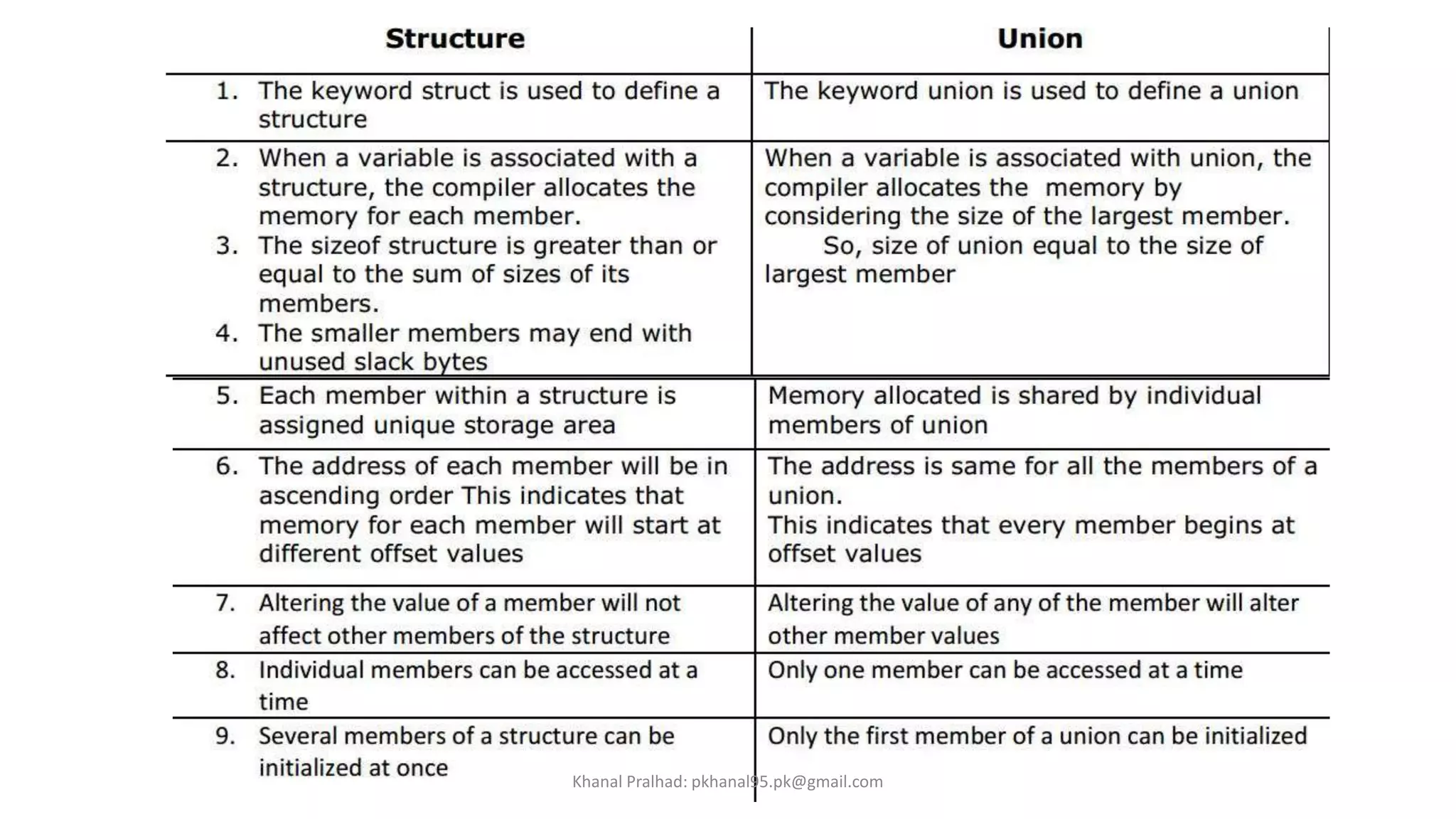
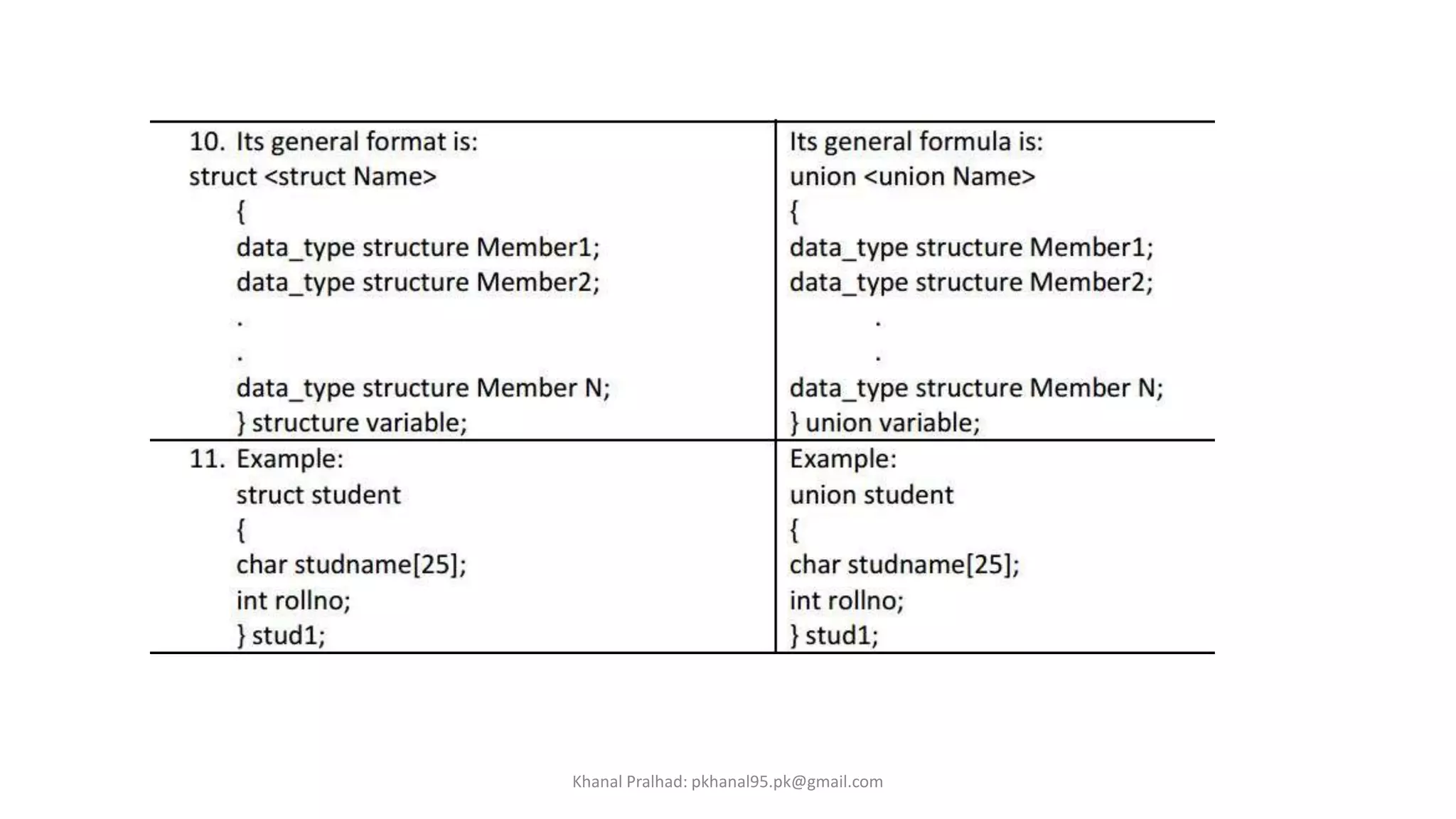
4. Unions are similar to structures but members share the same memory location, so only one can be accessed at a time.

![Why structures?
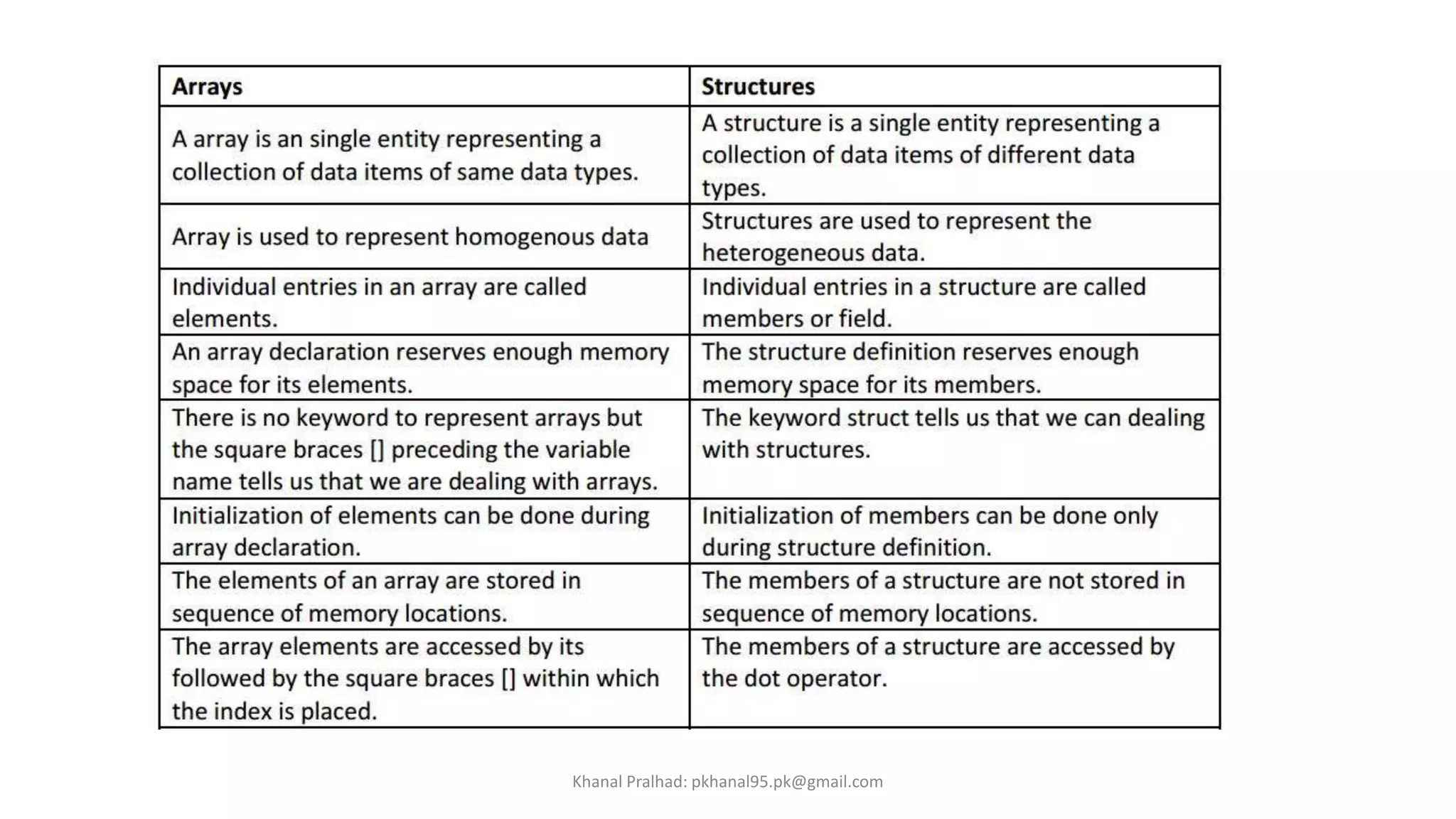
• We know that an Array is a collection of similar data items such as integer, float, char etc. If more
number of data items of same data type are grouped, we normally use arrays.
• For example, the marks of 5 students can be stored using array as shown below:
• marks[5] = {80, 90, 45, 99, 100};
• For collection of dissimilar data types. For example, suppose we want to have the information
related to a student. We may be interested in:
♦ name of the student (string type)
♦ roll number (int type)
♦ average marks (float type)
• Note :
That the above information is a collection of various items of dissimilar data types.So, arrays
cannot be used (because, array is a collection of similar data types). This is where the structures
are used.
Khanal Pralhad: pkhanal95.pk@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureunion-200623031231/75/Structure-amp-union-5-2048.jpg)

![Example:Structure
struct Student
{
char stud_name[30];
int roll_number;
float percentage;
} ;
Struct student s1;
struct Student
{
char stud_name[30];
int roll_number;
float percentage;
} s1 ;
Khanal Pralhad: pkhanal95.pk@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureunion-200623031231/75/Structure-amp-union-9-2048.jpg)
![Structure Initialization
• The syntax of initializing structure variables is similar to that of arrays
i.e., all the elements will be enclosed within curly braces i.e., ‘{‘ and ‘}’
and are separated by commas.The syntax is shown below:
struct tag_name variable = {v1, v2, ...vn };
• struct employee {
char name[20];
int salary;
int id;
} a = {"Shivashankar", 10950, 2001};
Khanal Pralhad: pkhanal95.pk@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureunion-200623031231/75/Structure-amp-union-10-2048.jpg)
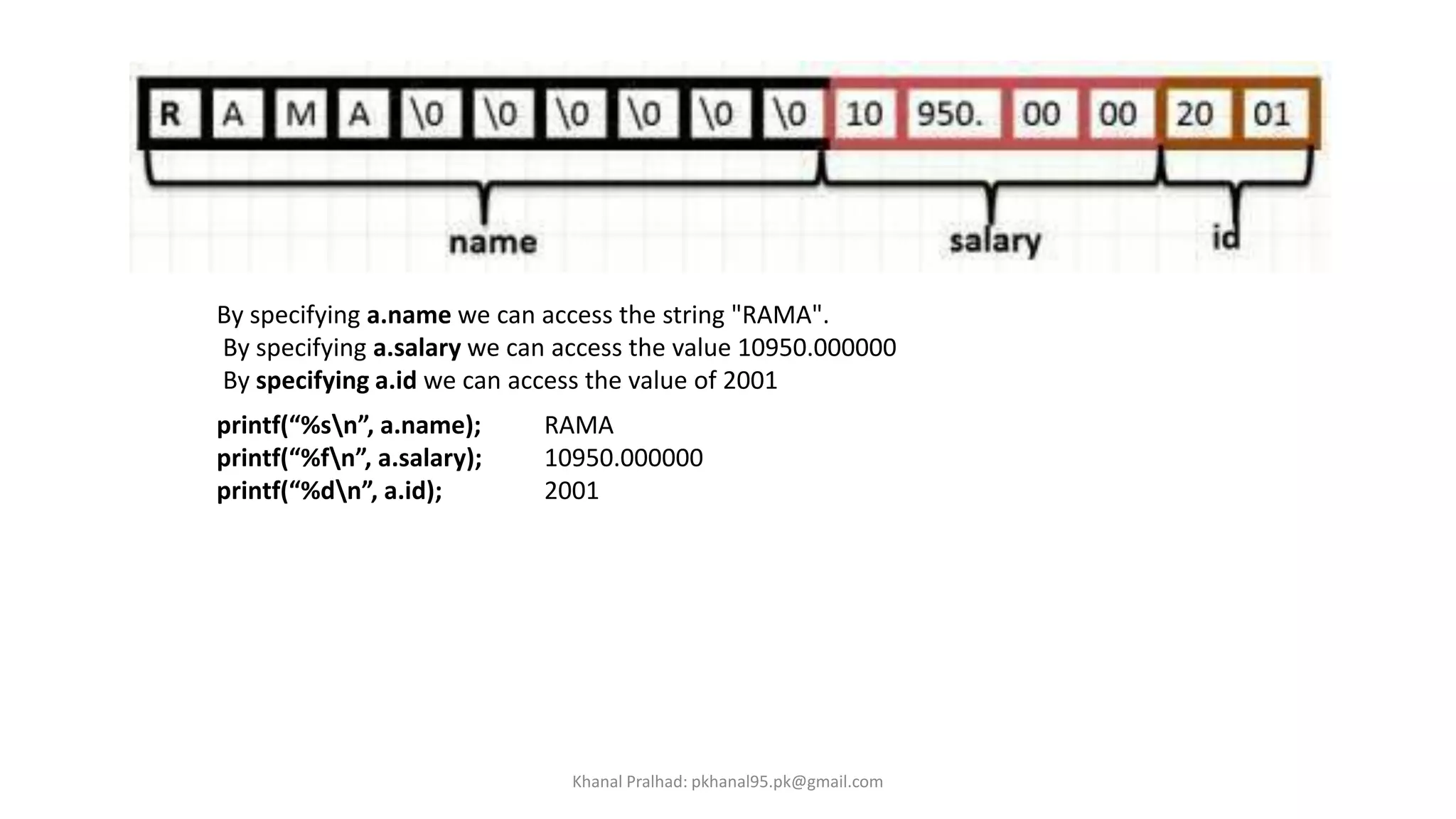
![Accessing Structure Member
-The members of a structure are separate entities and so should be processed individually.
-A member of a structure can be accessed by specifying the variable name followed by a
period (also called dot) which in turn is followed by the member name using the syntax
shown below:
variable.member
Consider the structure definition and initialization shown below:
struct employee {
char name[10];
float salary;
int id;
}
struct employee a = {“RAMA", 10950, 2001};
Khanal Pralhad: pkhanal95.pk@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureunion-200623031231/75/Structure-amp-union-11-2048.jpg)
![Example
struct Student
{
char stud_name[30];
int roll_number;
float percentage;
} stud_1 ;
void main(){
struct Student stud_2;
printf("Enter details of stud_1 : n");
printf("Name : ");
scanf("%s", stud_1.stud_name);
printf("Roll Number : ");
scanf("%d", &stud_1.roll_number);
printf("Percentage : ");
scanf("%f", &stud_1.percentage);
printf("Name of the Student : %sn",
stud_1.stud_name);
printf("Roll Number of the Student :
%in", stud_1.roll_number);
printf("Percentage of the Student :
%fn", stud_1.percentage);
}
Khanal Pralhad: pkhanal95.pk@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureunion-200623031231/75/Structure-amp-union-13-2048.jpg)

![struct student{
char name[25];
int rno;
int marks[3];
};
void main(){
struct student s;
int i;
float total=0,avg;
printf("Enter Student Name:");
gets(s.name);
printf("Enter Student Rollno:");
scanf("%d",&s.rno);
printf("ntttEnter Student Marks Detailsn");
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
printf("Enter Student Subject %d Marks: ",i+1);
scanf("%d",&s.marks[i]);
total= total+s.marks[i];}
avg=total/3;
printf("tt Student Detailsn");
printf("Student Name : ");
puts(s.name);
printf("nStudent Roll no: %dn",s.rno);
printf("ttStudent Marksn");
printf("tt------- -----nn");
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
printf("ttSubject %d : %dn",i+1,s.marks[i]);
printf("tt ====n");
printf("ttTotal : %fn",total);
printf("ttAverage : %fn",avg);
getch();
}
Khanal Pralhad: pkhanal95.pk@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureunion-200623031231/75/Structure-amp-union-15-2048.jpg)



![Example: Union
union Student
{
char stud_name[30];
int roll_number;
float percentage;
} ;
Khanal Pralhad: pkhanal95.pk@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureunion-200623031231/75/Structure-amp-union-19-2048.jpg)
![union Student
{
char stud_name[30];
int roll_number;
float percentage;
} stud_1 ; // while defining union
void main(){
union Student stud_2; // using union keyword
printf("Enter details of stud_1 : n");
printf("Name : ");
scanf("%s", stud_1.stud_name);
printf("Roll Number : ");
scanf("%d", &stud_1.roll_number);
printf("Percentage : ");
scanf("%f", &stud_1.percentage);
printf("Name of the Student : %sn",
stud_1.stud_name);
printf("Roll Number of the Student : %in",
stud_1.roll_number);
printf("Percentage of the Student : %fn",
stud_1.percentage);
}
Khanal Pralhad: pkhanal95.pk@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureunion-200623031231/75/Structure-amp-union-20-2048.jpg)
![• Typedef
typedef struct Books {
char title[50];
char author[50];
char subject[100];
int book_id;
} Book;
• Nested structure
Khanal Pralhad: pkhanal95.pk@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureunion-200623031231/75/Structure-amp-union-23-2048.jpg)
![typedef struct student
{
int roll_no;
char name[30];
int phone_number;
}st;
int main()
{
st p1, p2, p3;
p1.roll_no = 1;
strcpy(p1.name,"Brown");
p1.phone_number = 123443;
p2.roll_no = 2;
strcpy(p2.name,"Sam");
p2.phone_number = 1234567822;
p3.roll_no = 3;
strcpy(p3.name,"Addy");
p3.phone_number = 1234567844;
printf("First Studentn");
printf("roll_no : %dn", p1.roll_no);
printf("name : %sn", p1.name);
printf("phone_number : %dn", p1.phone_number);
printf("Second Studentn");
printf("roll_no : %dn", p2.roll_no);
printf("name : %sn", p2.name);
printf("phone_number : %dn", p2.phone_number);
printf("Third Studentn");
printf("roll_no : %dn", p3.roll_no);
printf("name : %sn", p3.name);
printf("phone_number : %dn", p3.phone_number);
return 0;
}
Khanal Pralhad: pkhanal95.pk@gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureunion-200623031231/75/Structure-amp-union-24-2048.jpg)


