Downloaded 506 times




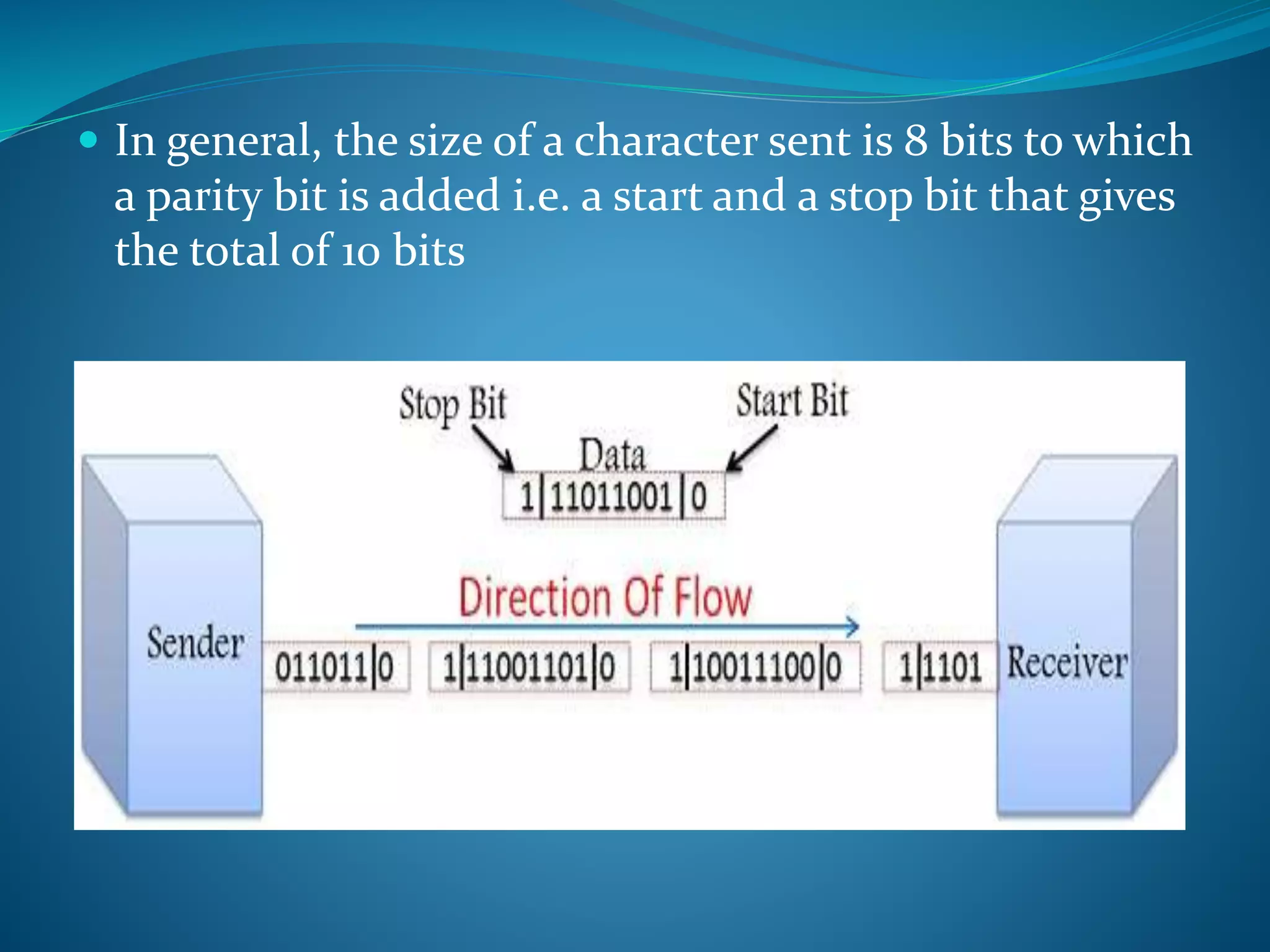



Synchronous communication requires that the transmitting and receiving devices have synchronized clocks running at the same rate to allow data to flow continuously in blocks or frames in a full duplex mode, making it efficient and reliable for transferring large amounts of data, as is used for chat rooms, video calls, and phone conversations. In asynchronous transmission, data is sent intermittently without an external clock, flowing in a half duplex mode one byte at a time, generally with 8 data bits plus a start and stop bit, and is used for letters, emails, television, and radio.








Synchronous transmission sends data continuously at a constant rate. Examples include chat rooms and video conferencing.
Asynchronous transmission sends data intermittently without a clock signal. Examples include letters, emails, and radios.