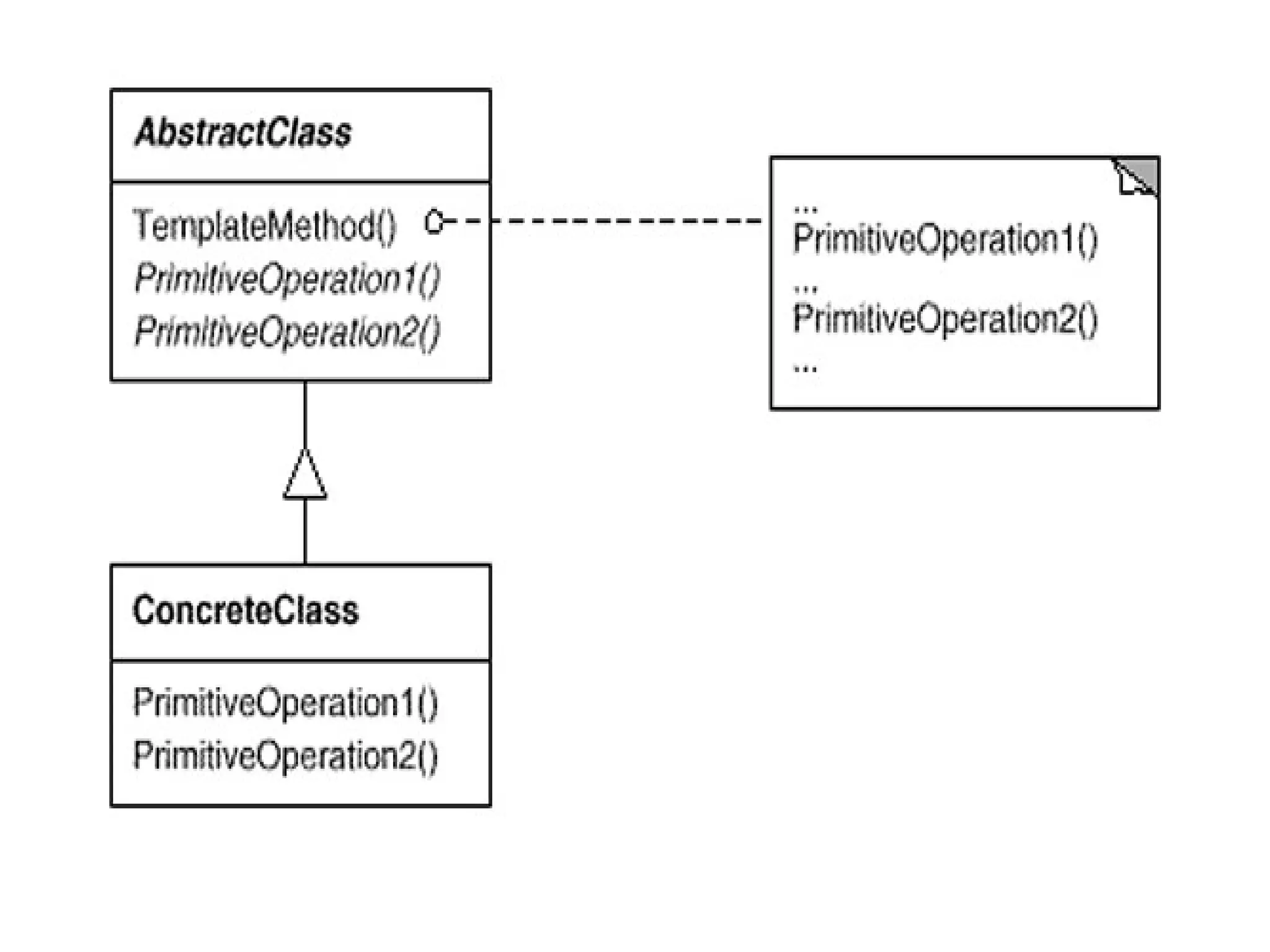
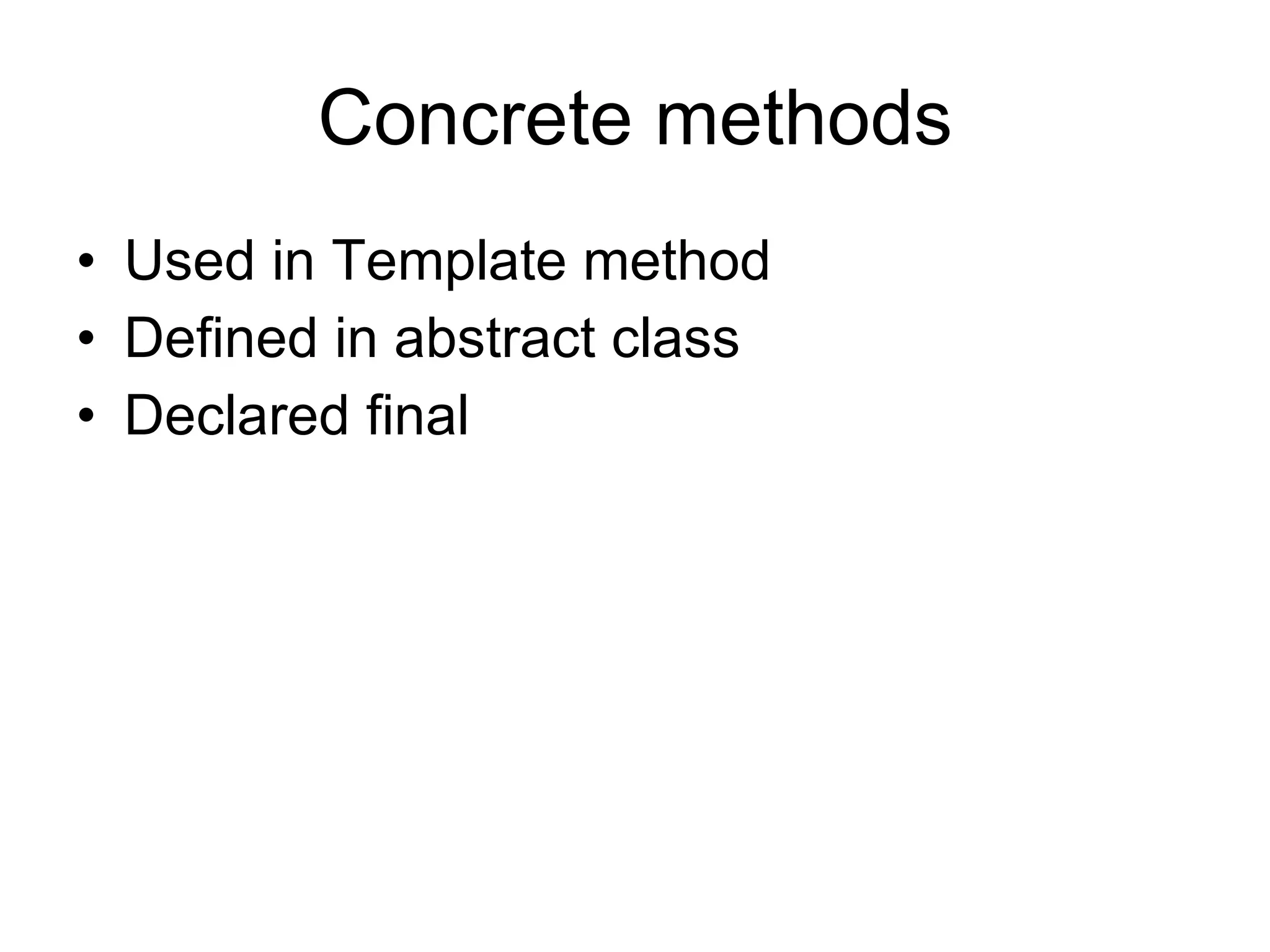
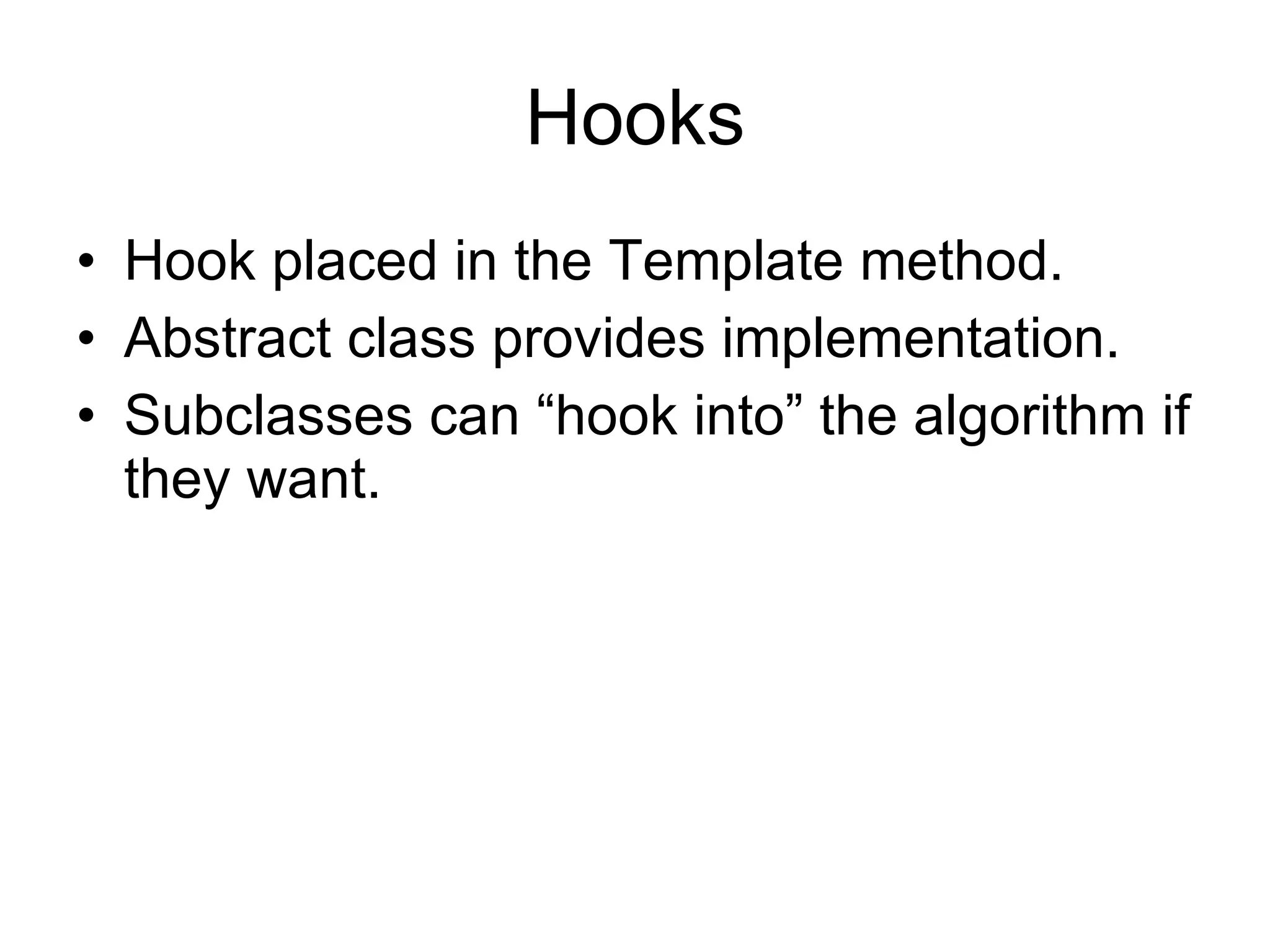
The Template Method pattern defines the skeleton of an algorithm in an abstract class, leaving some steps to be implemented by subclasses. This allows subclasses to redefine certain steps of the algorithm without changing its structure. The algorithm is encapsulated in a single class, with subclasses only needing to provide specialized implementation details for certain steps. The abstract class declares primitive methods that subclasses must implement, as well as concrete methods and hooks to allow subclasses to optionally modify the algorithm's behavior.