The document outlines the history and evolution of free and open source software, highlighting key figures, milestones, and cultural shifts from the 1960s through the present. It discusses the contributions of individuals like Richard Stallman and Linus Torvalds, the founding of significant organizations like the Free Software Foundation and Red Hat, and the impact of open source on business and technology. Additionally, it touches on the ethical principles guiding the hacker community and the ongoing relevance of open source in modern computing.
![THE OPEN SOURCE WAY
History of Free & Open Source Software[info]
David Kašpar [Dee'Kej]
Associate Software Engineer
c b a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thehistoryoffloss-180924095428/75/The-Open-Source-Way-1-2048.jpg)
![CC BY-SA 3.07
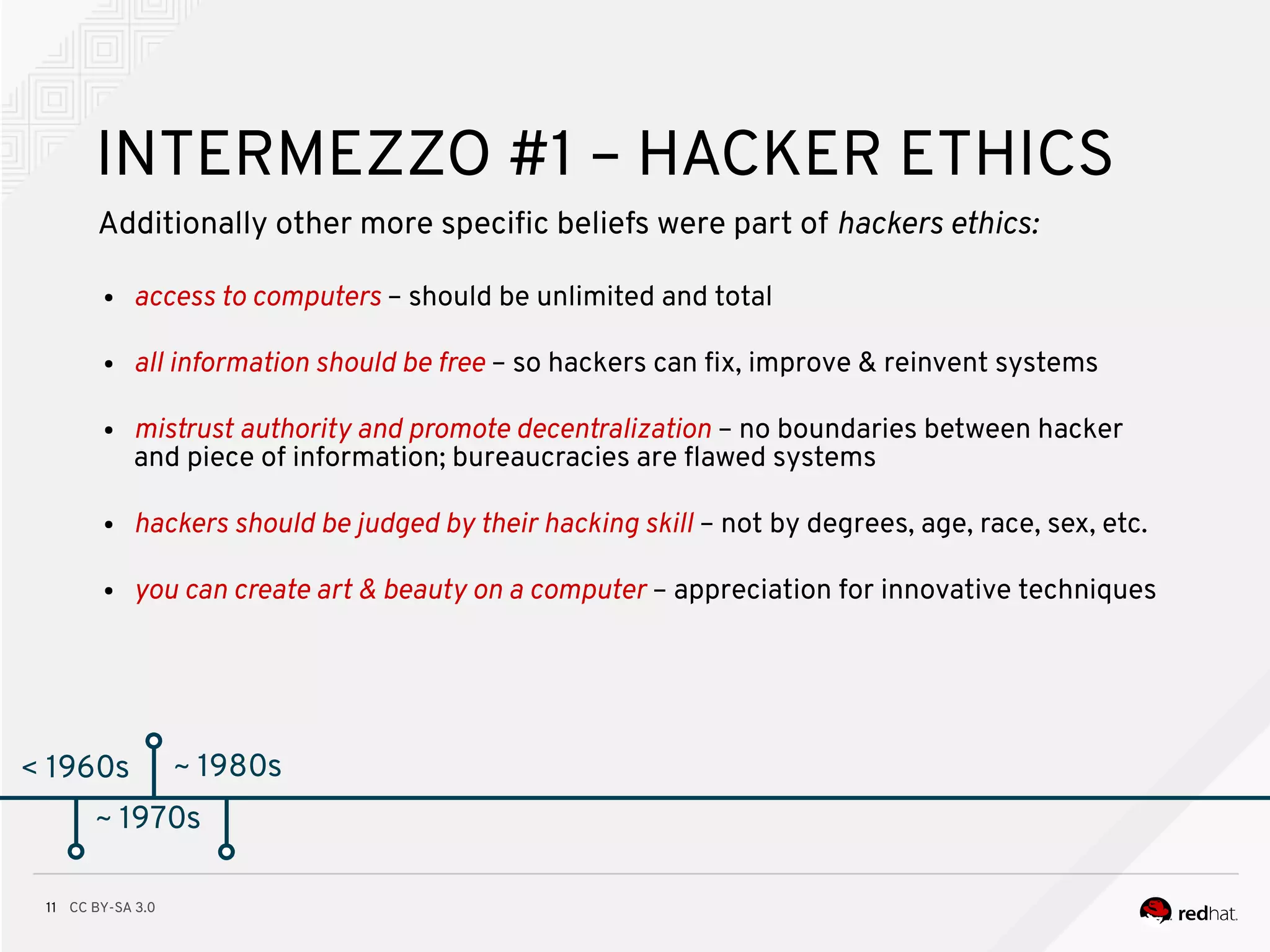
< 1960s
HOW IT ALL STARTED #2
In the early 1970s, AT&T distributed early versions of UNIX to
government and academic researchers at no cost...
● no permission to (re)distribute any modifed versions
● UNIX has become widespread in the early 1980s
● AT&T started charging money for system patches
● software-only companies started charging money for licenses (new restrictions)
● Bill Gates wrote an essay Open Letter to Hobbyists [1976]
(illegal usage of Altair BASIC by hobbyists)
~ 1970s
~ 1980s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thehistoryoffloss-180924095428/75/The-Open-Source-Way-4-2048.jpg)









![CC BY-SA 3.025
INTERMEZZO #3
“Which leads me to 3 fundamental
theories about the whole IT
industry:
1) It all happened by accident.
2) It was done by amateurs.
3) Nothing has really changed.”
– Jan Wildeboer
[Free & Open Source Evangelist]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thehistoryoffloss-180924095428/75/The-Open-Source-Way-21-2048.jpg)







![CC BY-SA 3.035
< 1960s
INTERMEZZO #4
~ 1970s
~ 1980s
~ 1970s 1991
During early days of Linux, it was not taken seriously...
“Linux is the Hype de Jour.” - Gartner Group [1999]
“We think of Linux as a competitor in the student and hobbyist market.
But I really don't think in the commercial market we'll see it in any
signifcant way” - Bill Gates [2001]
“Linux is a cancer that attaches itself in an intellectual property sense to
everything it touches.” - Steve Ballmer [2001]
1993
1994
1995
1998
1999
2001](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thehistoryoffloss-180924095428/75/The-Open-Source-Way-31-2048.jpg)
![CC BY-SA 3.036
INTERMEZZO #4
Q1: Why should I bother with something
which is not taken seriously?
Q2: Why should I work on something that can be used for free?
That will not pay my monthly bills…
Have you ever heard the follow up quote before?
“640K ought to be enough for anybody.”
!= Bill Gates [1981]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thehistoryoffloss-180924095428/75/The-Open-Source-Way-32-2048.jpg)

![CC BY-SA 3.039
< 1960s
HOW IT ALL STARTED #12
~ 1970s
~ 1980s
~ 1970s 1991
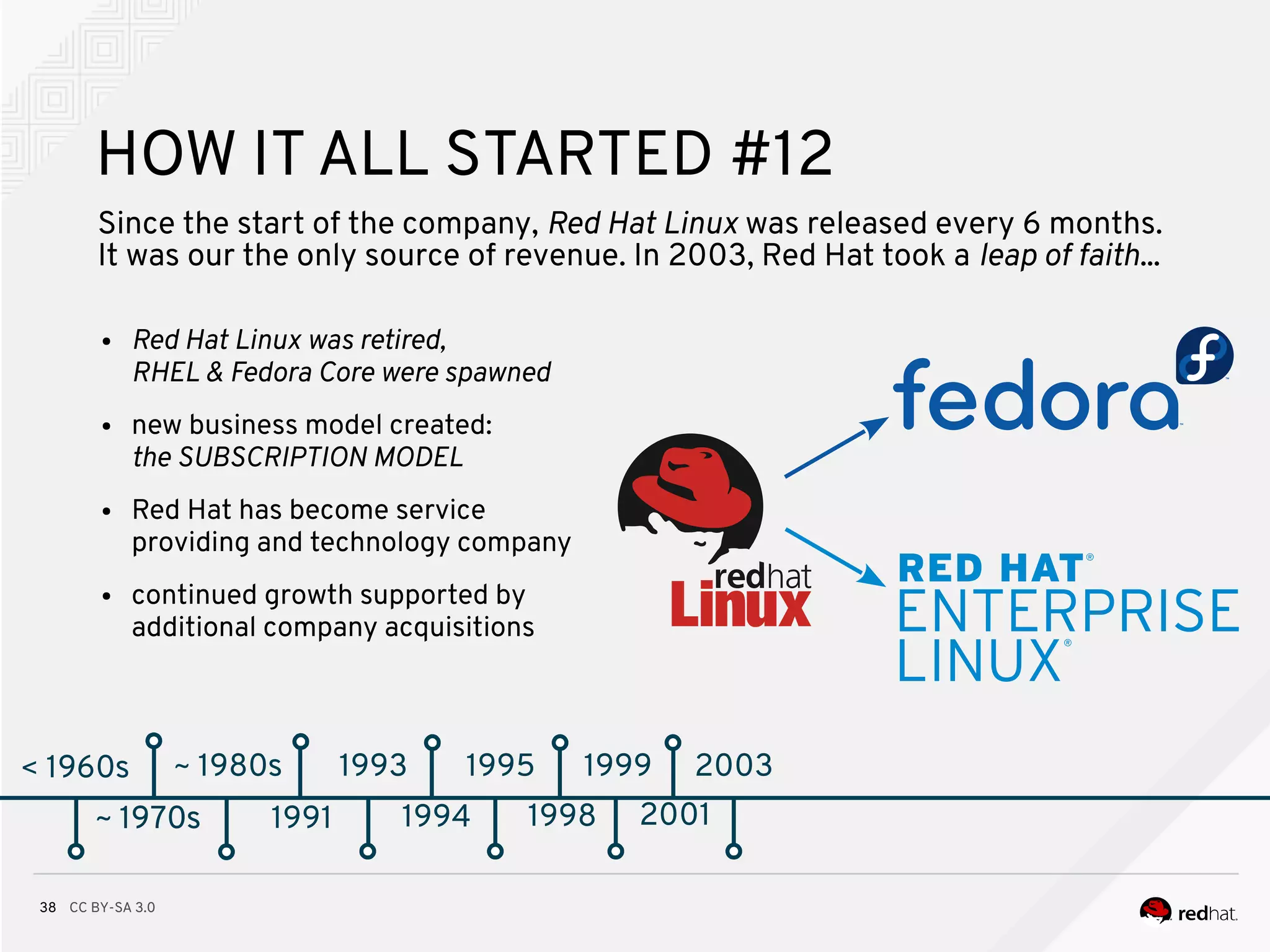
Since the start of the company, Red Hat Linux was released every 6 months.
It was our the only source of revenue. In 2003, Red Hat took a leap of faith...
1993
1994
1995
1998
1999
2001
2003
“Linux isn’t going away.
Linux is a serious competitor.
We will rise to this challenge.”
– Steve Ballmer [2003]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thehistoryoffloss-180924095428/75/The-Open-Source-Way-35-2048.jpg)












![CC BY-SA 3.055
APPLYING THE PRINCIPLES
What can we achieve when we use the Open Source Way? [Click for videos]
VENKY HARIHARAN
Fmr Corporate Affairs Dir
Red Hat India
TOM DELBANCO, MD
Co-founder of OpenNotes
Harvard Medical School
JON SHCULL
Research scientist & founder of
e-NABLE
“If you get it right, if you are
able to drive some good
changes, it’s not just a small
localized dis, but it has an
effect on a lot of people.”
“It’s basically the notion we
should share equally.
We should be totally
transparent with what
we’re thinking”
“I like to say we make
children smile, we make
parents weep, and
we make nerds rejoice.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thehistoryoffloss-180924095428/75/The-Open-Source-Way-49-2048.jpg)


