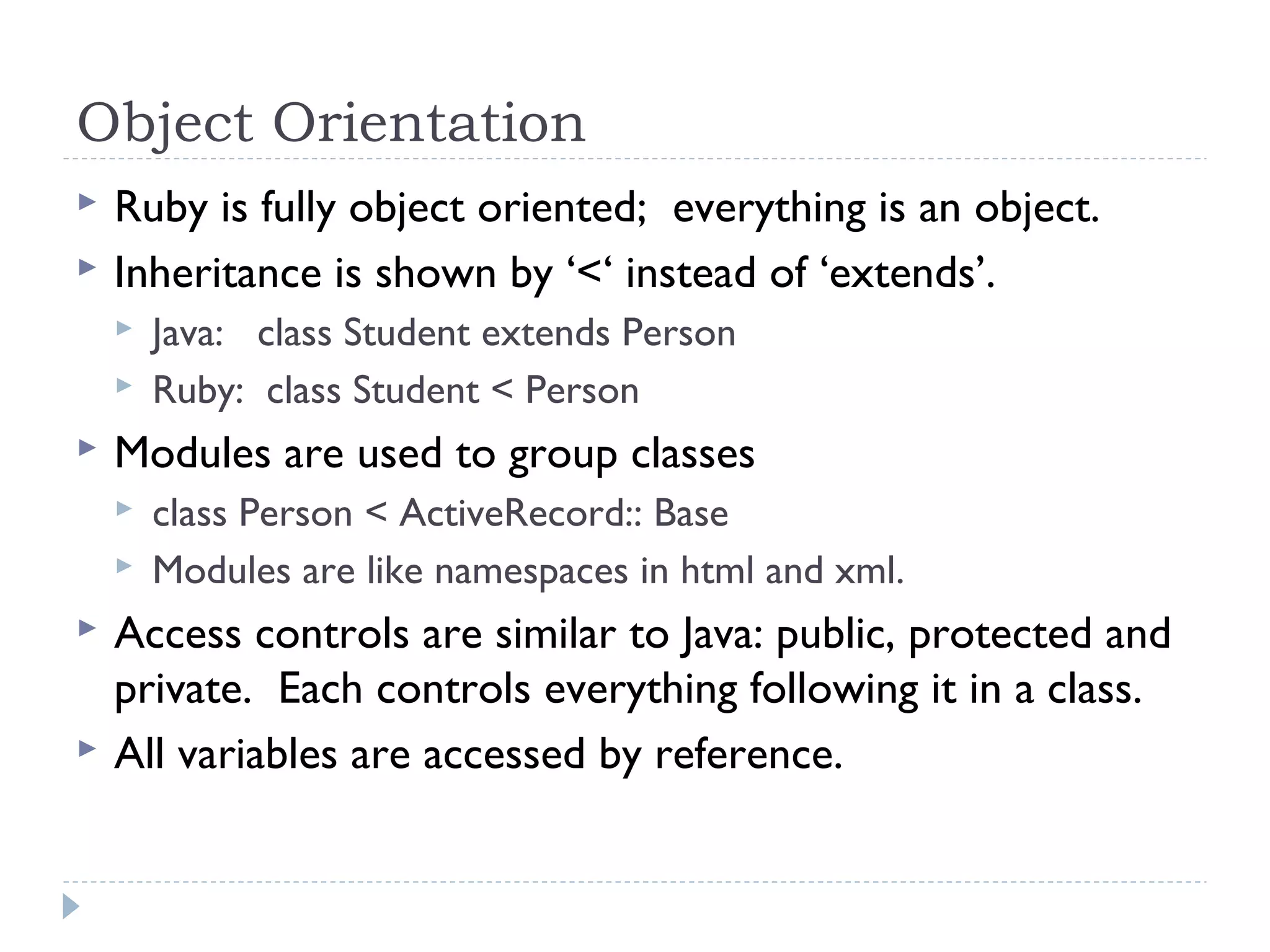
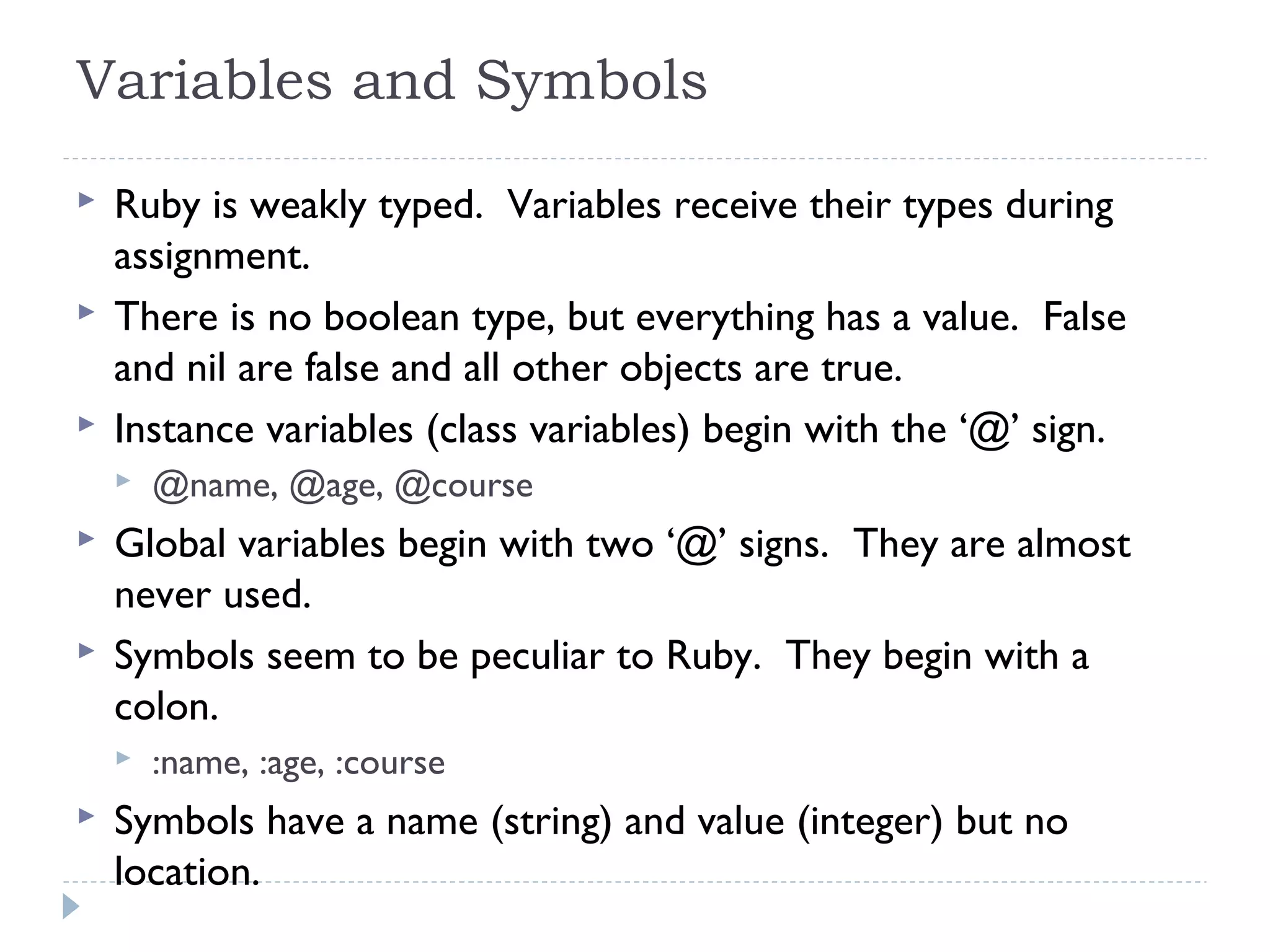
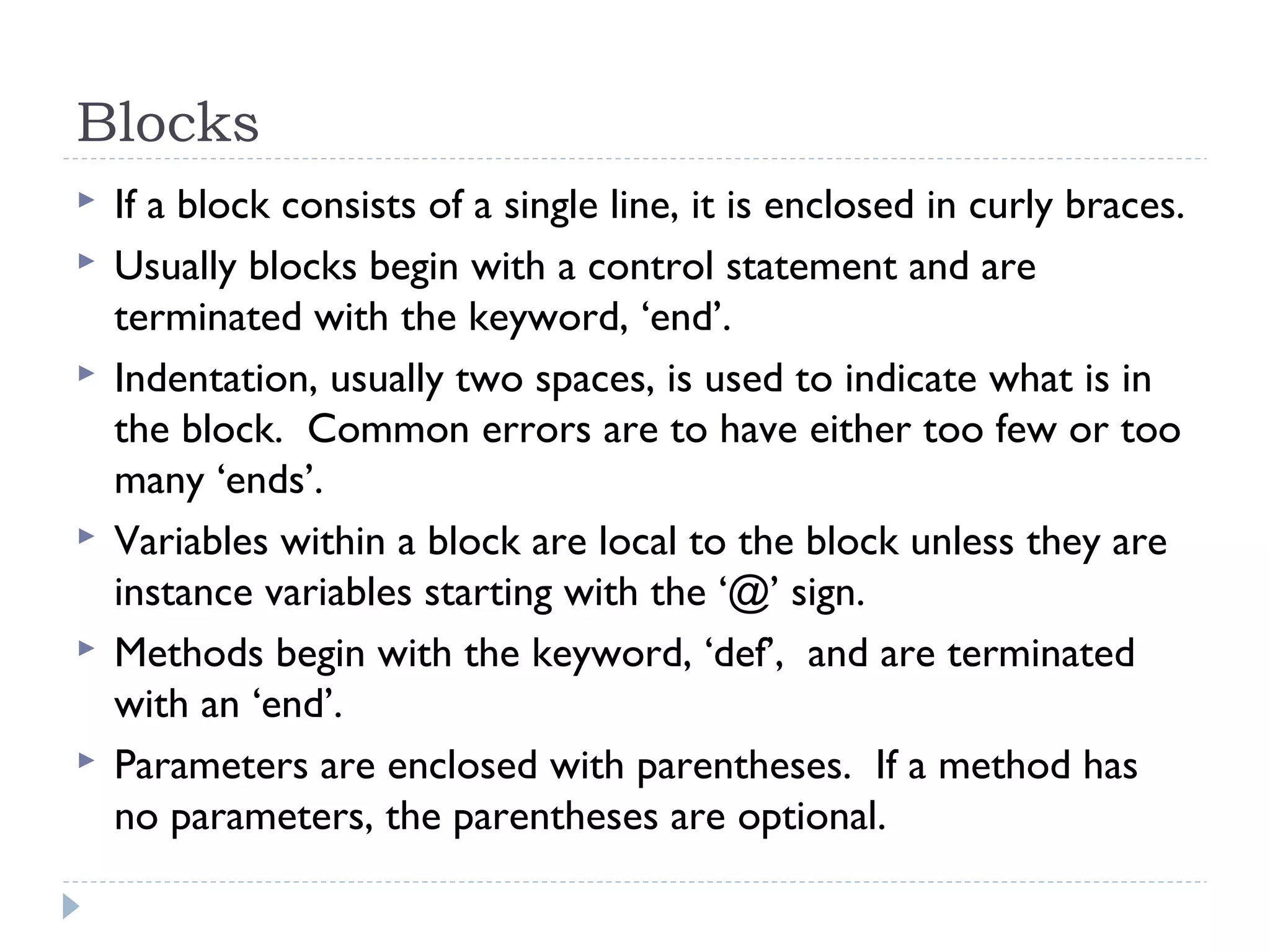
Ruby is a fully object-oriented programming language where everything is an object. It uses modules to group classes and symbols to name variables and methods. Ruby code is written in blocks delimited by keywords like 'if' and 'end'. An example program demonstrates how a Person class in Ruby compares to a similar class in Java, using object instantiation, attributes, and a method. Key differences between Ruby and Java include Ruby being dynamically typed, using '# ' for comments, and 'attr_accessor' for getters and setters.
![Example Program – Java
public class People
{ public static void main (String [] args)
{ Person girl = new Person ("Alice", 5);
girl.show_person ();
}
} // People
class Person
{ String name;
int age;
Person (String name, int age)
{ this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
protected void show_person ()
{ System.out.println (name);
System.out.println (age);
}
} // Person](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/therubyprogramminglanguage-151029182908-lva1-app6892/75/The-ruby-programming-language-5-2048.jpg)


![Data Structures
Arrays
Indexed with integers starting at 0.
Contents do not have to all be the same type.
Contents can be assigned in a list using square brackets.
order = [“blue”, 6, 24.95]
Arrays are objects so must be instantiated with ‘new’.
Hash Tables
Key – value pairs
Keys are almost always symbols
Contents can be assigned in a list of key-value pairs using curly
braces.
order = {:color => “blue”, :size => 6, :price => 24.95}
To retrieve an element, use square brackets
@size = order[:size]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/therubyprogramminglanguage-151029182908-lva1-app6892/75/The-ruby-programming-language-8-2048.jpg)
![Control Structures: Conditionals
if order[:color] == “blue”
…
elsif order[:size] == 6
…
else
…
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/therubyprogramminglanguage-151029182908-lva1-app6892/75/The-ruby-programming-language-9-2048.jpg)
![Control Structures: Iteration
for, while and until
for item in order do
puts item
Iterator ‘each’
sum = 0
[1..10].each do |count|
sum += count
end
puts sum
count is a parameter to the block and has no value outside of
it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/therubyprogramminglanguage-151029182908-lva1-app6892/75/The-ruby-programming-language-10-2048.jpg)


