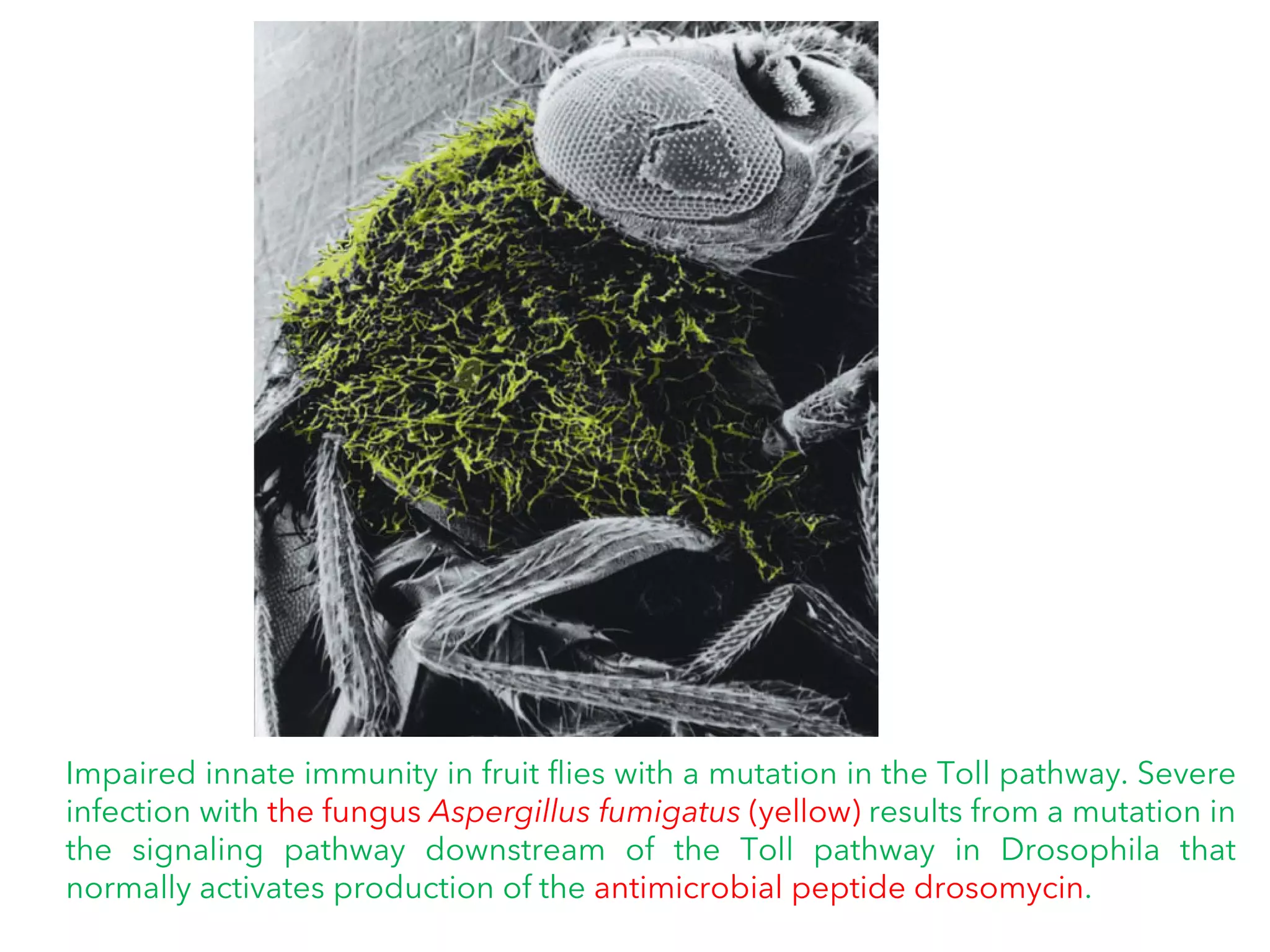
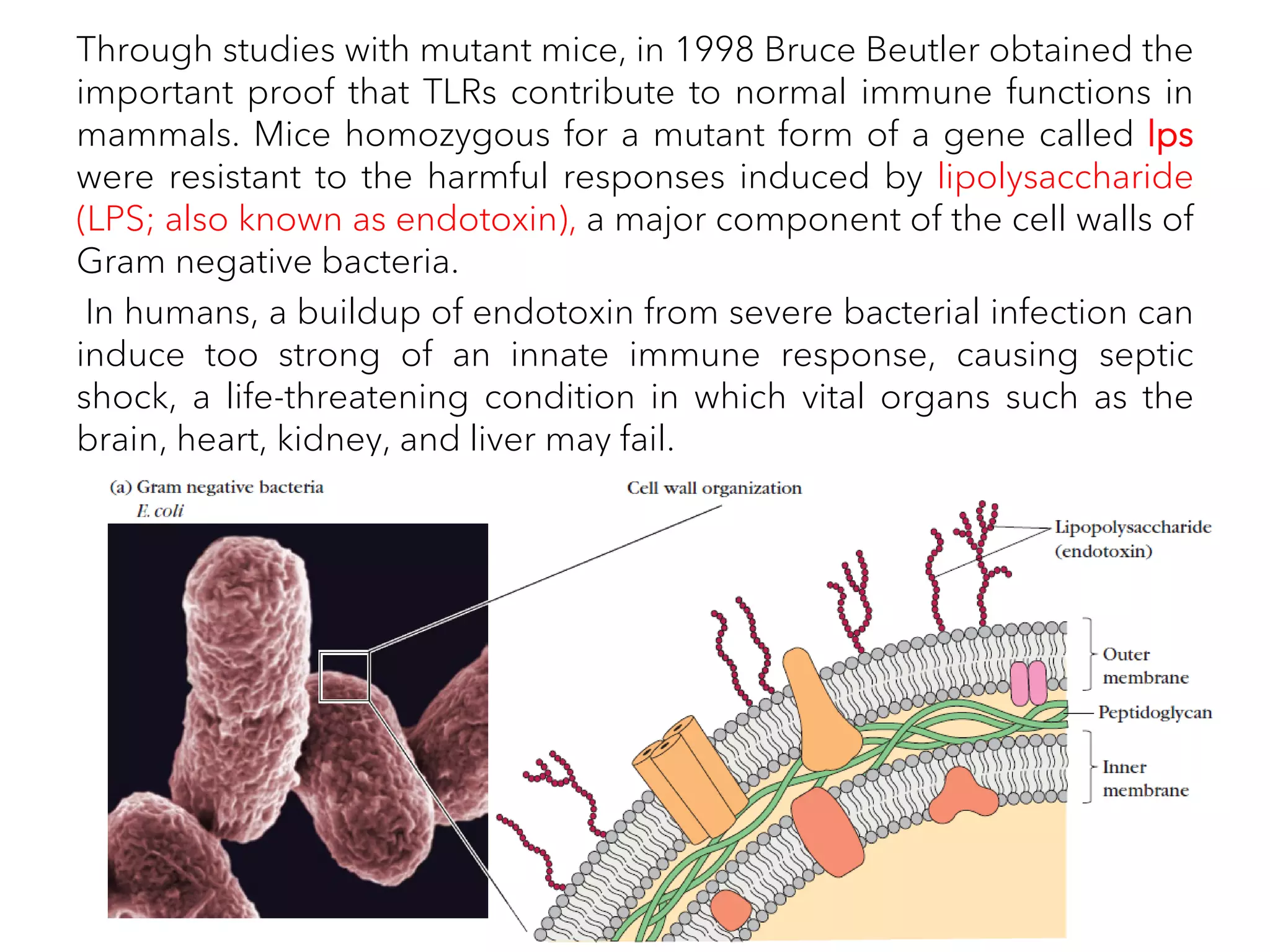
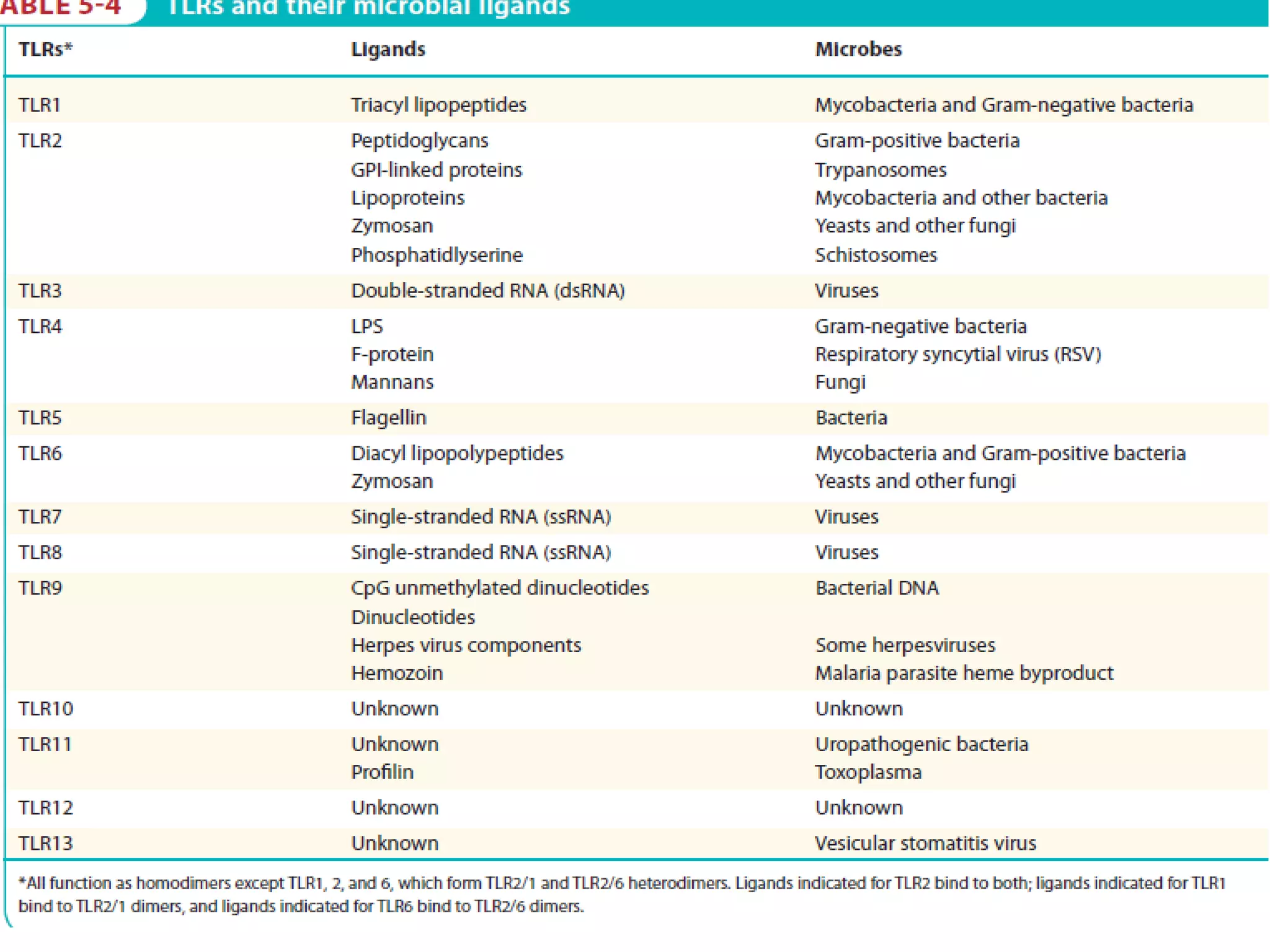
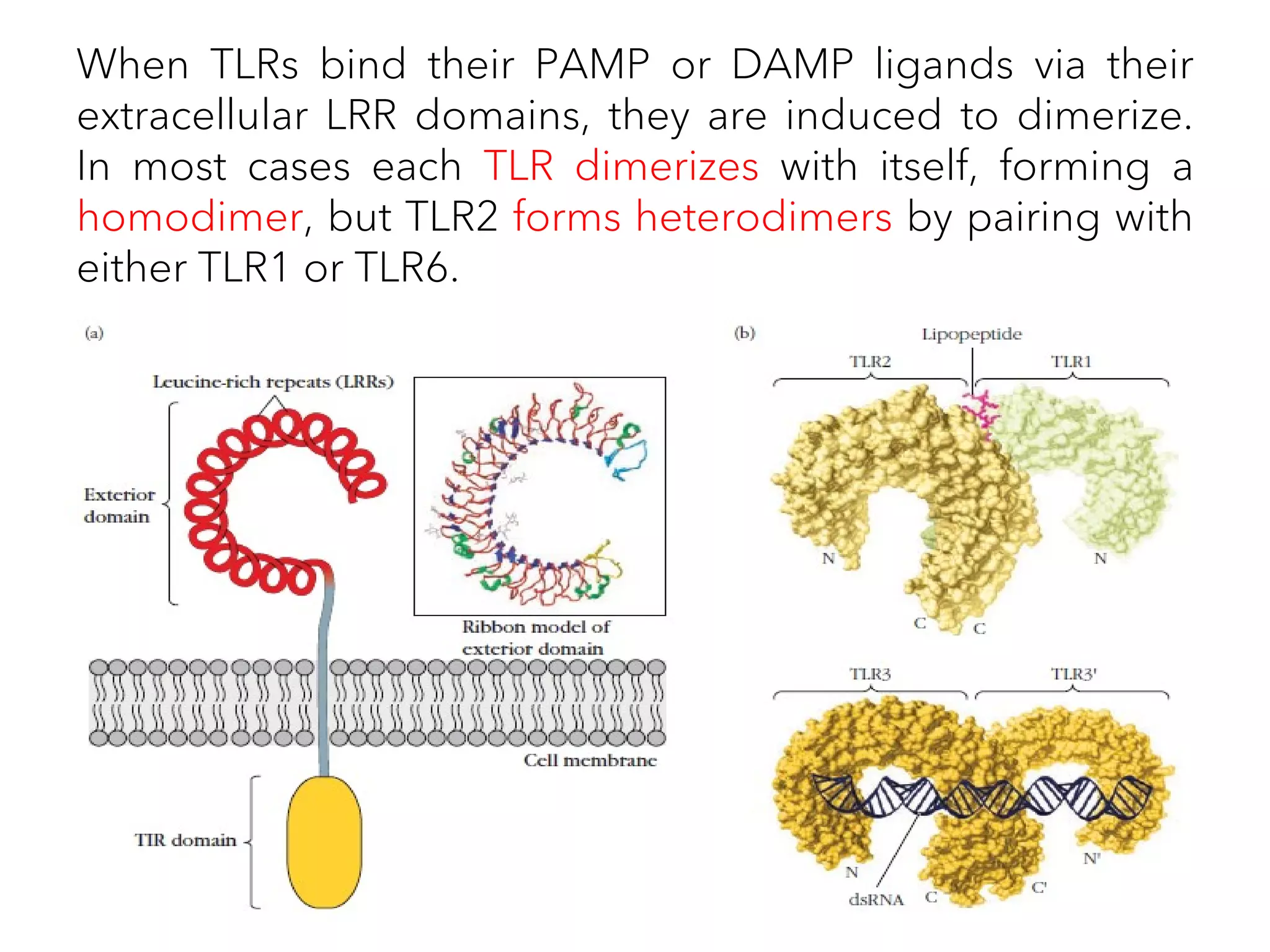
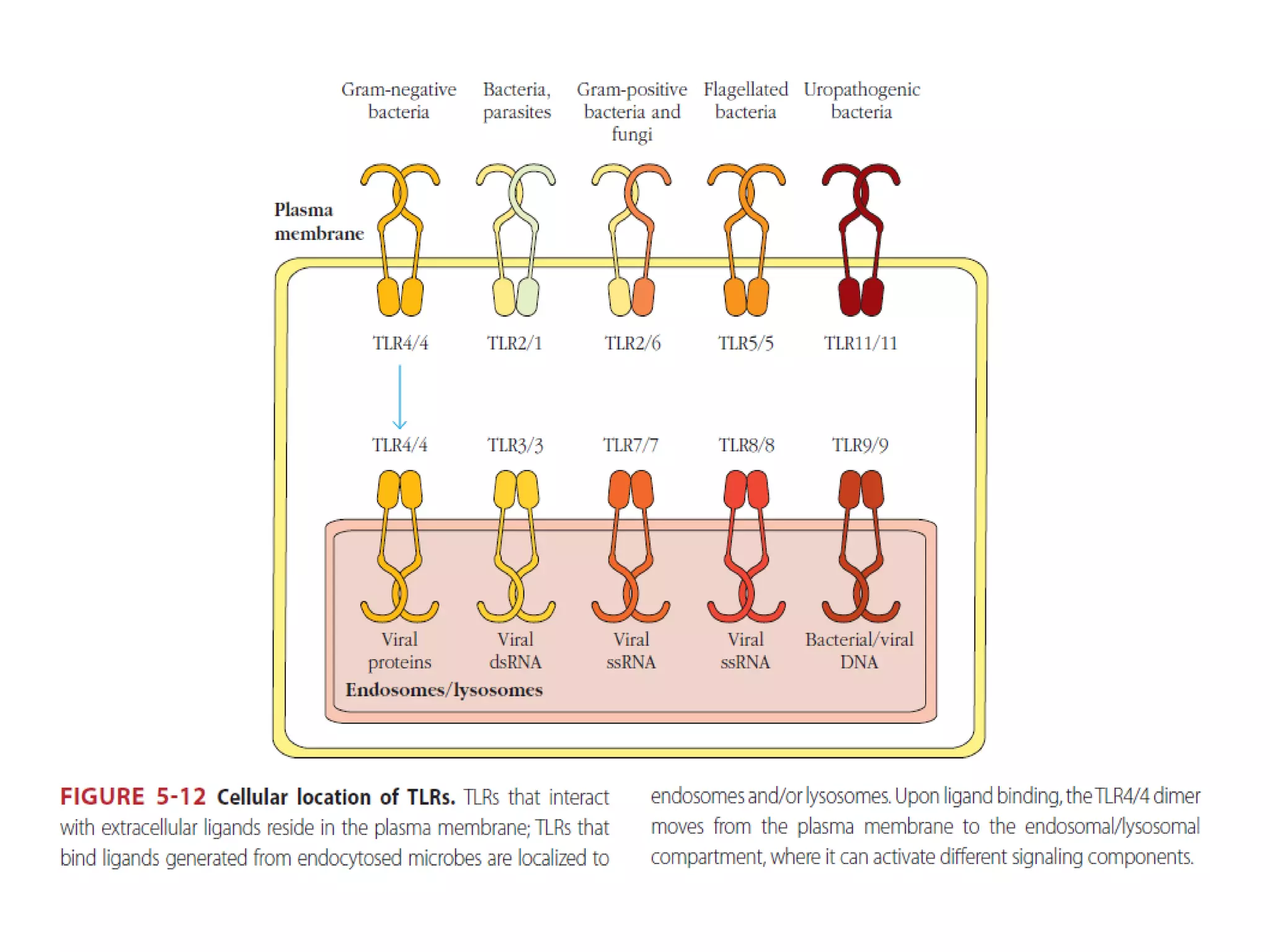
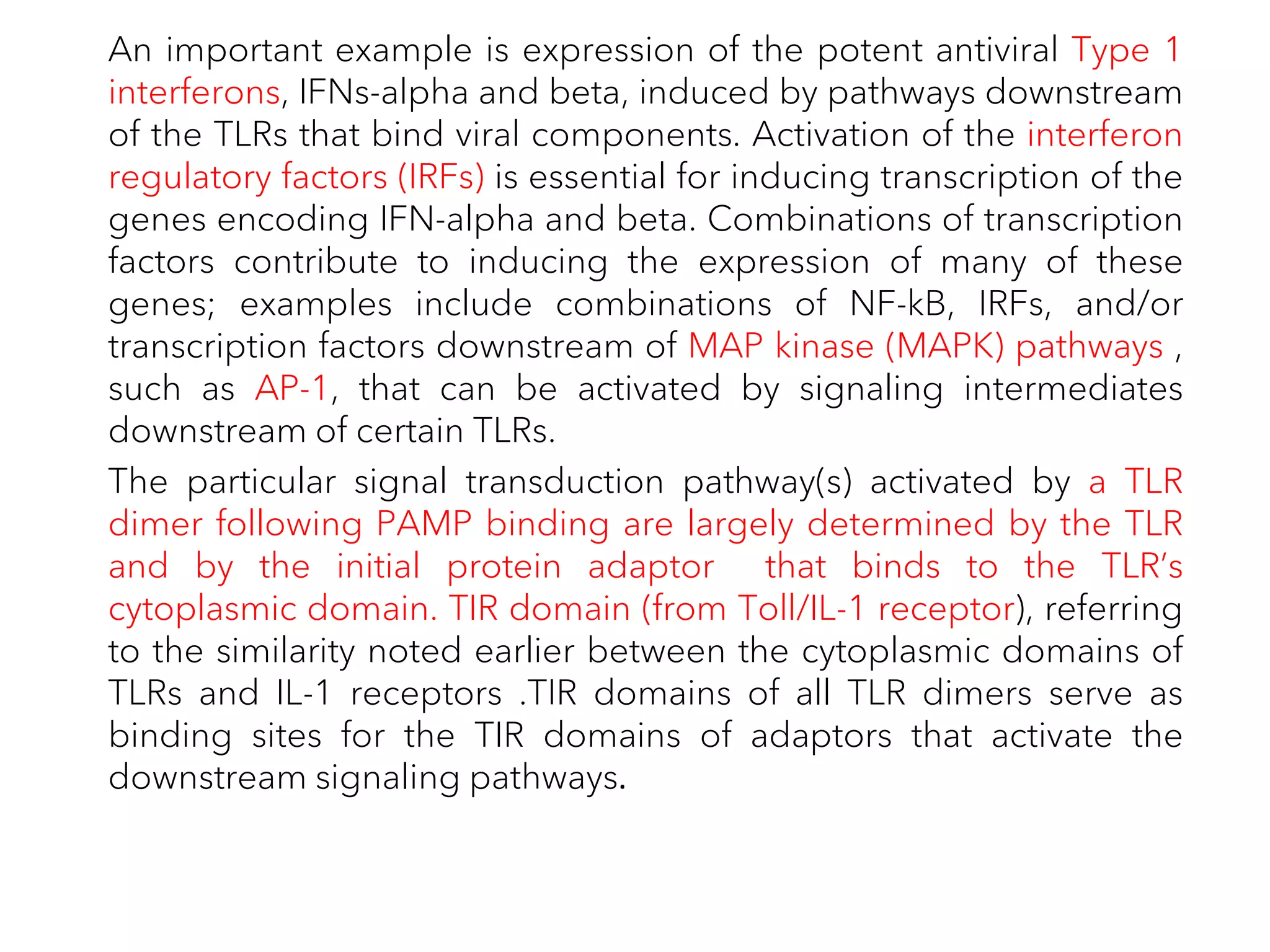
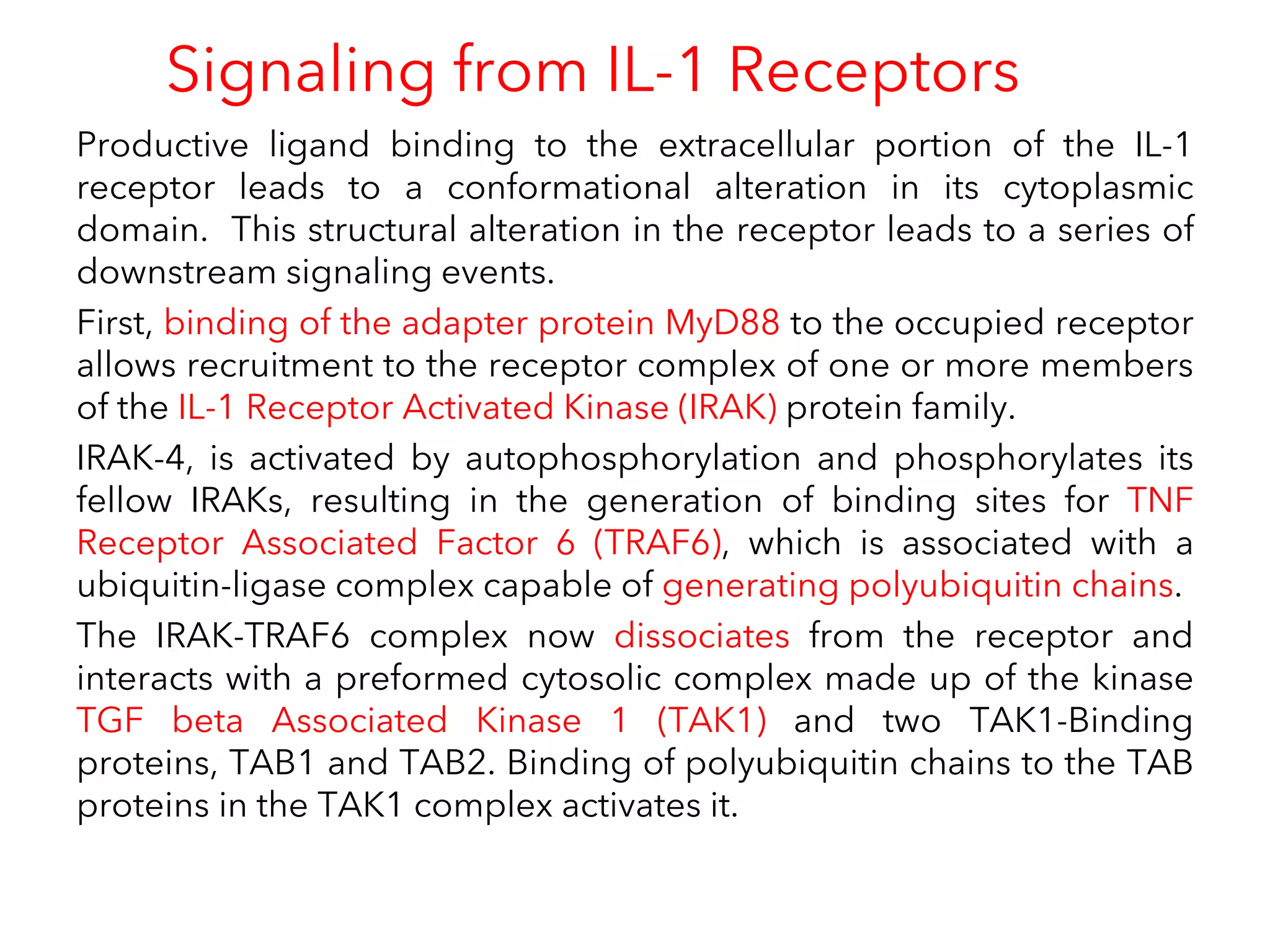
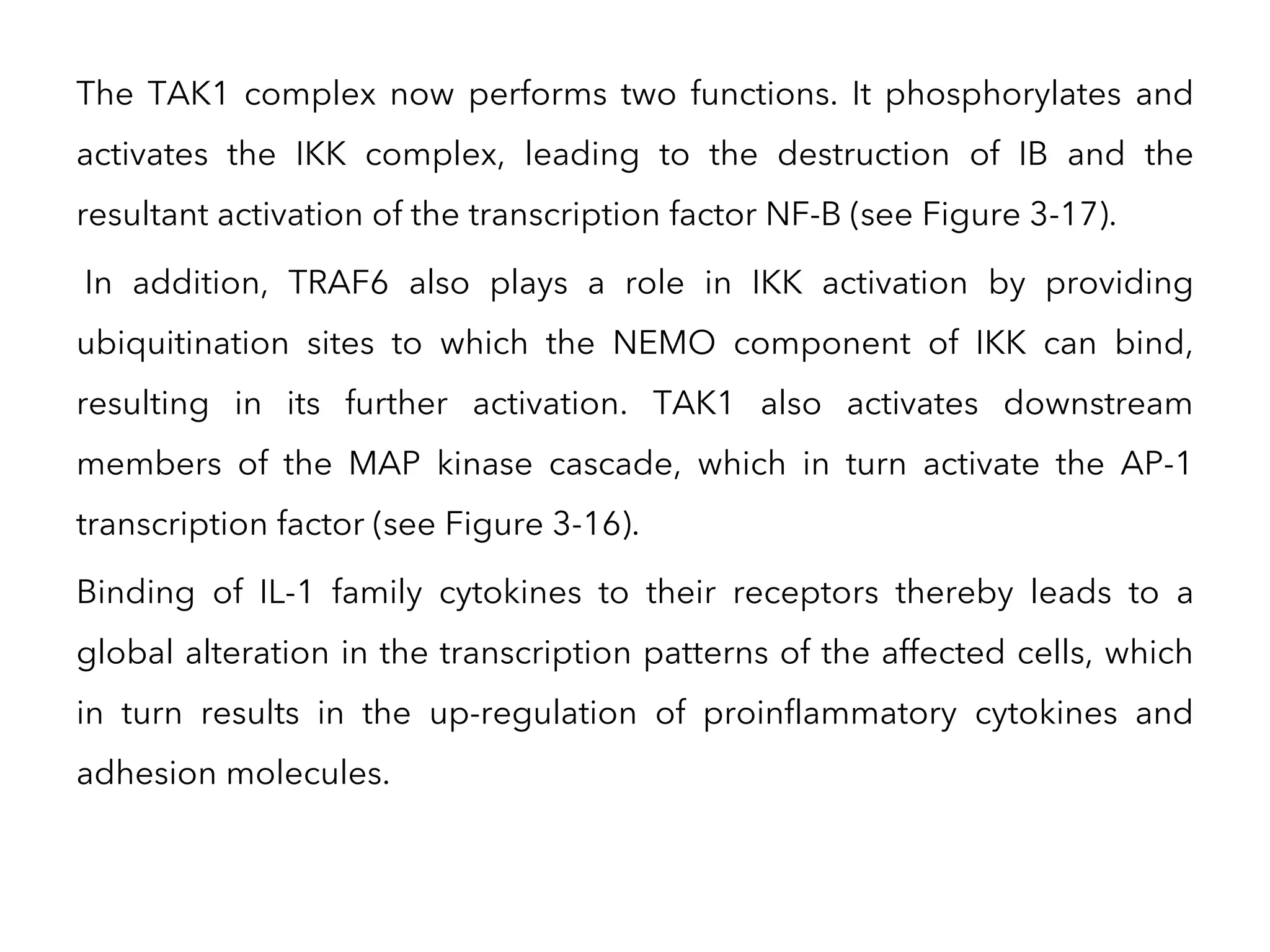
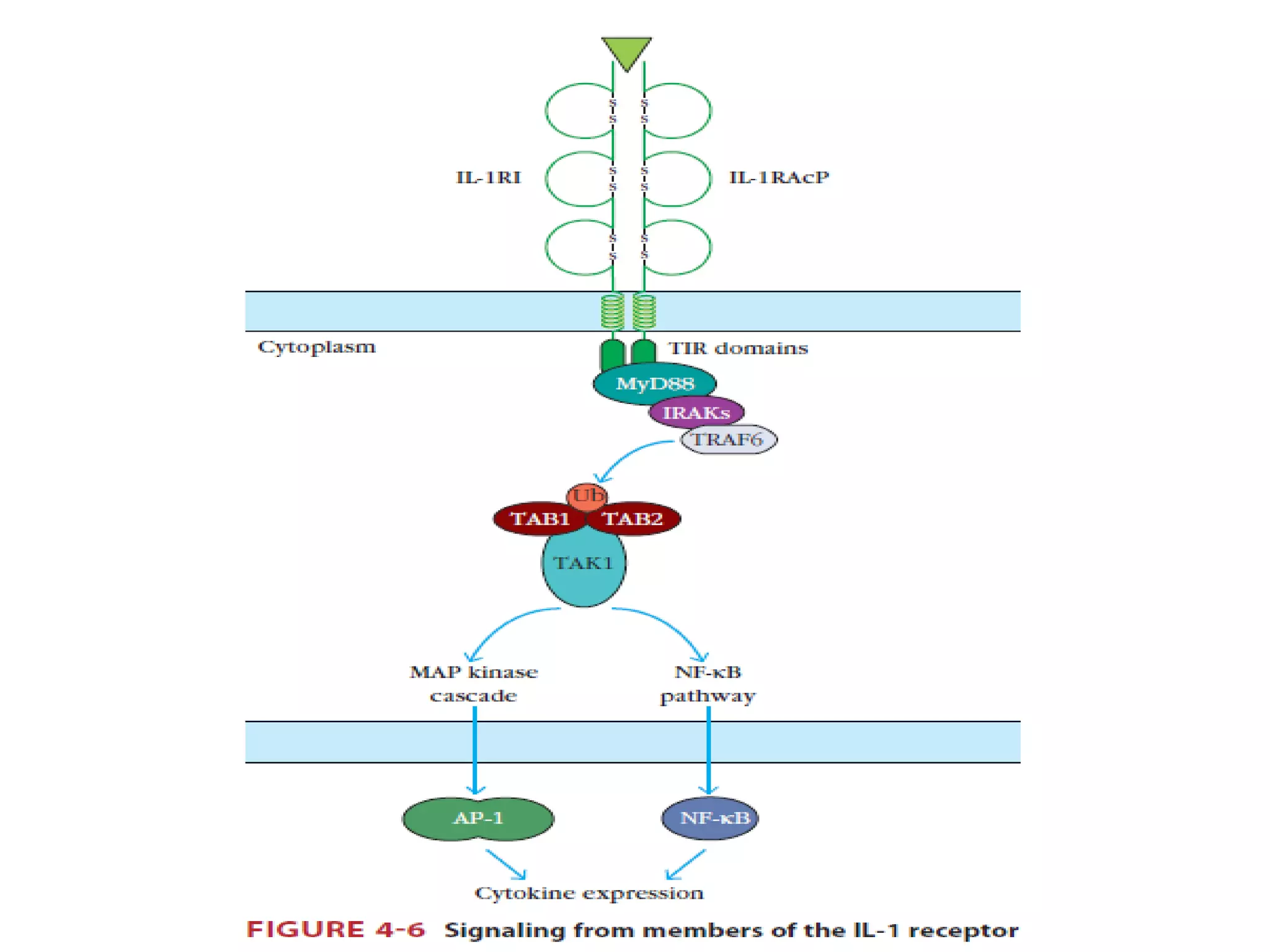
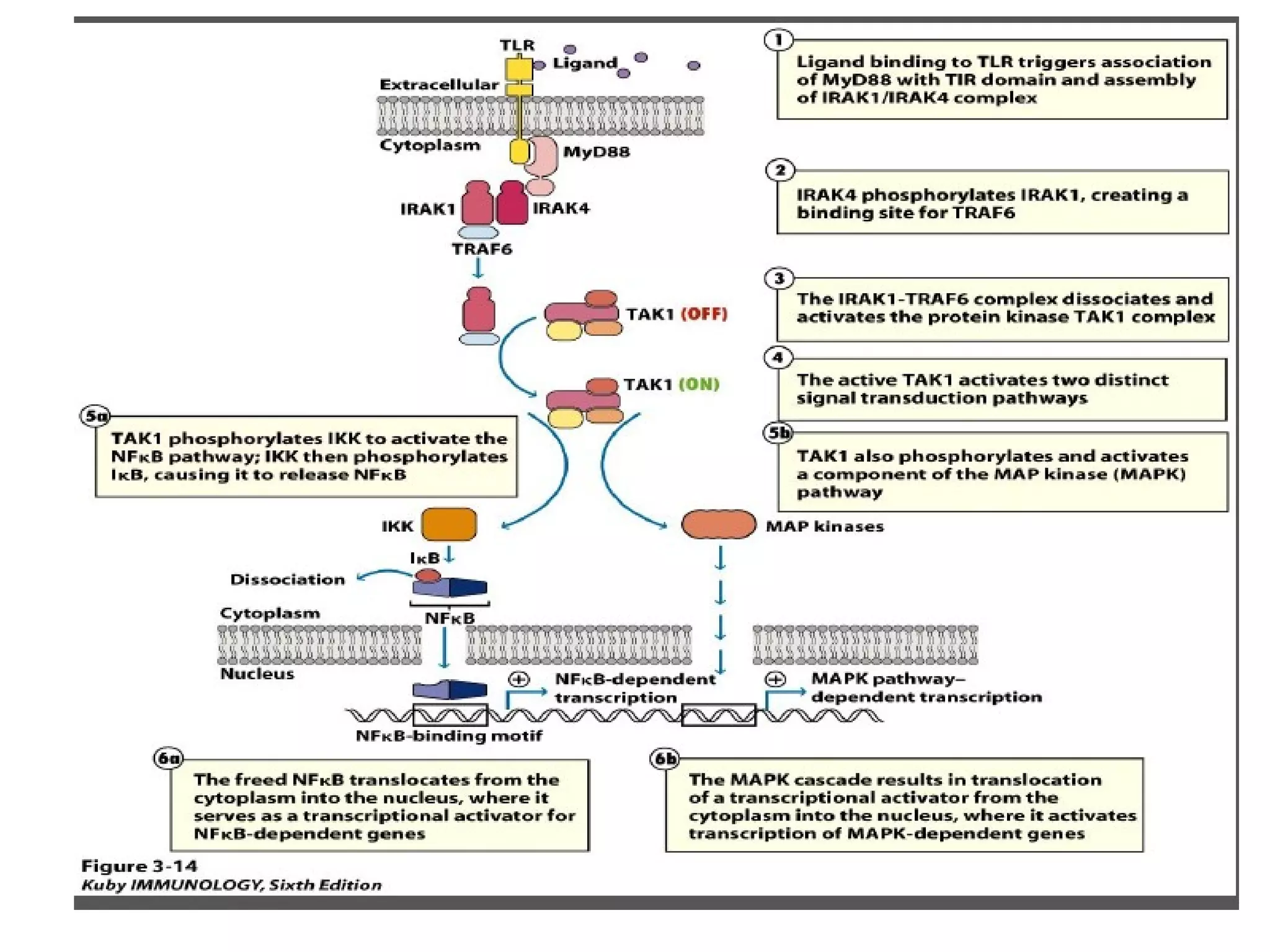
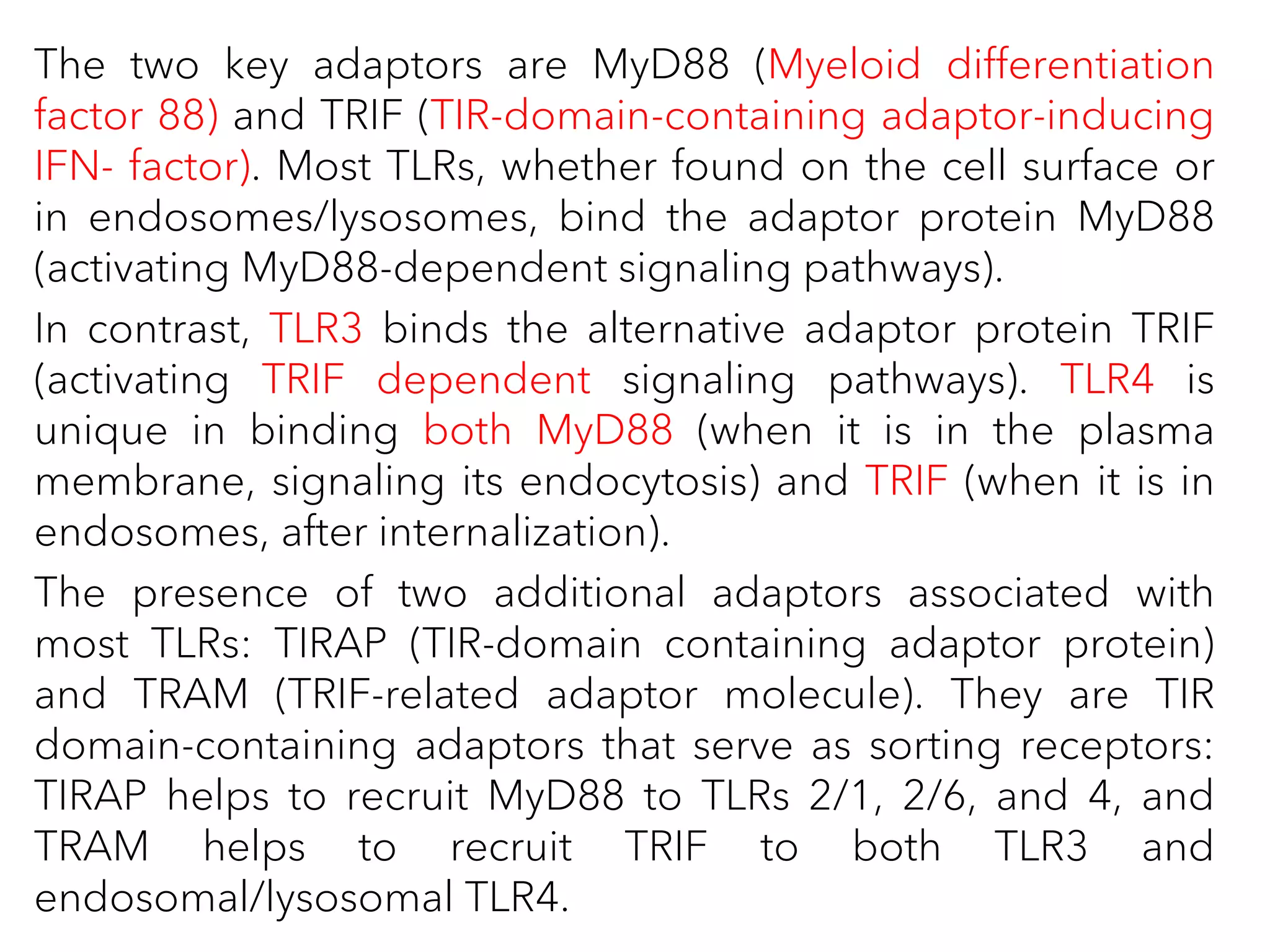
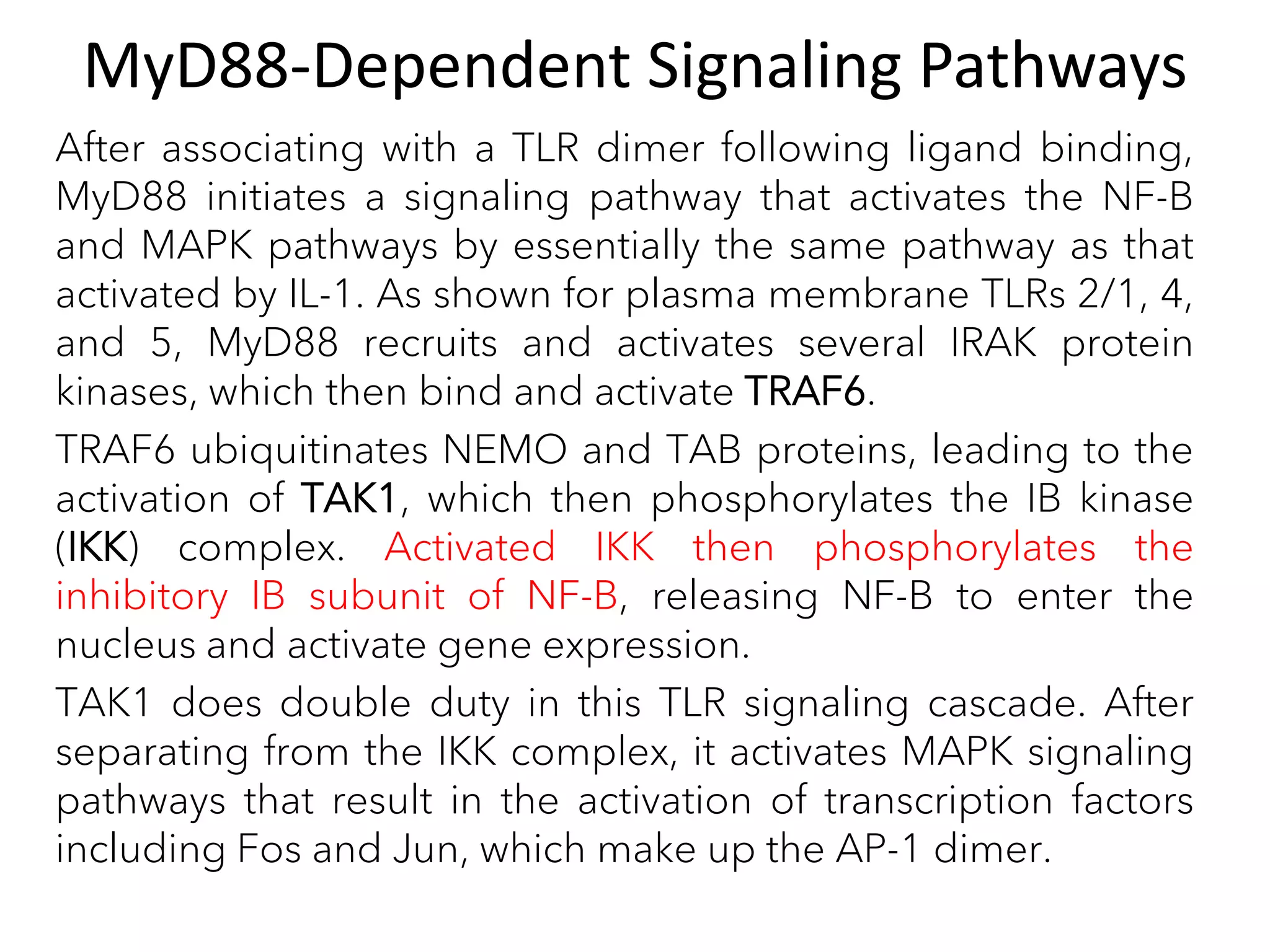
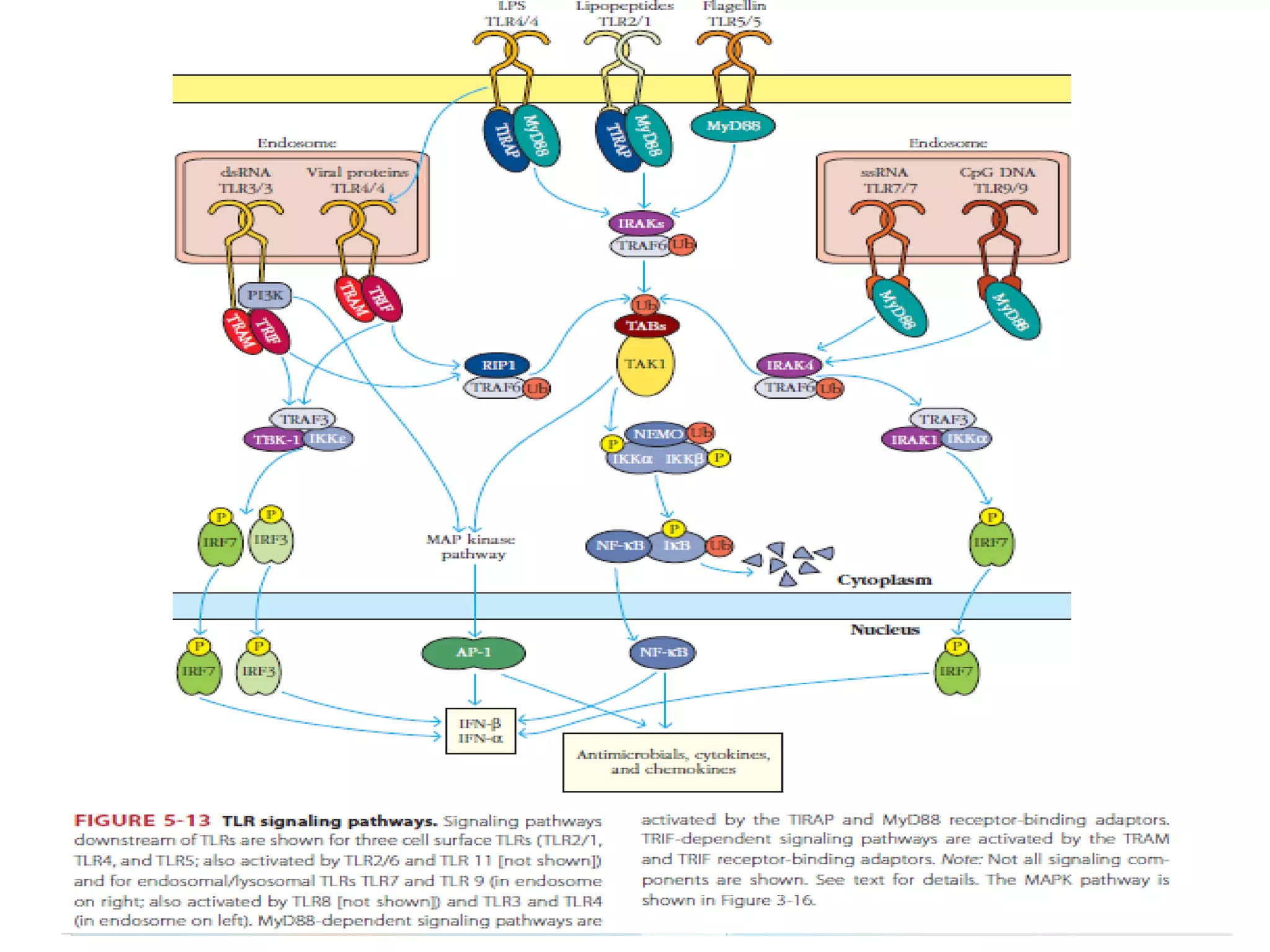
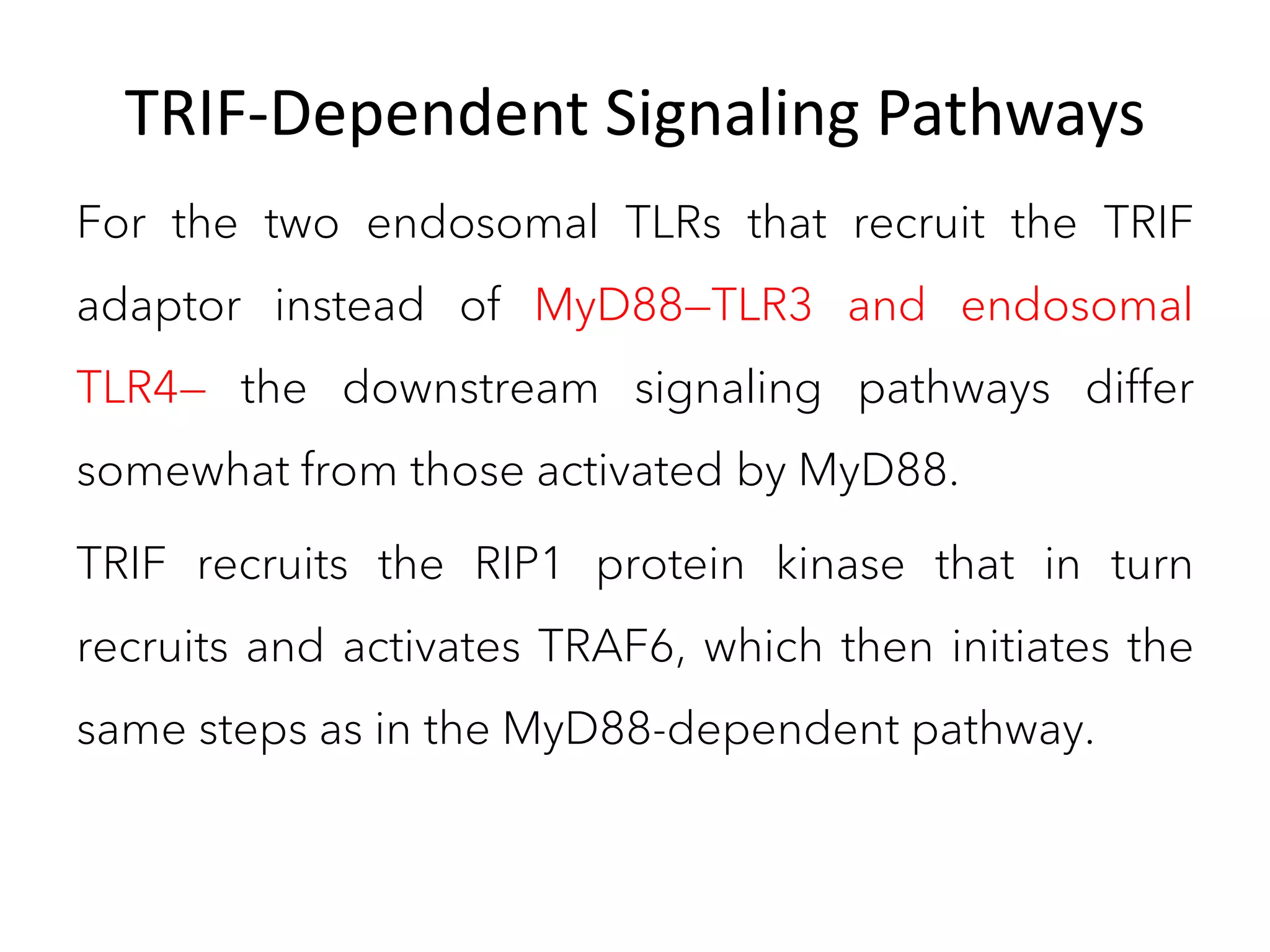
The document summarizes Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and their role in innate immunity. It discusses how TLRs were first discovered in invertebrates and then found to have vertebrate homologs. TLRs recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns and trigger signaling pathways that induce antimicrobial responses. There are 10 TLRs in humans that recognize distinct microbial ligands. TLR signaling involves adaptor proteins and transcription factors that activate genes encoding inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and interferons.