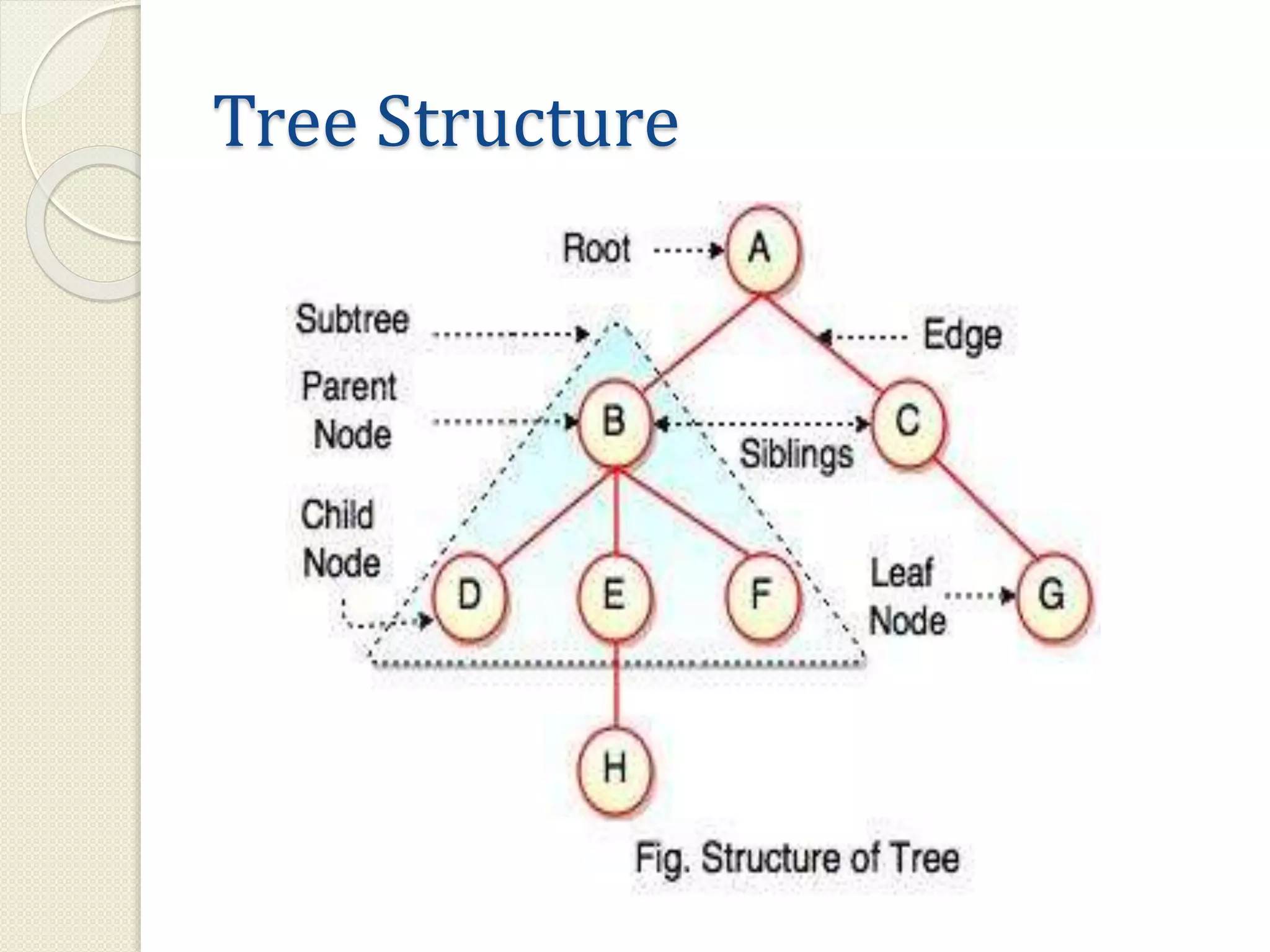
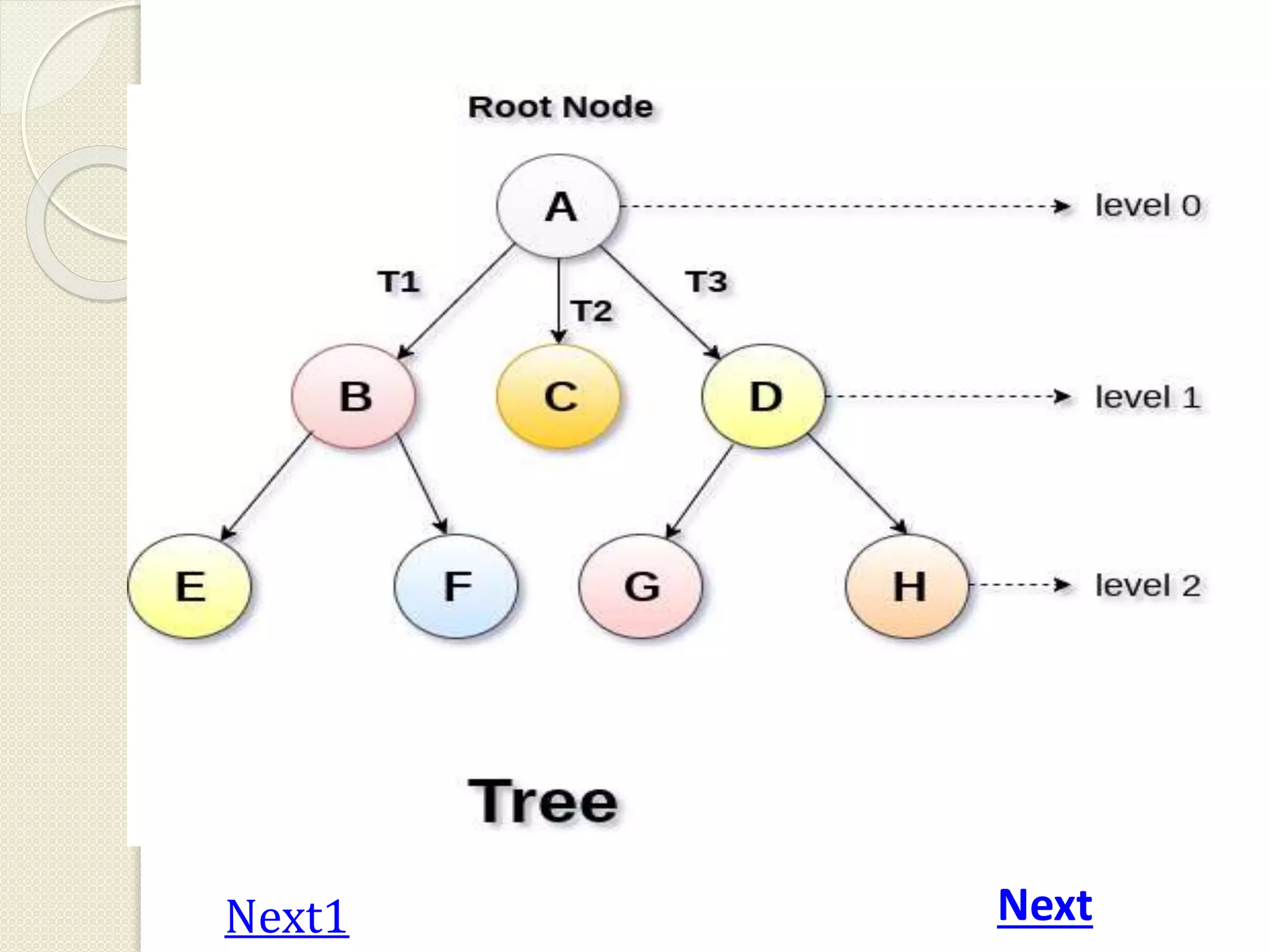
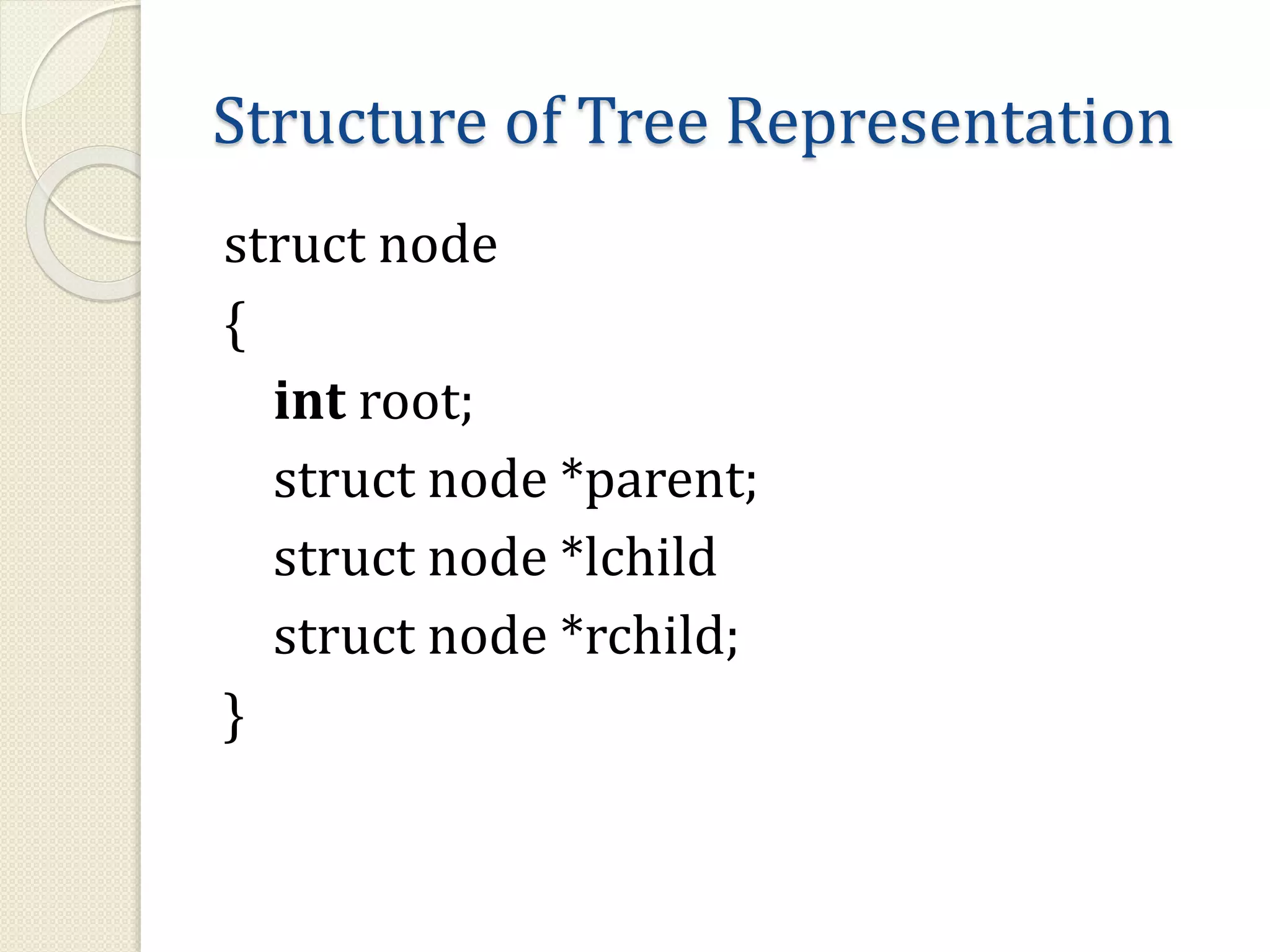
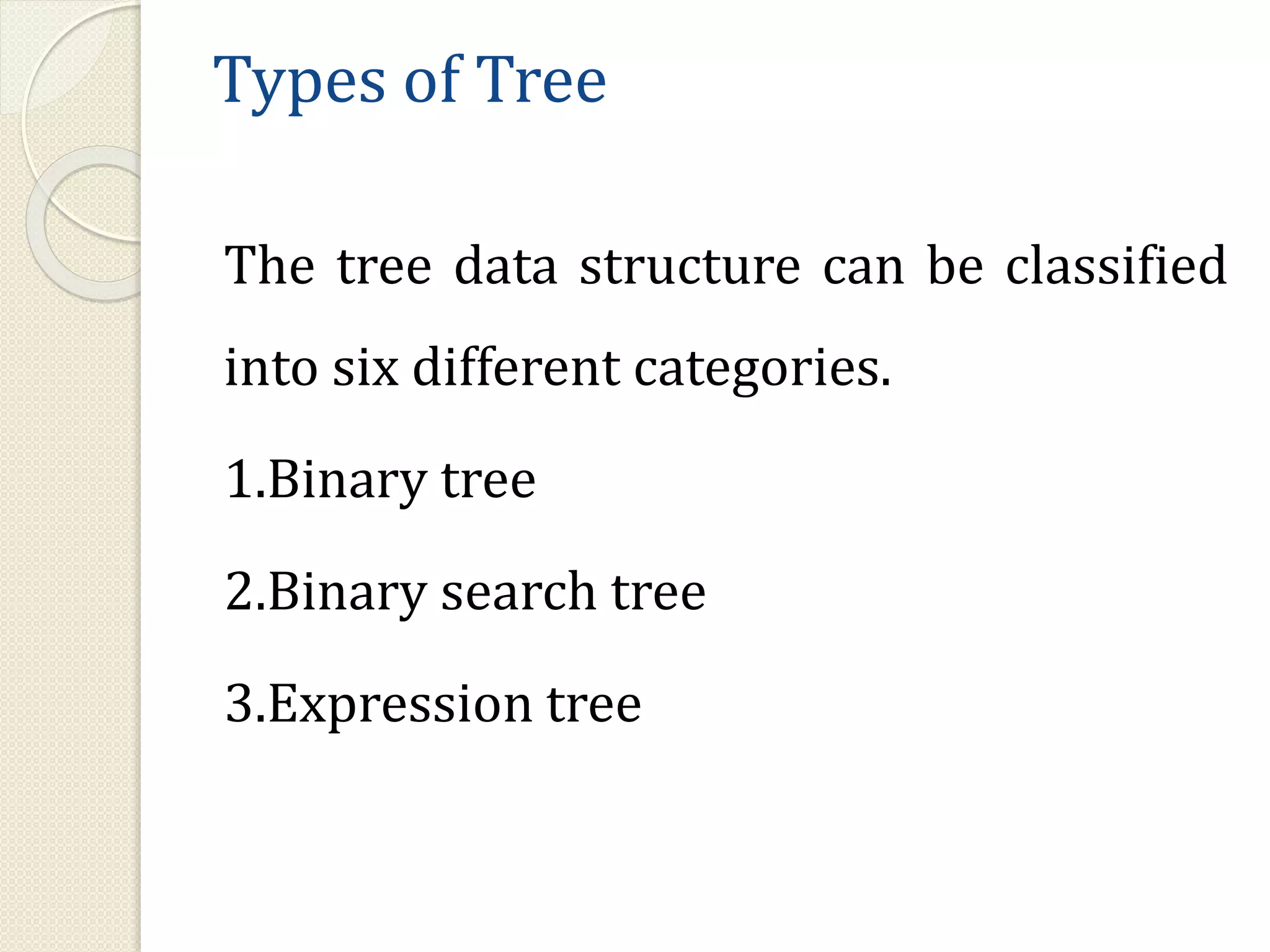
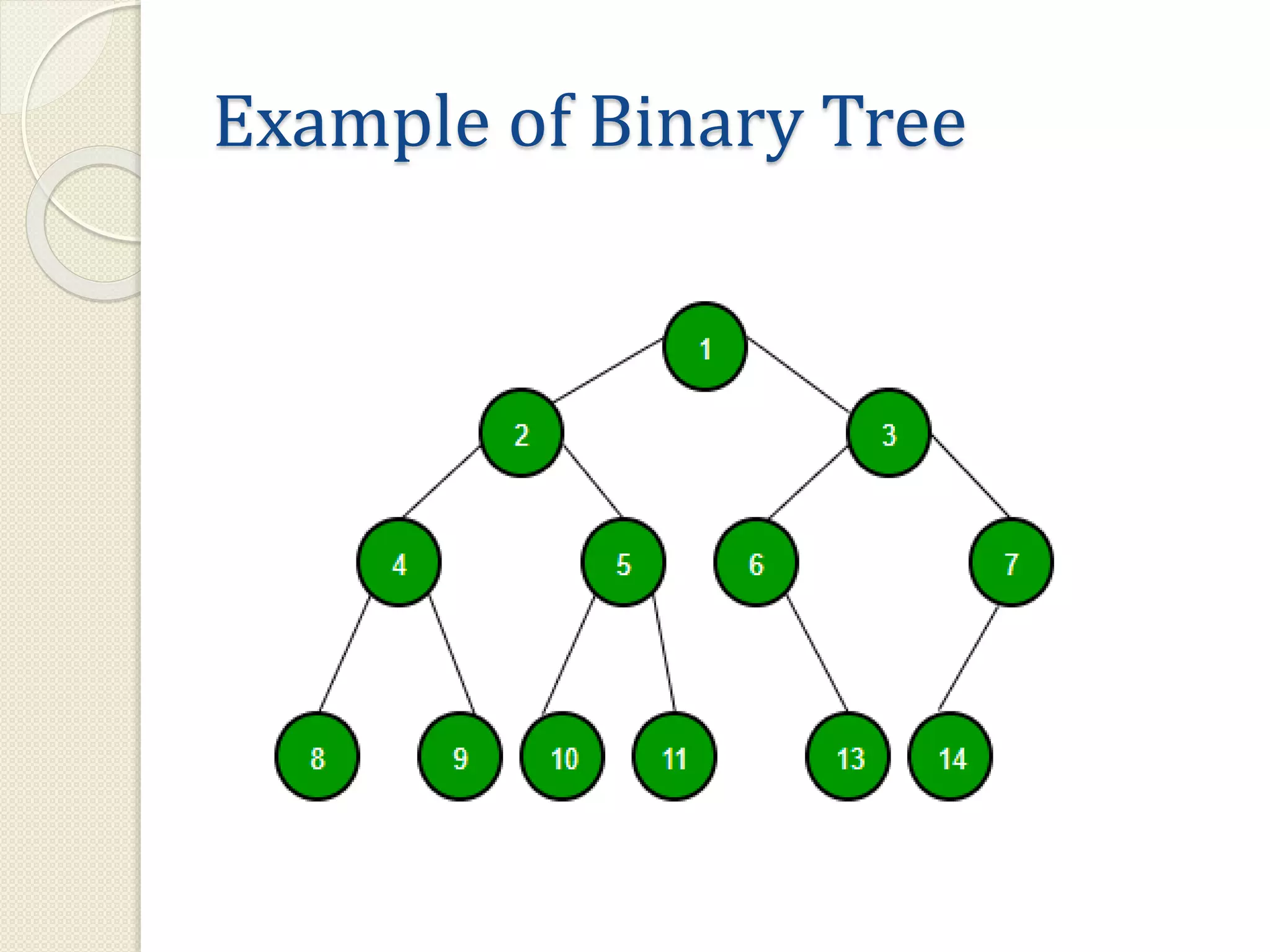
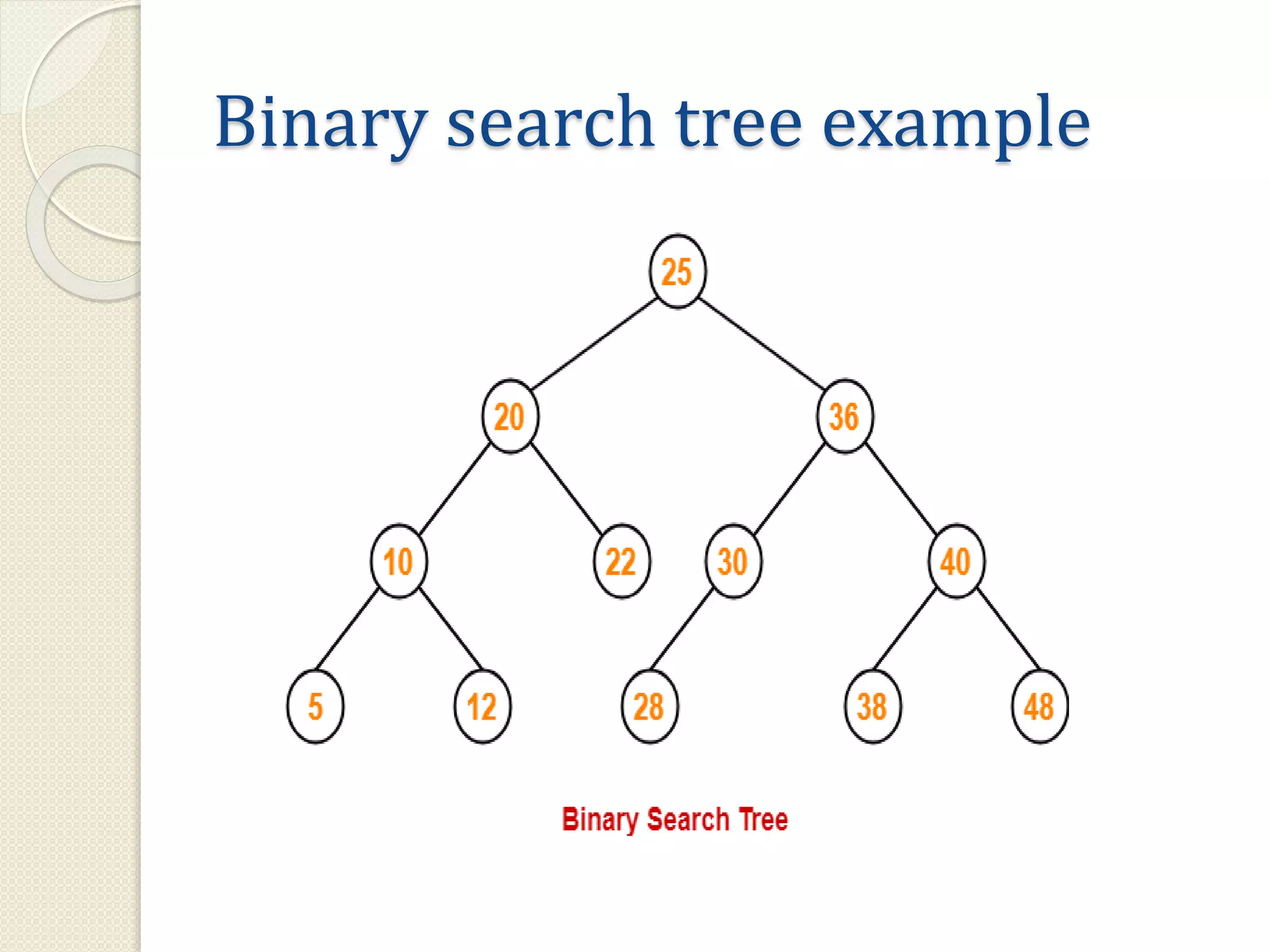
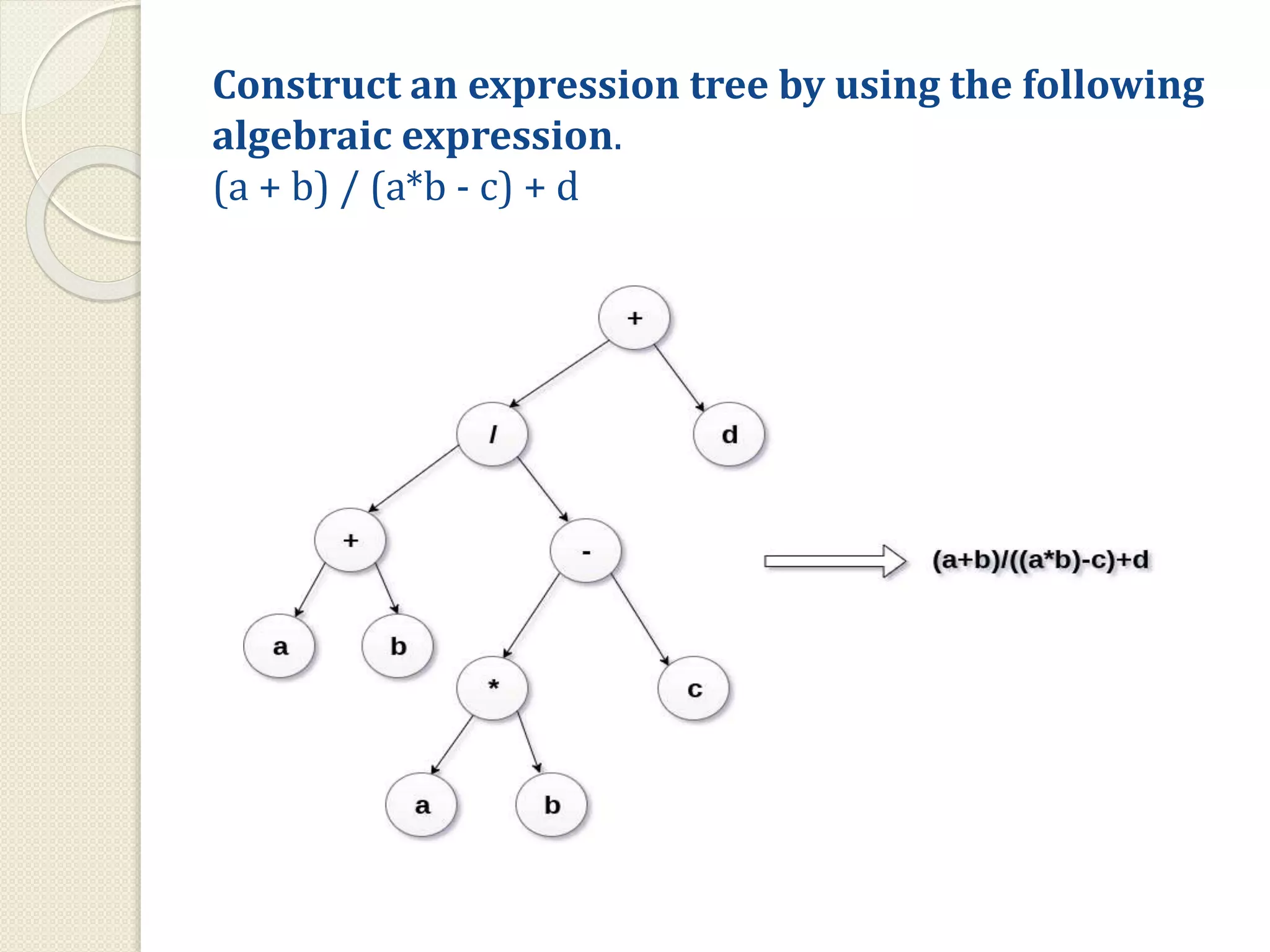
This document discusses trees as a non-linear data structure. It defines key tree terminology such as root node, leaf node, and describes different types of trees including binary trees, binary search trees, and expression trees. Binary trees can have at most two children per node and are used in applications like expression evaluation. Binary search trees store elements in sorted order with left subtrees containing smaller elements and right subtrees containing larger elements. Expression trees represent arithmetic expressions with operators as internal nodes and operands as leaf nodes.