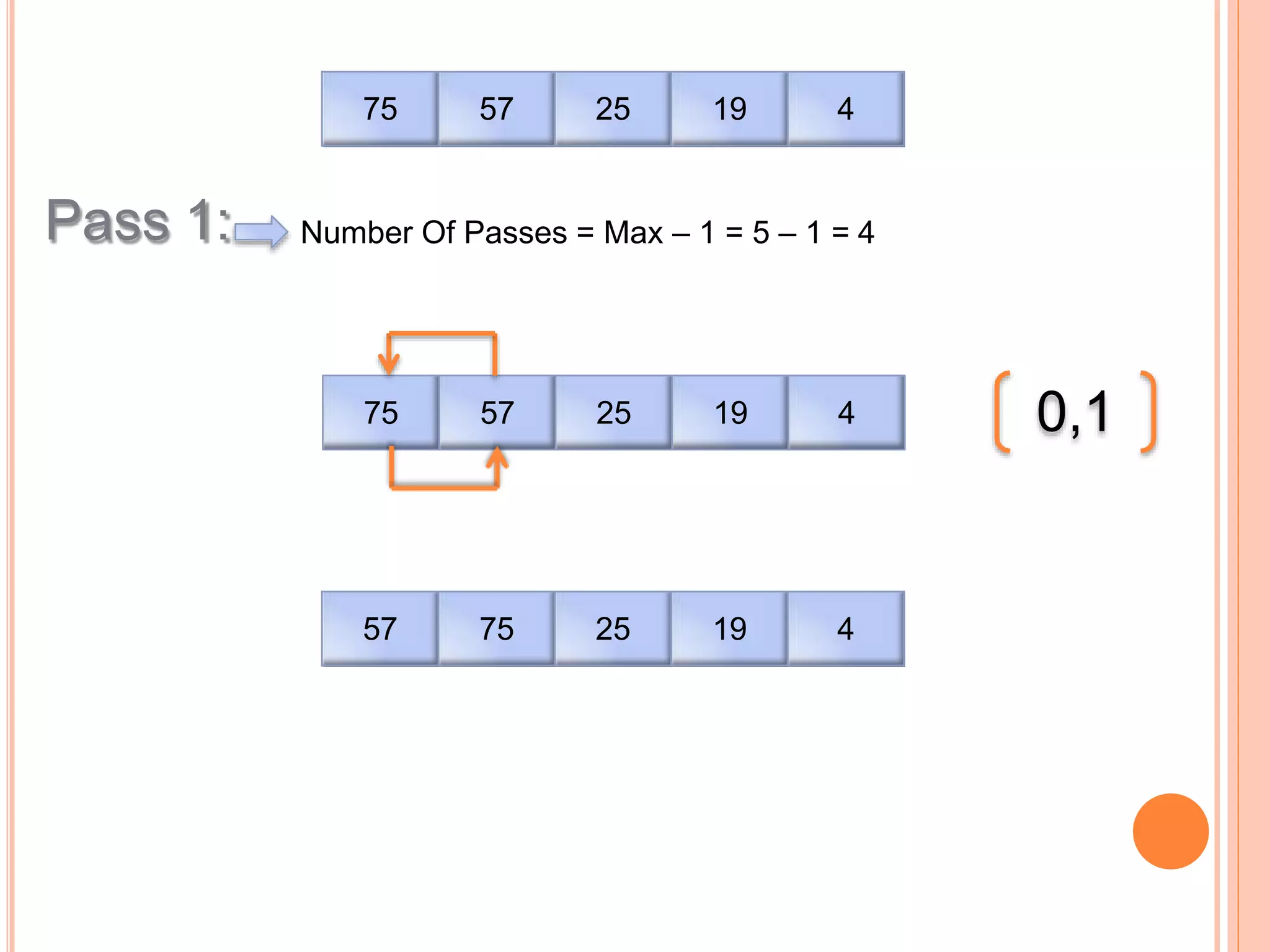
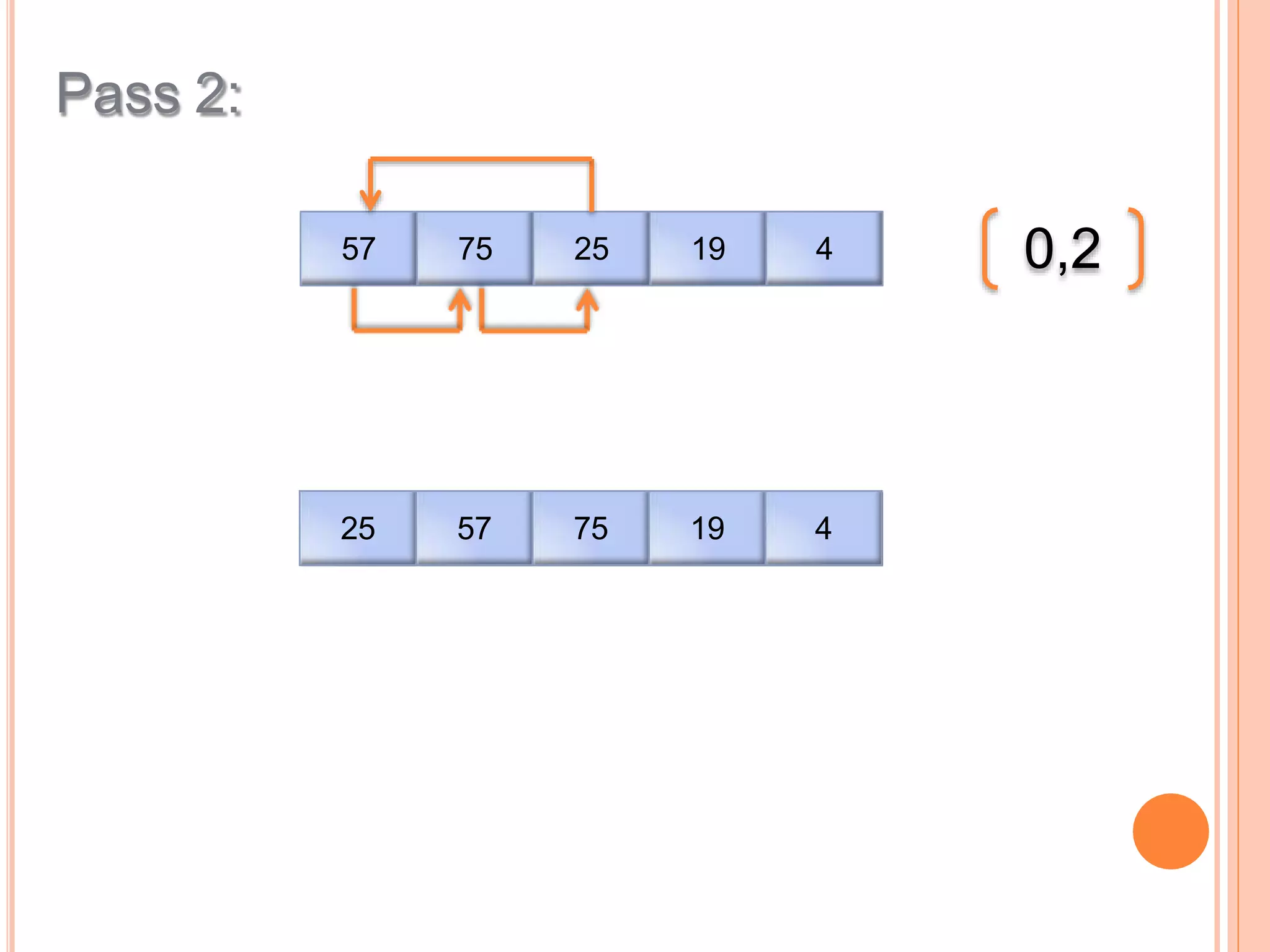
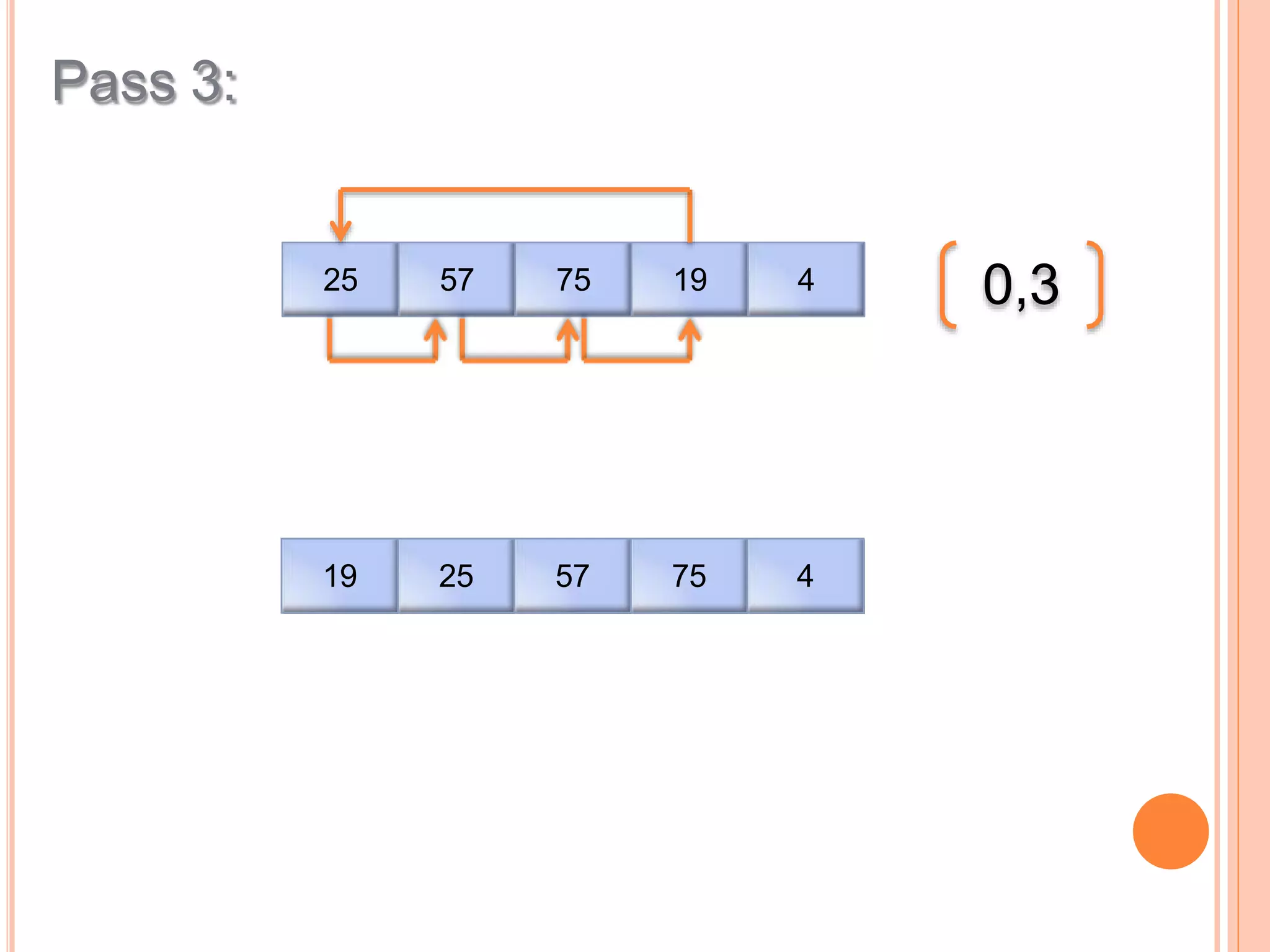
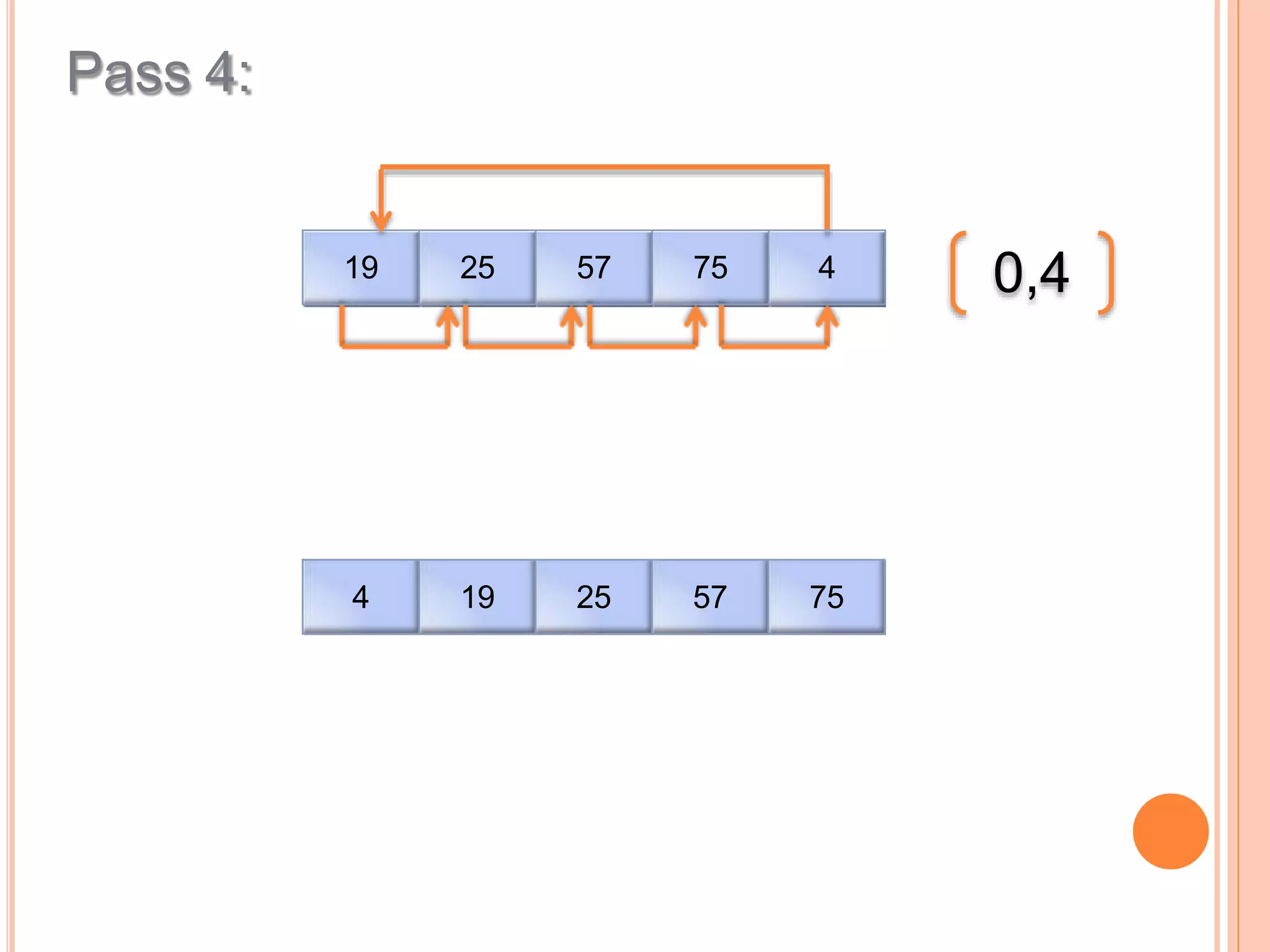
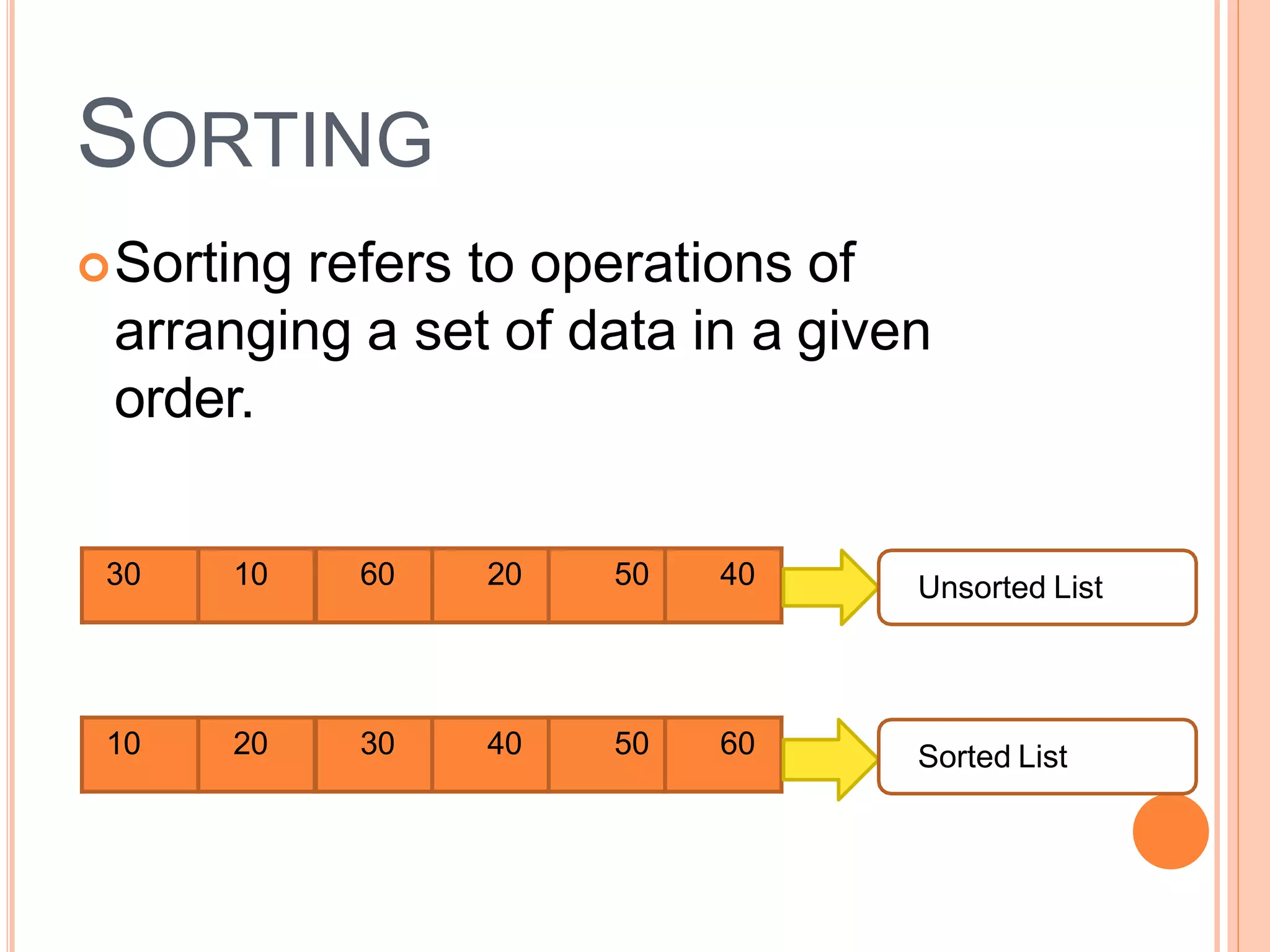
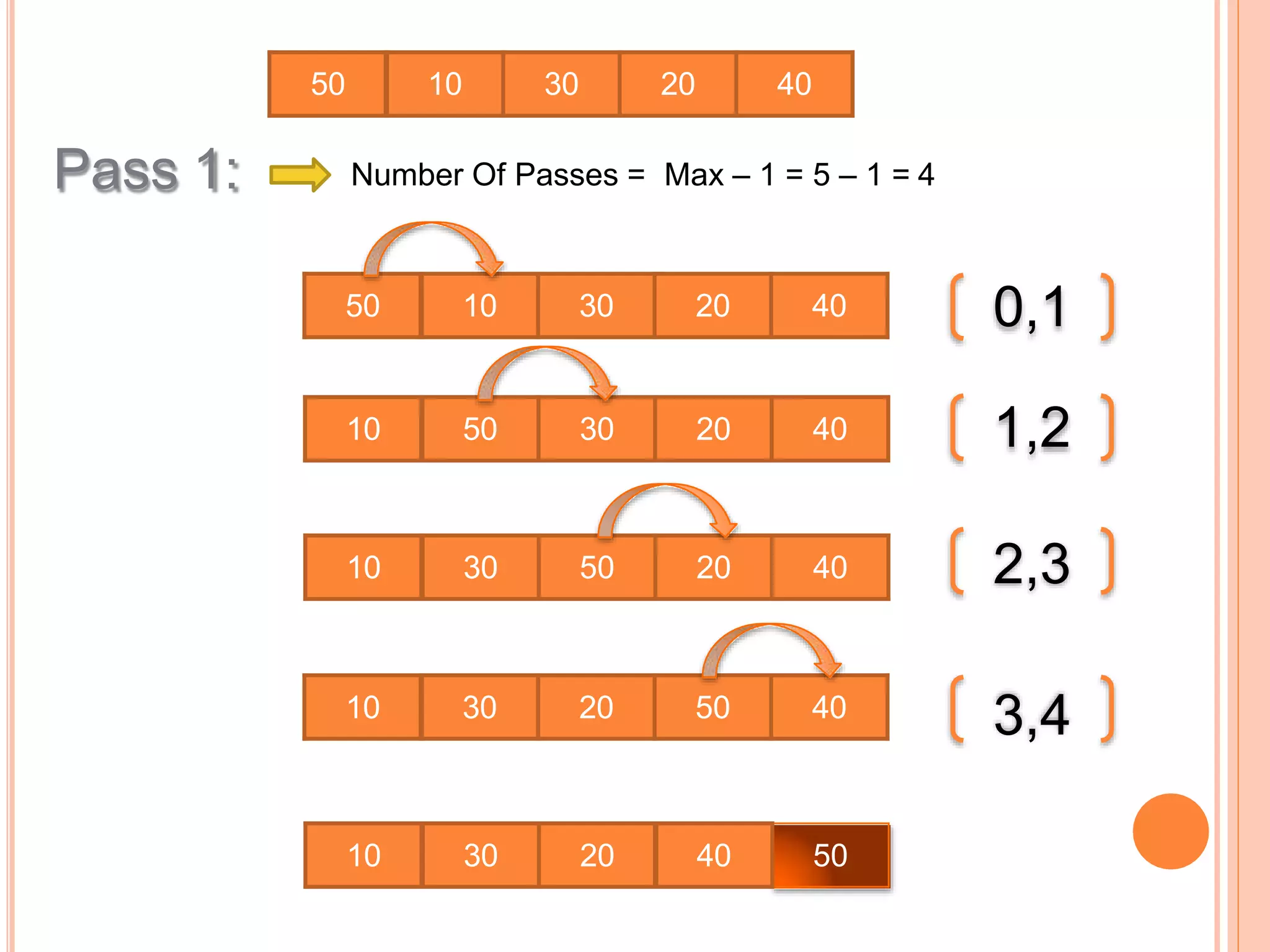
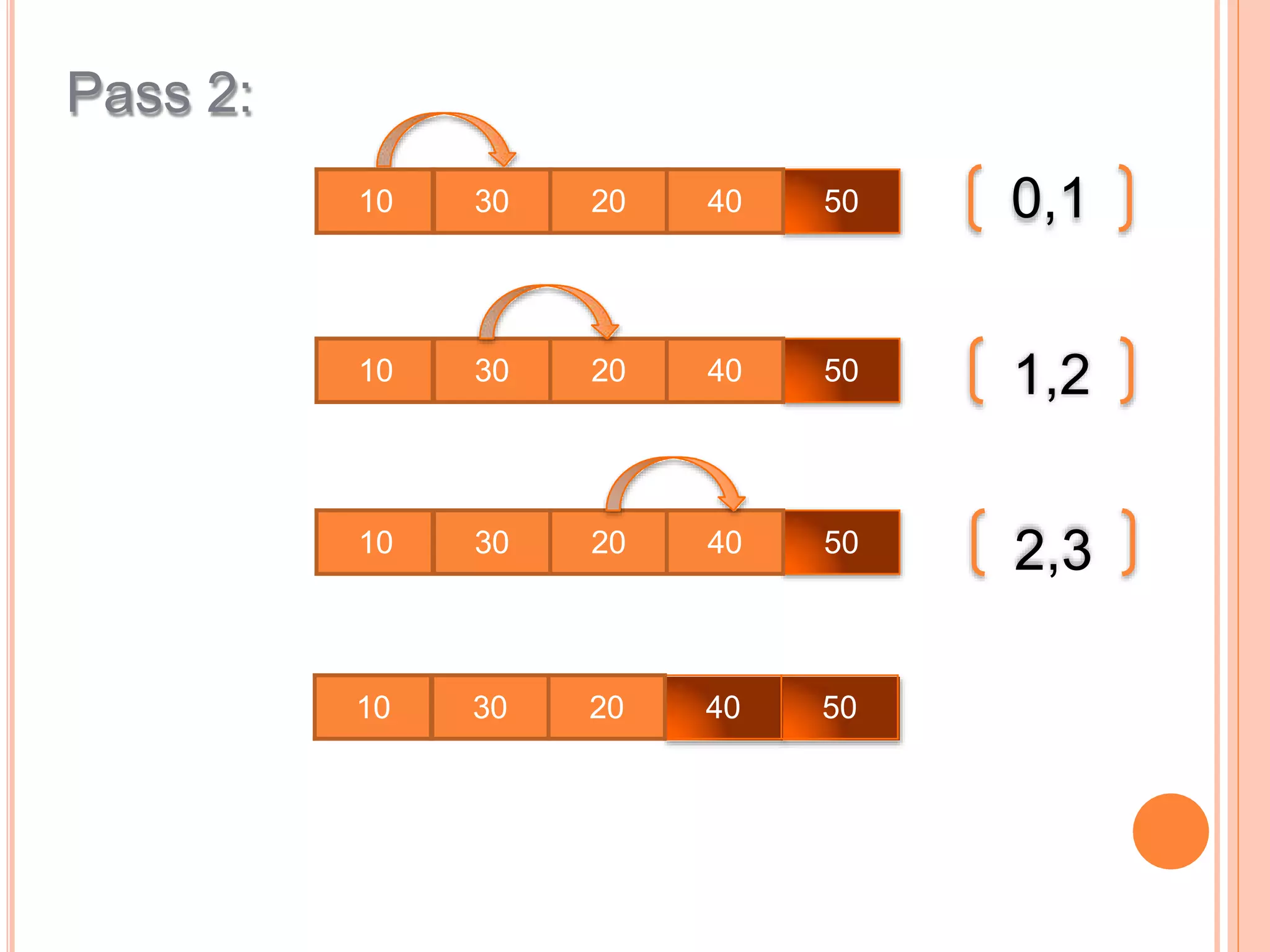
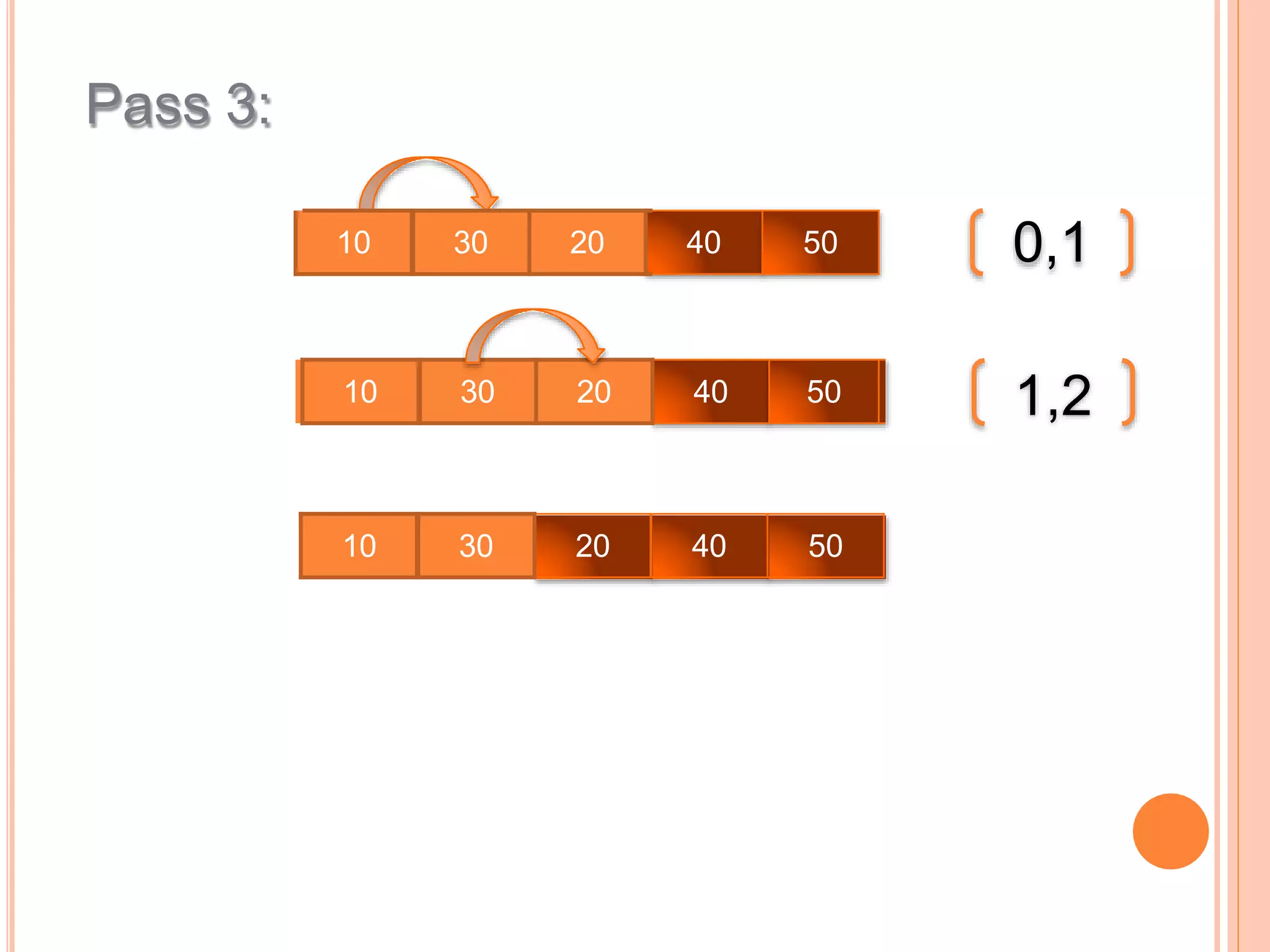
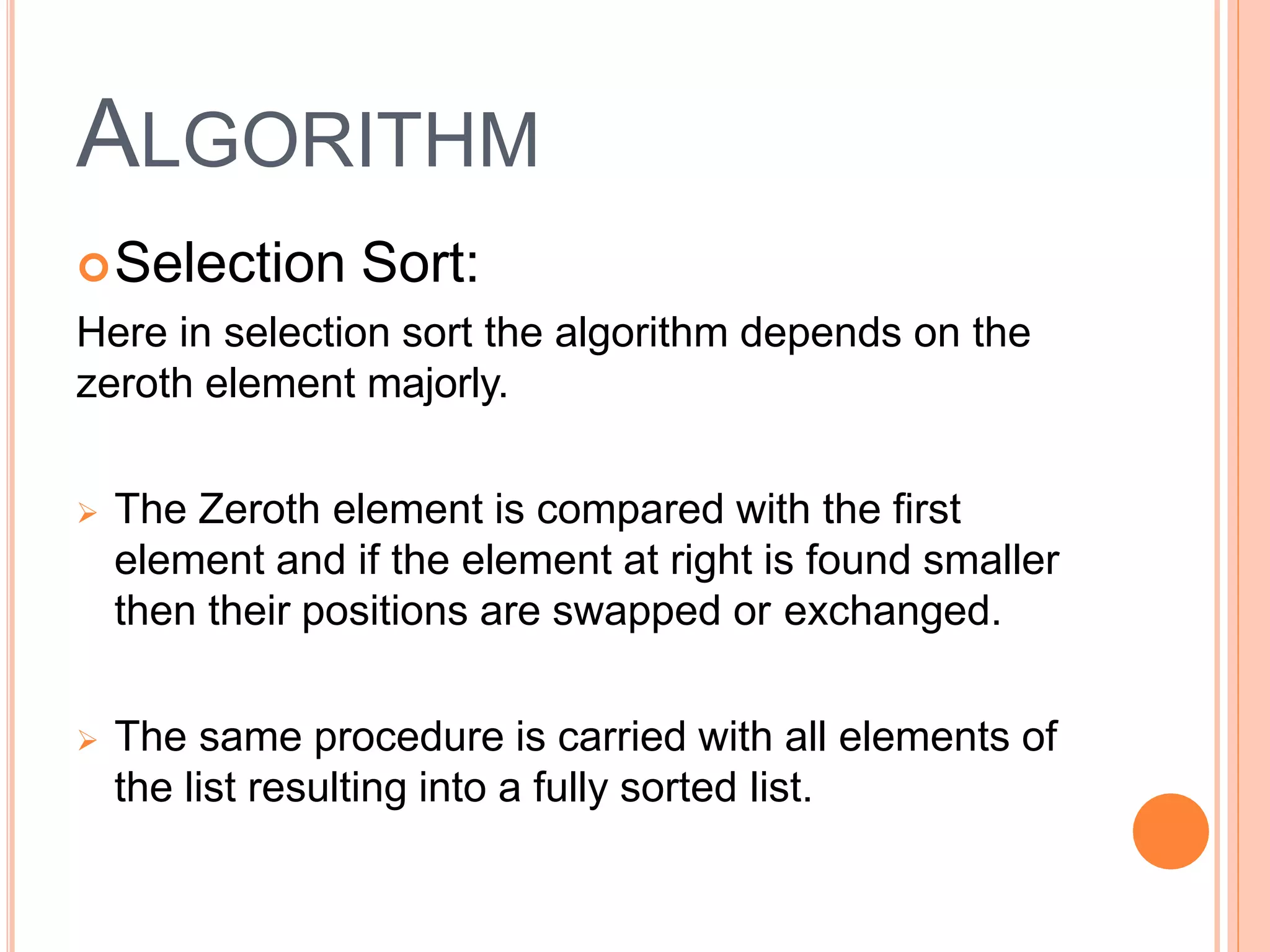
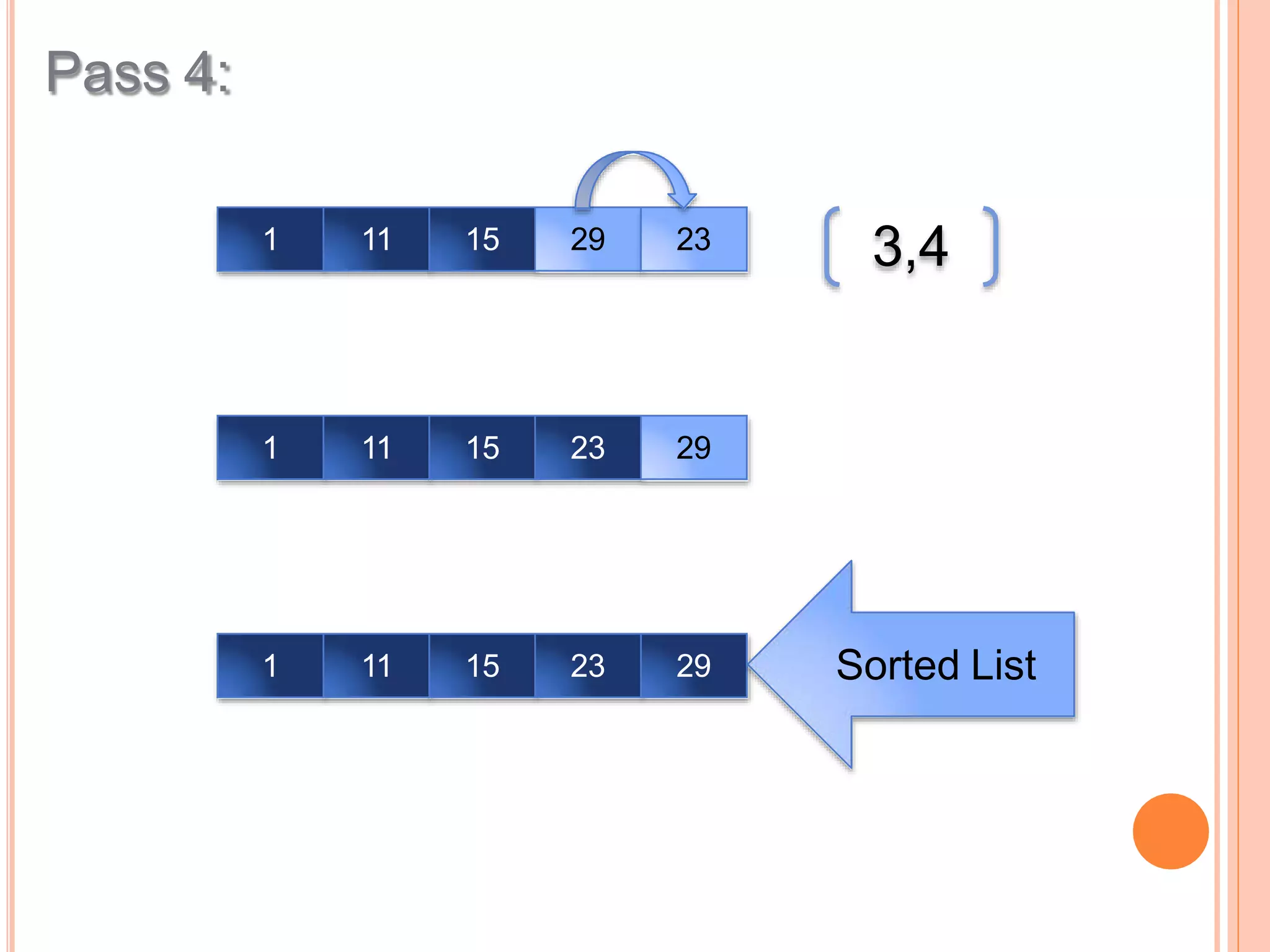
This document discusses different types of sorting algorithms. It describes internal sorting and external sorting, with internal sorting handling all data in memory and external sorting requiring external memory. Bubble sort, selection sort, and insertion sort are briefly explained as examples of sorting methods. Bubble sort works by comparing adjacent elements and swapping if out of order, selection sort finds the minimum element and selection sort inserts elements into the sorted position. Pseudocode and examples are provided for each algorithm.





![To sort numbers in ascending order using bubble sort
technique
import java.util.*;
public class bubbleSort{
public static void main(String a[]) throws Exception
{
int i,j,n;
int a[] = {50,10,30,20,40};
System.out.println("Values Before the sort:n");
for(i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
System.out.print( a[i]+" ");
System.out.println();
n=a.length;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bubbleinsertionselectionsort-200506172819/75/sorting-and-its-types-11-2048.jpg)
![for(i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < (n-i); j++)
{
if(a[j] > a[j+1]){
t = a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=t;
}
}
}
System.out.print("Values after the sort:n");
for(i = 0; i <a.length; i++)
System.out.print(a[i]+" ");
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bubbleinsertionselectionsort-200506172819/75/sorting-and-its-types-12-2048.jpg)


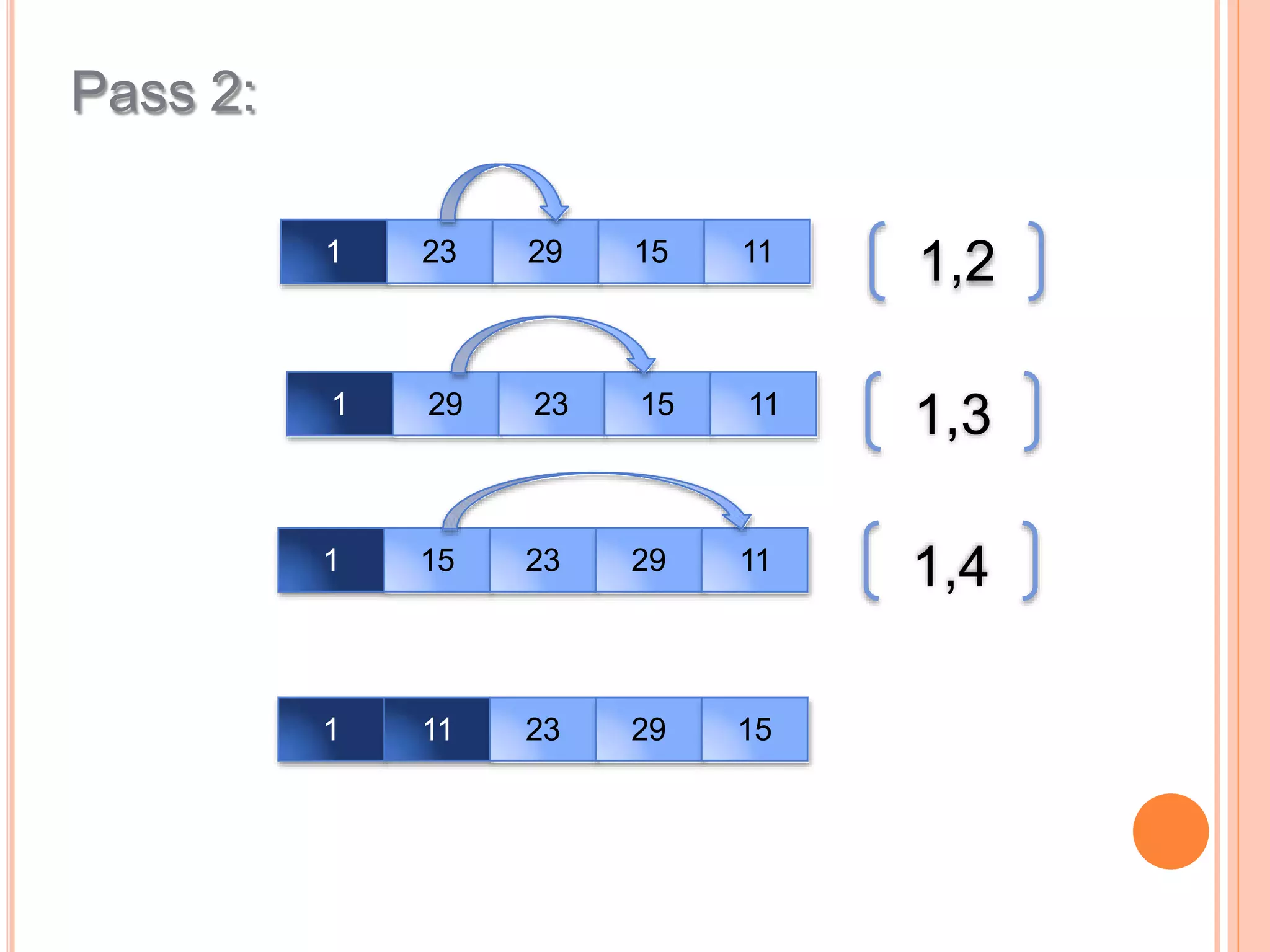
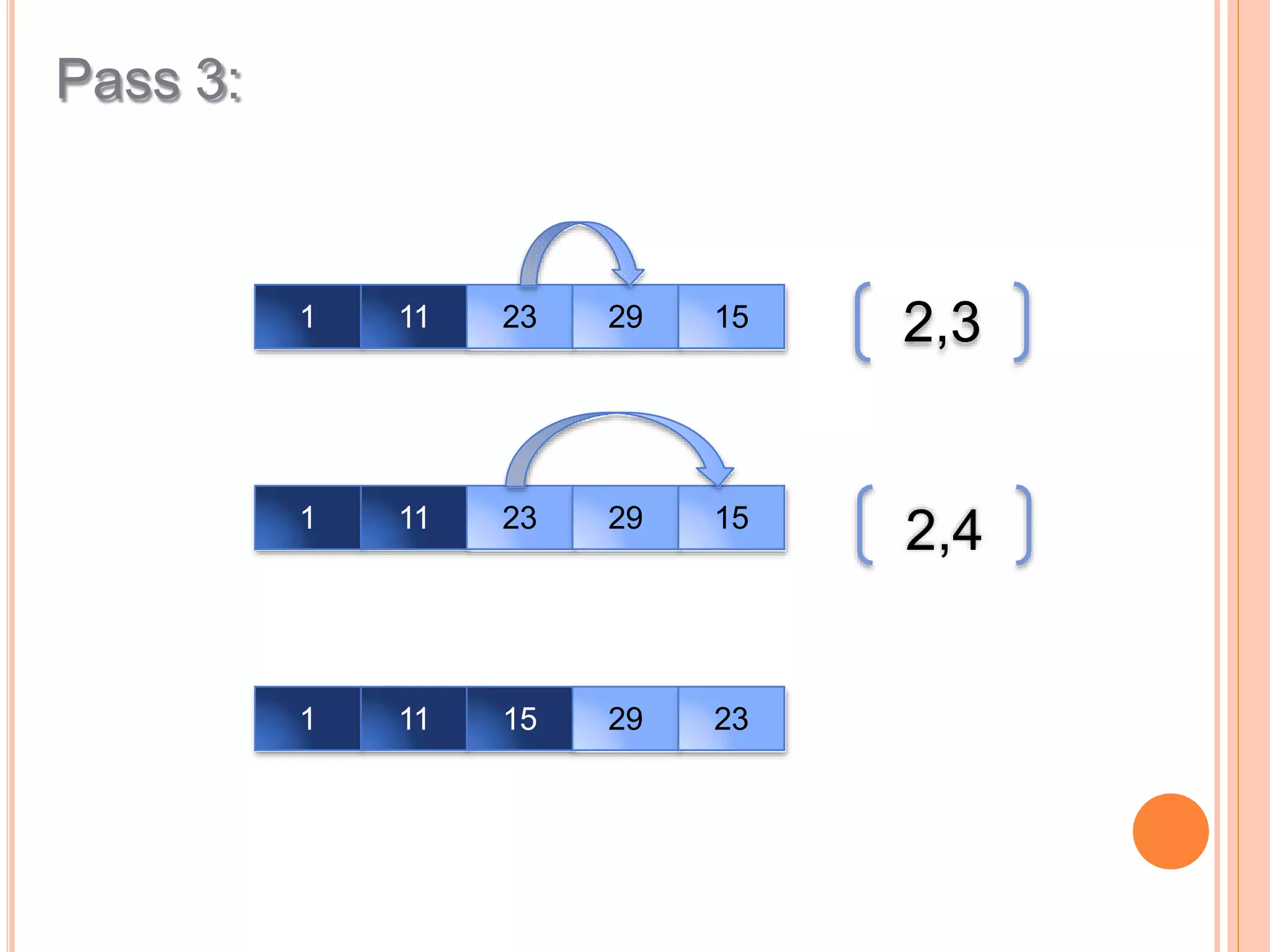
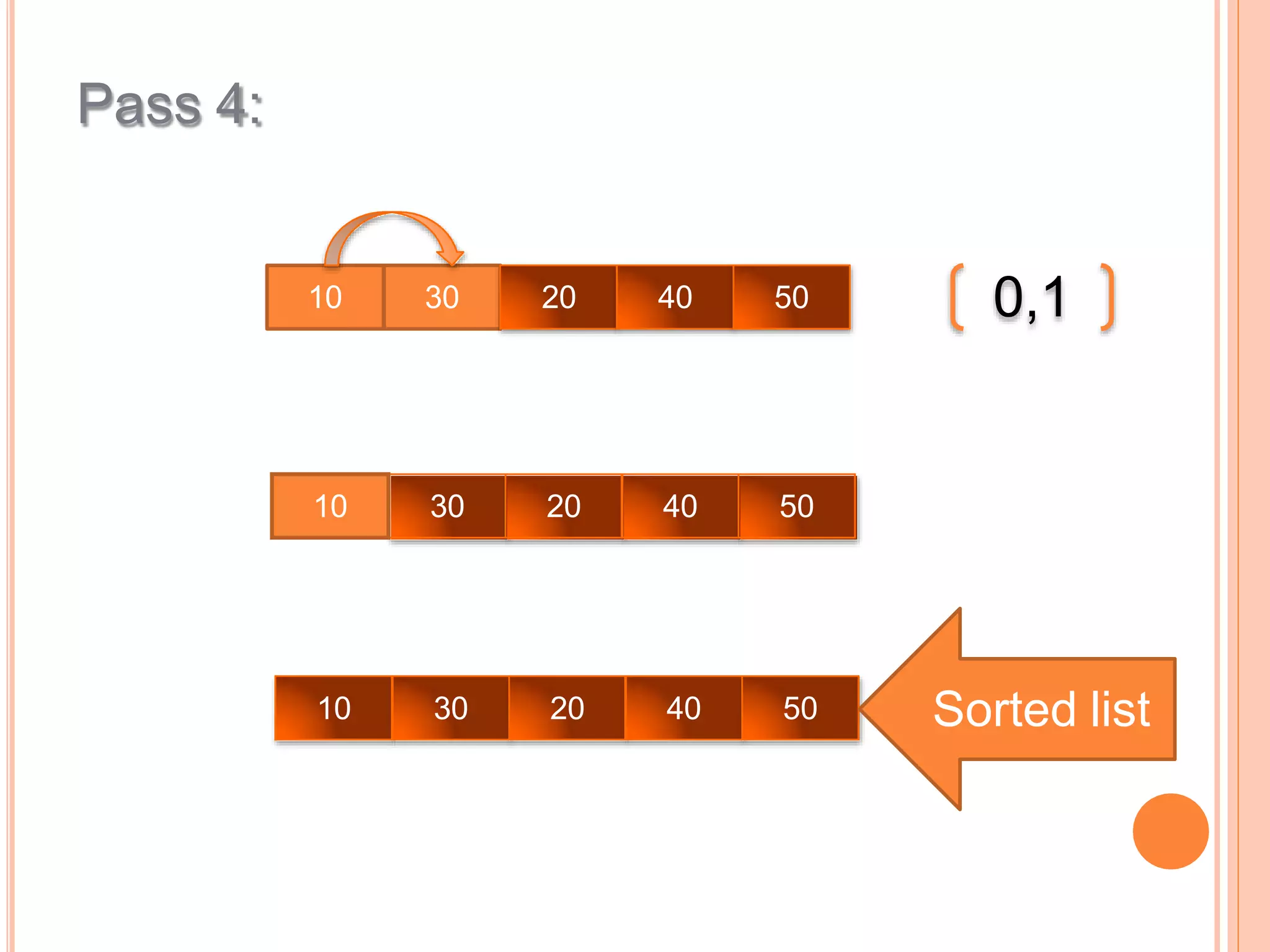
![To sort numbers in ascending order using selection
sort technique
import java.util.*;
public class selectionSort{
public static void main(String a[]) throws Exception
{
int i,j;
int a[] = {23,15,29,11,1};
System.out.println("Values Before the sort:n");
for(i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
System.out.print( a[i]+" ");
System.out.println();
n=a.length;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bubbleinsertionselectionsort-200506172819/75/sorting-and-its-types-19-2048.jpg)
![for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(j = i+1; j < n; j++)
{
if(a[i] > a[j]){
t = a[j];
a[j]=a[i];
a[i]=t;
}
}
}
System.out.print("Values after the sort:n");
for(i = 0; i <a.length; i++)
System.out.print(a[i]+" ");
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bubbleinsertionselectionsort-200506172819/75/sorting-and-its-types-20-2048.jpg)



![public insertionSort( int [] a r r )
{
f or ( i n t i = 1; i < arr.Length; ++i)
{
i n t temp = a r r [ i ] ;
i n t pos = i ;
}
arr[pos] = temp;
}
}
Select
while (arr[pos-1].CompareTo(temp) > 0 &&pos > 0)
{
Comparing
arr[pos] = arr[pos-1];
pos--;
Shift
Insert](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bubbleinsertionselectionsort-200506172819/75/sorting-and-its-types-24-2048.jpg)