Downloaded 81 times






![public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{ int i = 100;
long l = i; //no explicit type casting required
float f = l; //no explicit type casting required
System.out.println("Int value "+i);
System.out.println("Long value "+l);
System.out.println("Float value "+f);
}
}
Out put
Int value 100
Long value 100
Float value 100.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typecastinginjava-171205170636/75/Type-casting-in-java-7-2048.jpg)
![ public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{ double d = 100.04;
long l = (long)d; //explicit type casting required
int i = (int)l; //explicit type casting required
System.out.println("Double value "+d);
System.out.println("Long value "+l);
System.out.println("Int value "+i);
}
}
Output
Double value 100.04
Long value 100
Int value 100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typecastinginjava-171205170636/75/Type-casting-in-java-9-2048.jpg)

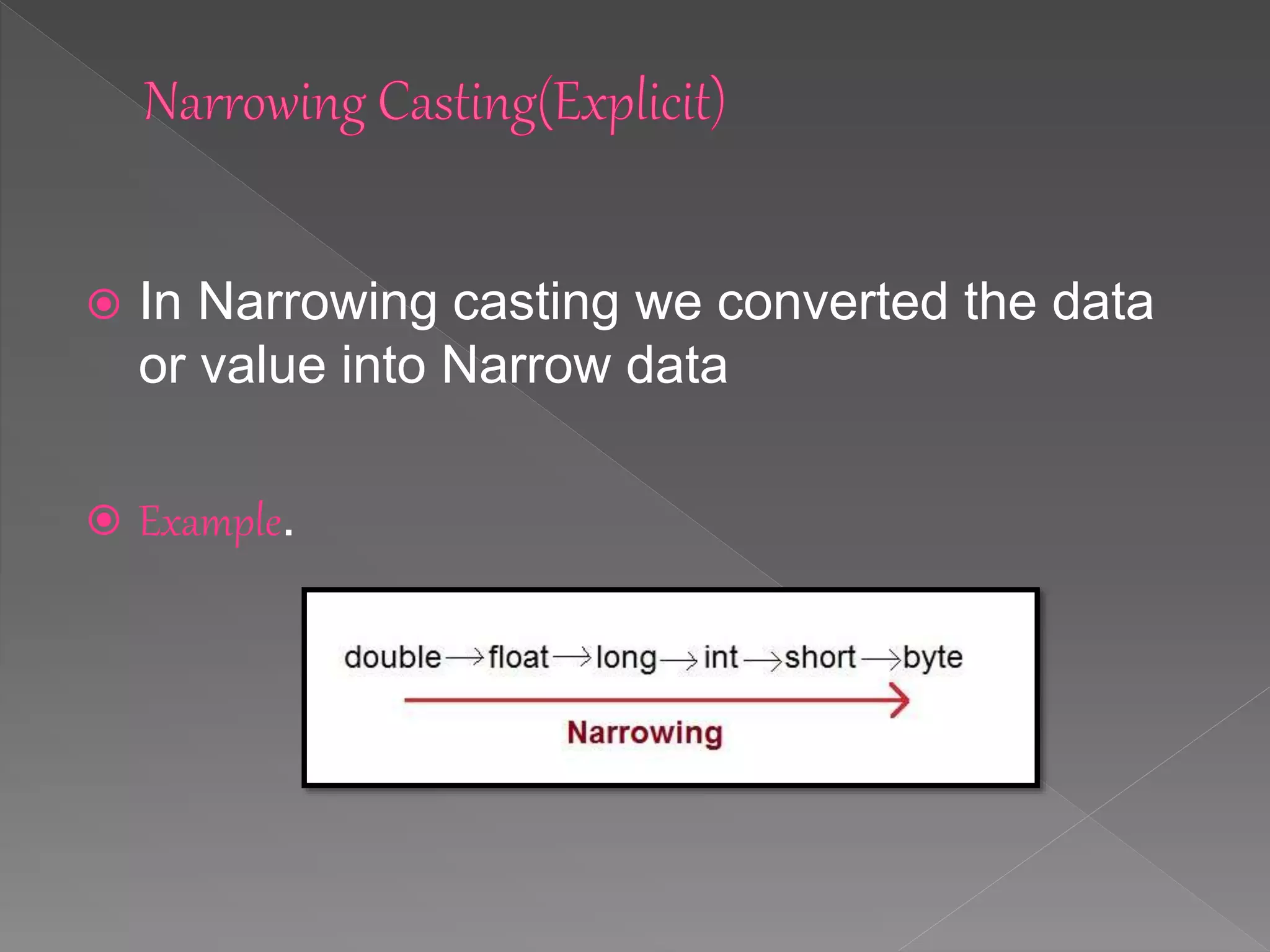
Type casting involves assigning a value of one data type to a variable of another type. There are two types of casting: widening (implicit) and narrowing (explicit). Widening casting converts data to a broader type without needing explicit casting, like converting an int to a long. Narrowing casting converts to a narrower data type and requires explicit casting, such as converting a double to a long.






![public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{ int i = 100;
long l = i; //no explicit type casting required
float f = l; //no explicit type casting required
System.out.println("Int value "+i);
System.out.println("Long value "+l);
System.out.println("Float value "+f);
}
}
Out put
Int value 100
Long value 100
Float value 100.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typecastinginjava-171205170636/75/Type-casting-in-java-7-2048.jpg)

![ public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{ double d = 100.04;
long l = (long)d; //explicit type casting required
int i = (int)l; //explicit type casting required
System.out.println("Double value "+d);
System.out.println("Long value "+l);
System.out.println("Int value "+i);
}
}
Output
Double value 100.04
Long value 100
Int value 100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typecastinginjava-171205170636/75/Type-casting-in-java-9-2048.jpg)
