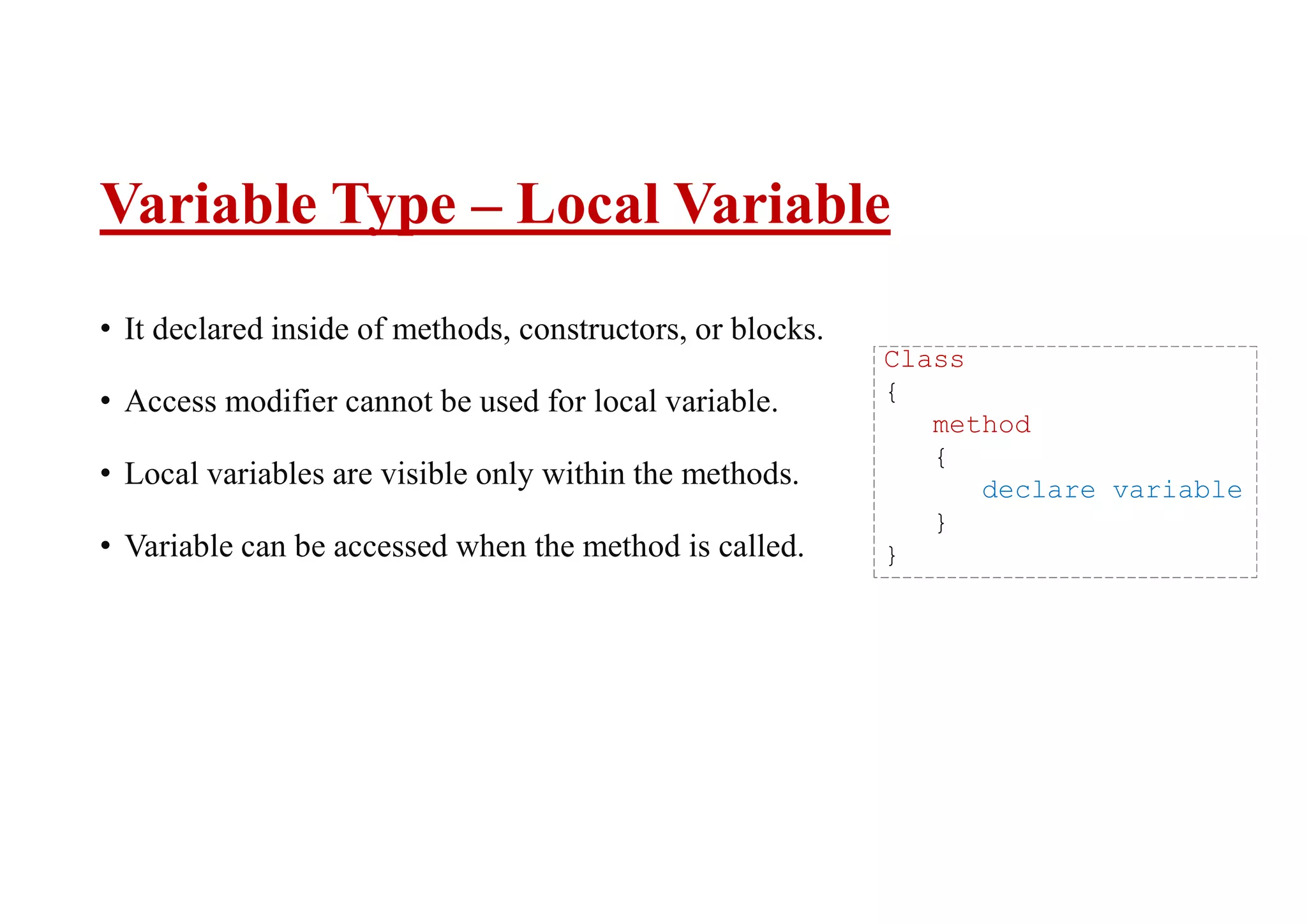
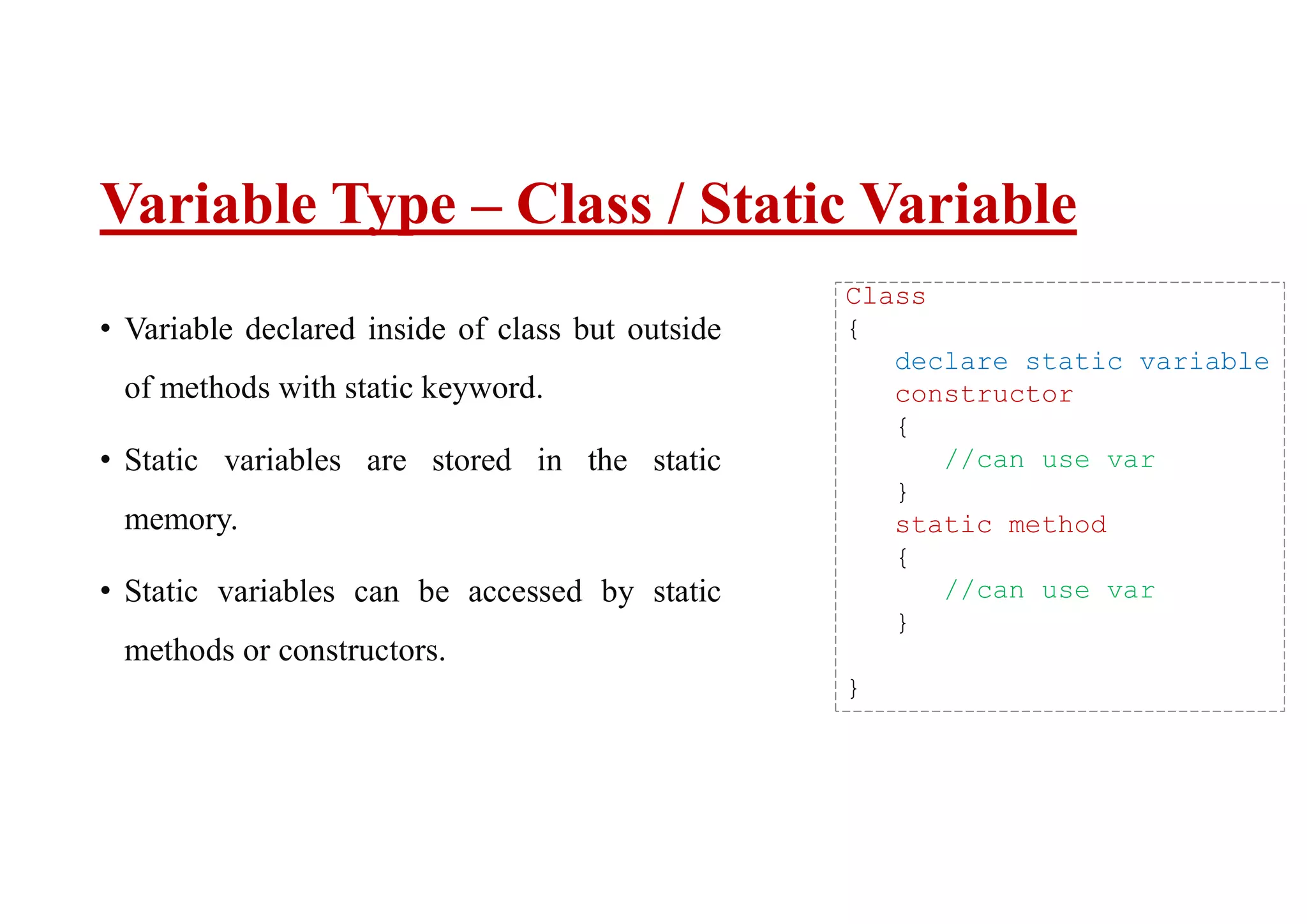
There are three types of variables in Java: local, instance, and class/static variables. Local variables are declared within methods and can only be accessed within that method. Instance variables are declared within a class but outside of methods, and can be accessed by any non-static method of that class. Class/static variables are also declared within a class but with the static keyword, and can be accessed from both static and non-static contexts.



![Variable Type – Local Variable
public class Dog
{
public void dogAge()
{
int age = 0;
age = age + 7;
System.out.println(“Dog age is : “ + age);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.pupAge();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javavariabletypes-191130054304/75/Java-variable-types-6-2048.jpg)

![Variable Type – Instance Variable
public class Dog {
int age;
public void Dog(int i) {
age = i;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println(“Dog age is : “ + age);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Dog dog = new Dog(30);
dog.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javavariabletypes-191130054304/75/Java-variable-types-8-2048.jpg)
![Variable Type – Class / Static Variable
public class Dog {
static int age;
public void Dog(int i) {
age = i;
System.out.println(age); //30
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Dog dog = new Dog(30);
dog.display();
age= 40;
System.out.println(age); //40
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javavariabletypes-191130054304/75/Java-variable-types-10-2048.jpg)