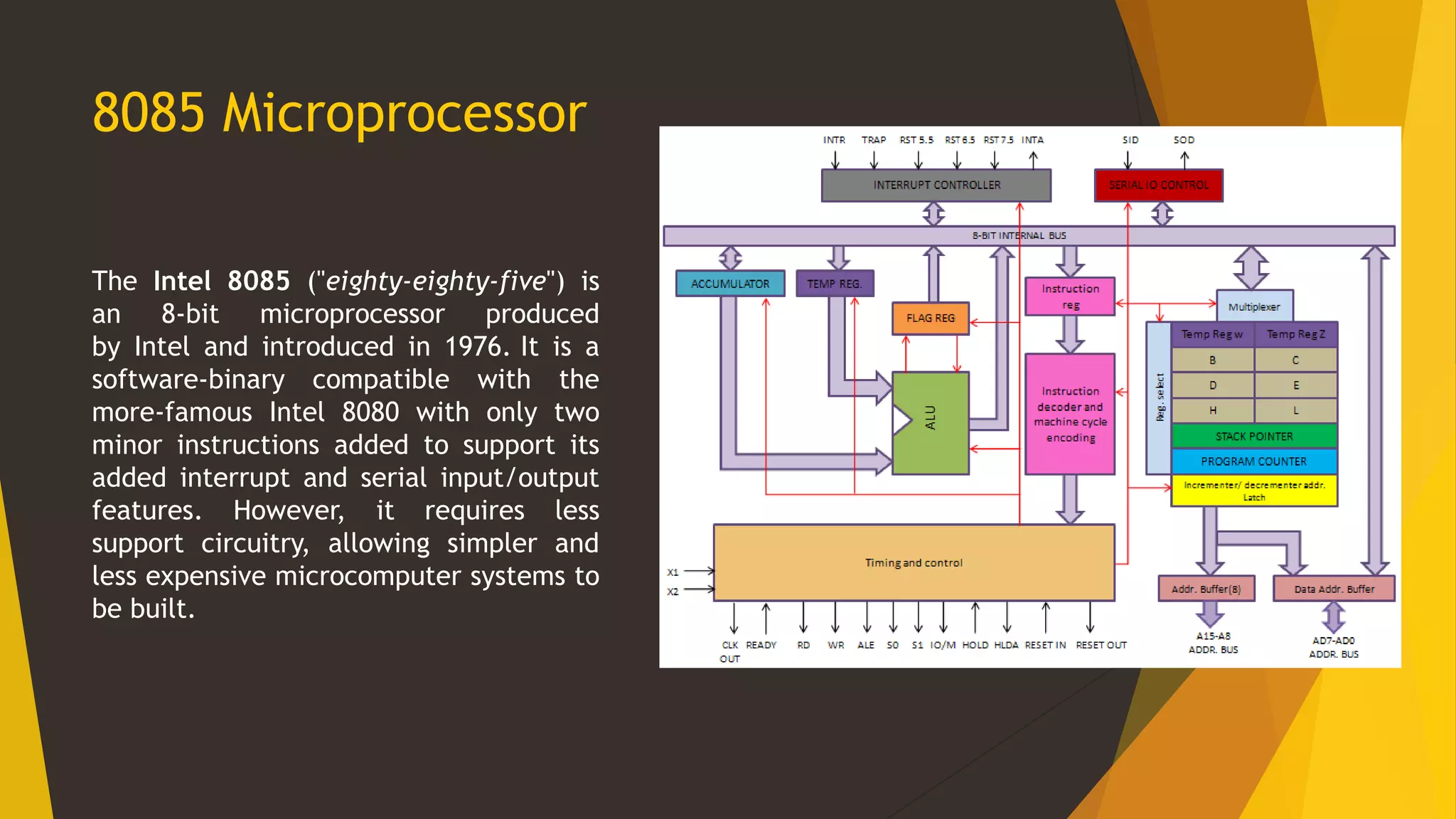
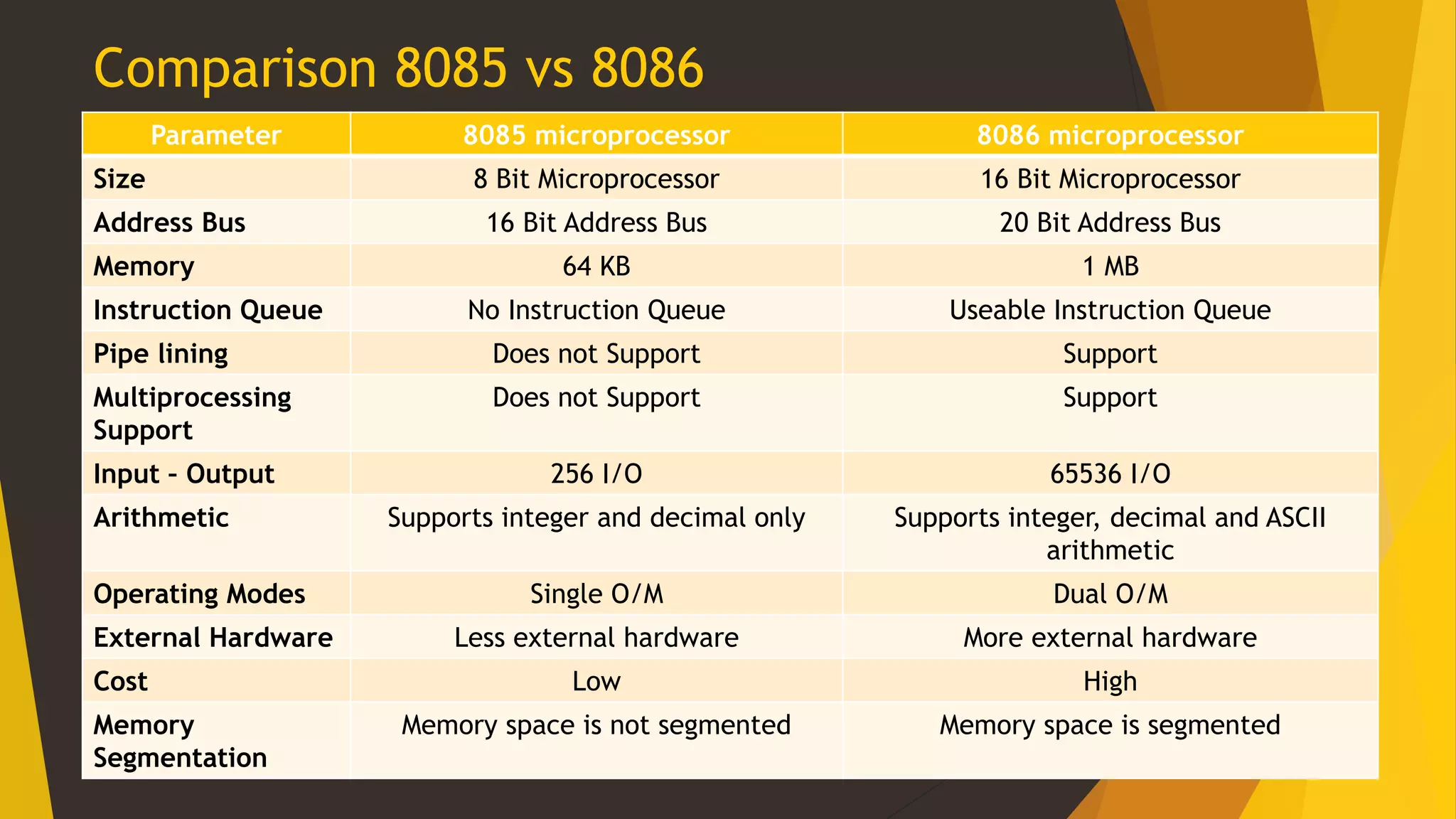
The 8085 microprocessor is an 8-bit microprocessor introduced in 1976 that requires less support circuitry than the Intel 8080, allowing for simpler and cheaper computer systems. The 8086 microprocessor is a 16-bit microprocessor released in 1978 that gave rise to the x86 architecture and was used in early IBM PCs. Key differences are that the 8085 is 8-bit with a 16-bit address bus and 64KB memory while the 8086 is 16-bit with a 20-bit address bus and 1MB memory, and requires more external hardware.