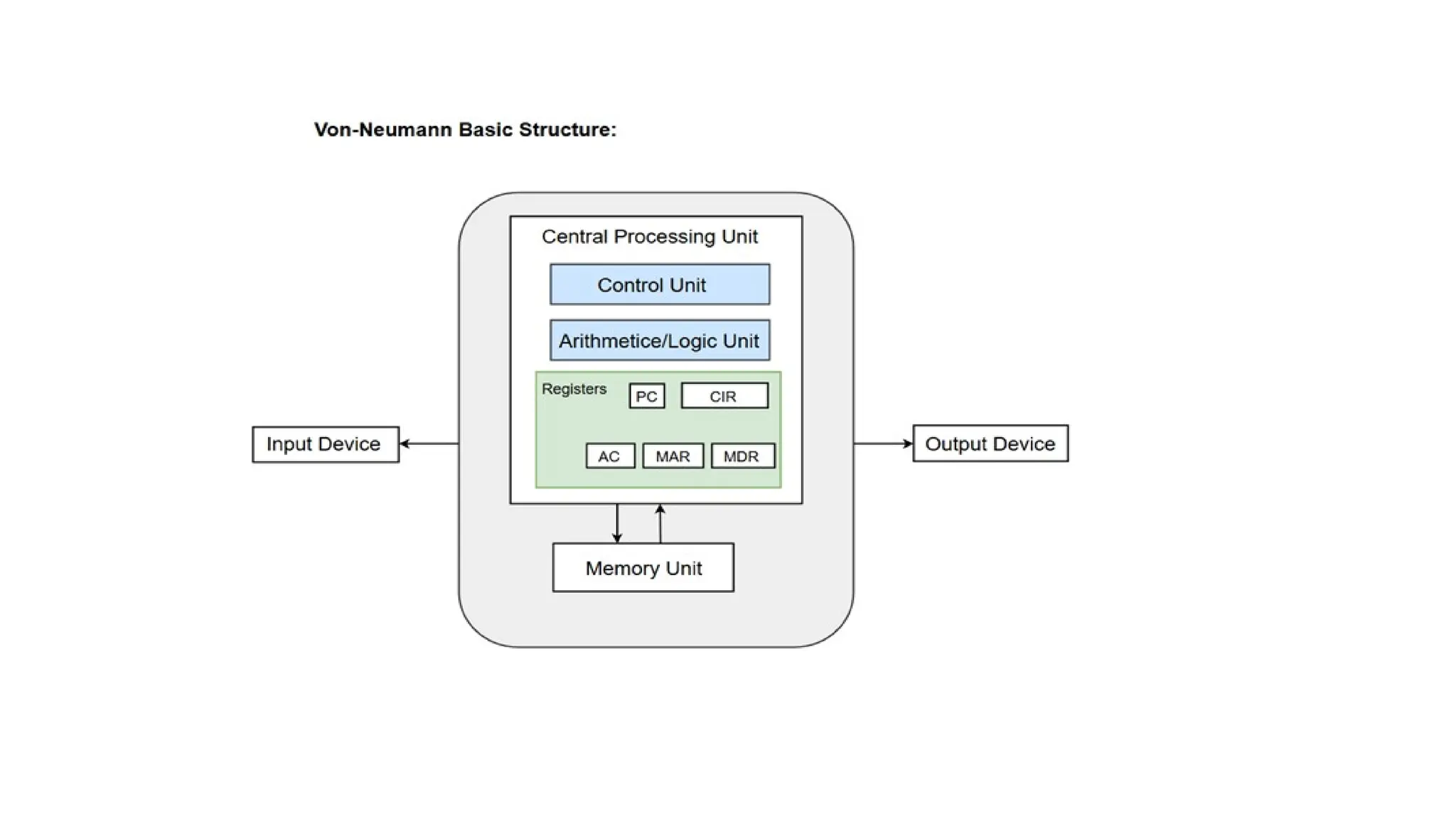
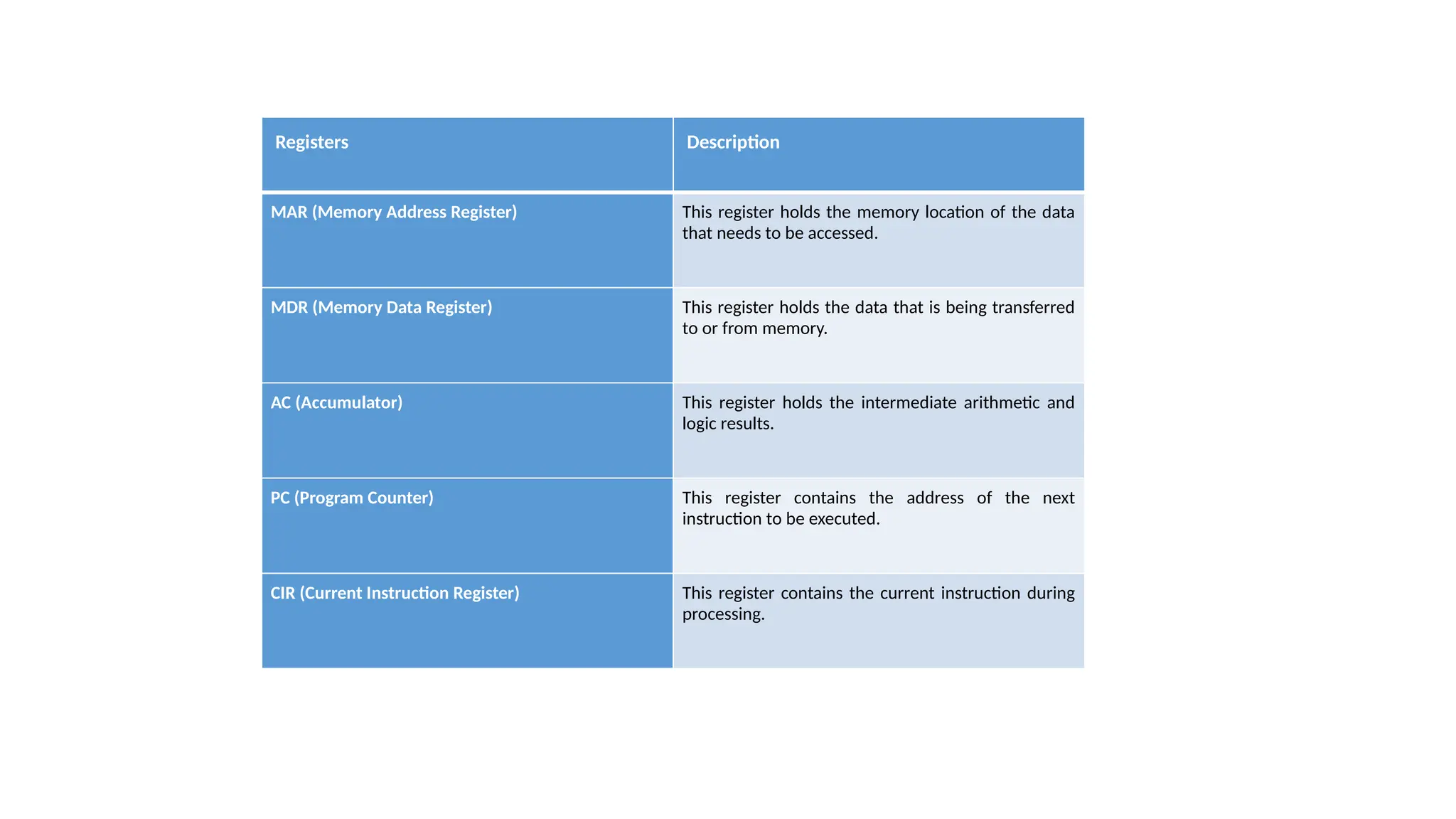
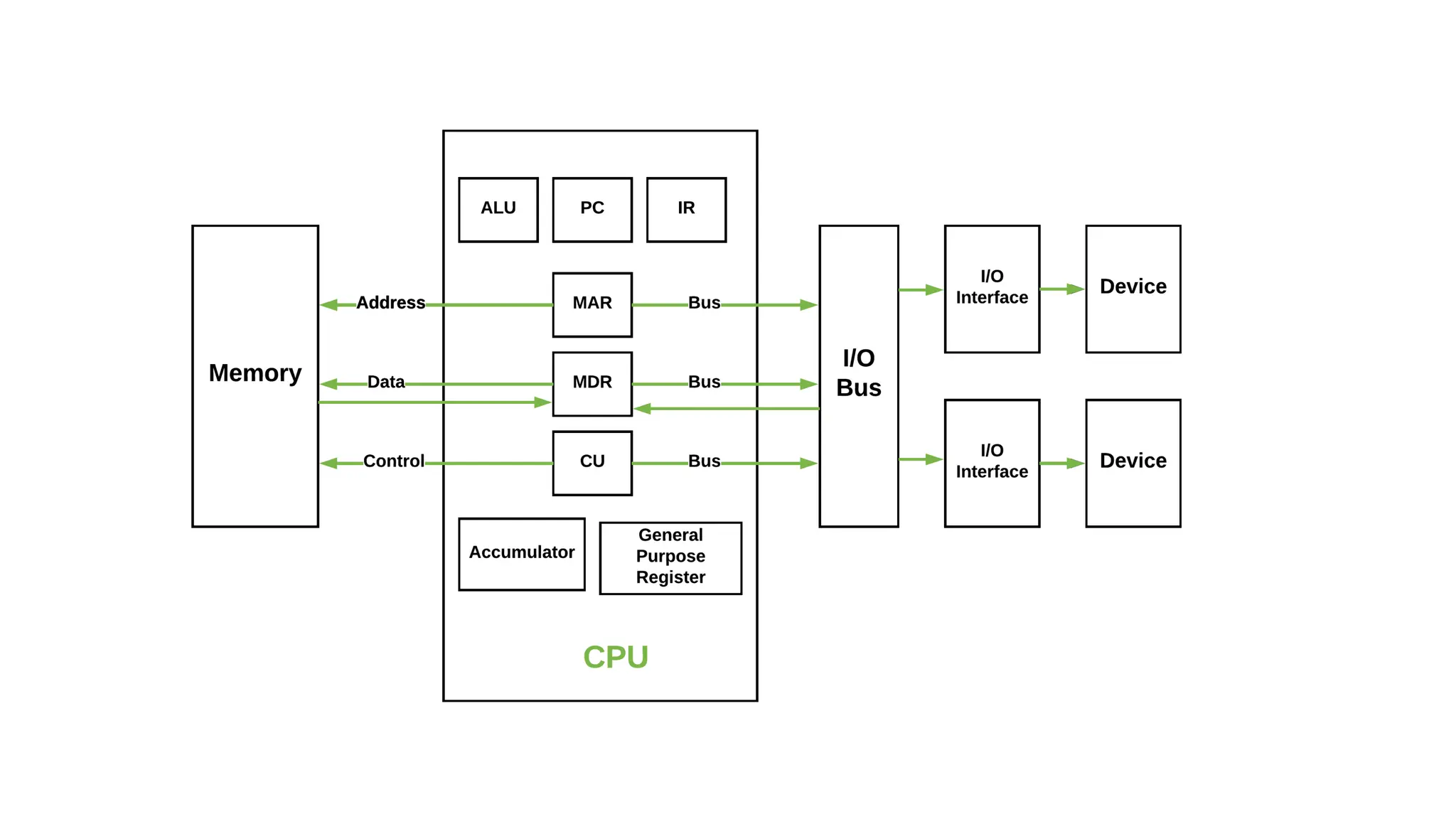
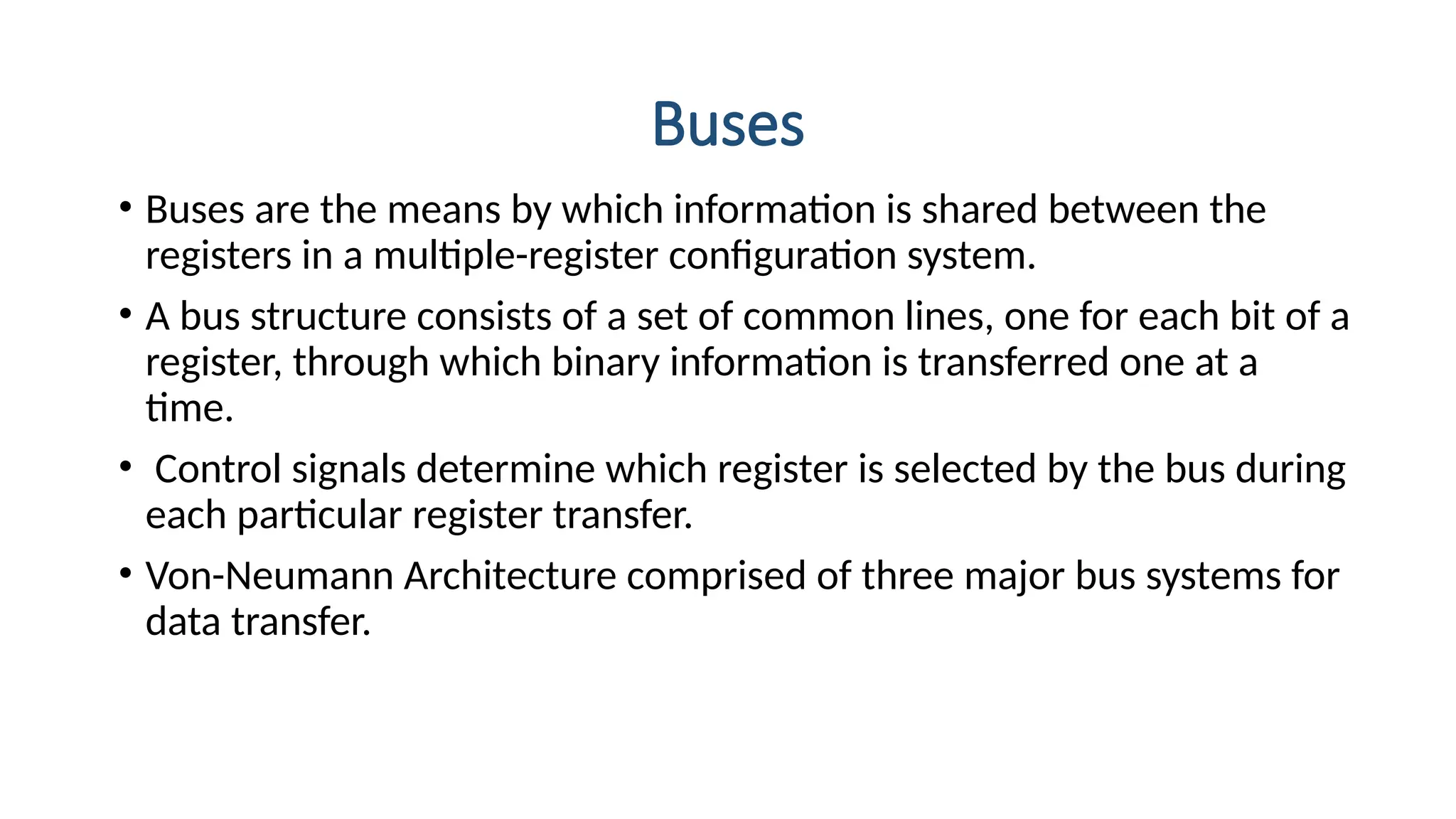
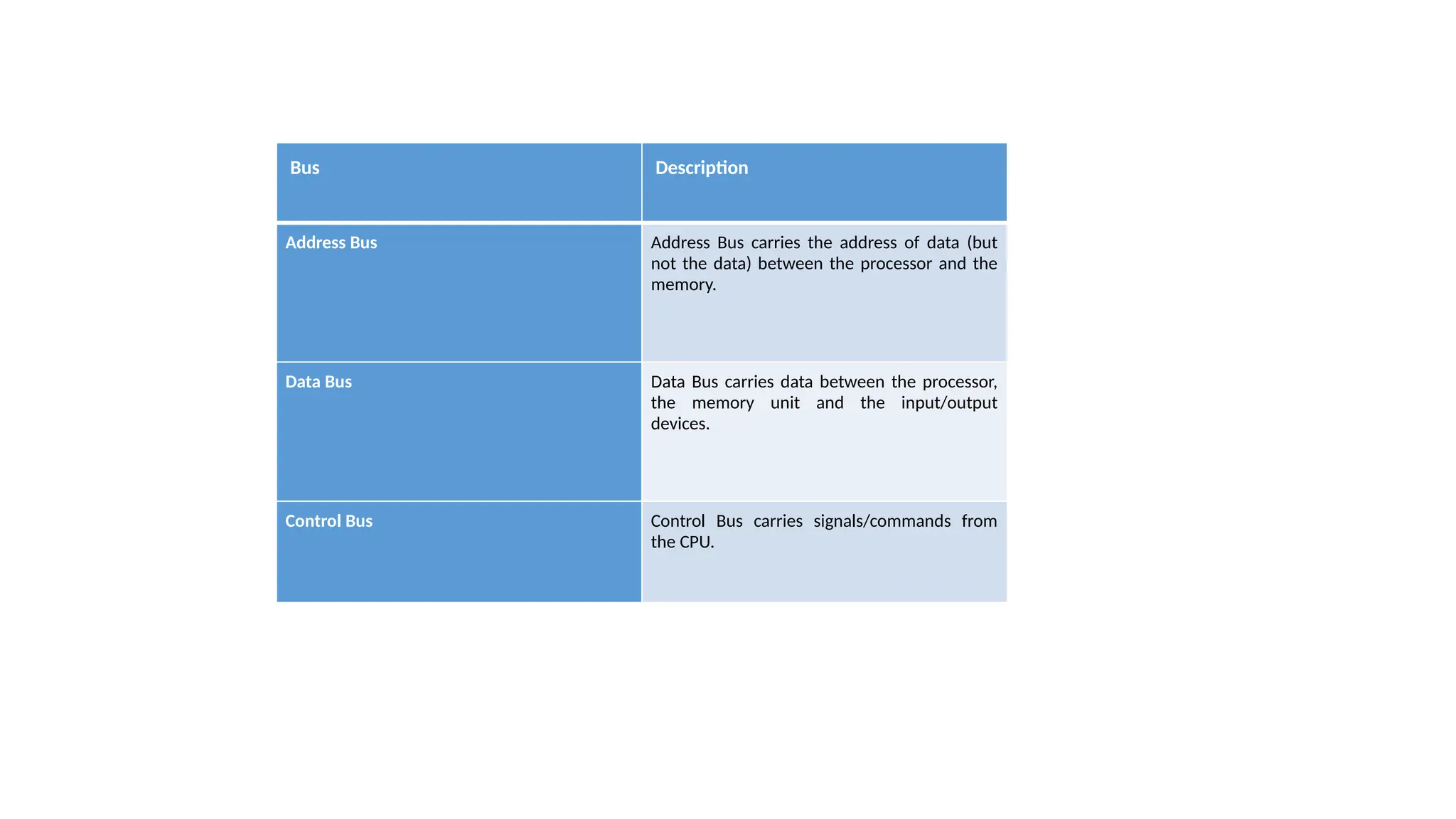
The von Neumann model, proposed in 1945, is a computer architecture design that includes a control unit, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), registers, and I/O interfaces, based on the stored-program computer concept. It differentiates between fixed program computers, which are task-specific and non-reprogrammable, and stored program computers, which are easily reprogrammable. The architecture includes major components like the CPU, memory unit, and buses, which facilitate data transfer and operations within the system.