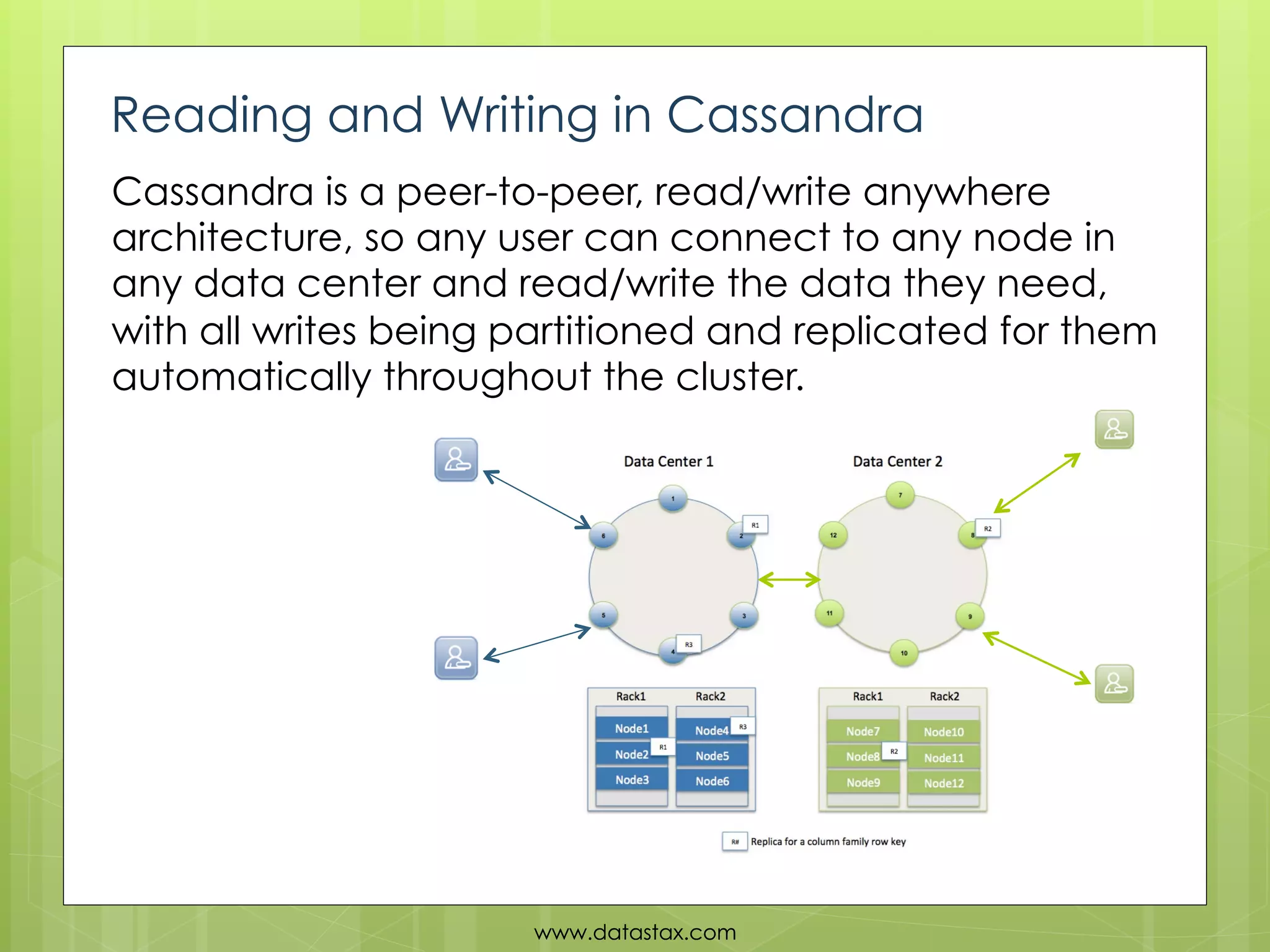
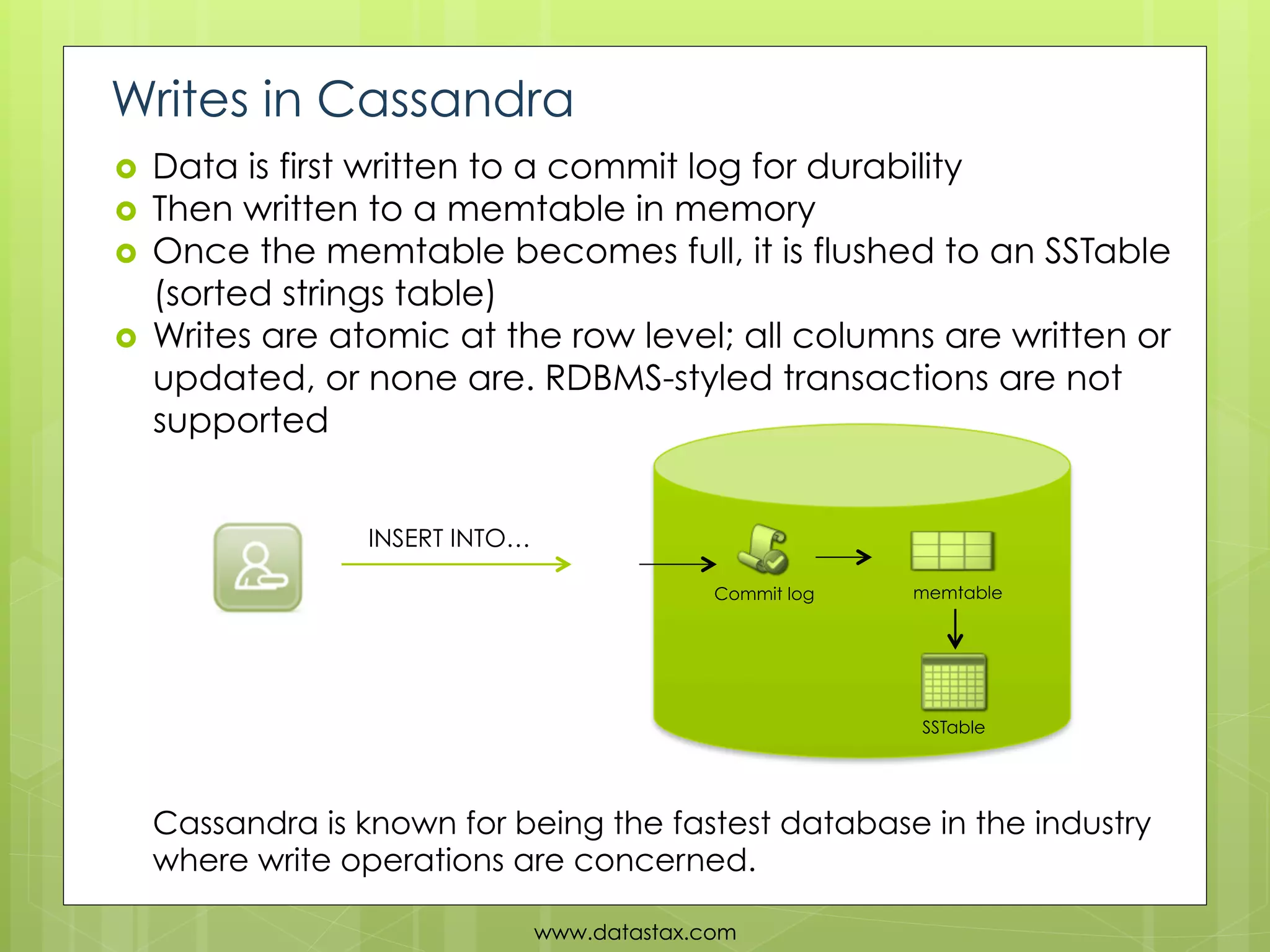
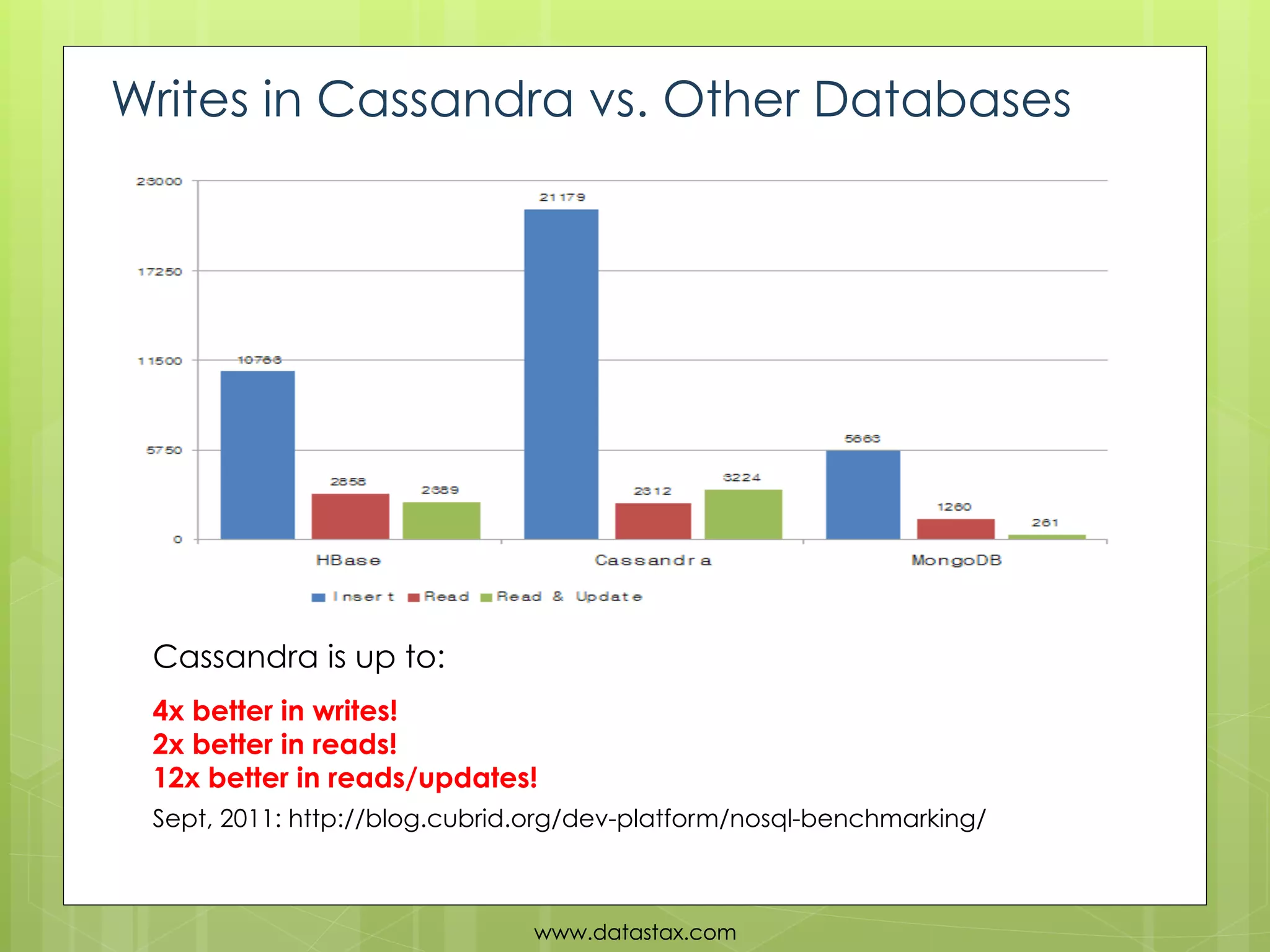
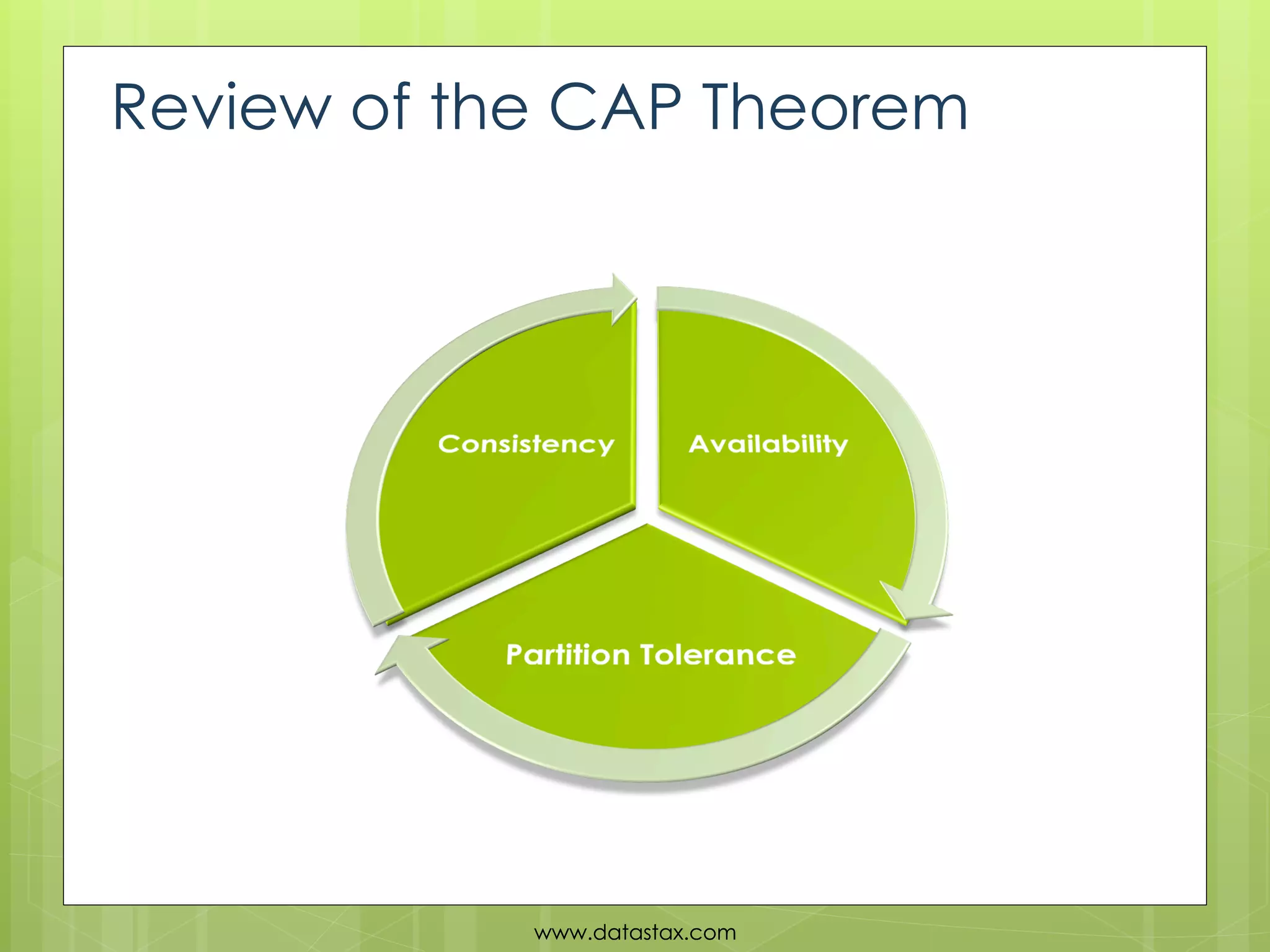
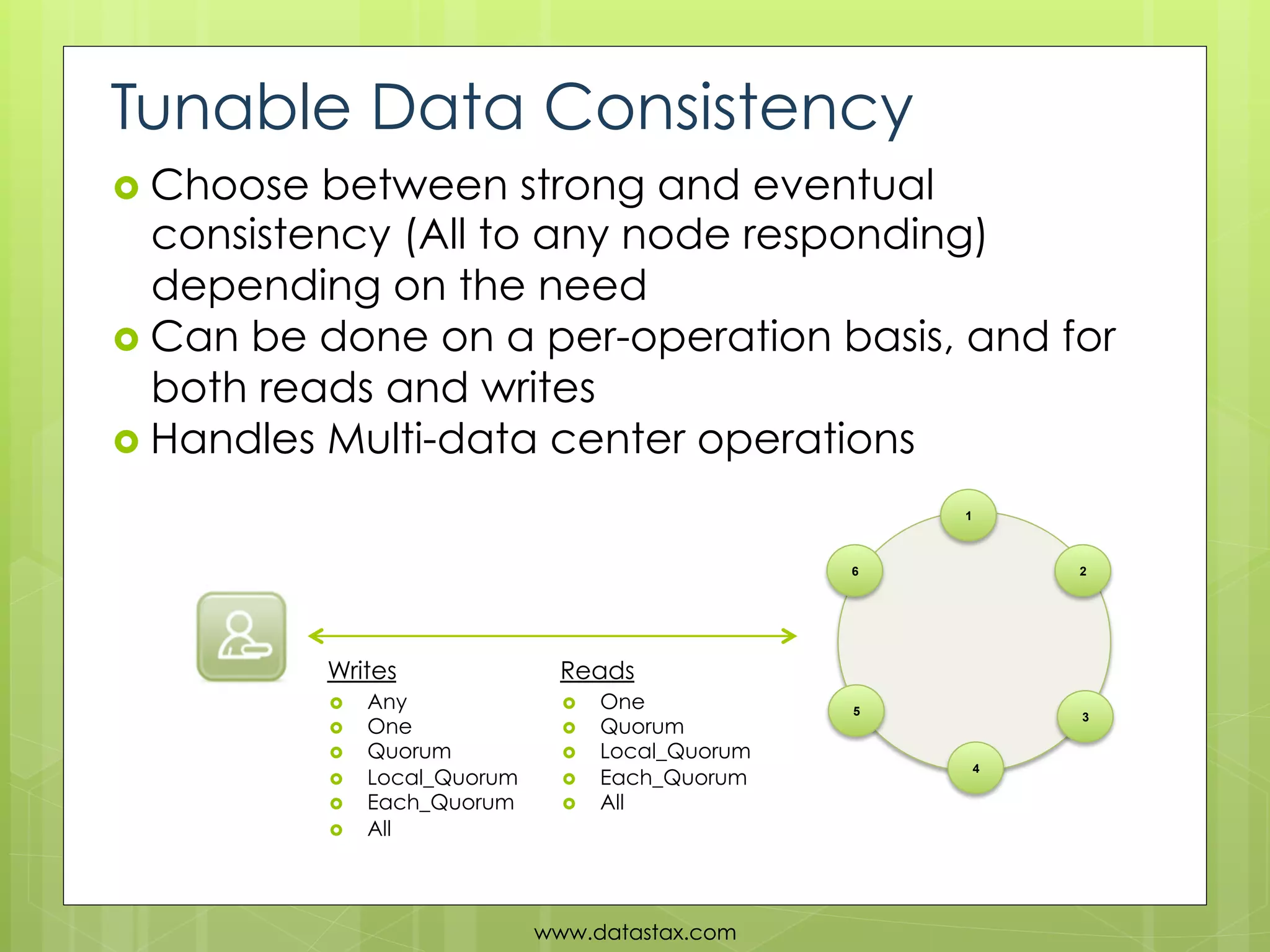
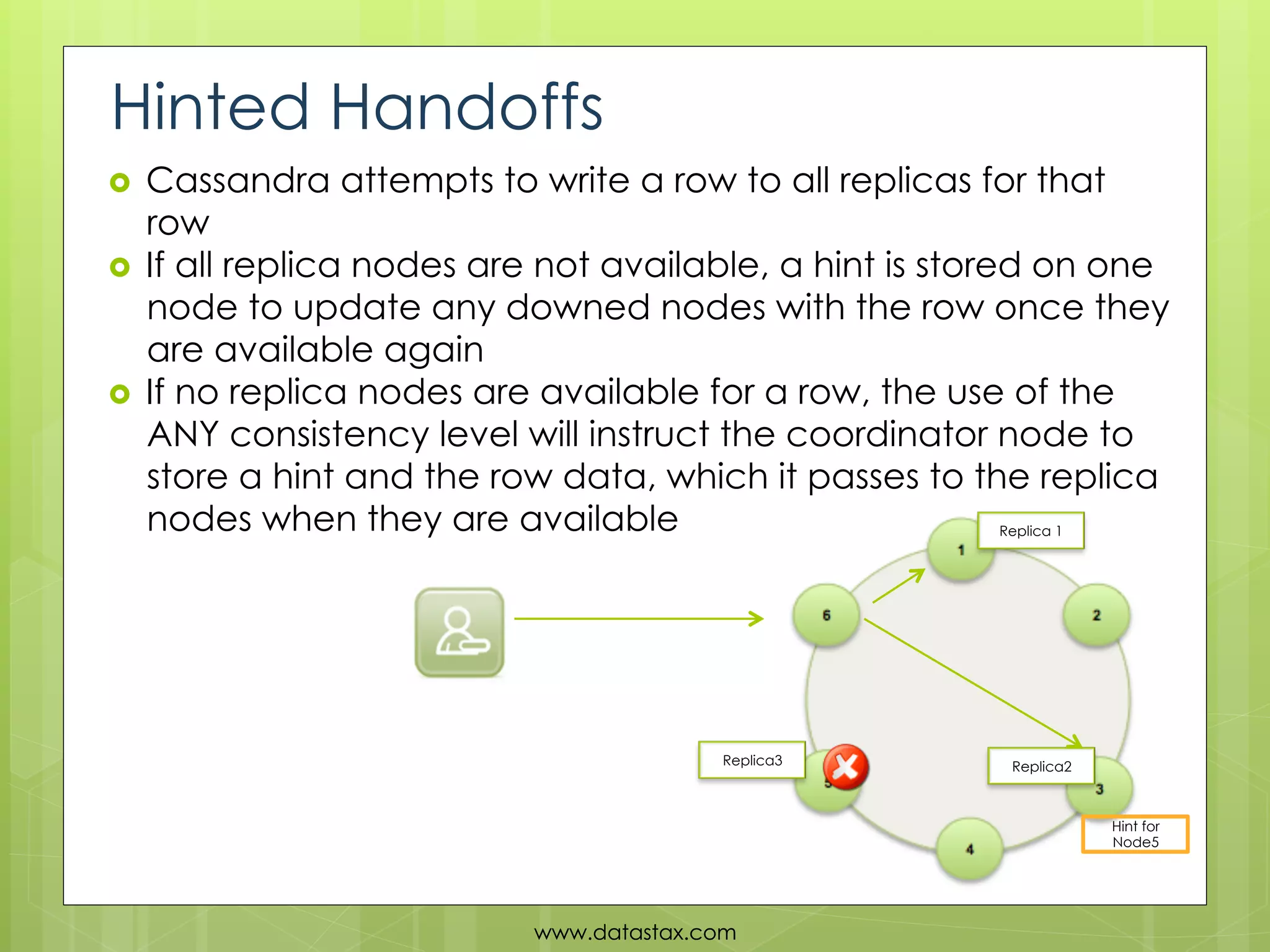
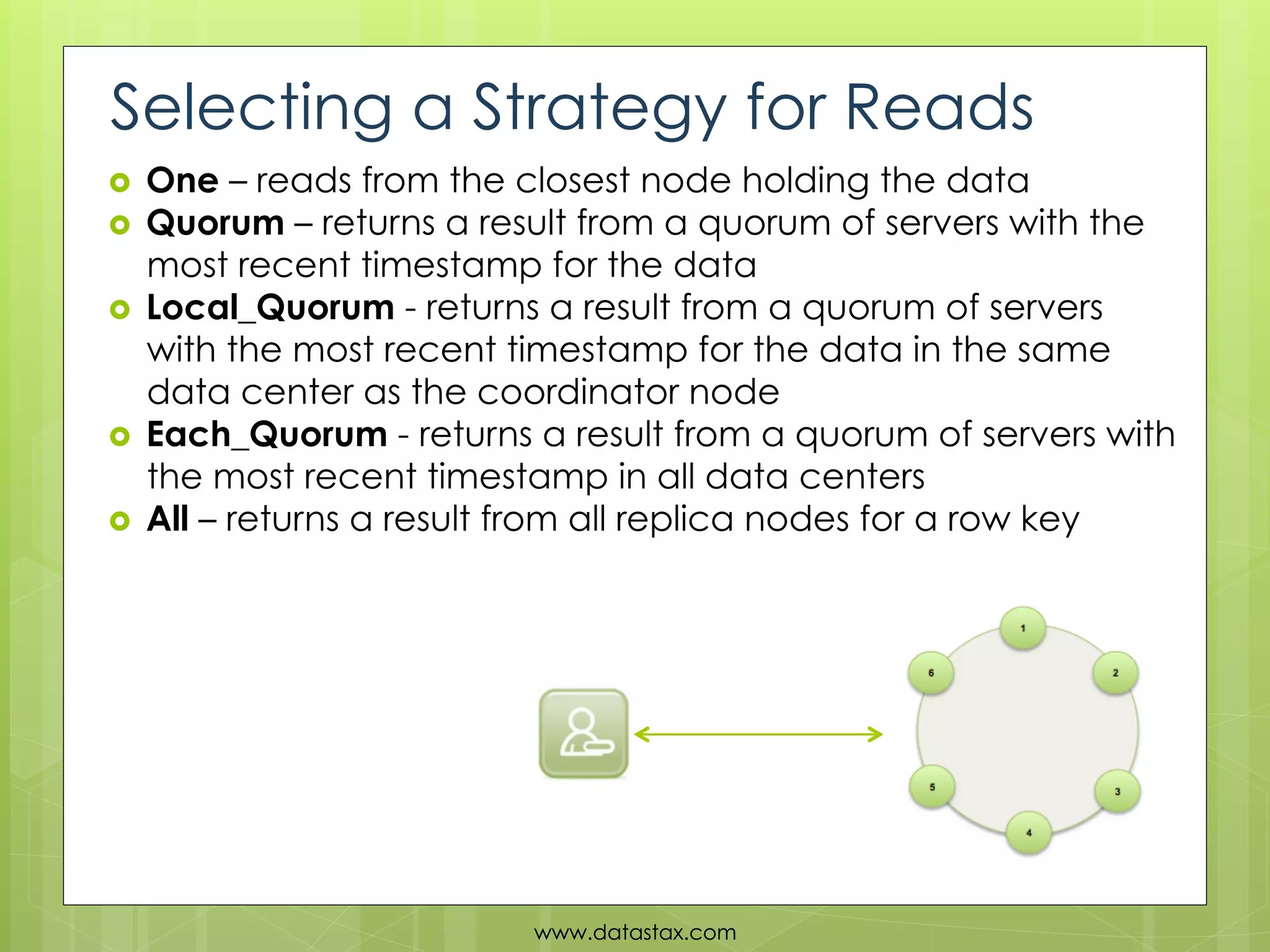
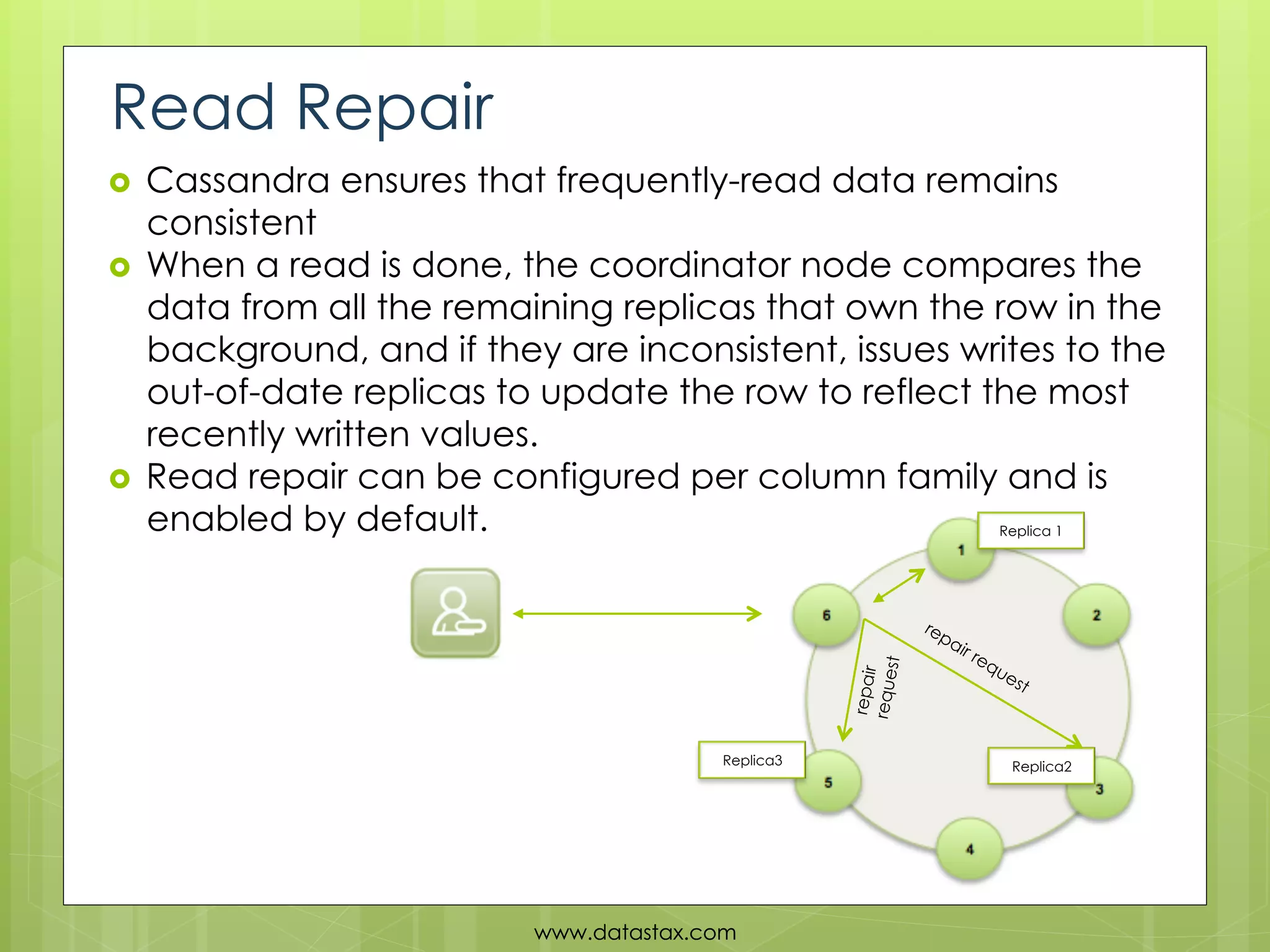
This document provides an overview of data consistency in Apache Cassandra. It discusses how Cassandra writes data to commit logs and memtables before flushing to SSTables. It also reviews the CAP theorem and how Cassandra offers tunable consistency levels for both reads and writes. Strategies for choosing consistency levels for writes, such as ANY, ONE, QUORUM, and ALL are presented. The document also covers read repair and hinted handoffs in Cassandra. Examples of CQL queries with different consistency levels are given and information on where to download Cassandra is provided at the end.