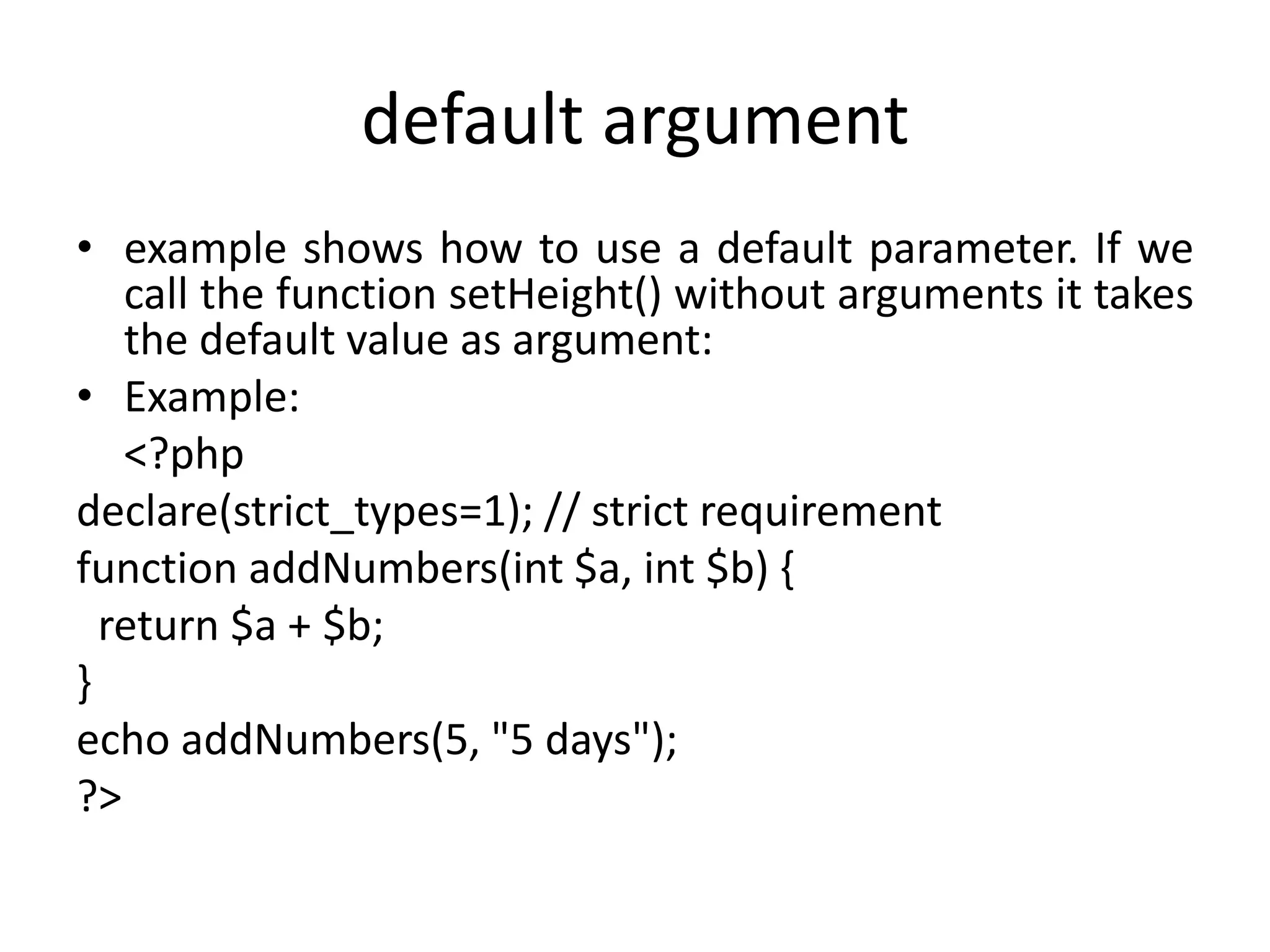
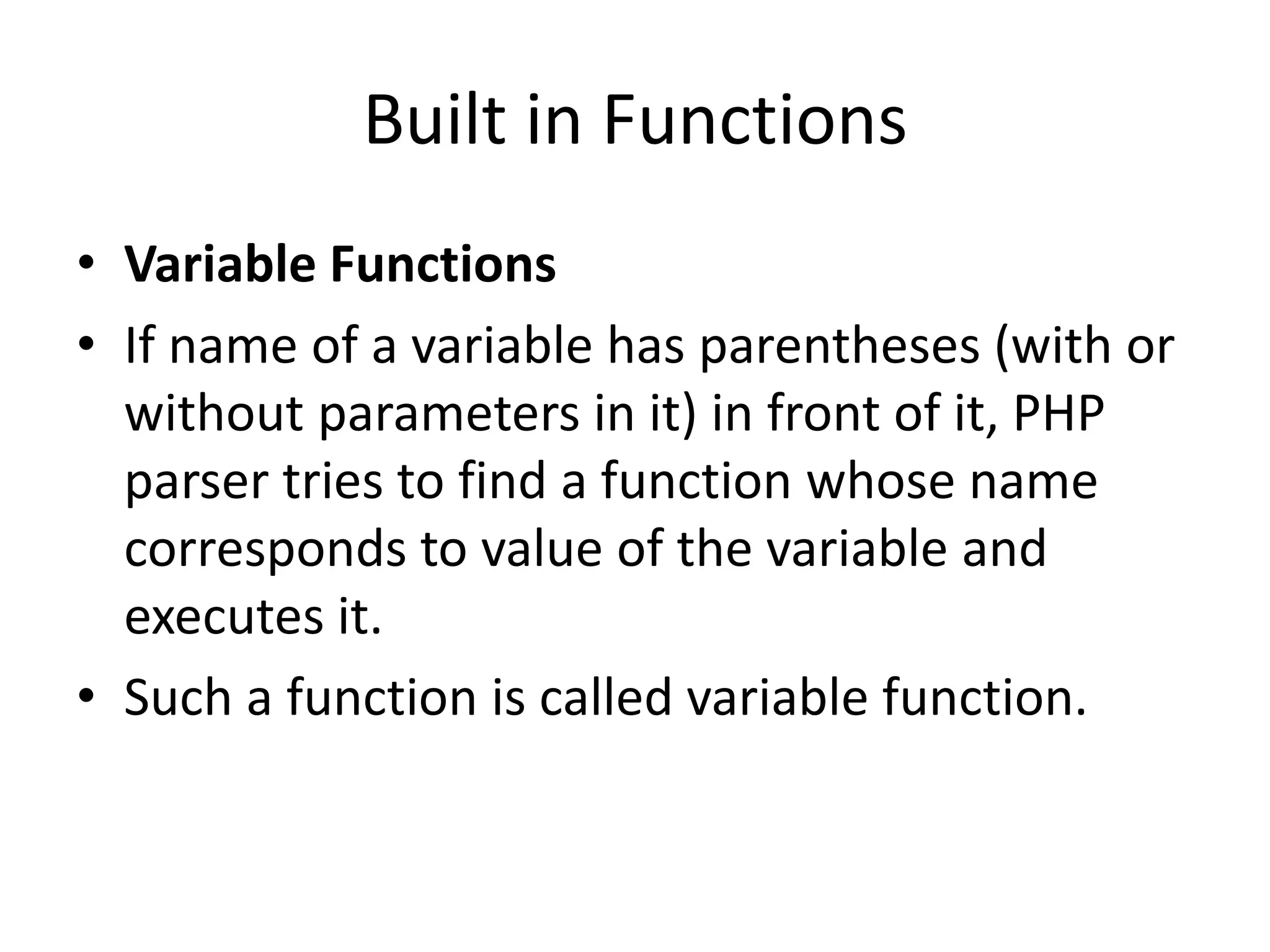
This document provides an introduction and overview of PHP including:
- PHP was created in 1994 and is a widely used open source scripting language.
- PHP code is executed on the server and returns HTML to the browser.
- Common PHP file extensions are .php. PHP can generate dynamic web page content.
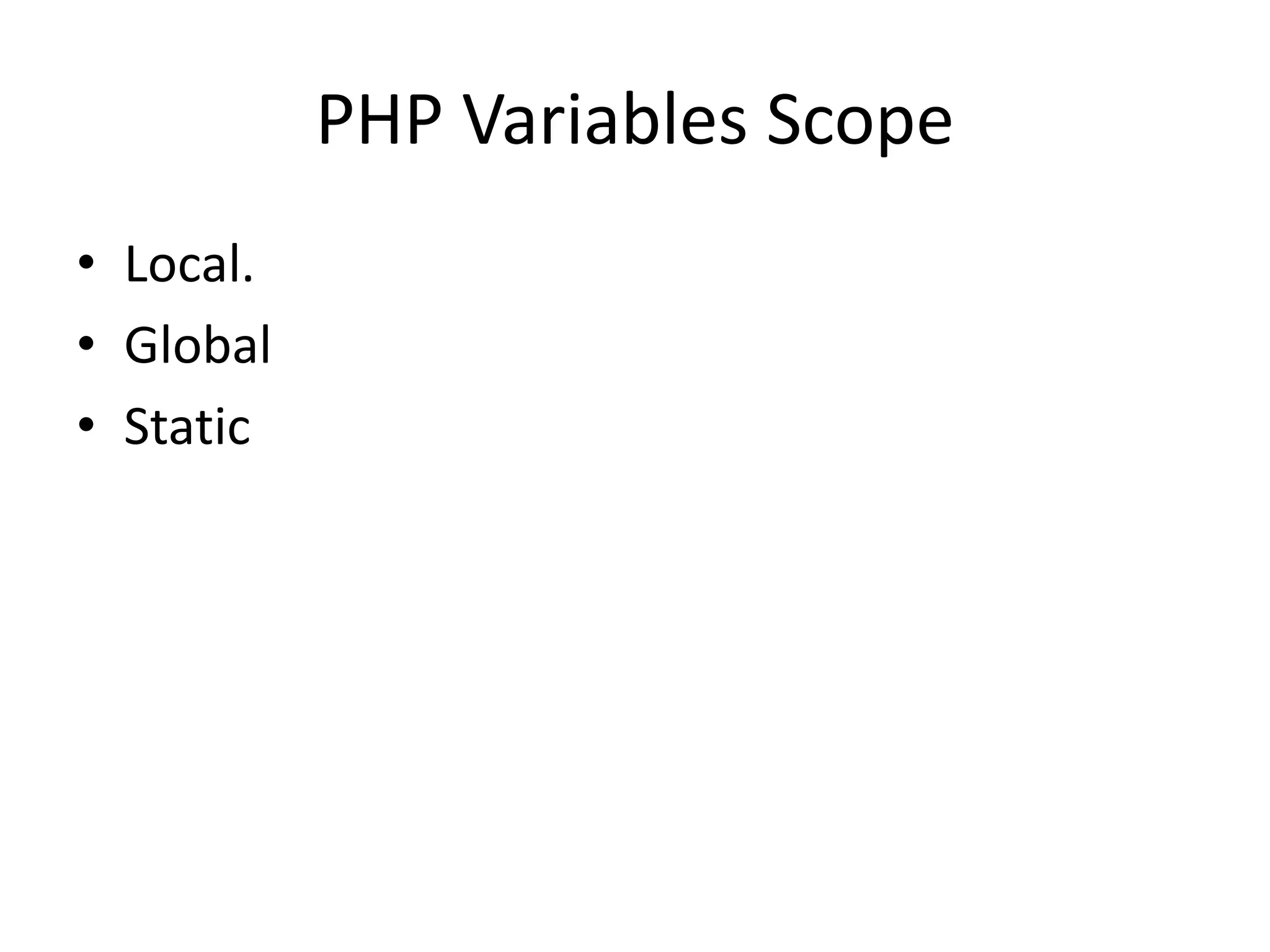
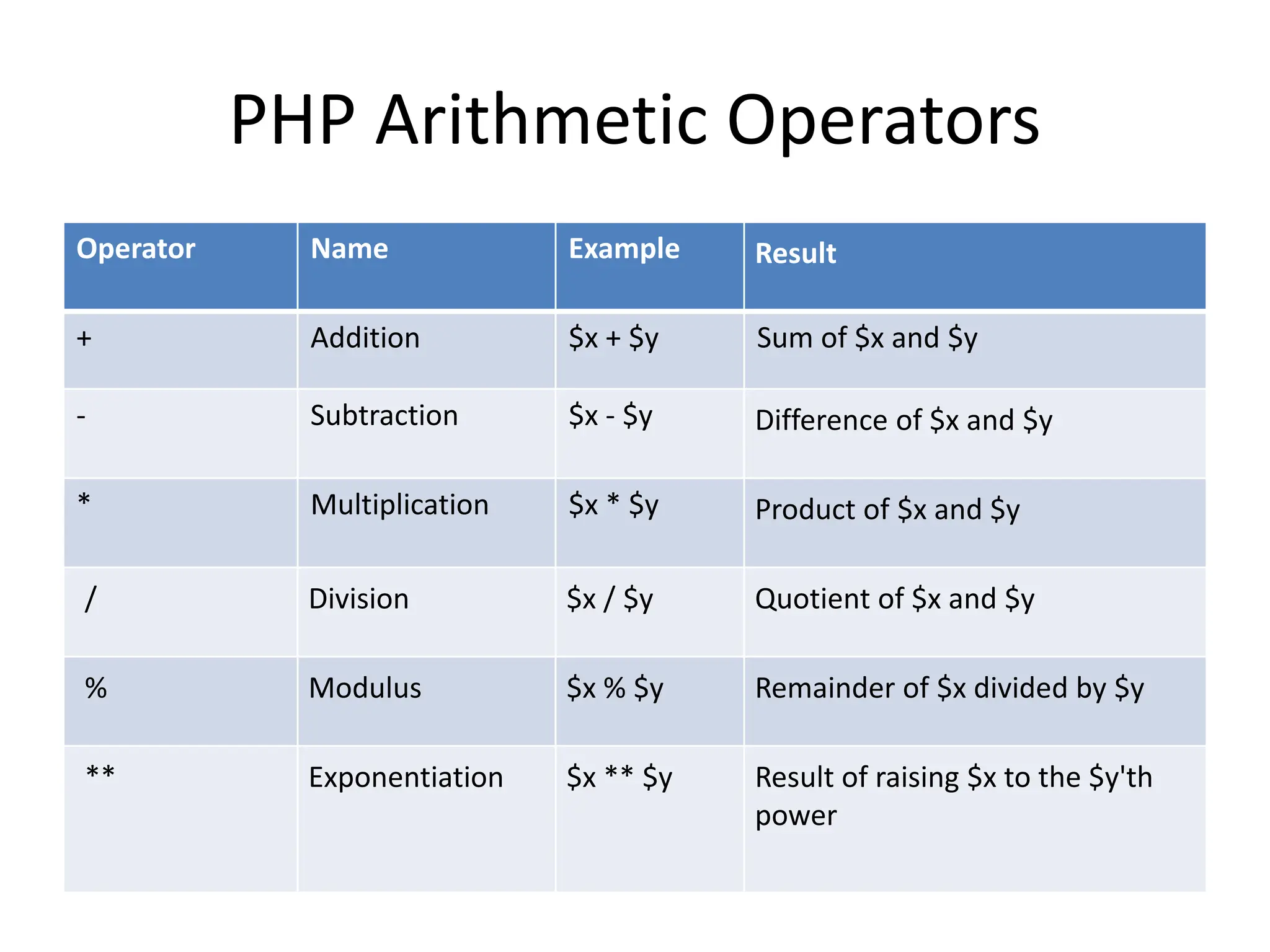
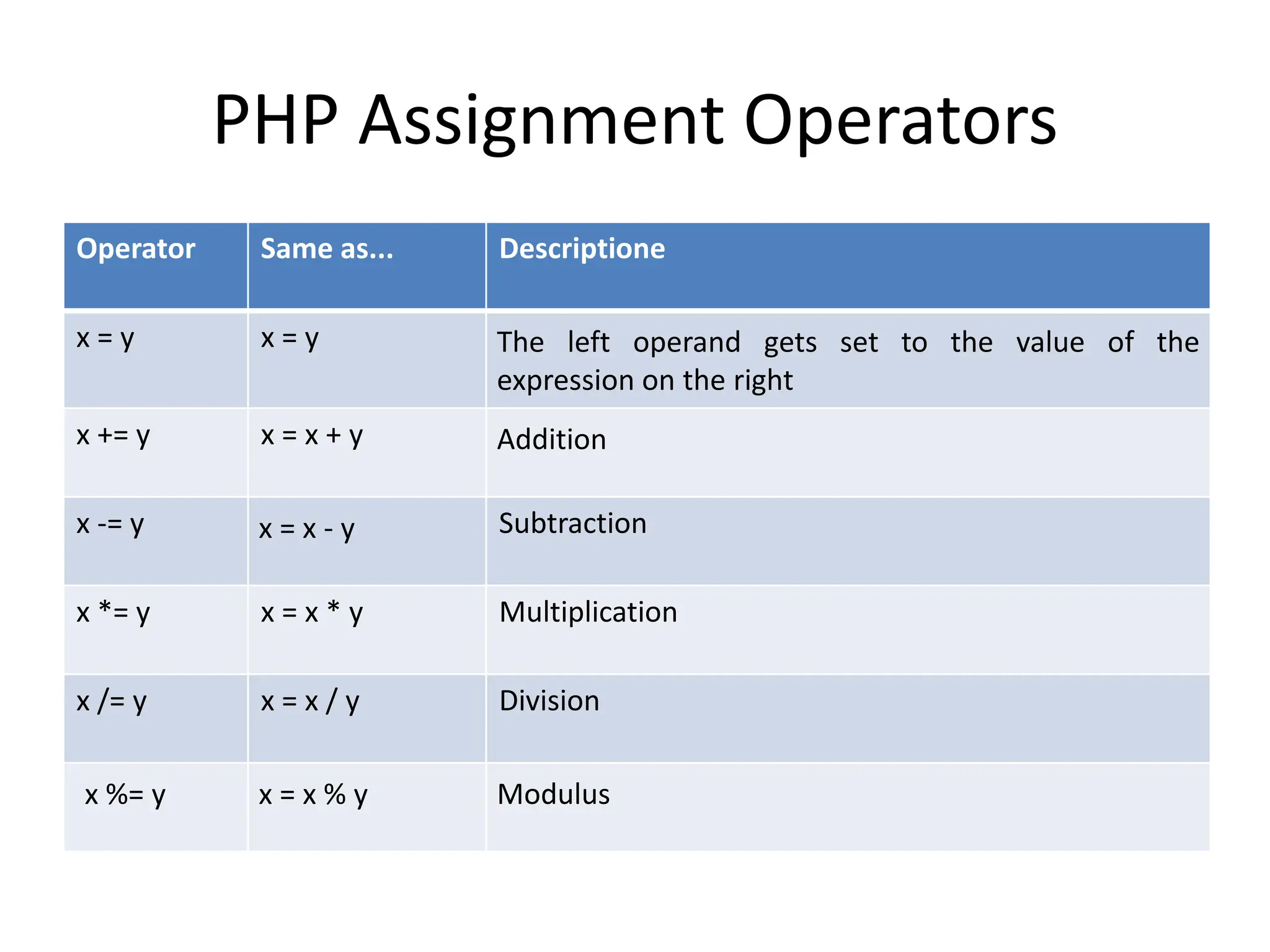
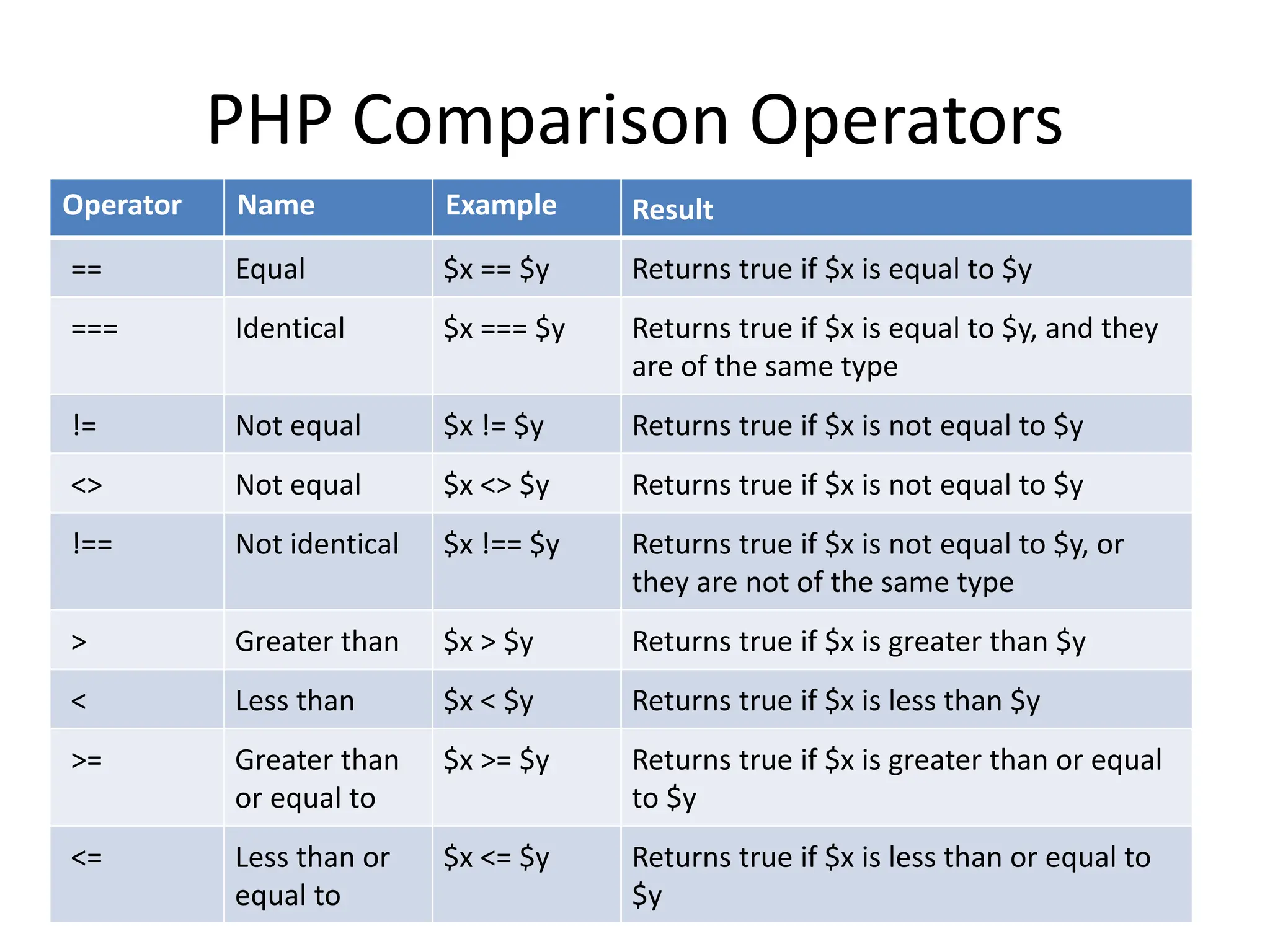
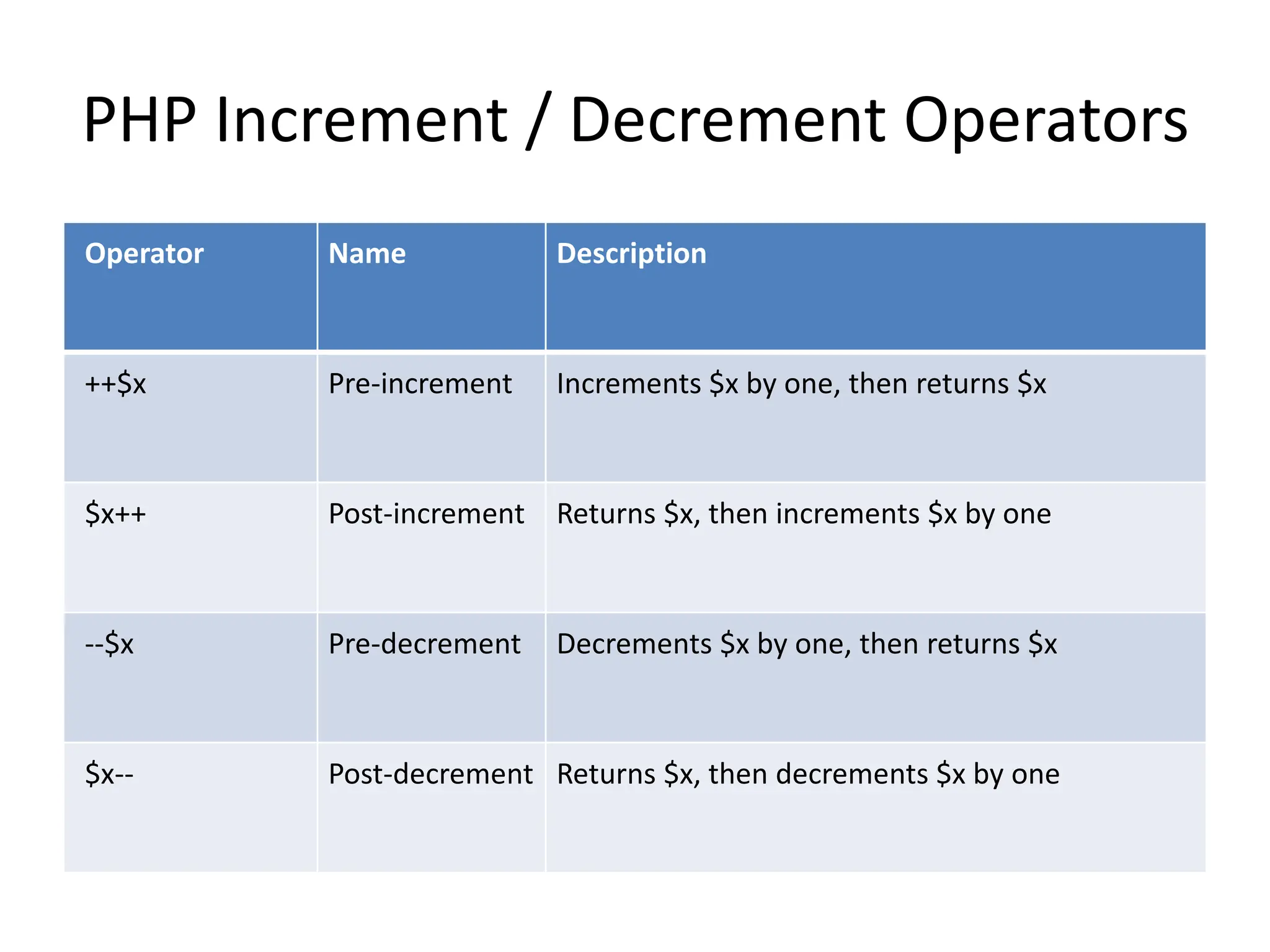
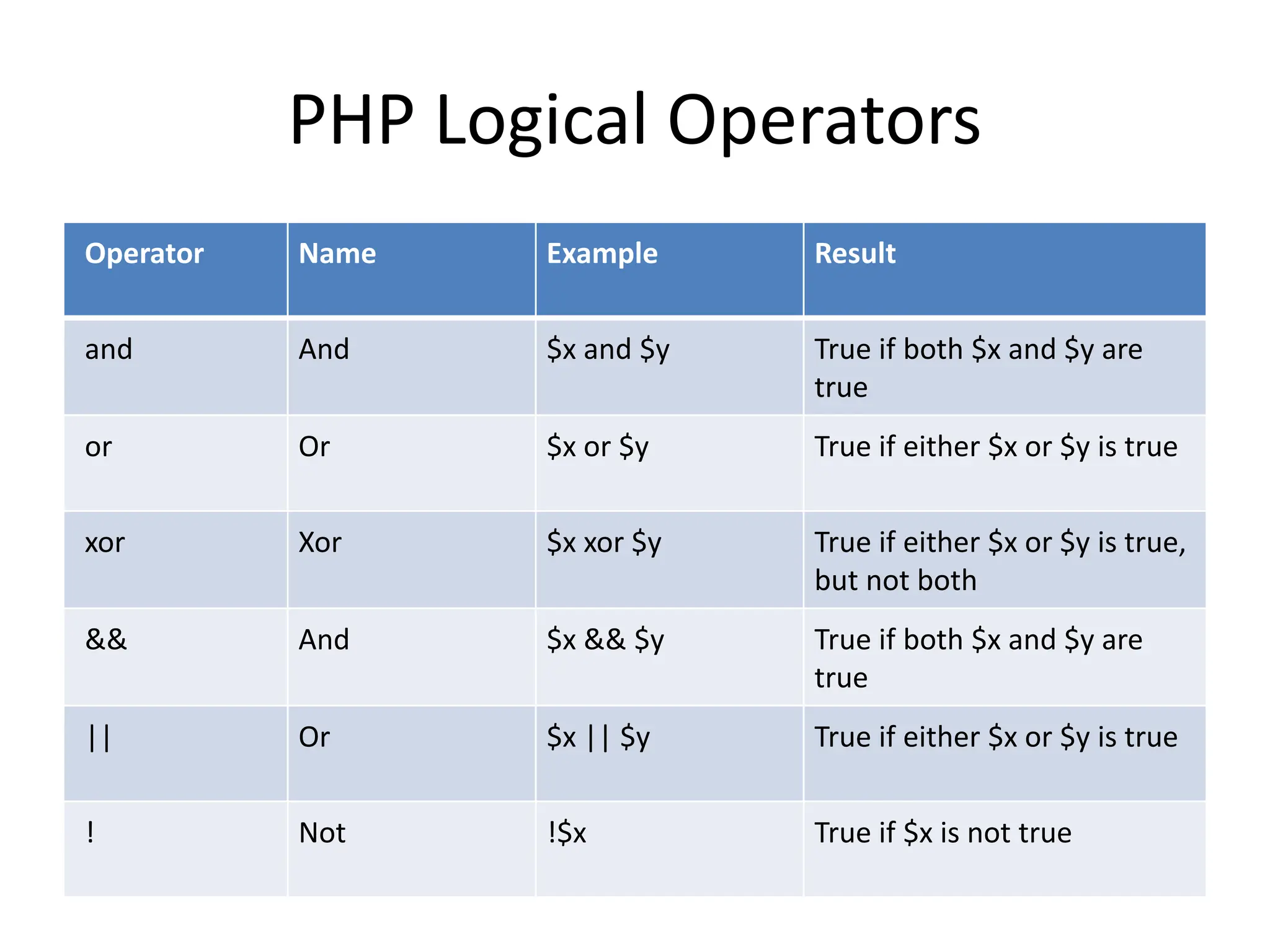
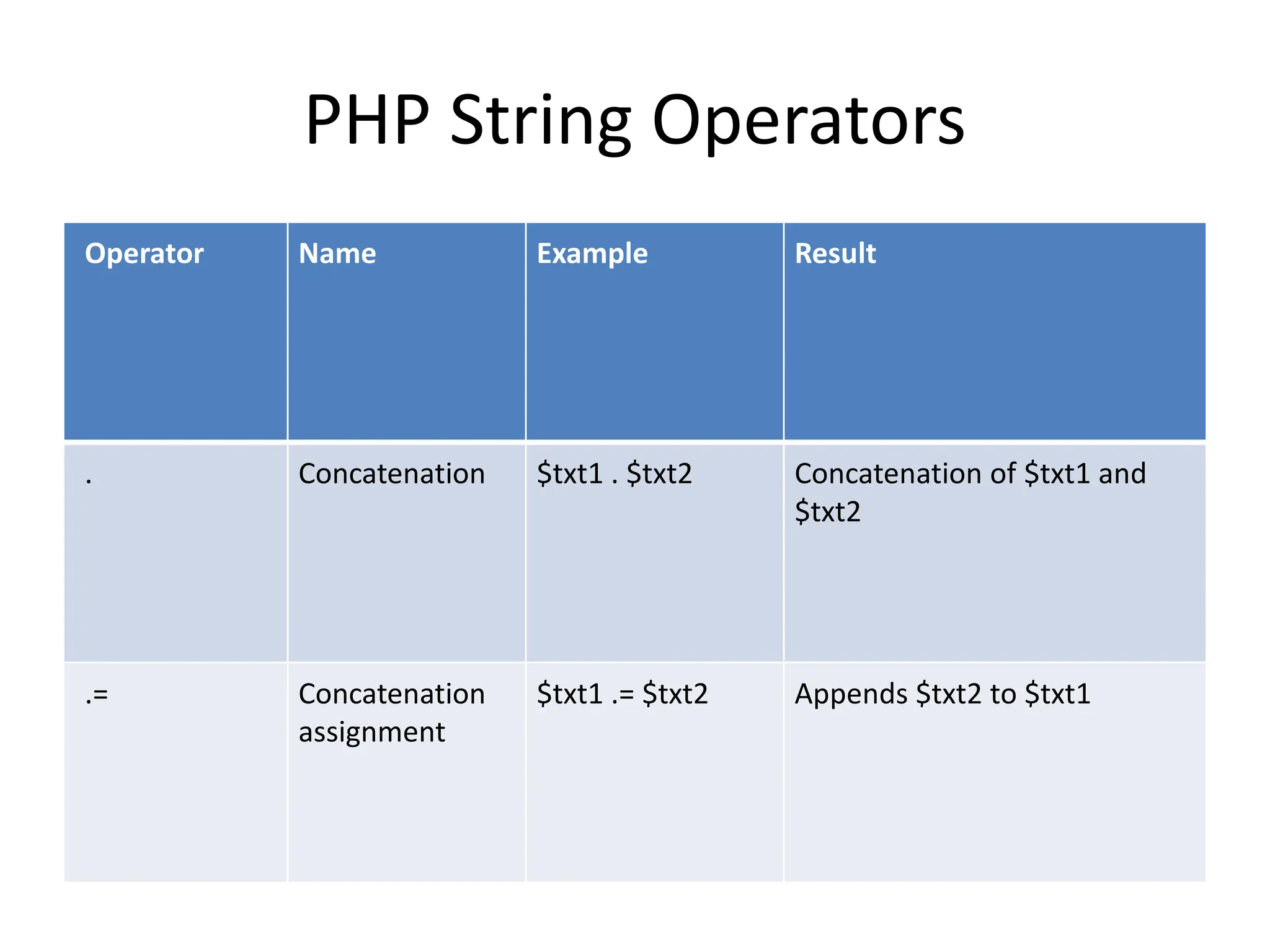
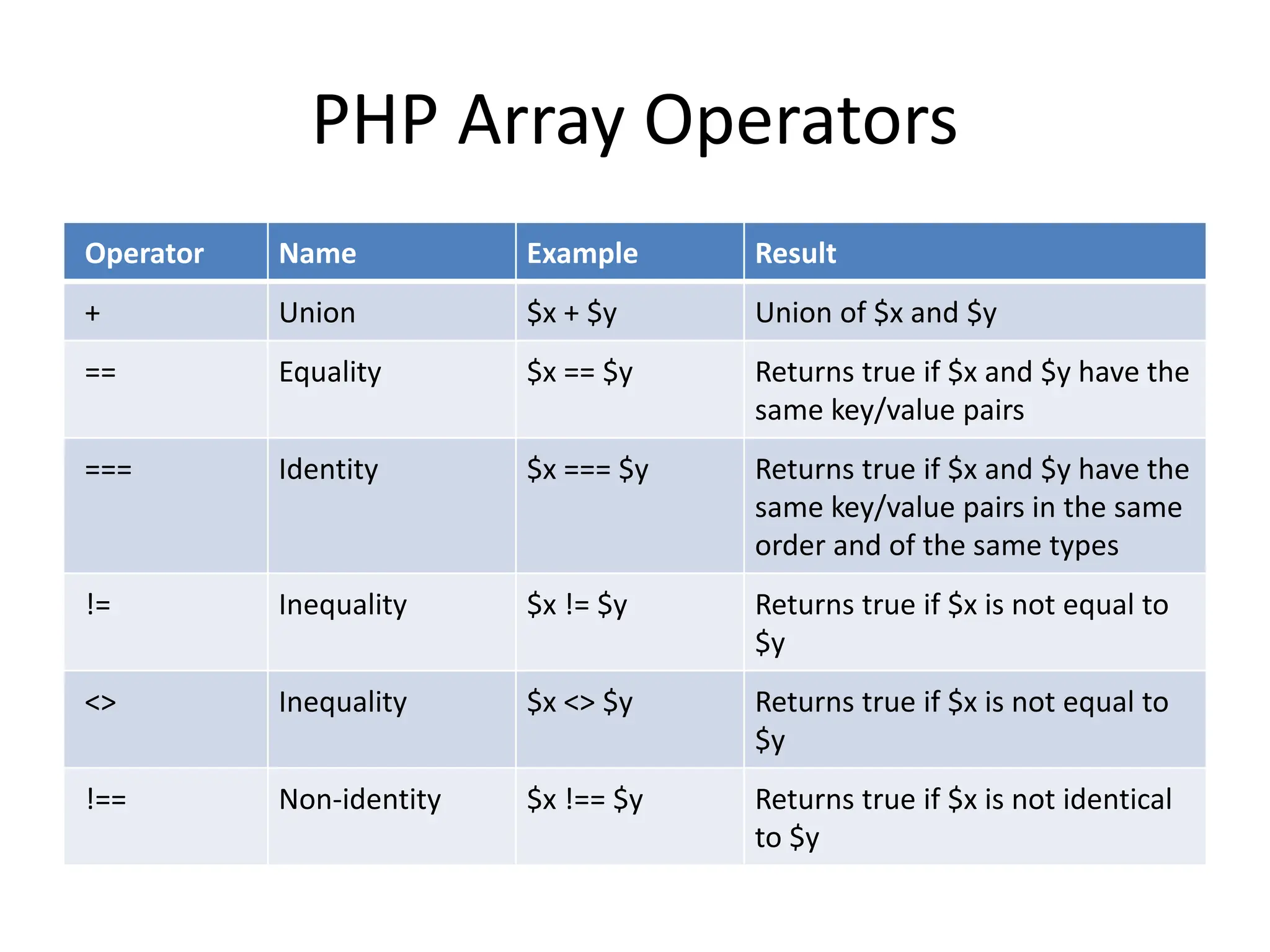
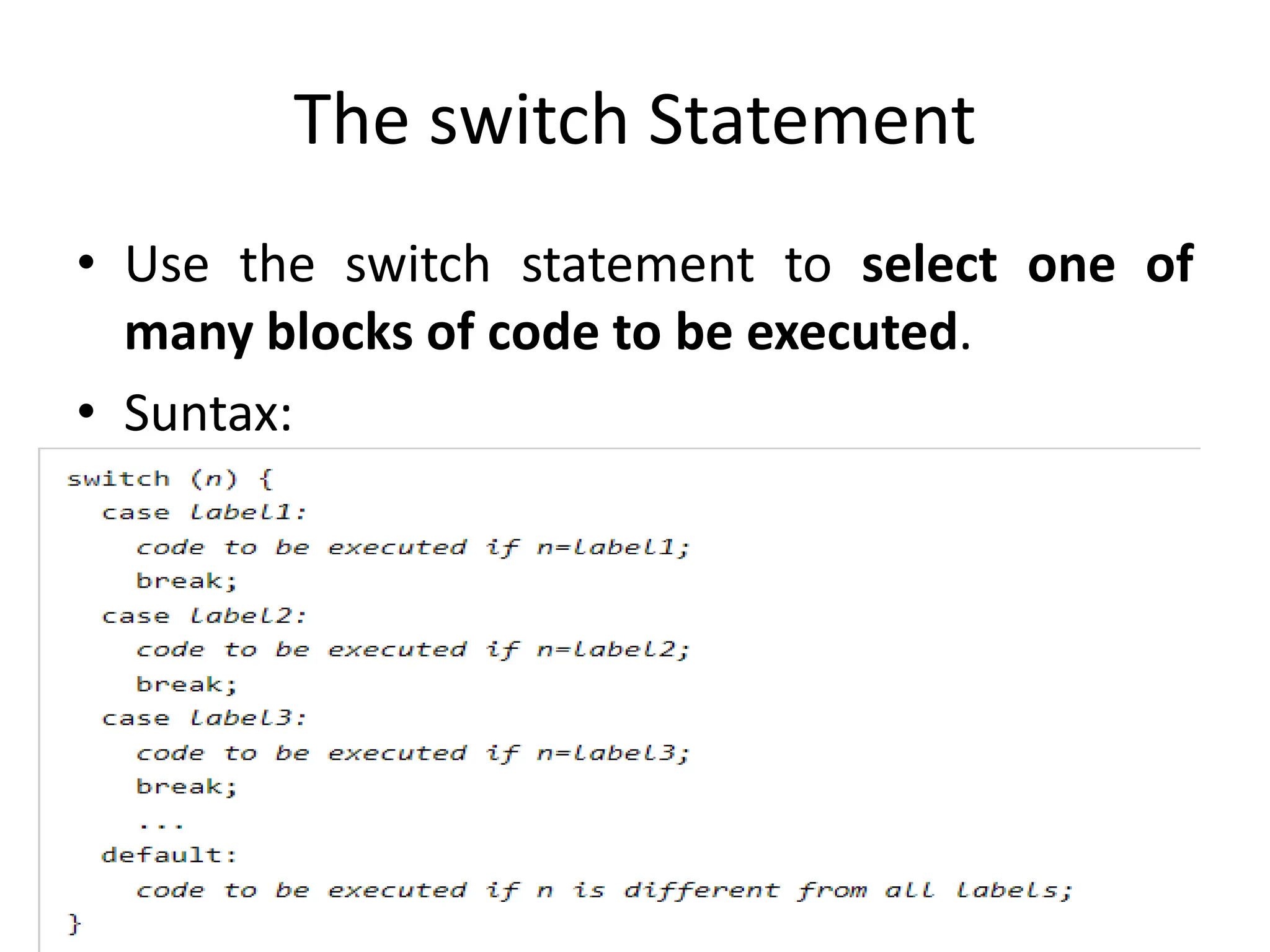
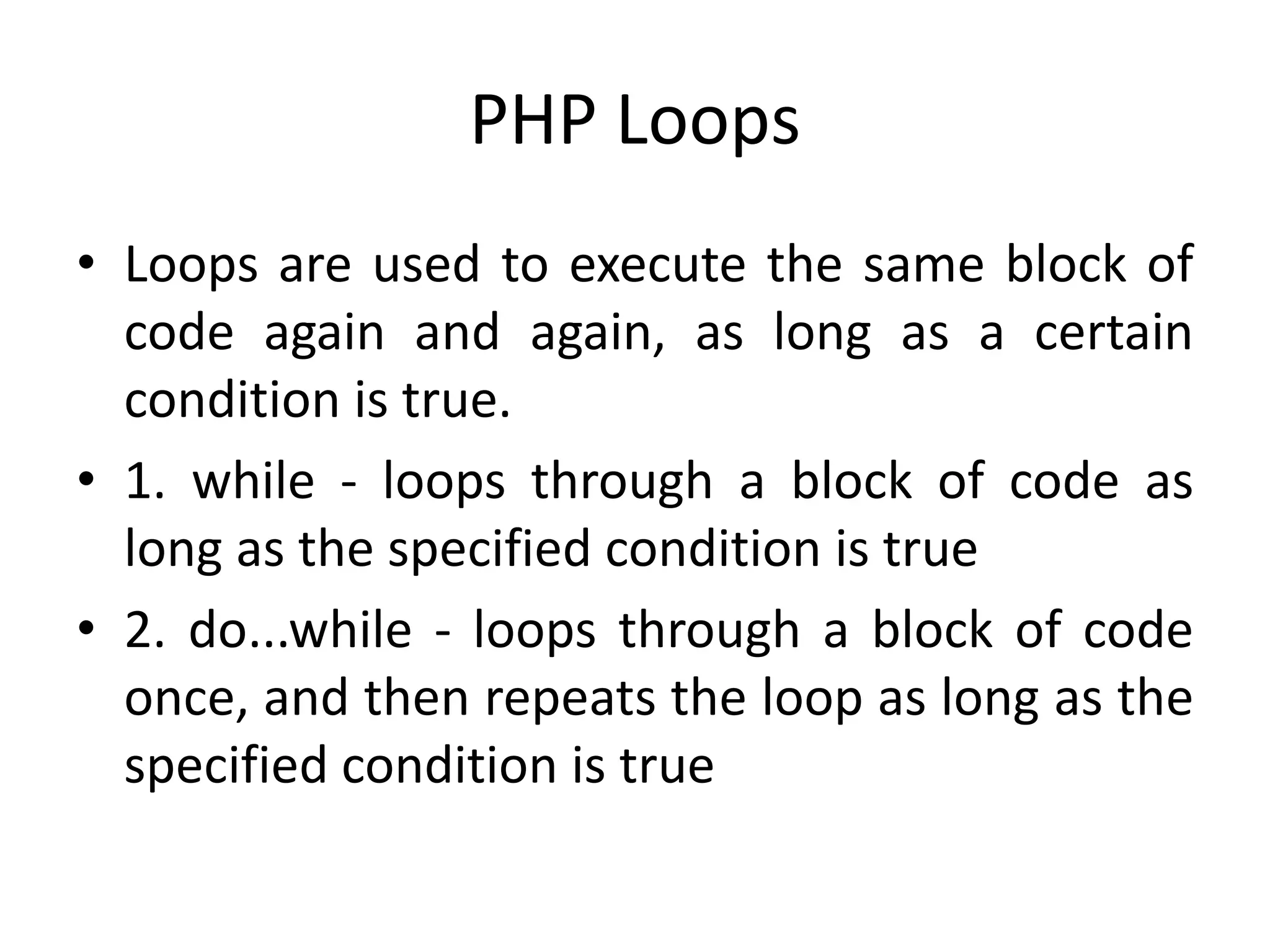
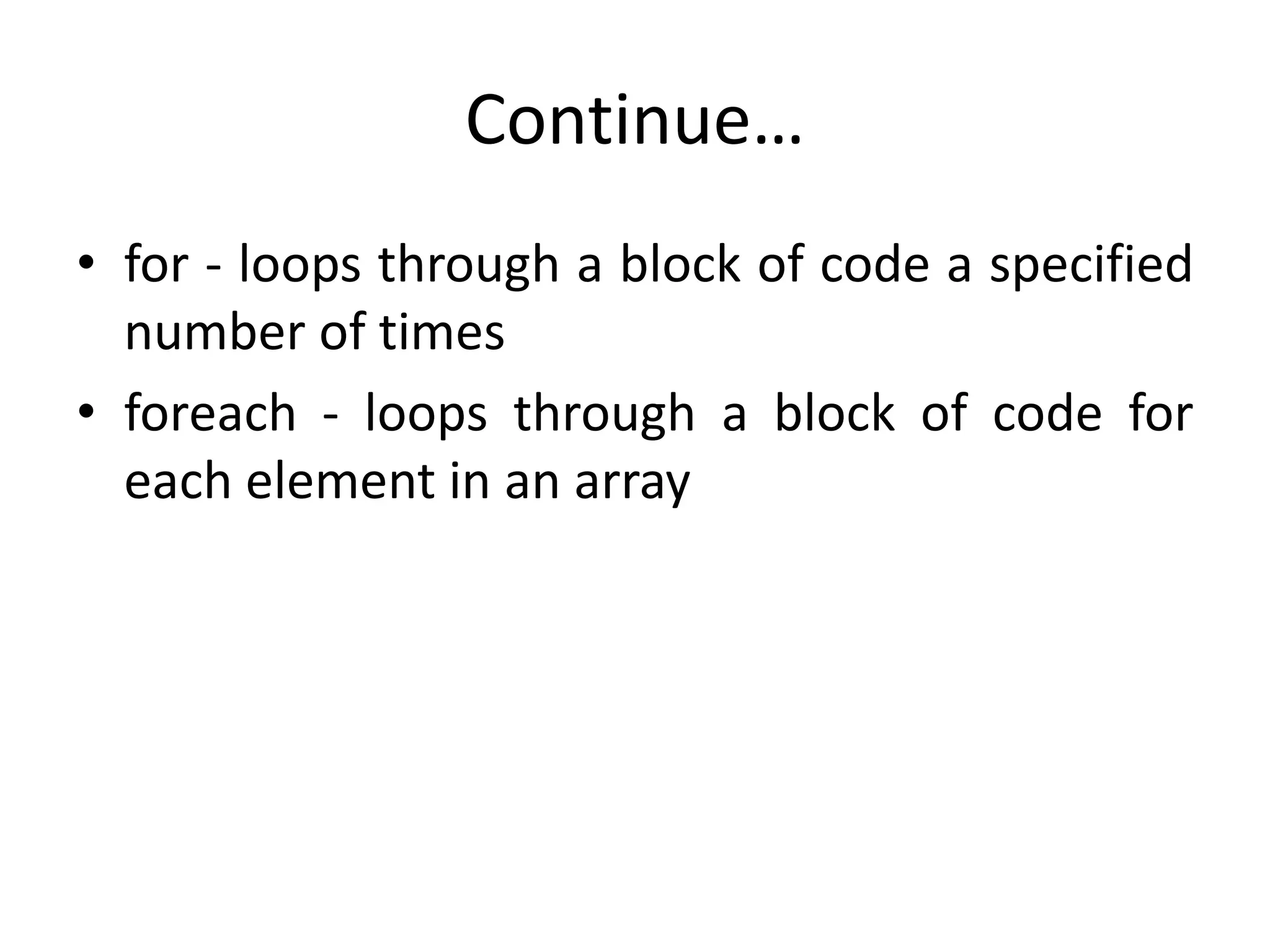
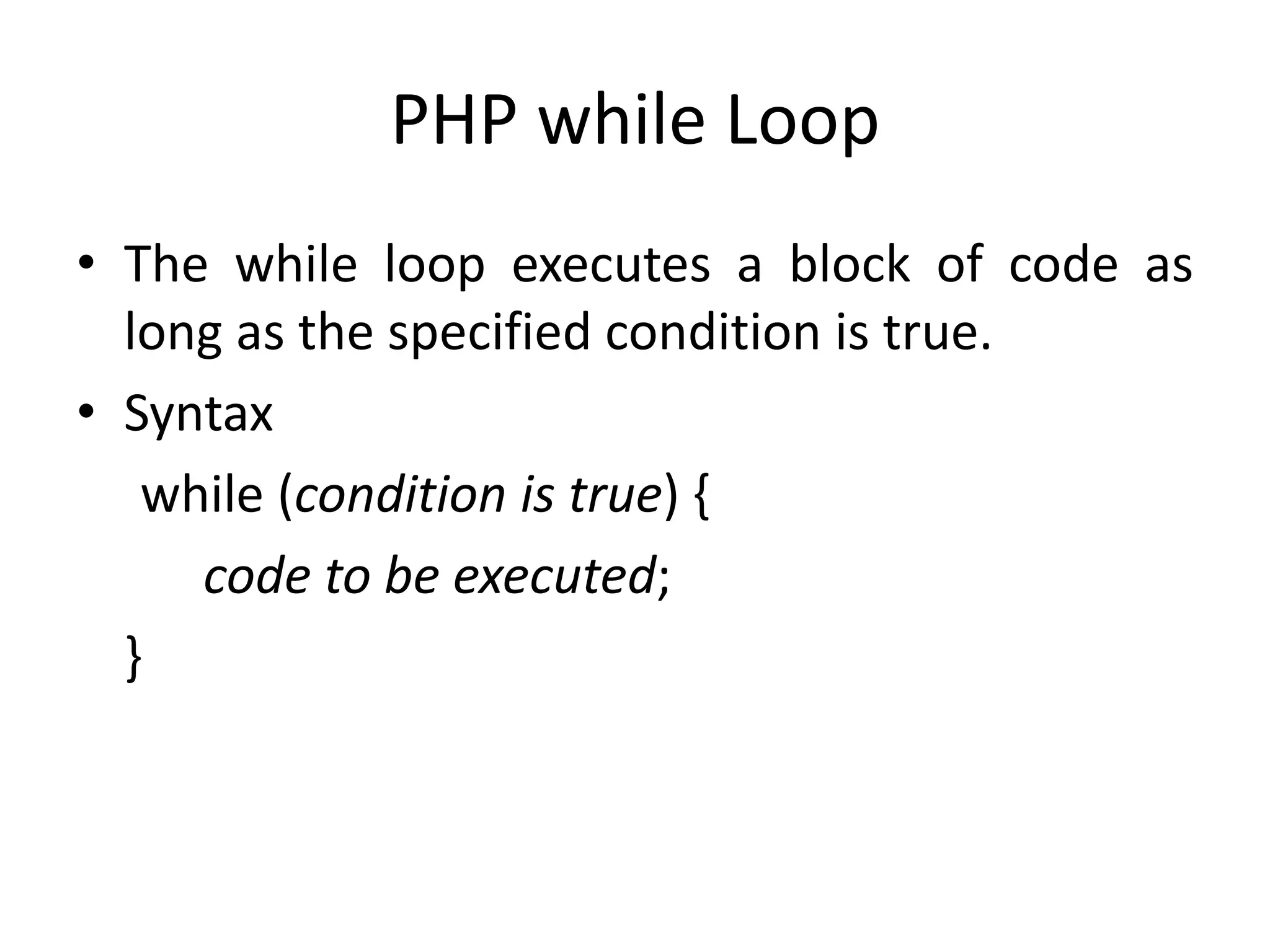
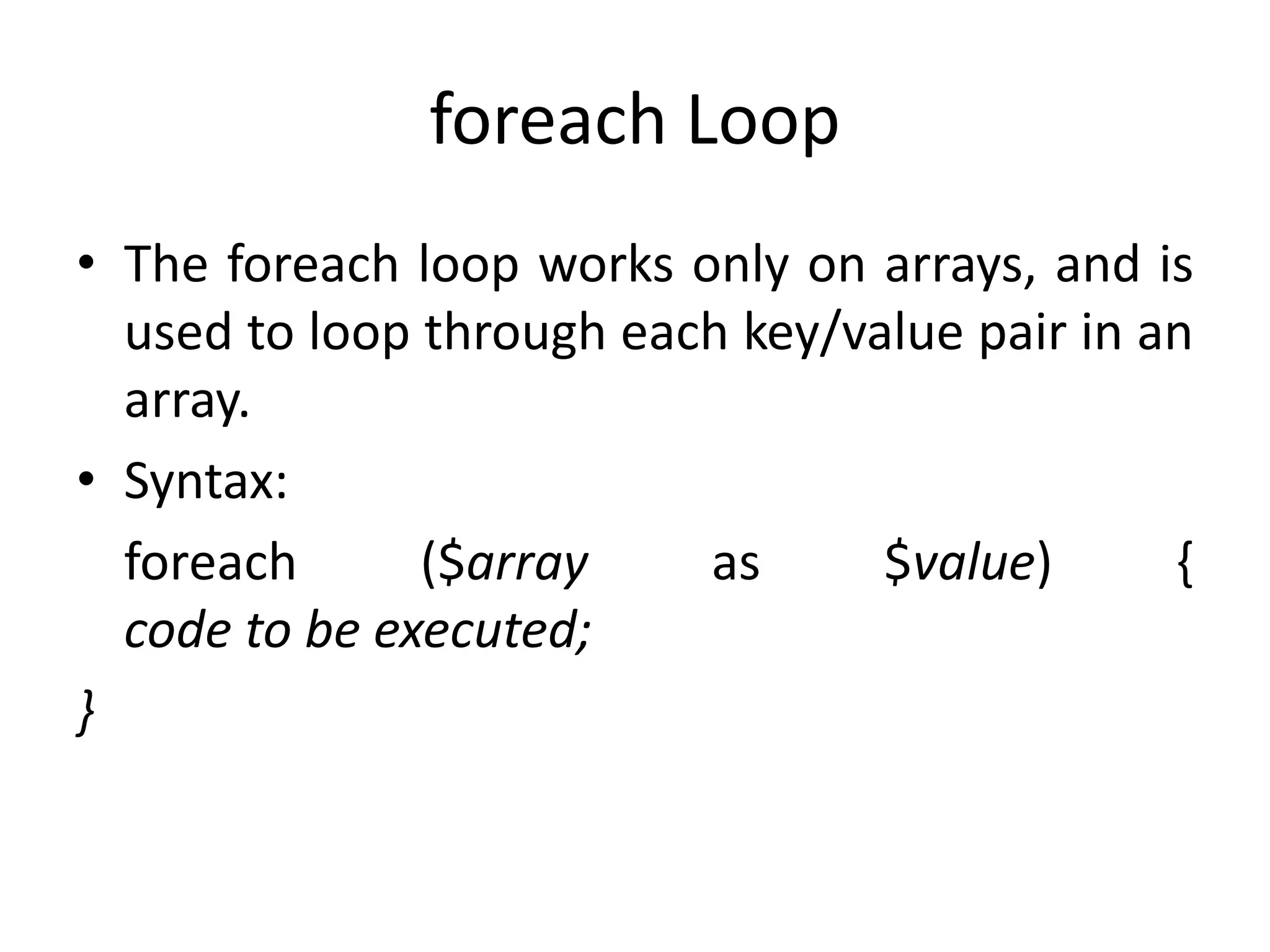
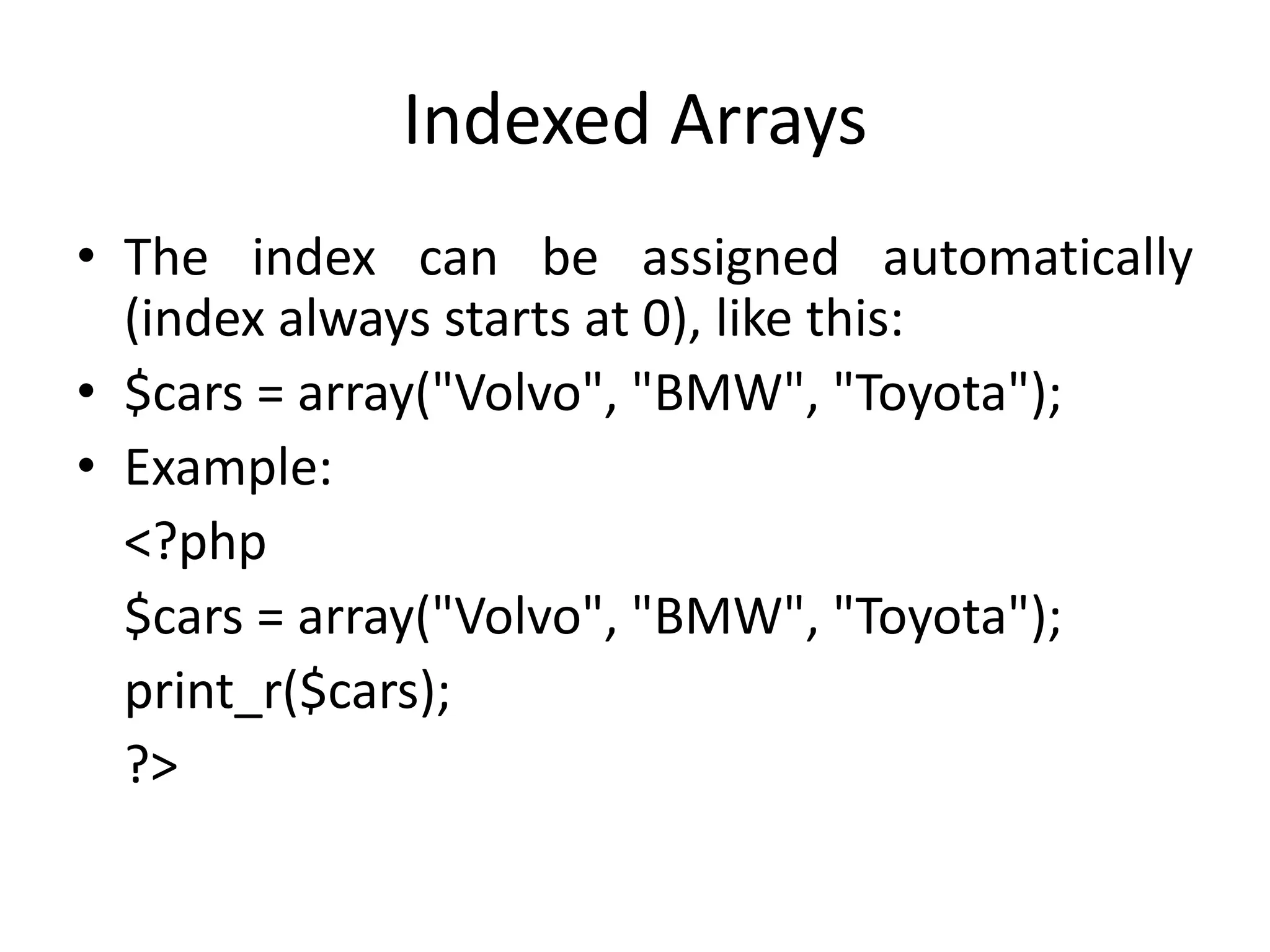
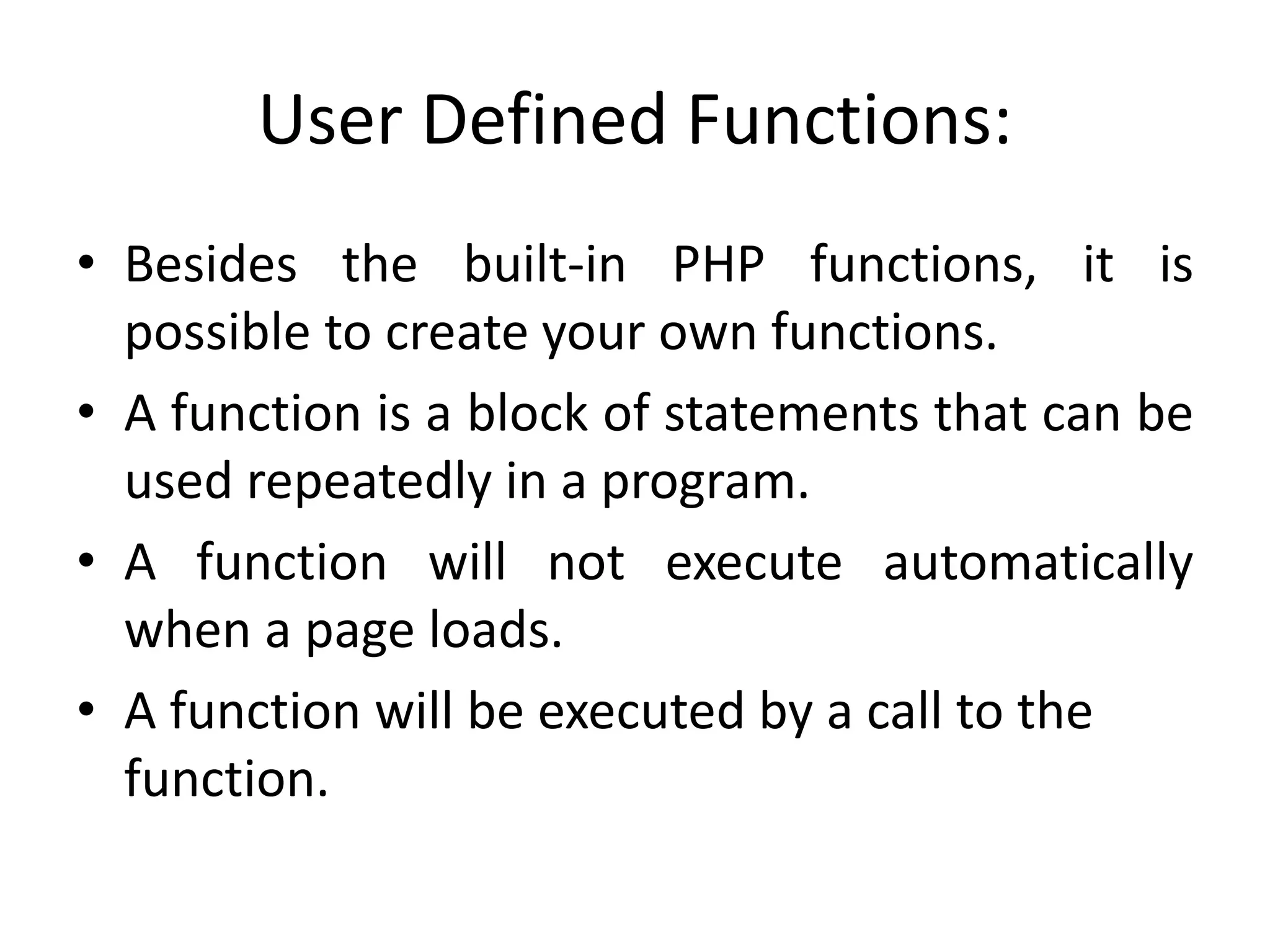
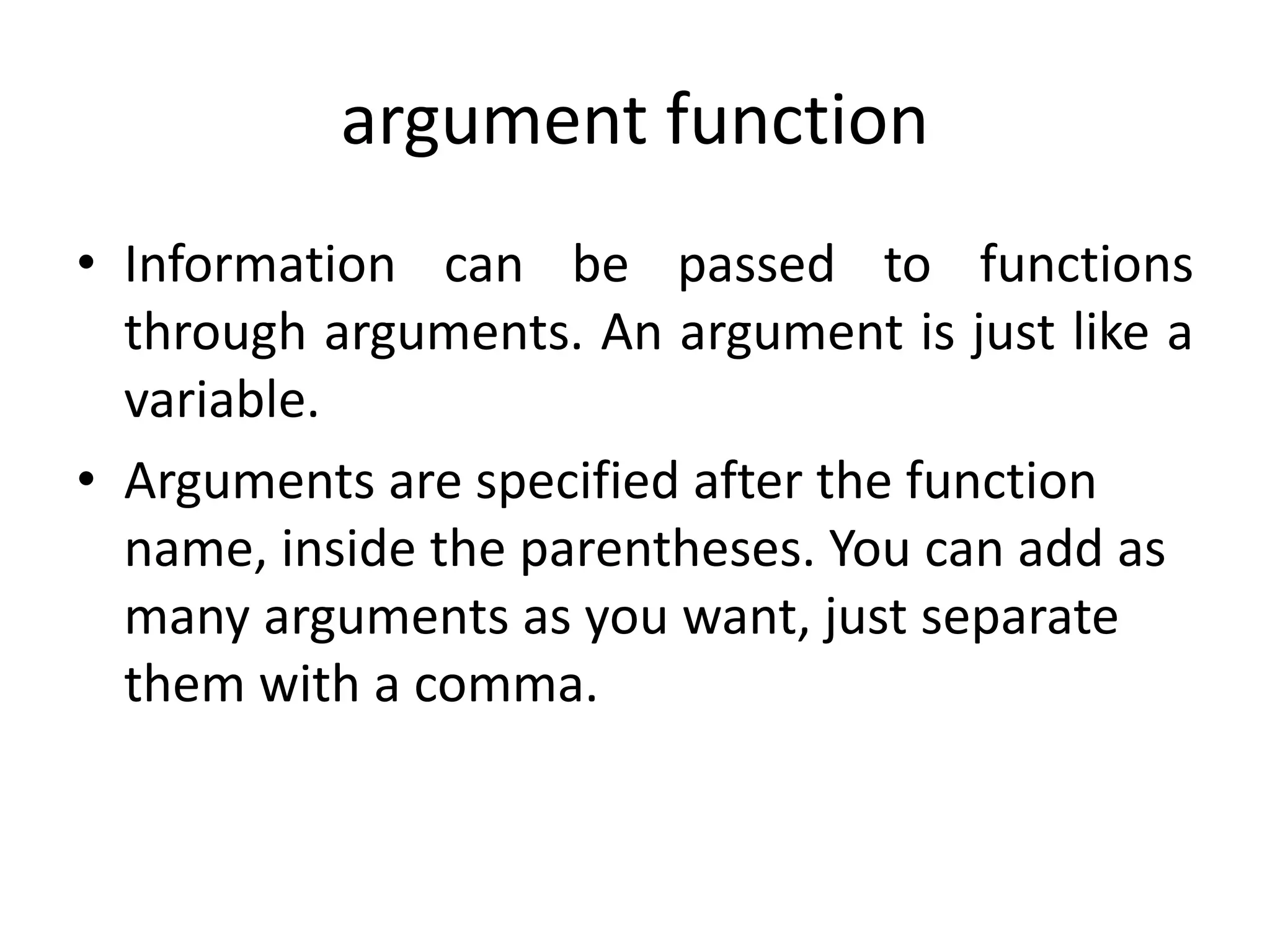
- The document then covers PHP variables, data types, operators, conditional and loop structures, functions, and arrays.