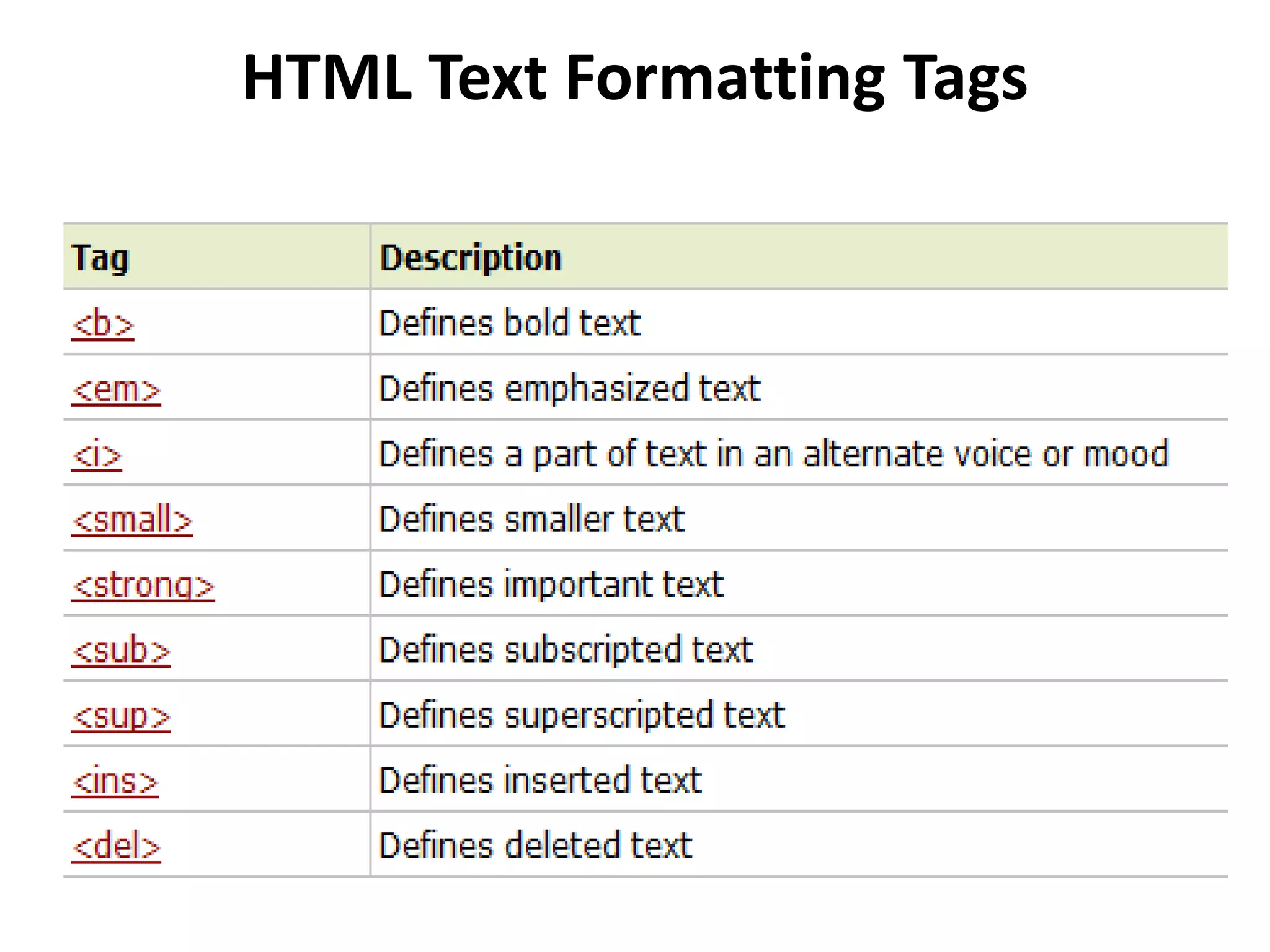
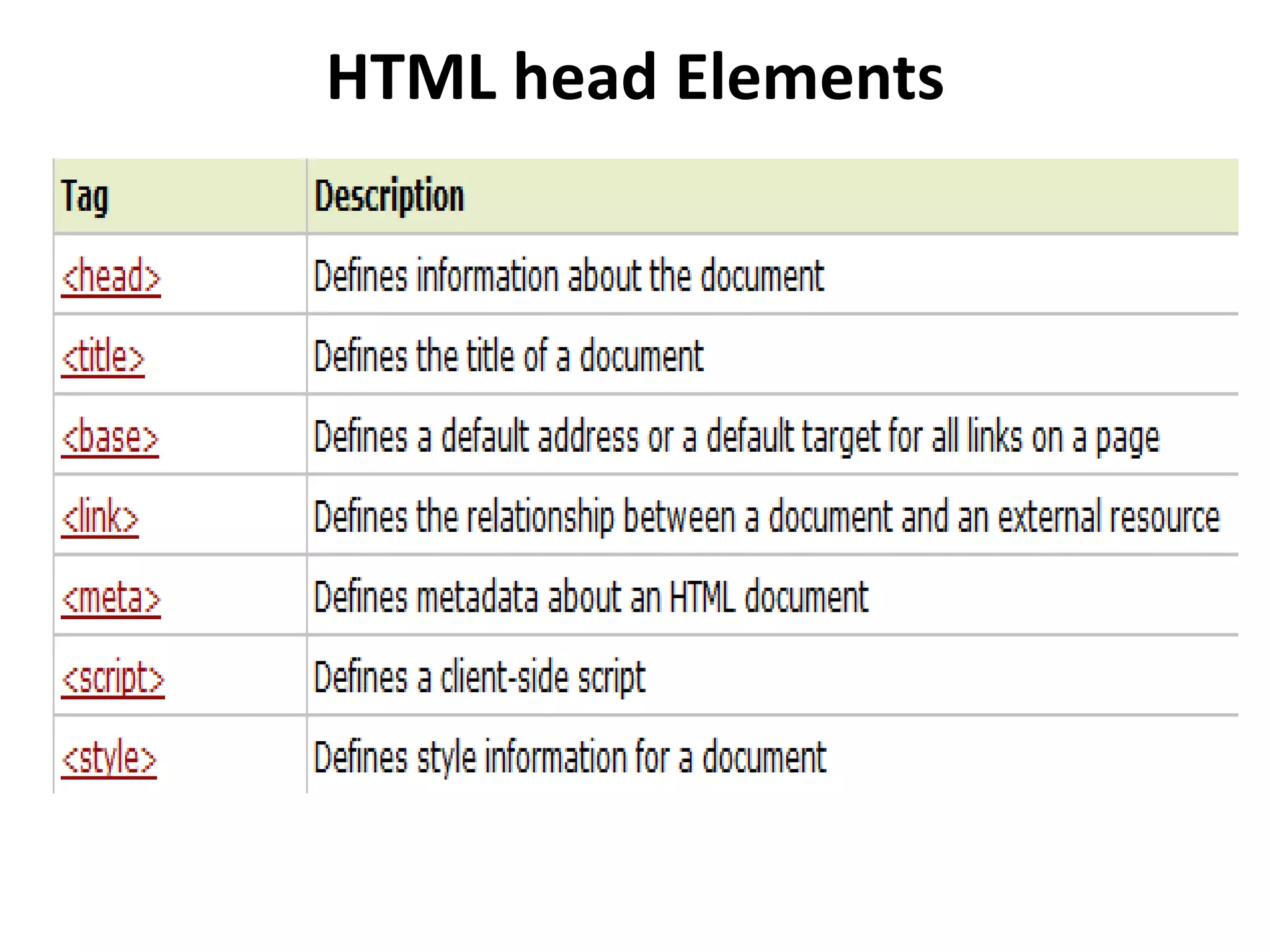
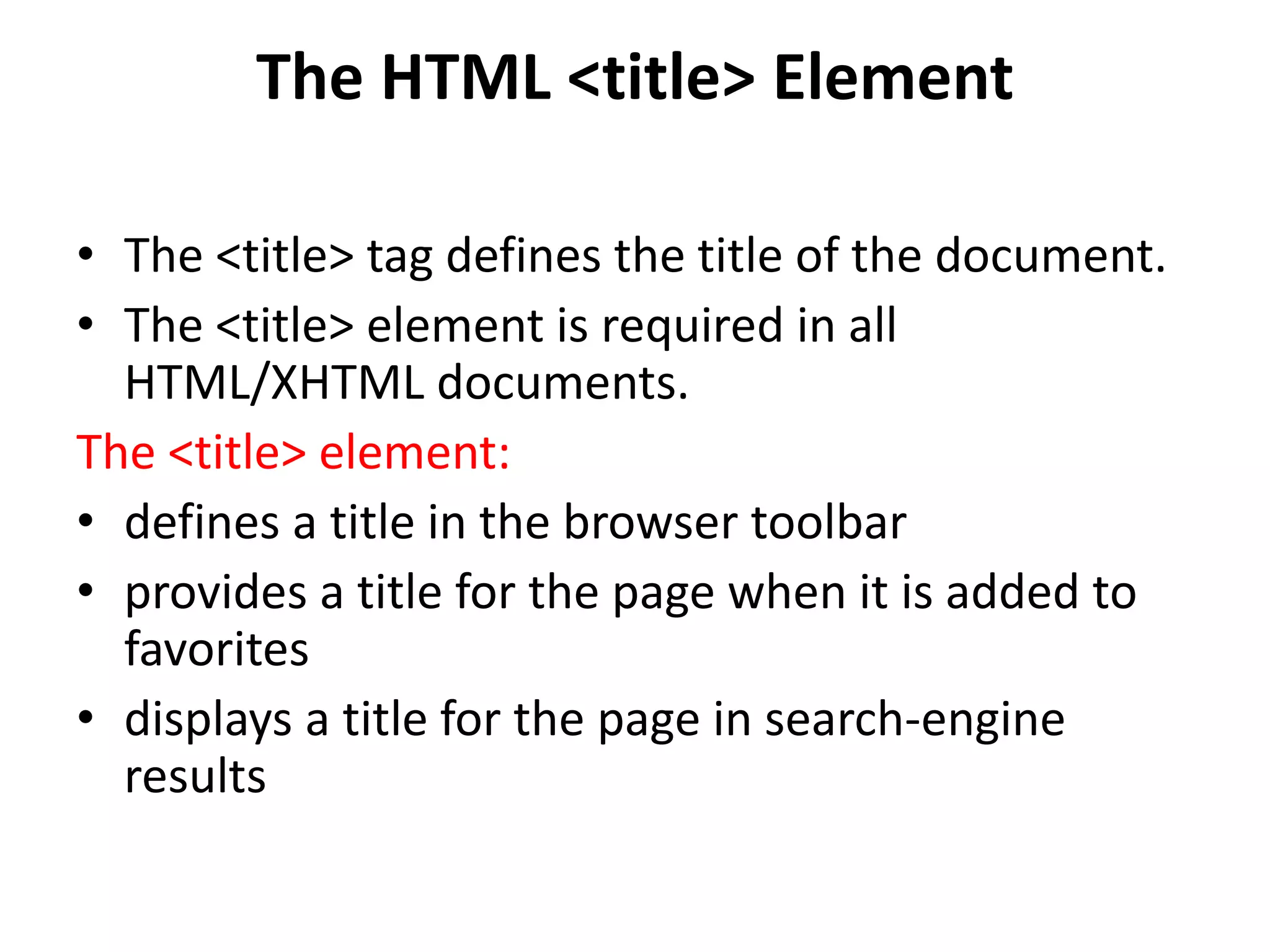
This document provides an overview of common HTML tags used for text formatting, links, and adding metadata to web pages. It describes tags such as <p>, <b>, <a>, <title>, <style>, <script>, <link>, and <meta> and provides examples of how to use each tag. It also explains how links are defined and styled in HTML and how images can be used as links. The document is intended as a tutorial on basic HTML tags and their usage.