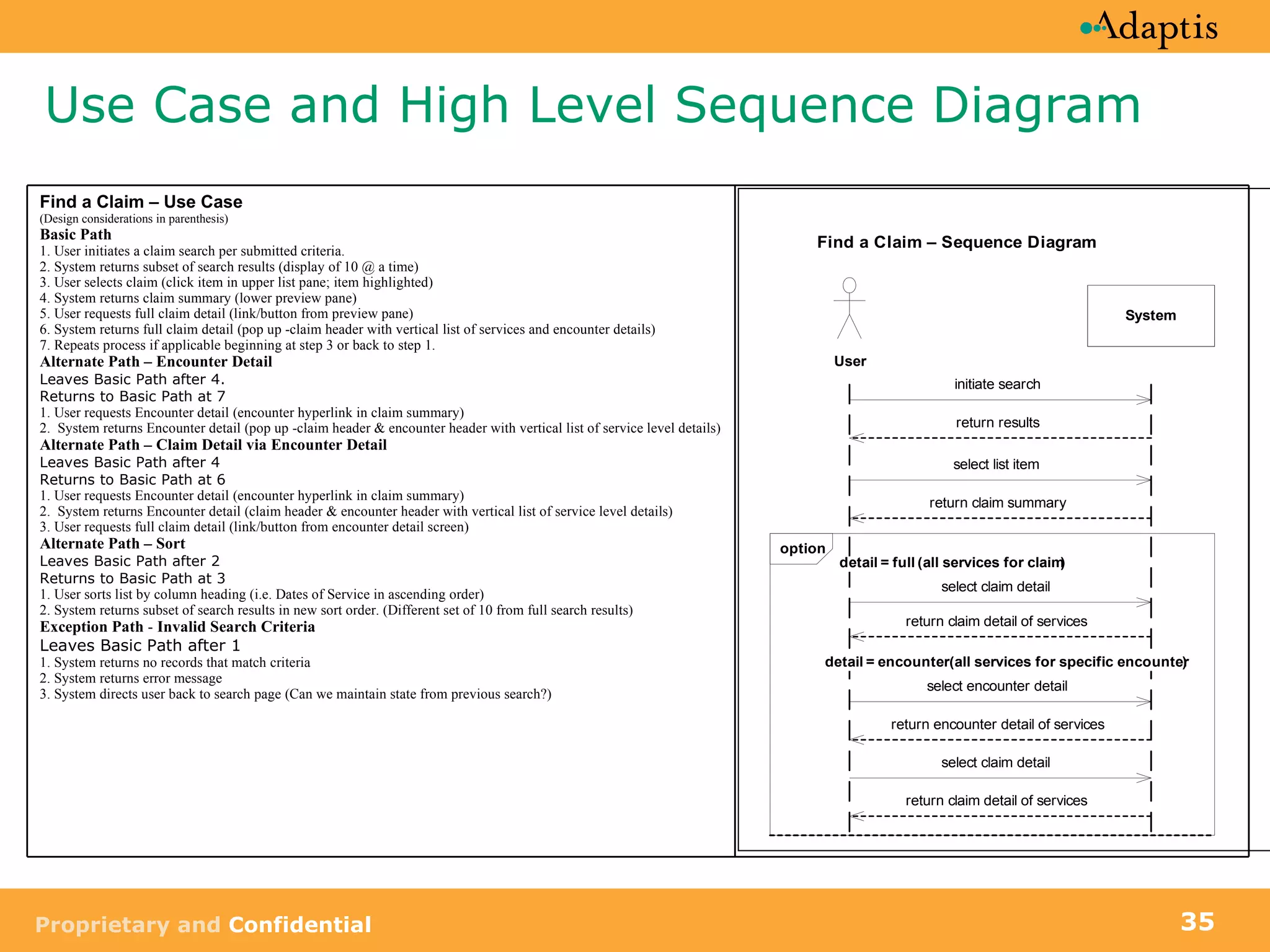
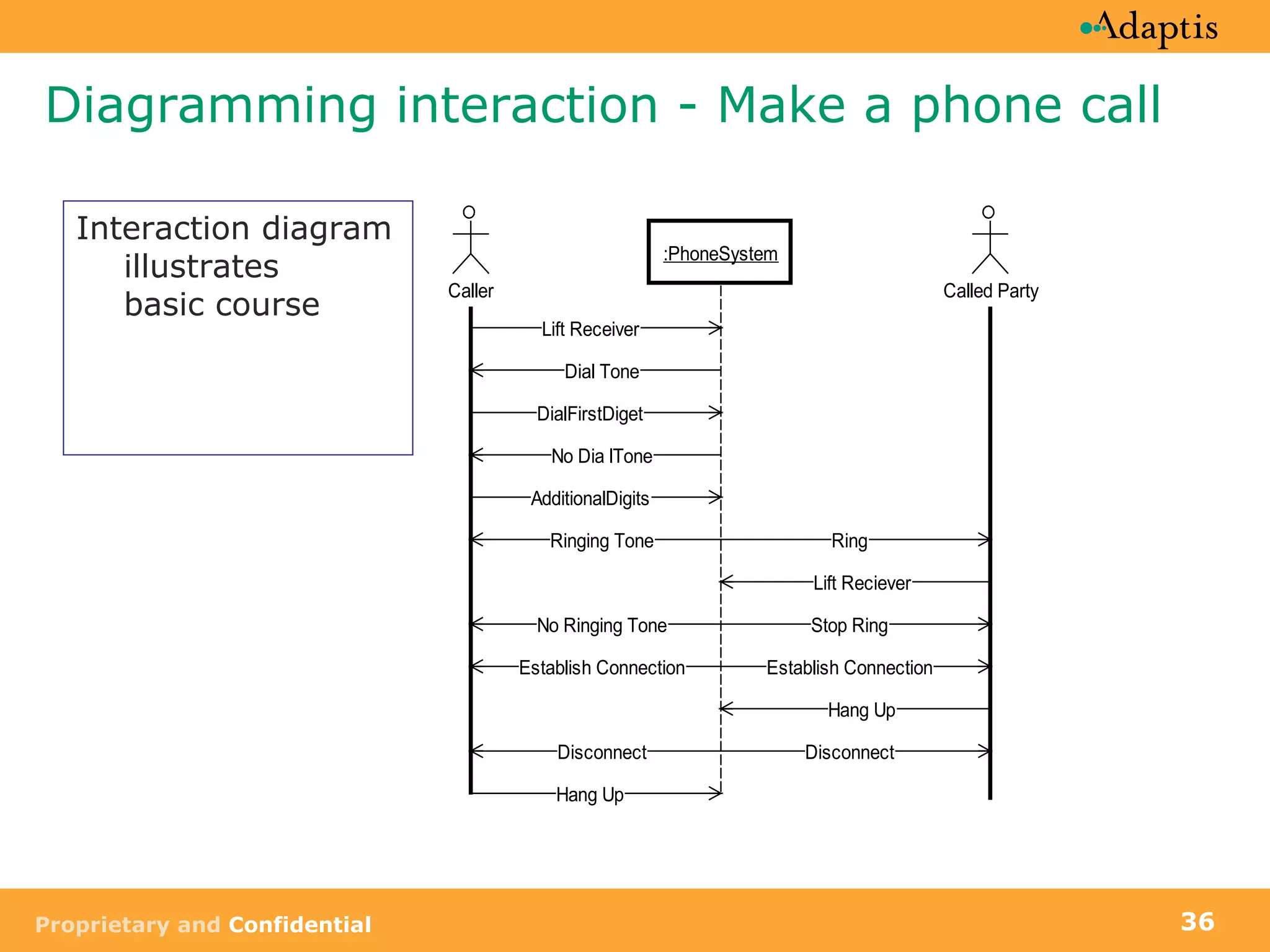
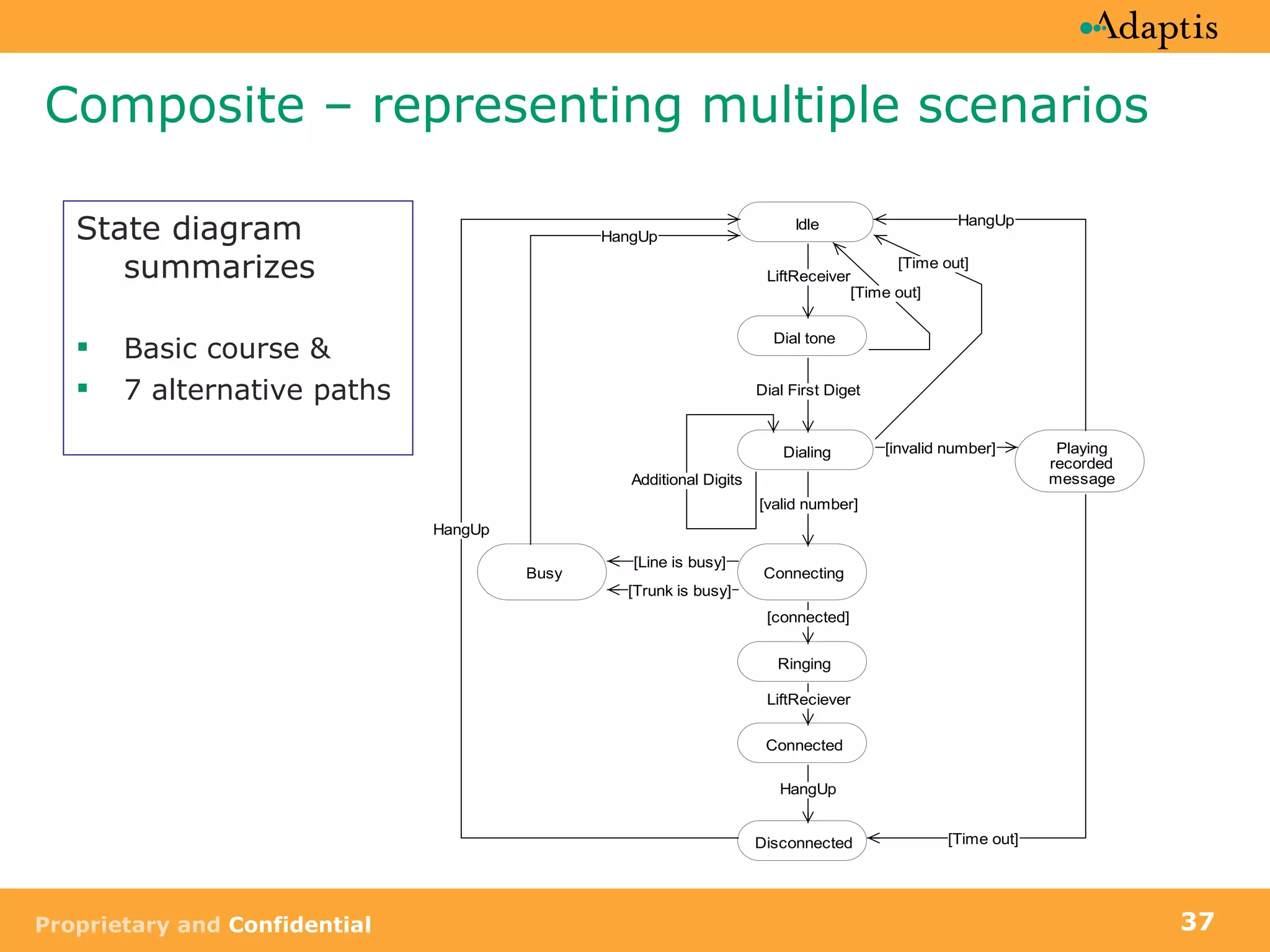
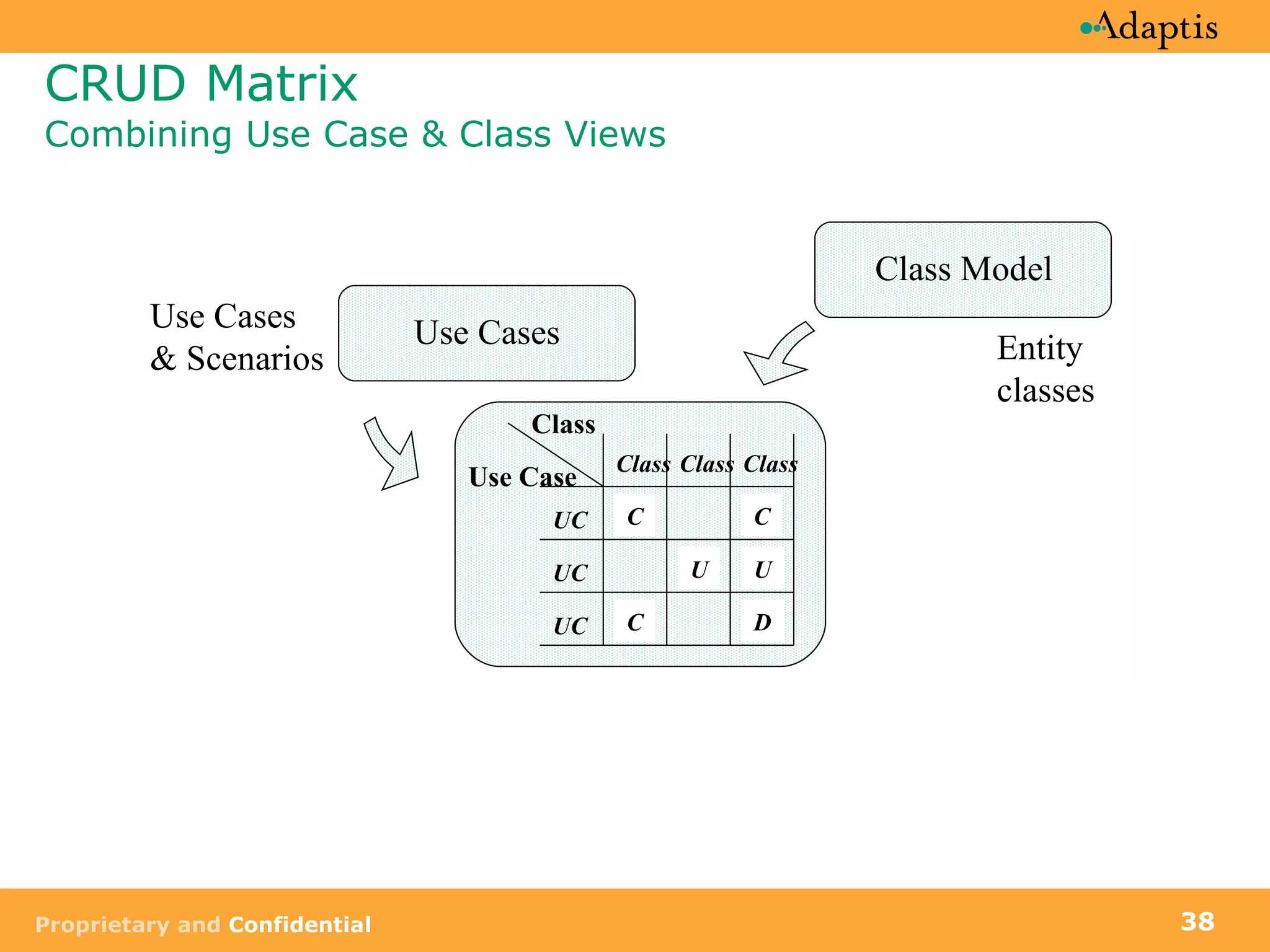
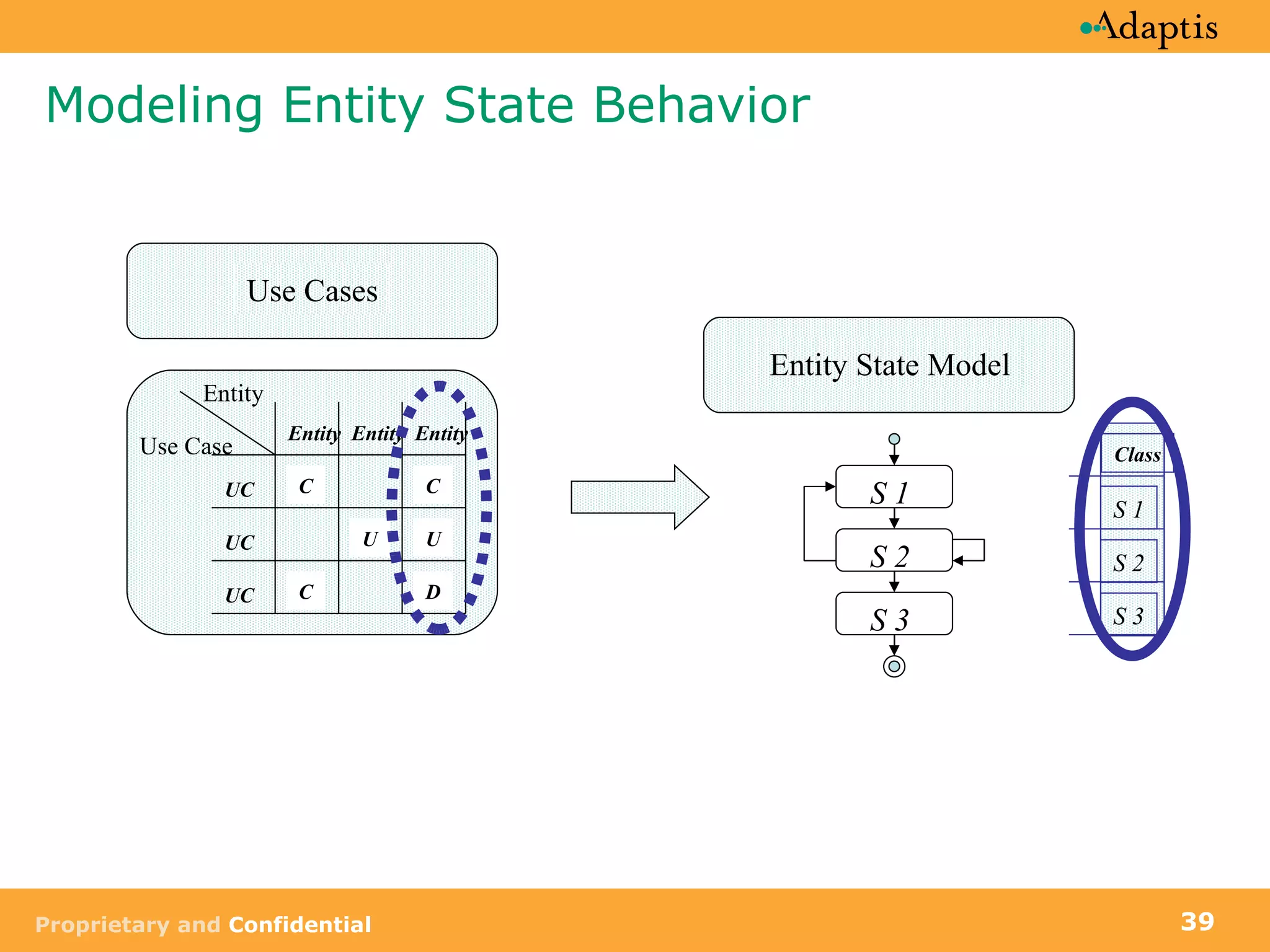
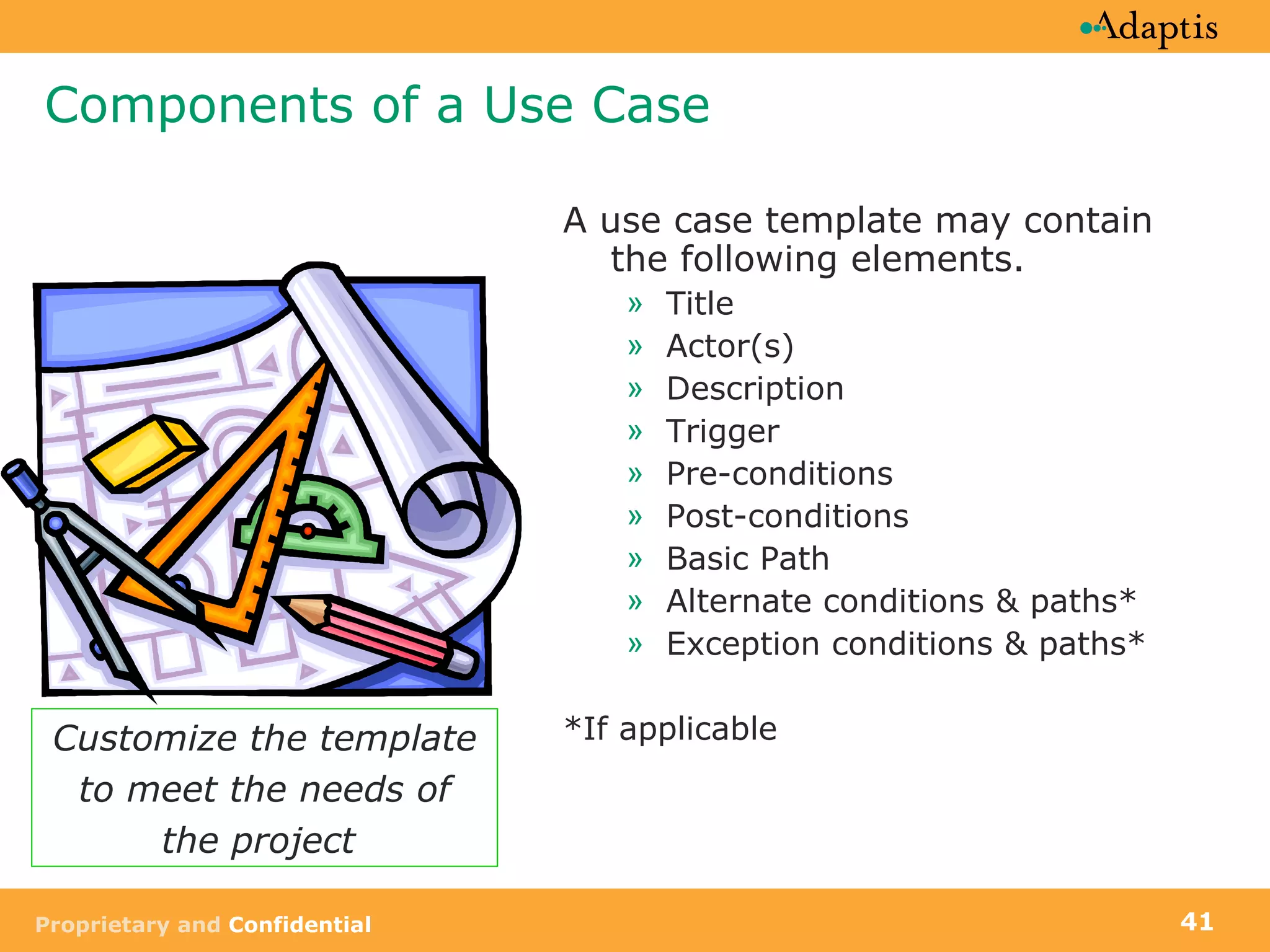
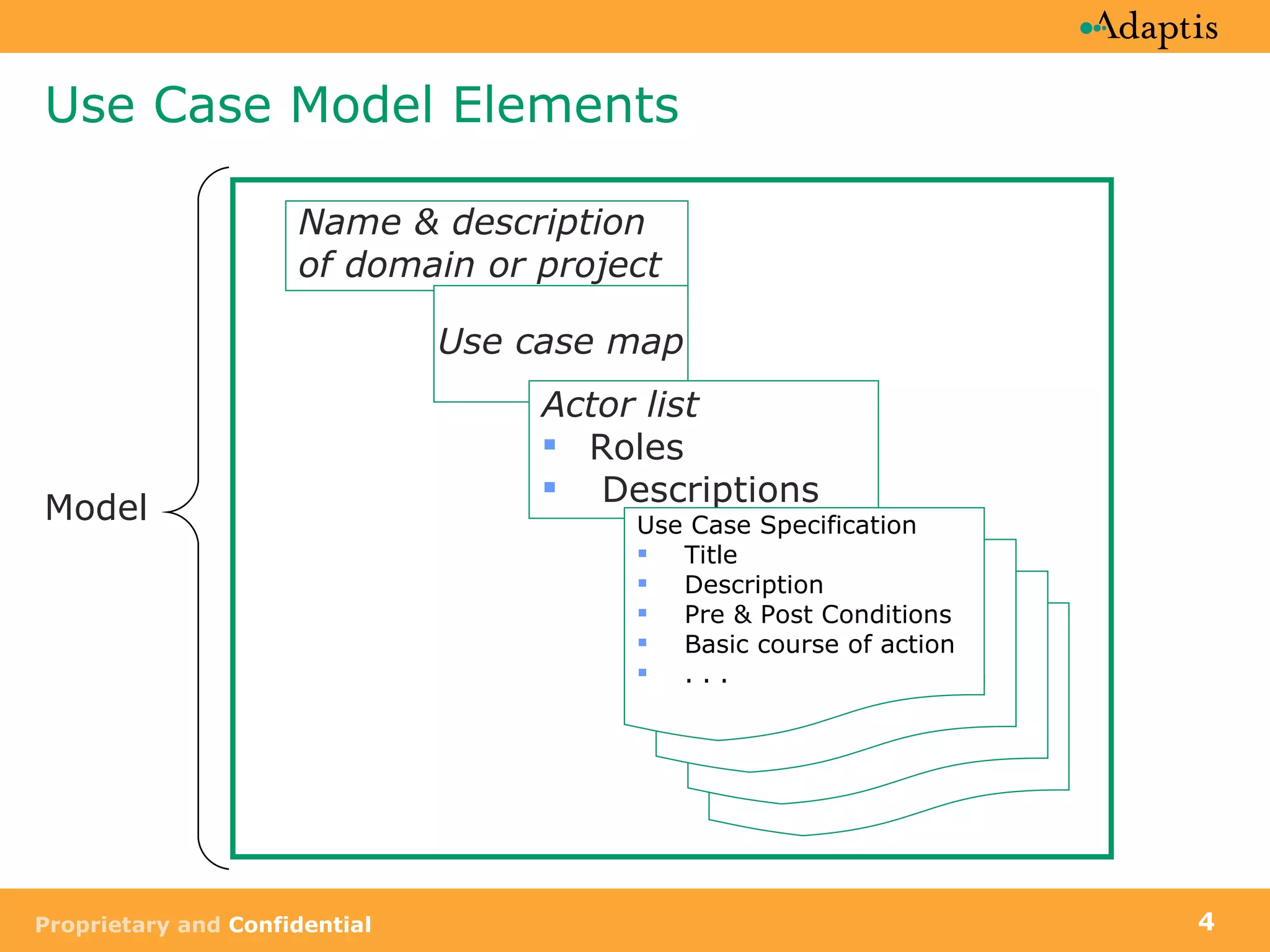
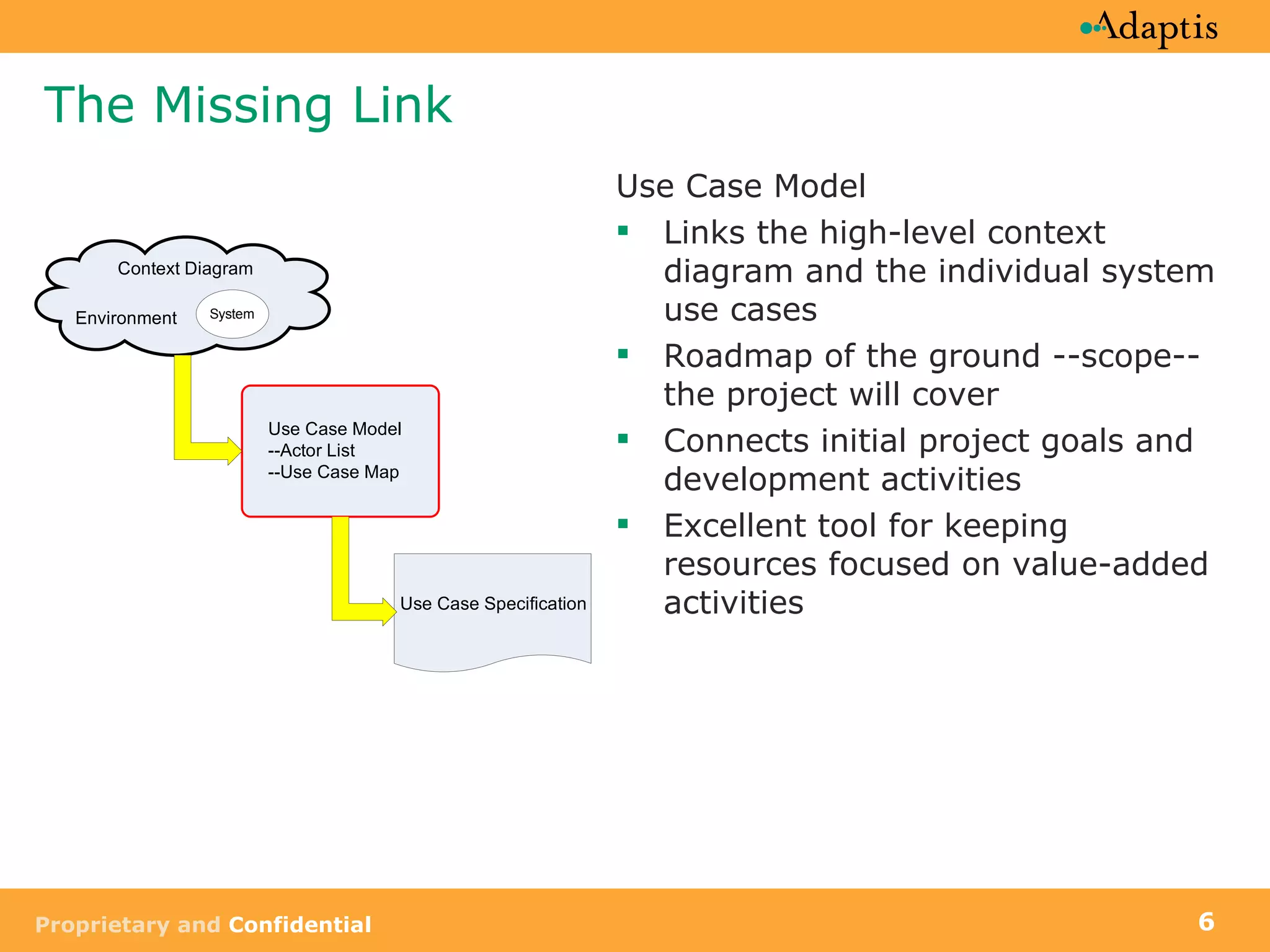
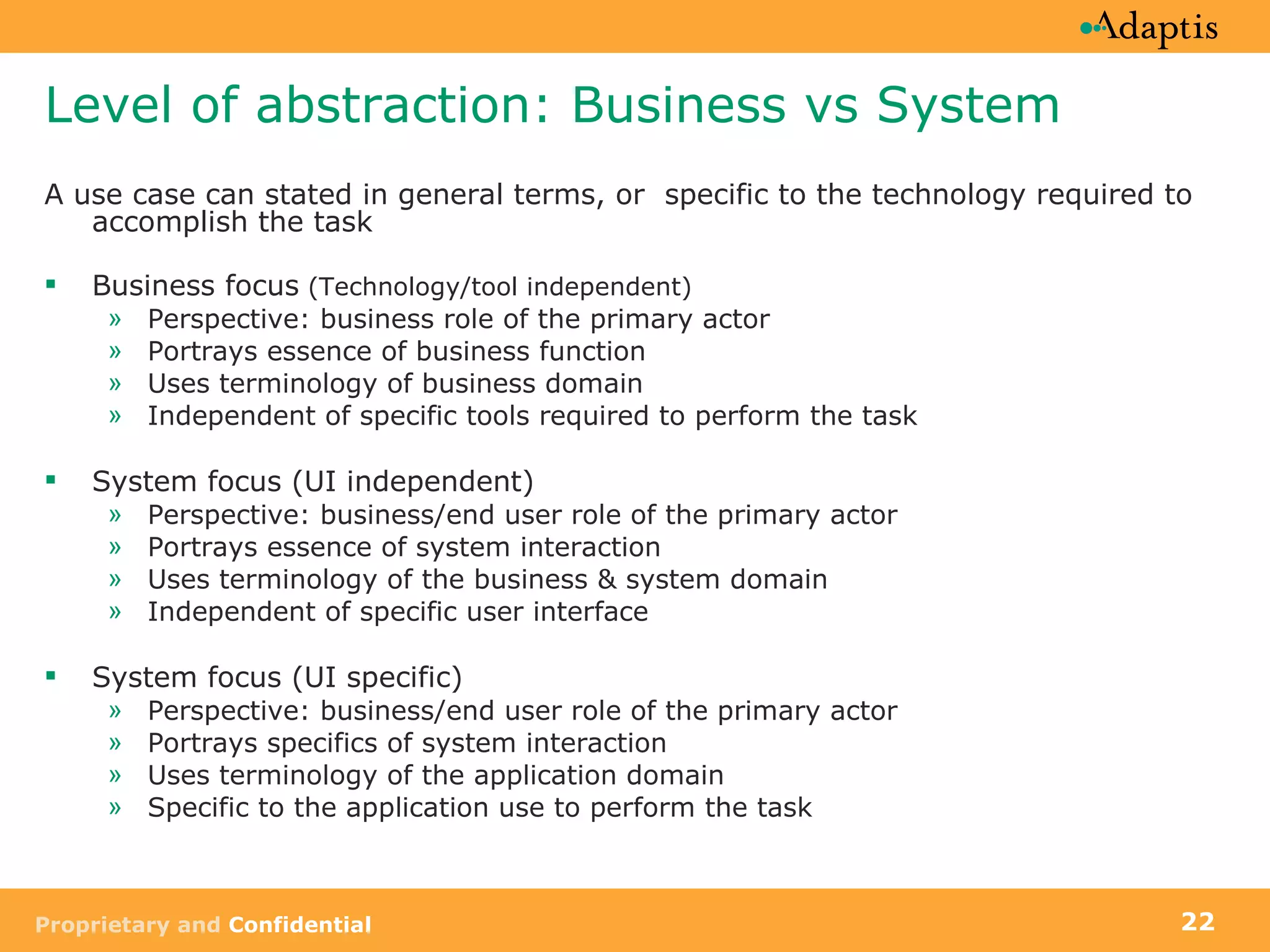
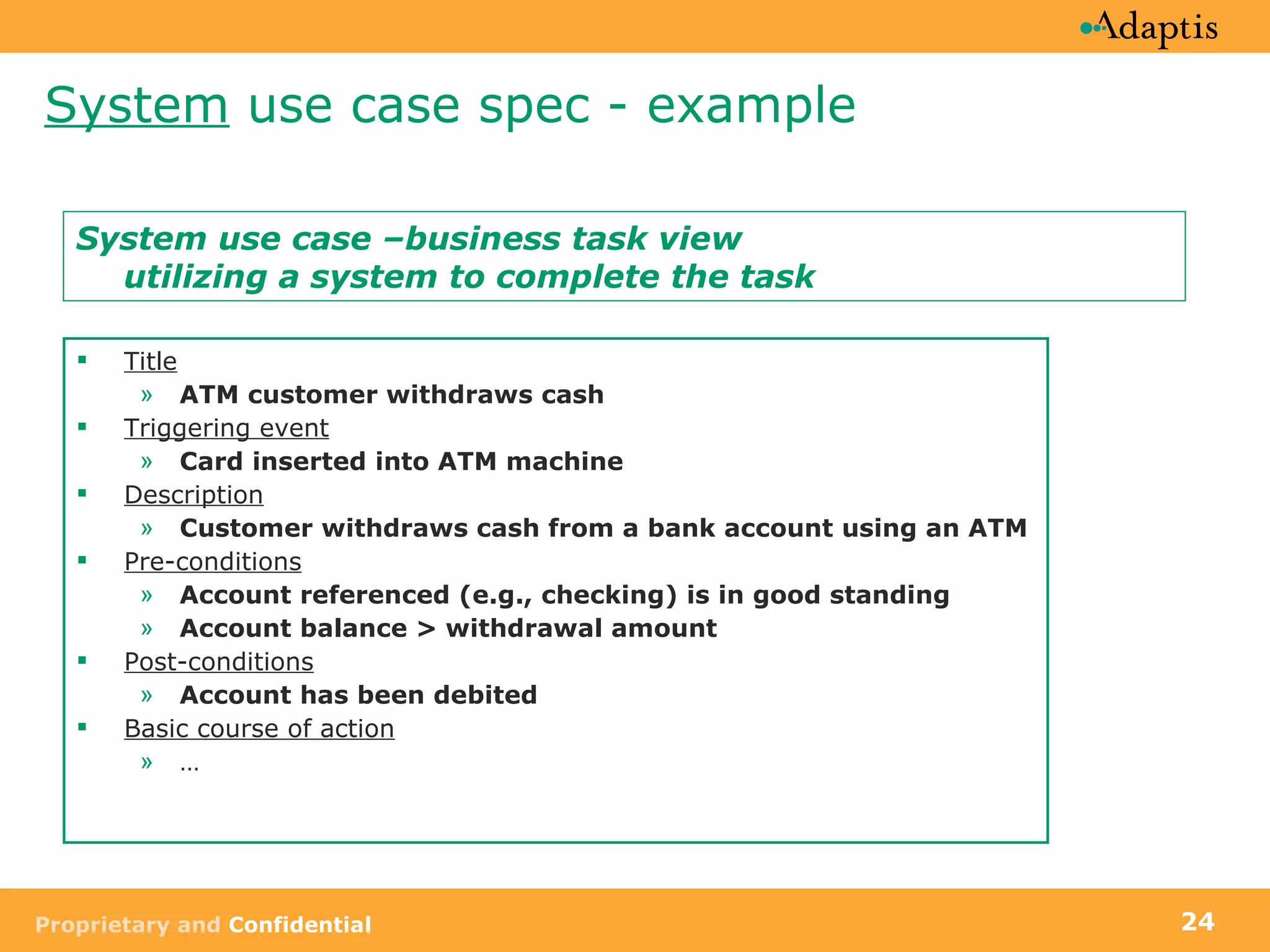
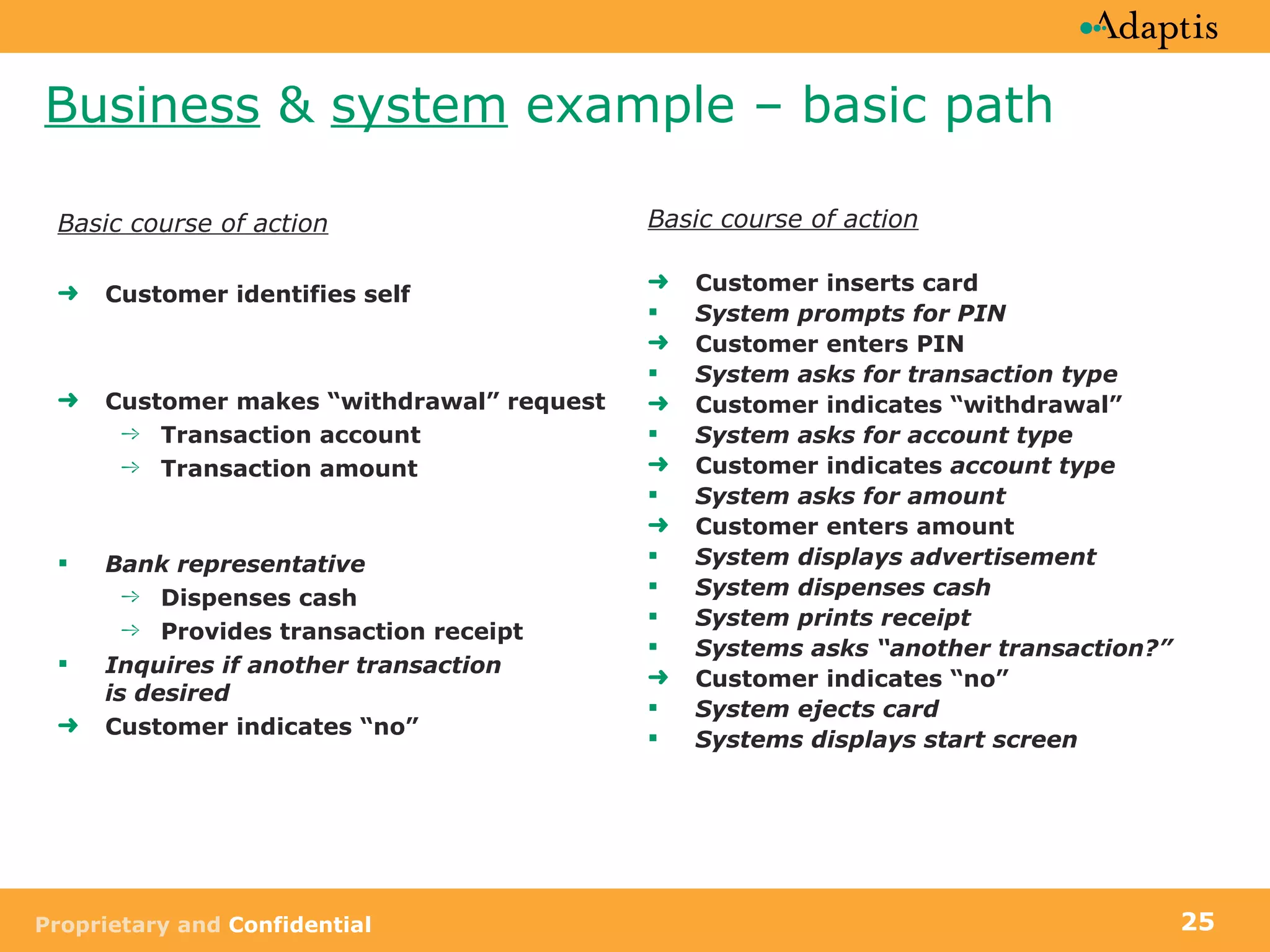
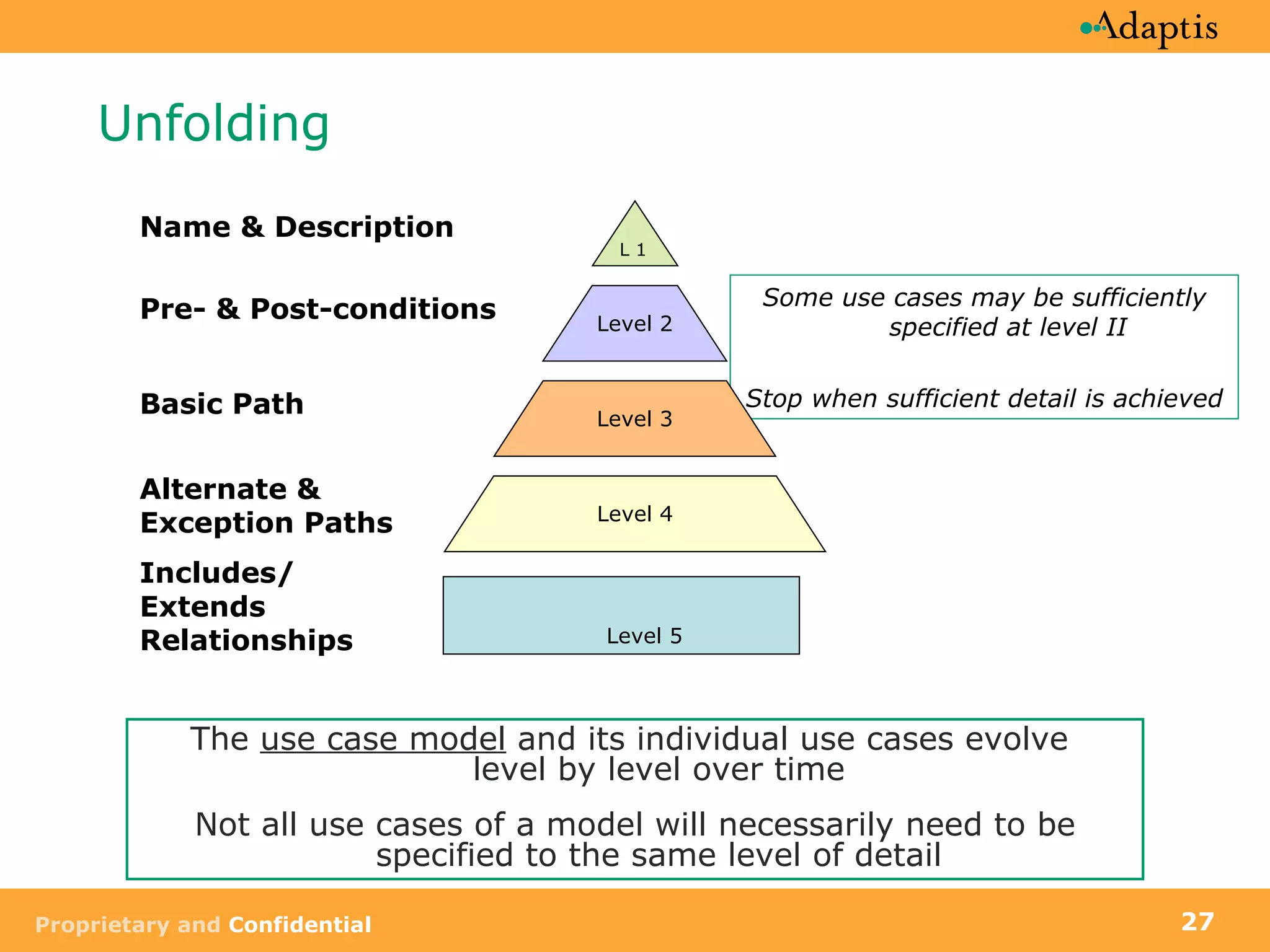
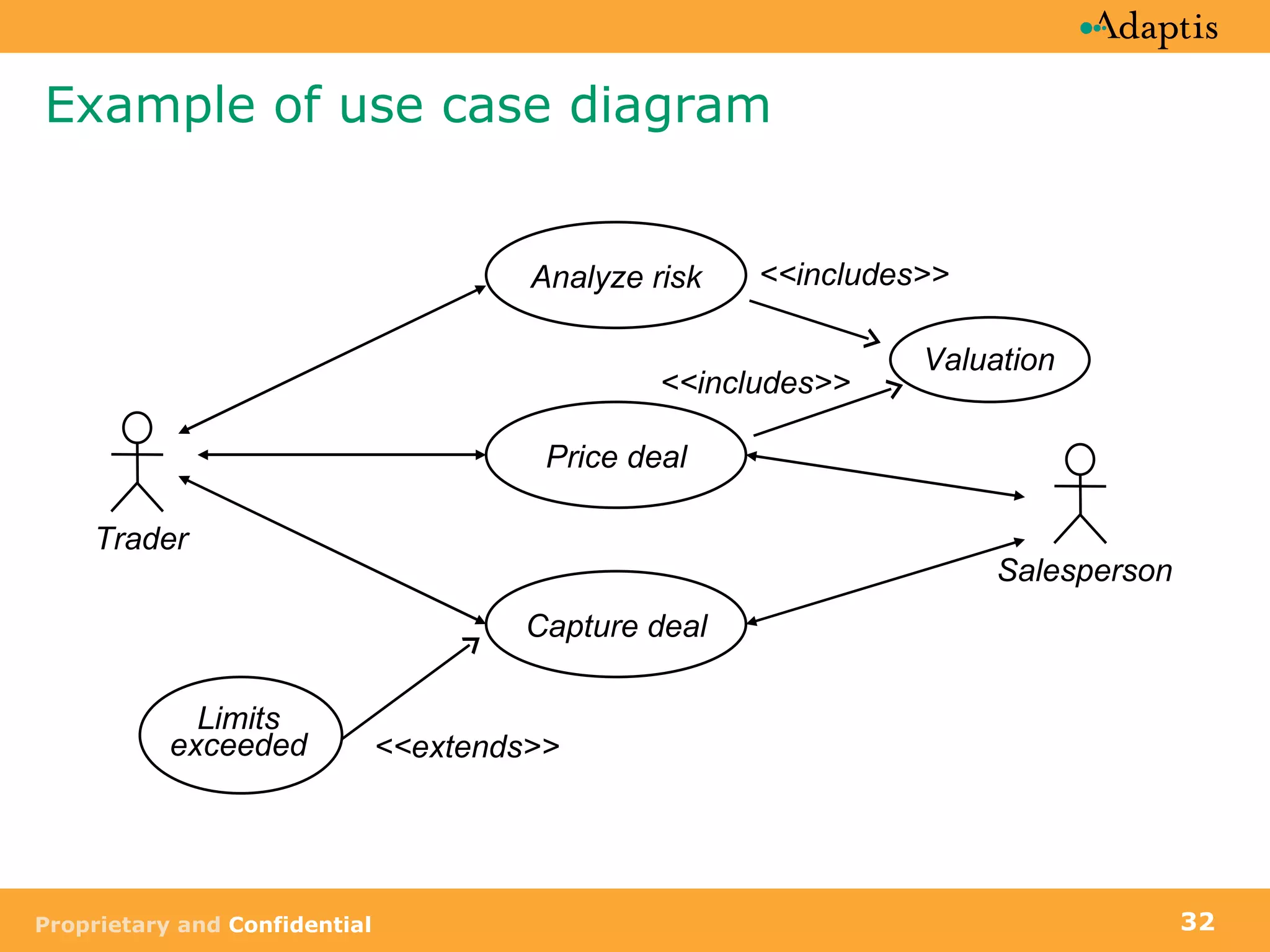
The document discusses use case modeling and provides details on key elements of use case models including:
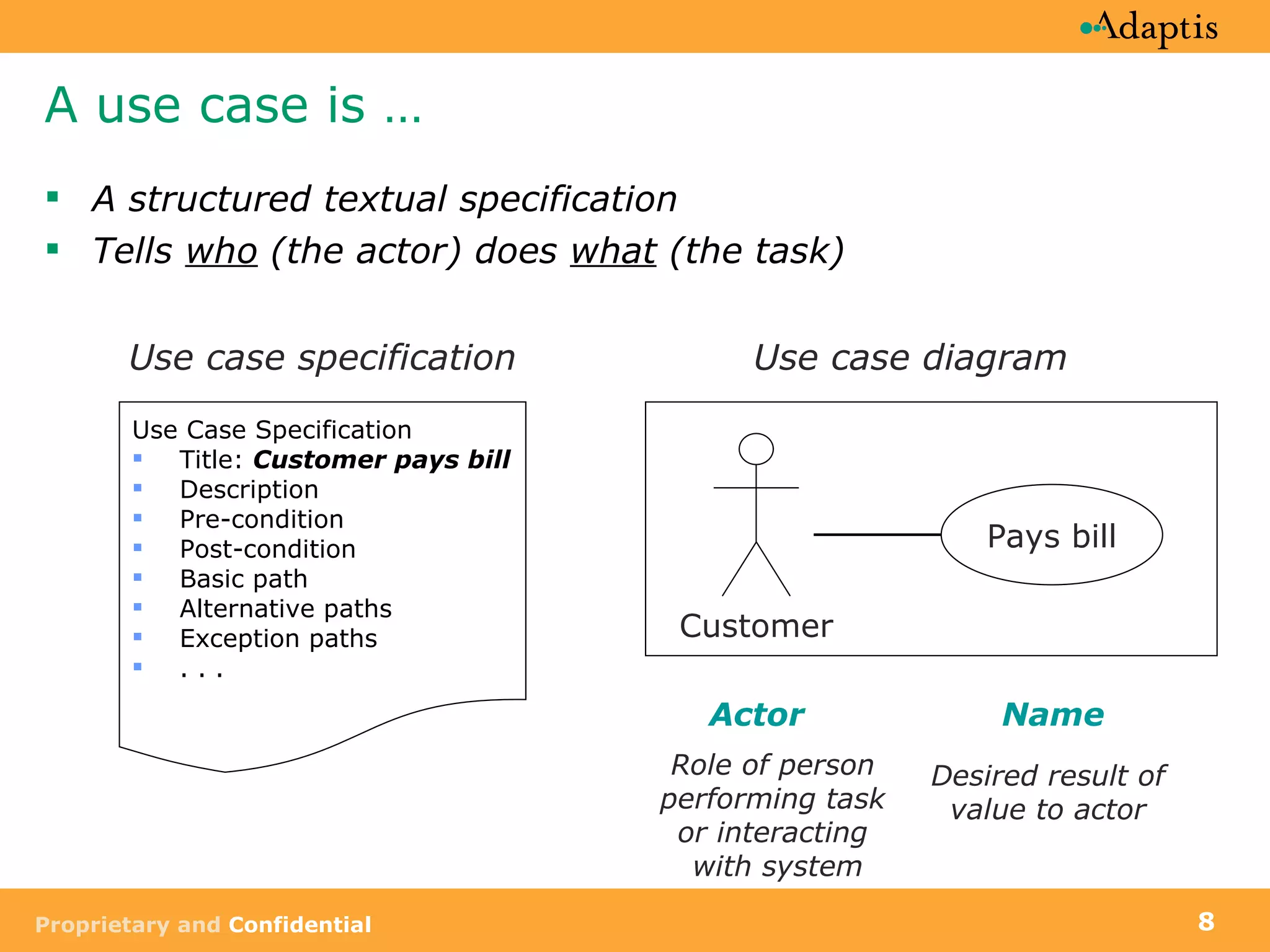
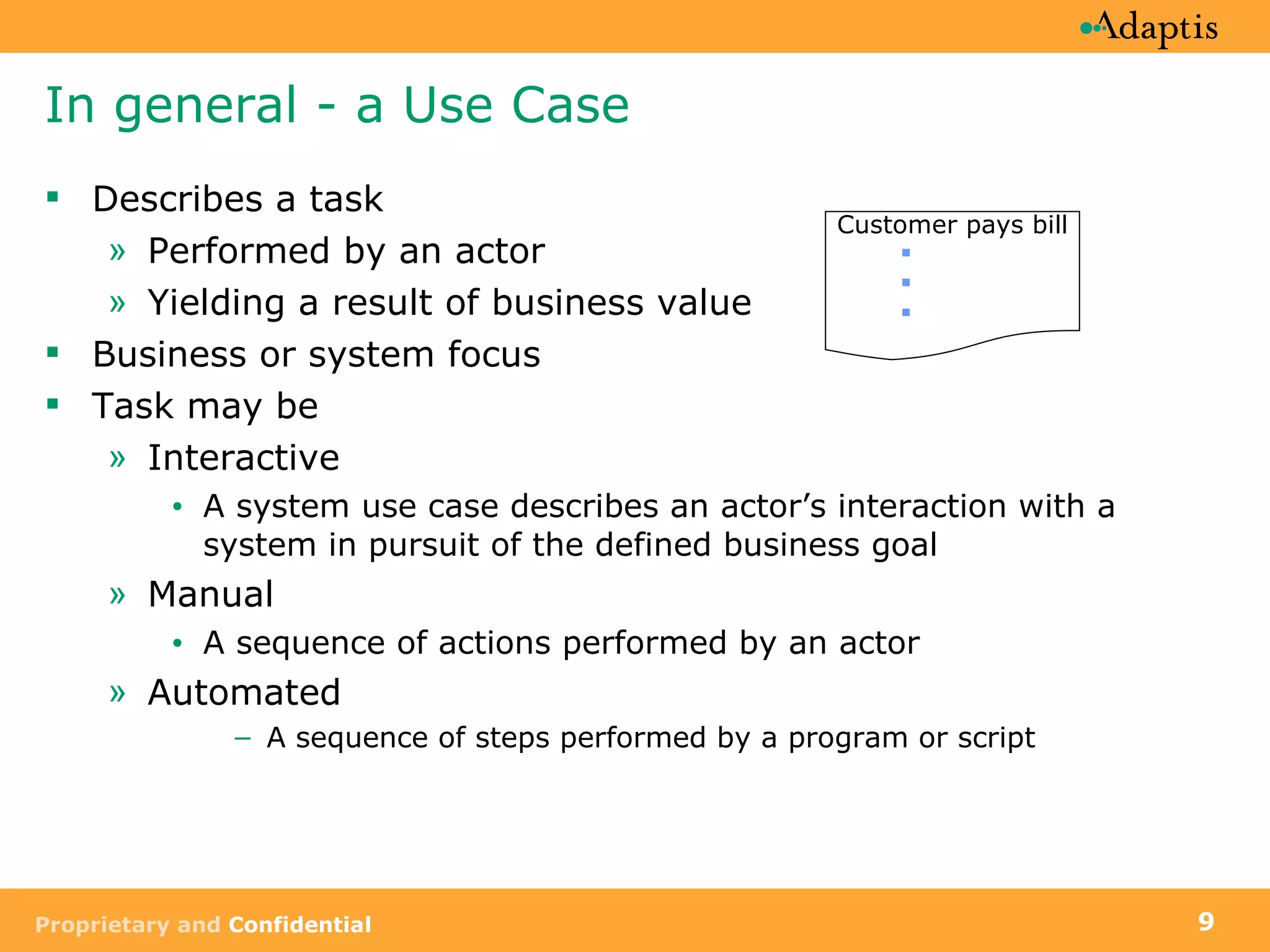
- A use case describes a task performed by an actor to achieve a goal
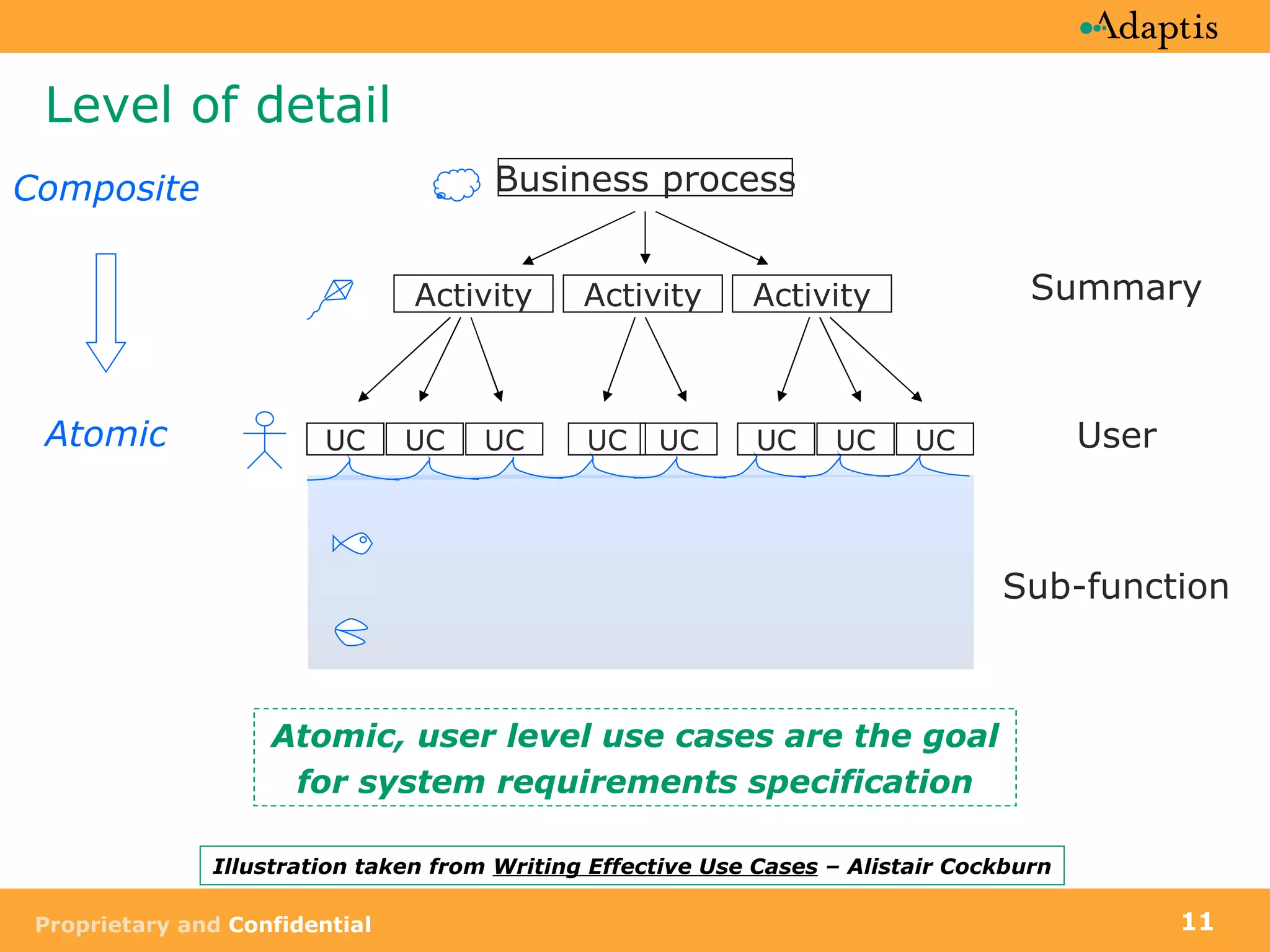
- Use cases can be at different levels of detail from summary to atomic
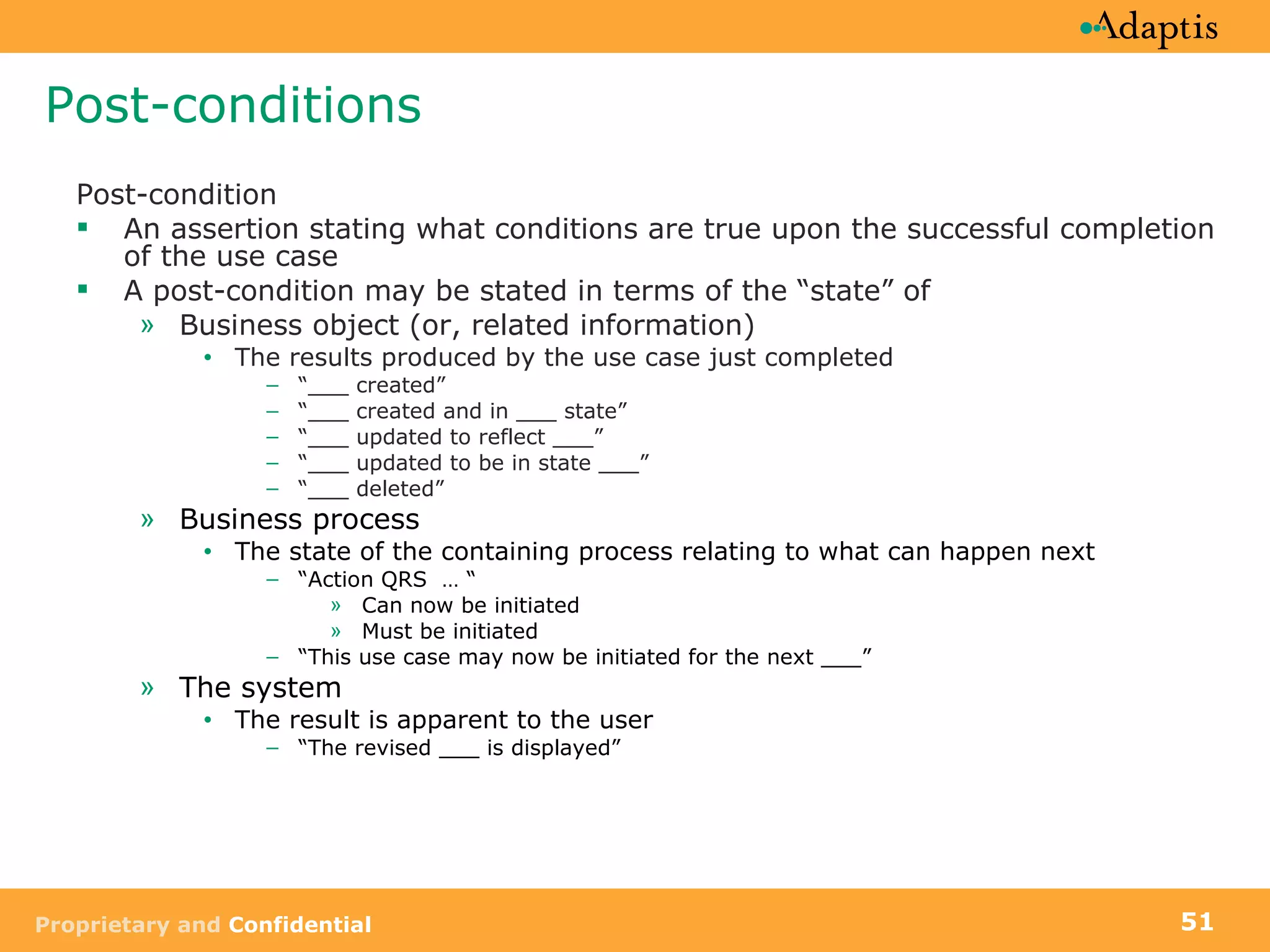
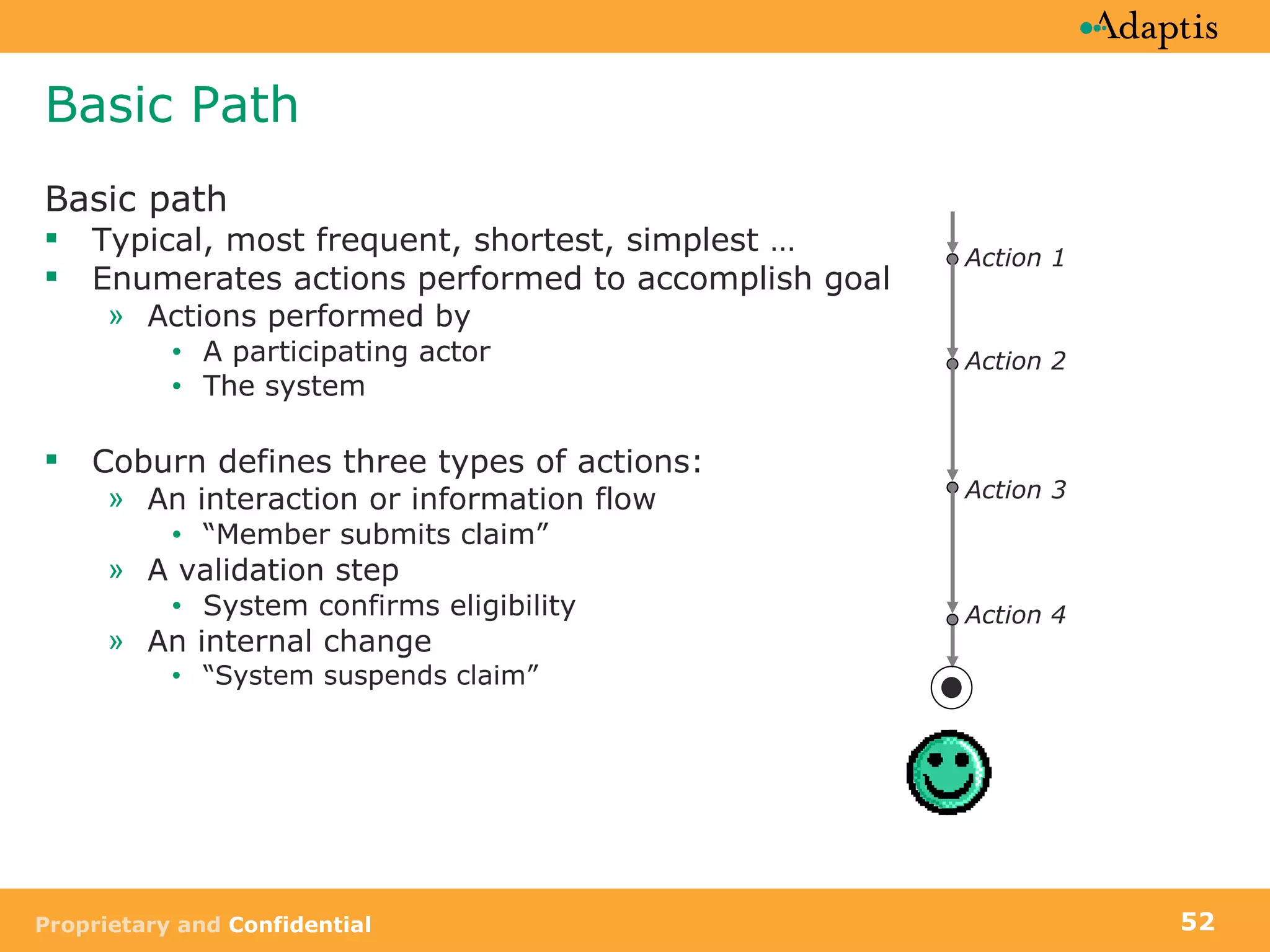
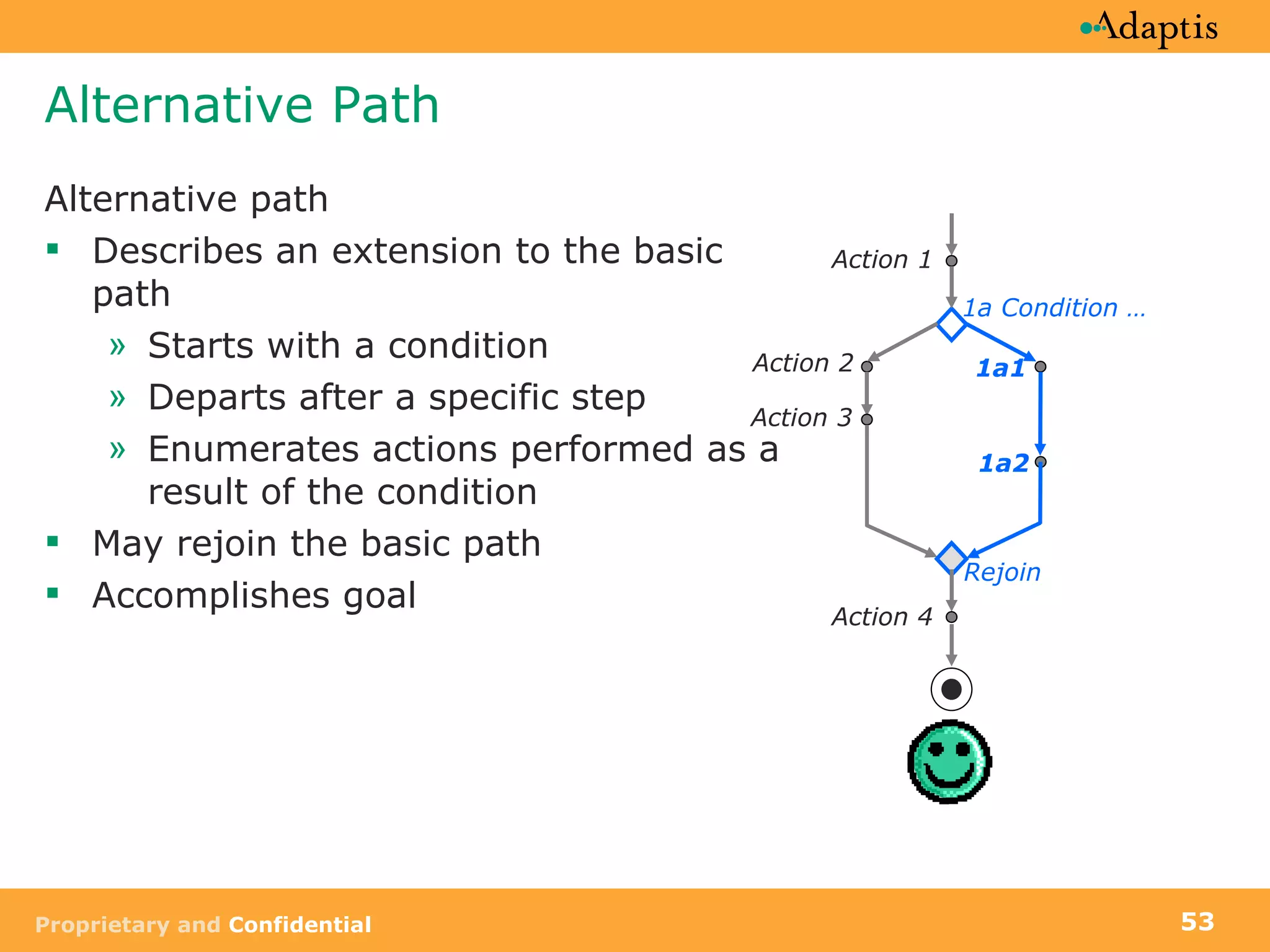
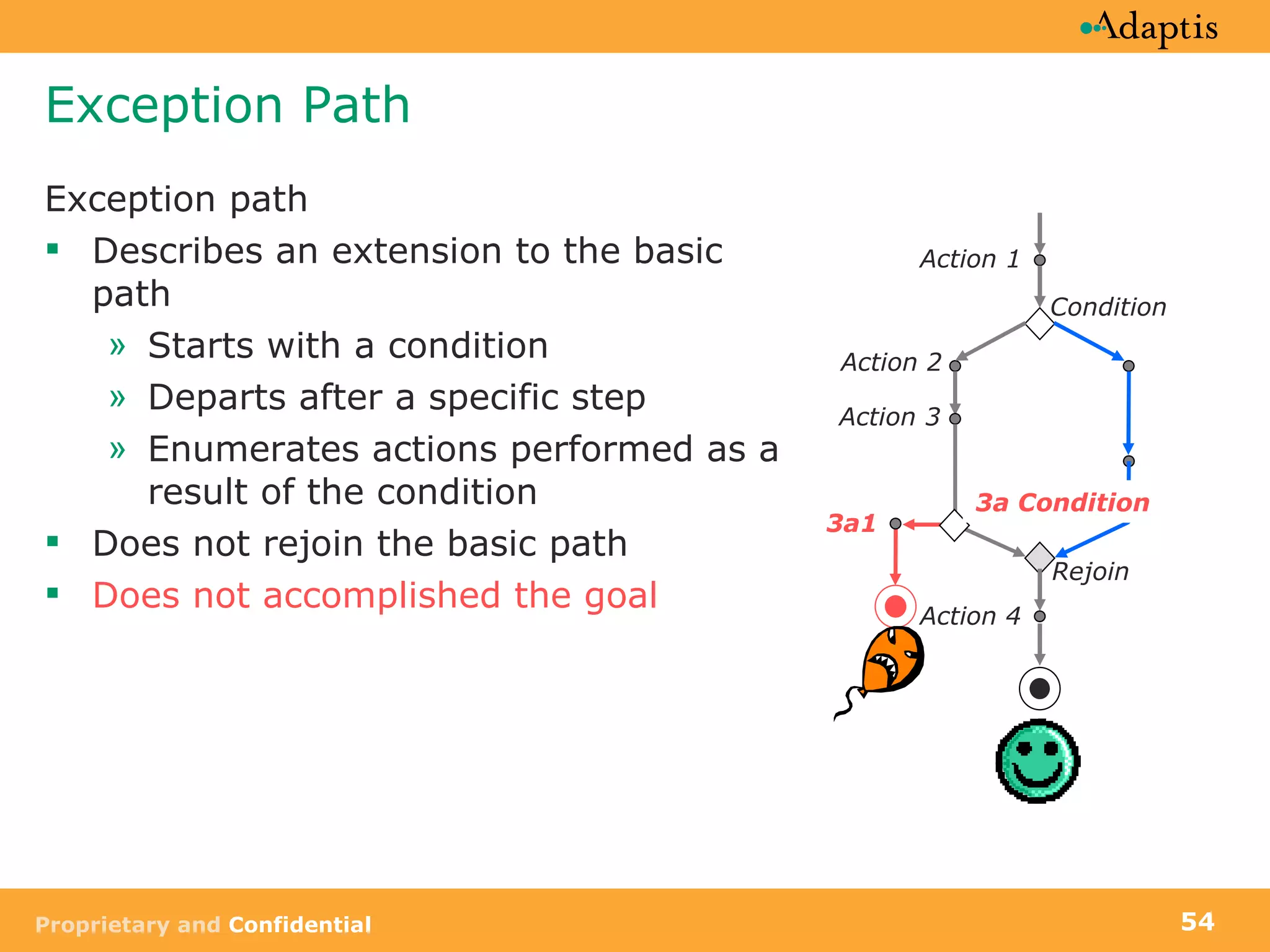
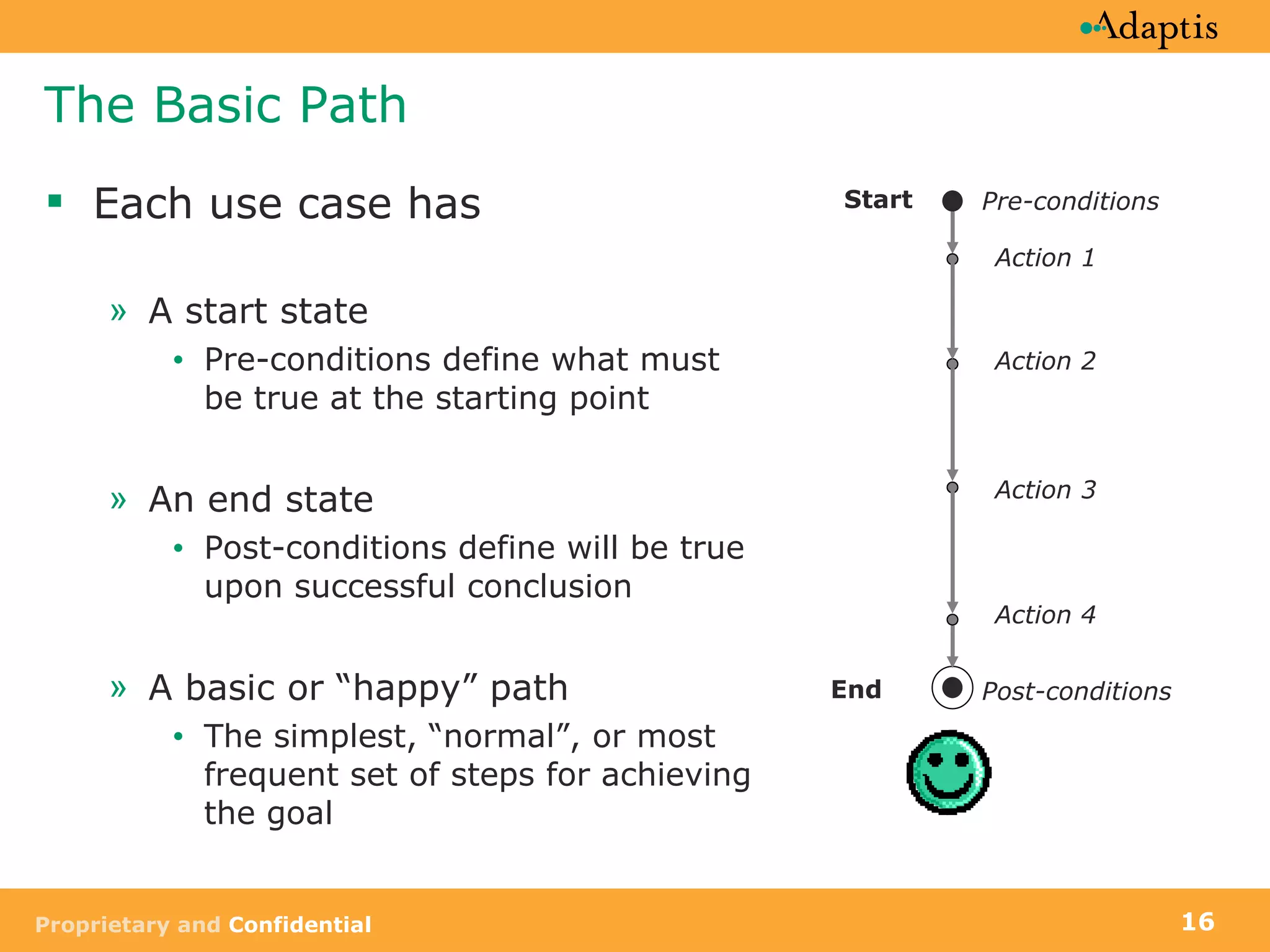
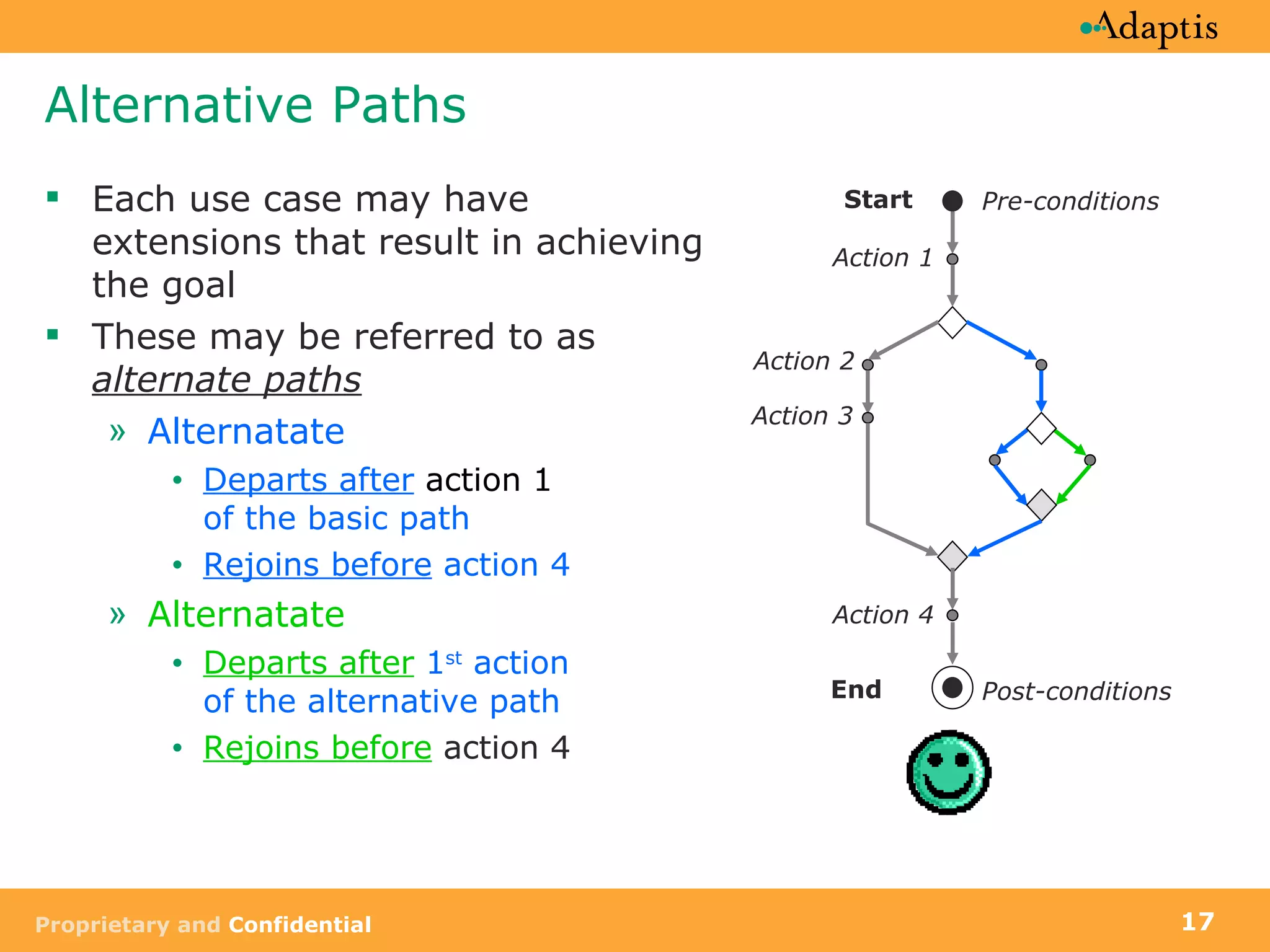
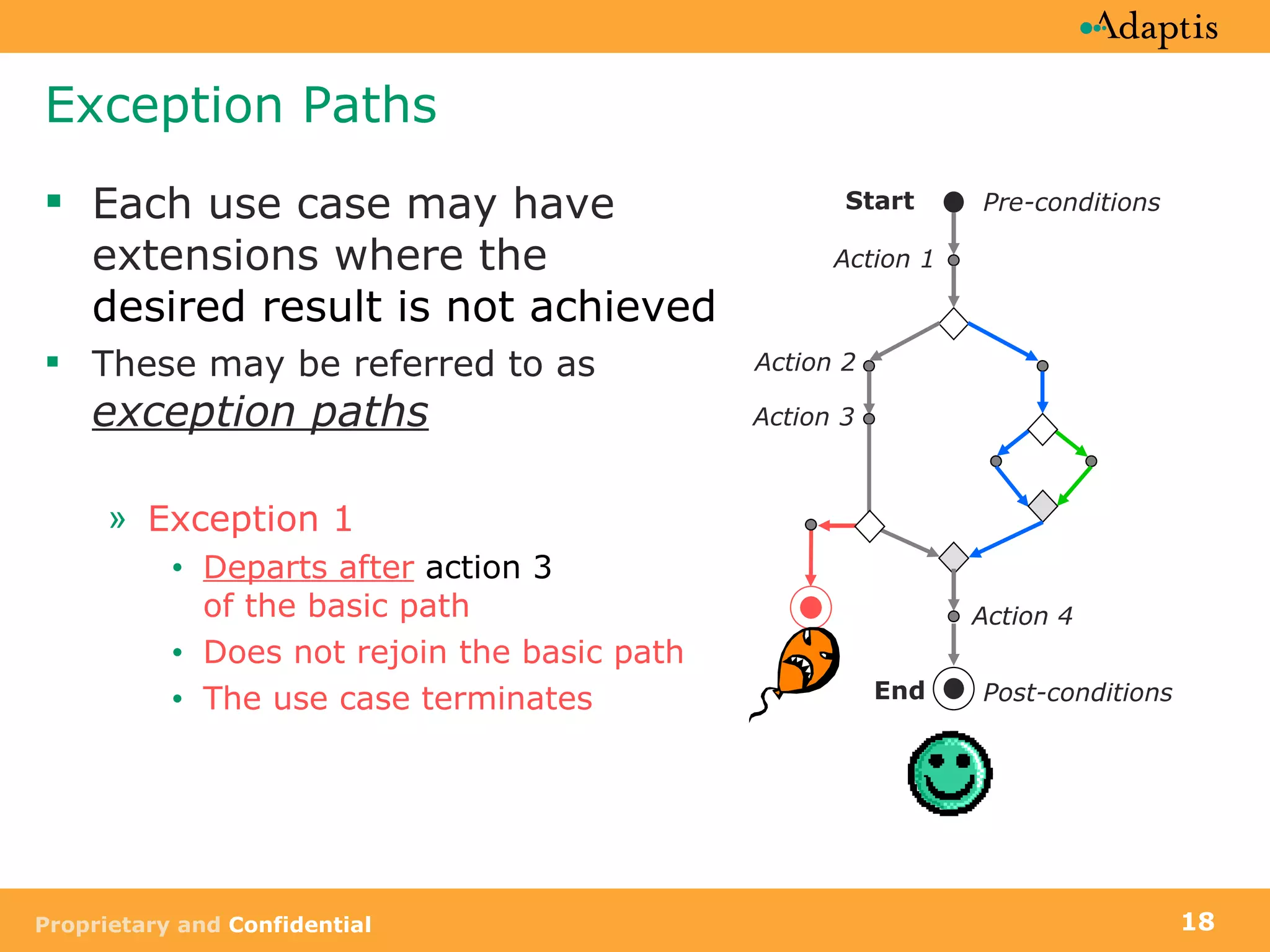
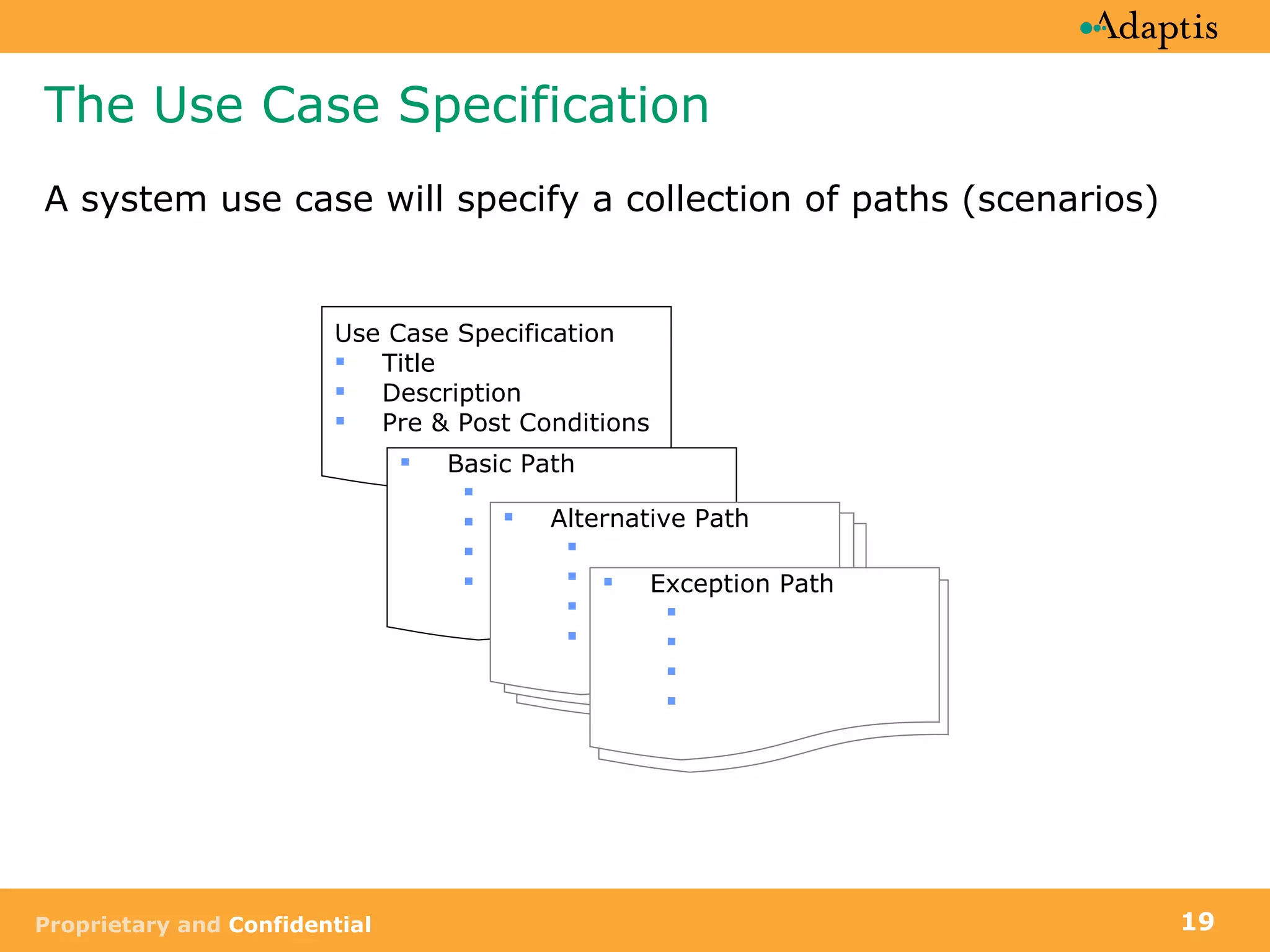
- Use cases specify basic, alternative, and exception paths to achieving the goal
- Use cases are written from both a business and system perspective
![An Examination of Use Cases Mark Smith Director Operations Support Services Adaptis, Inc. ( [email_address] )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usecases-acomprehensivelook-090902061610-phpapp01/75/Use-Cases-A-Comprehensive-Look-1-2048.jpg)
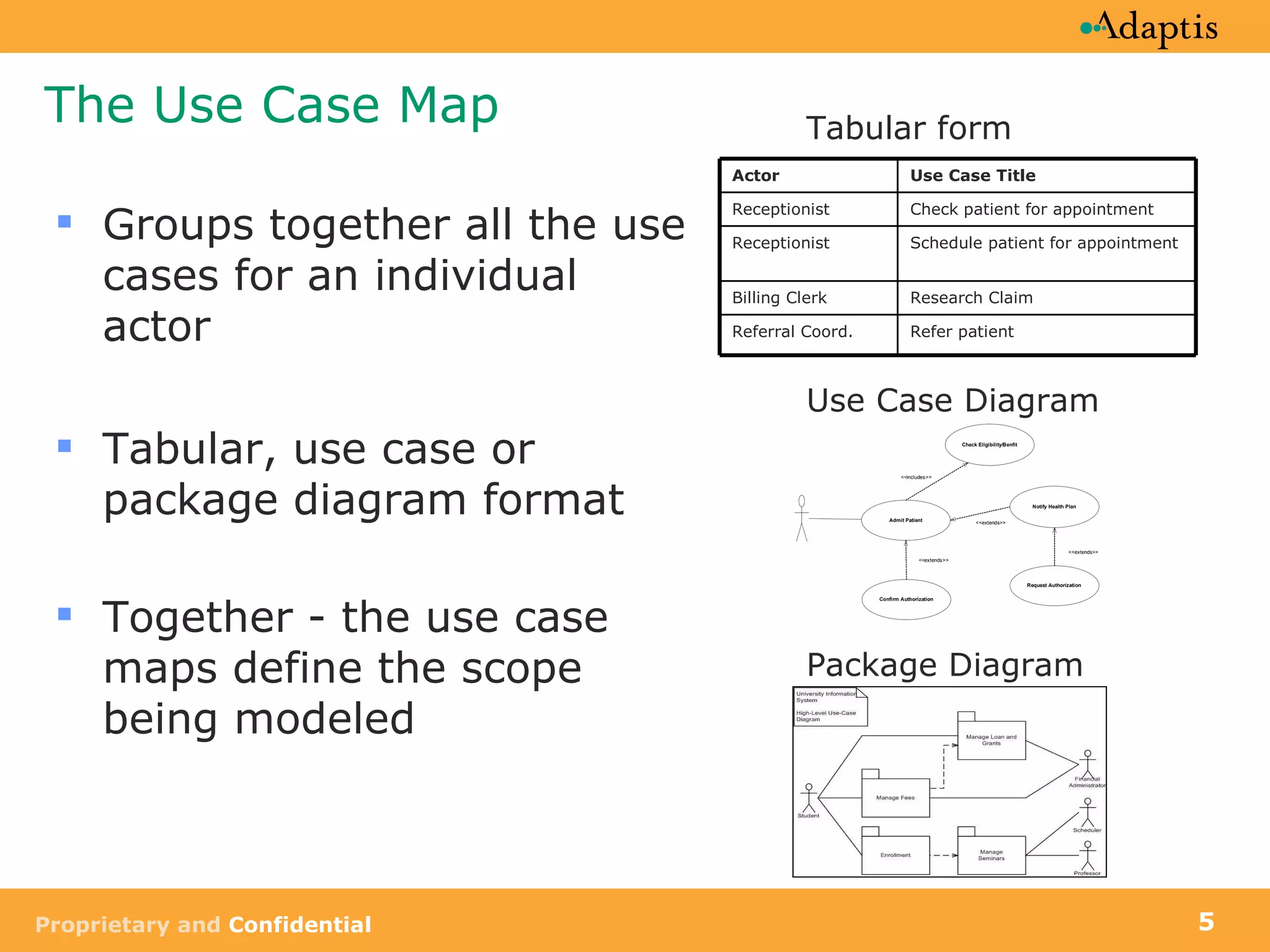






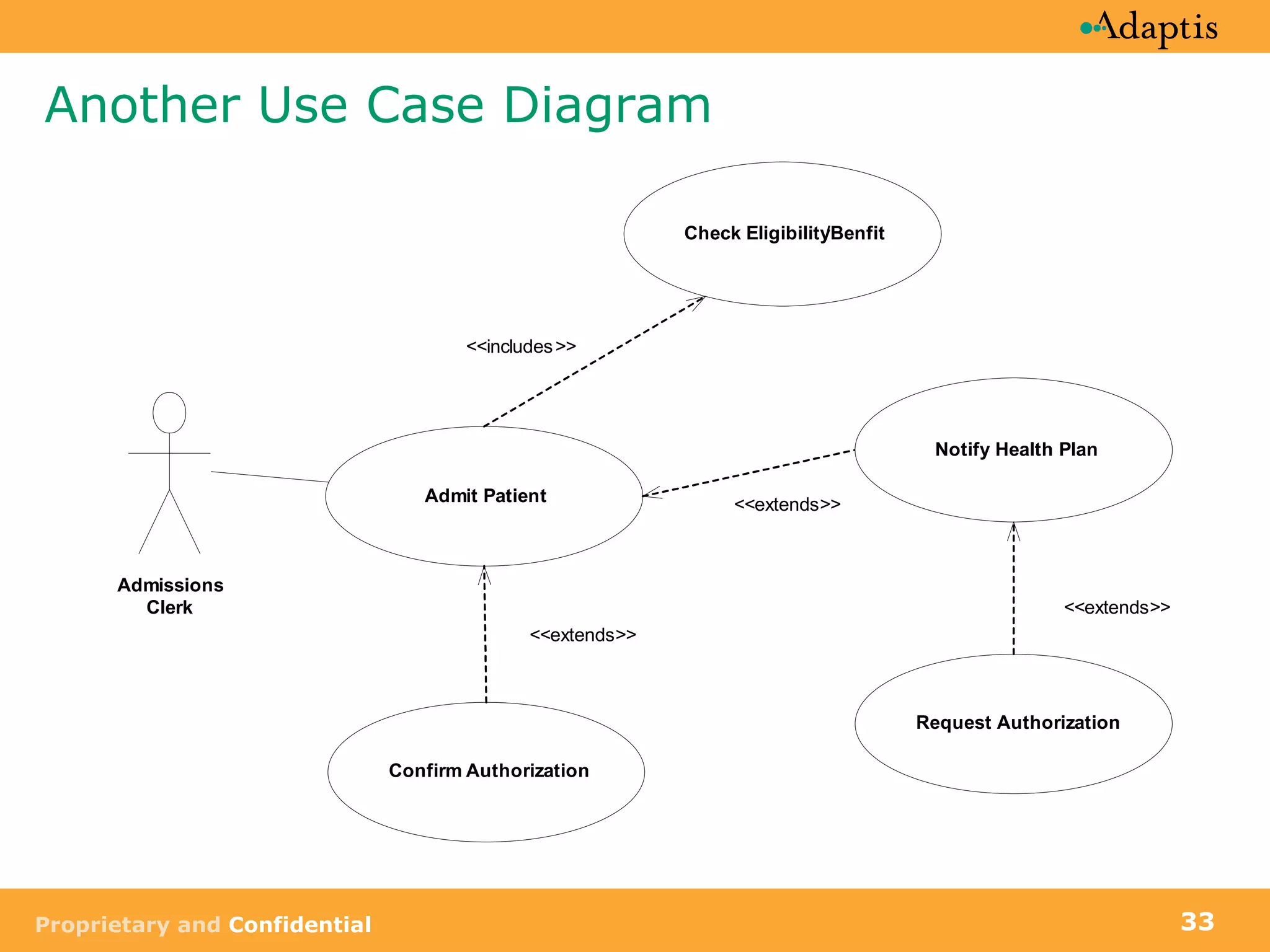
![Diagramming Use Case Dependencies UML activity diagrams may be used to Show use case sequence Provide a view of a the business activity [No covered] [Authorization not required] [Covered] Admit Patient Check Eligibility /Benefit Notify Health Plan Request authorization Confirm authorization [Authorization required]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usecases-acomprehensivelook-090902061610-phpapp01/75/Use-Cases-A-Comprehensive-Look-34-2048.jpg)