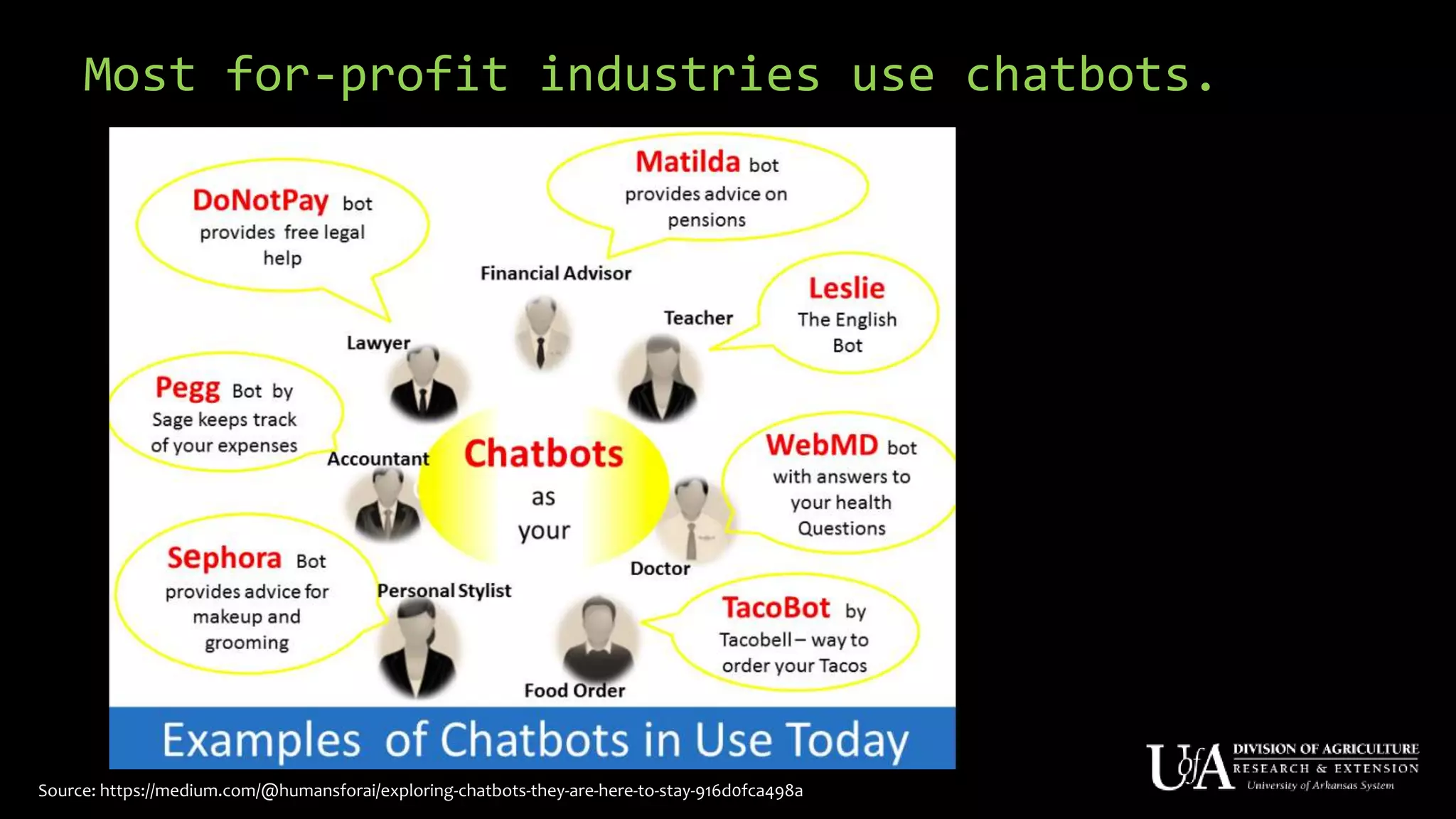
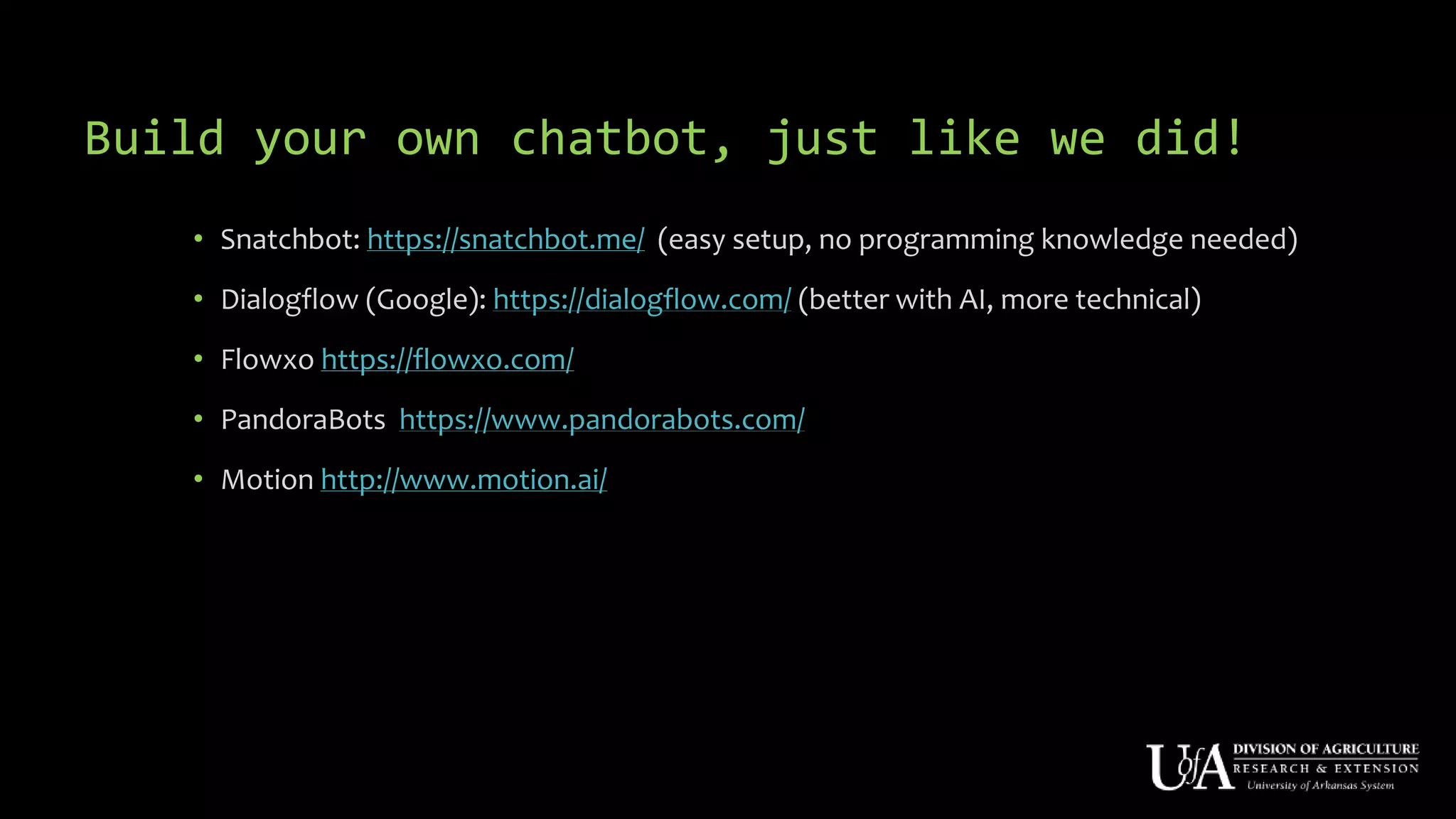
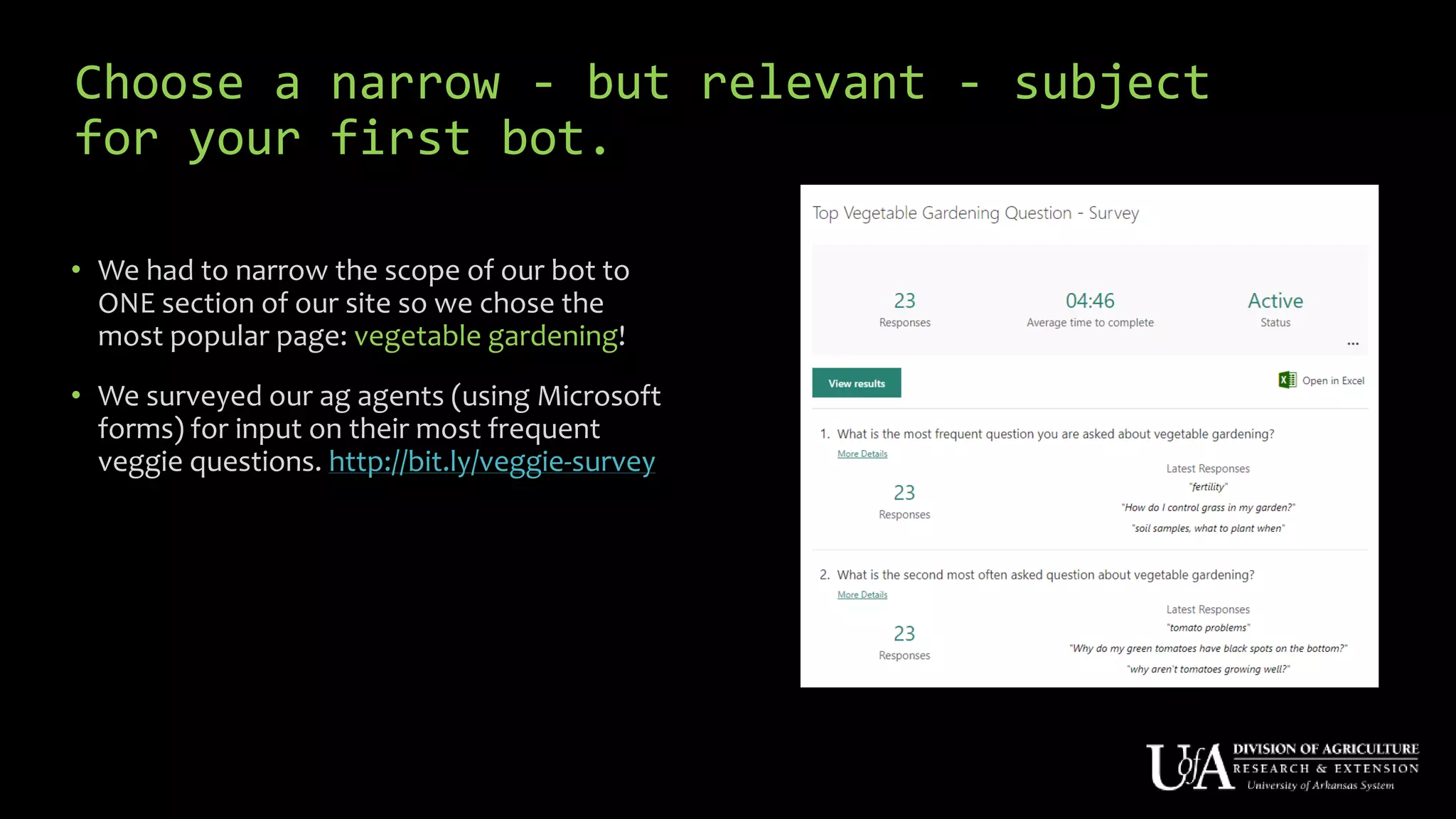
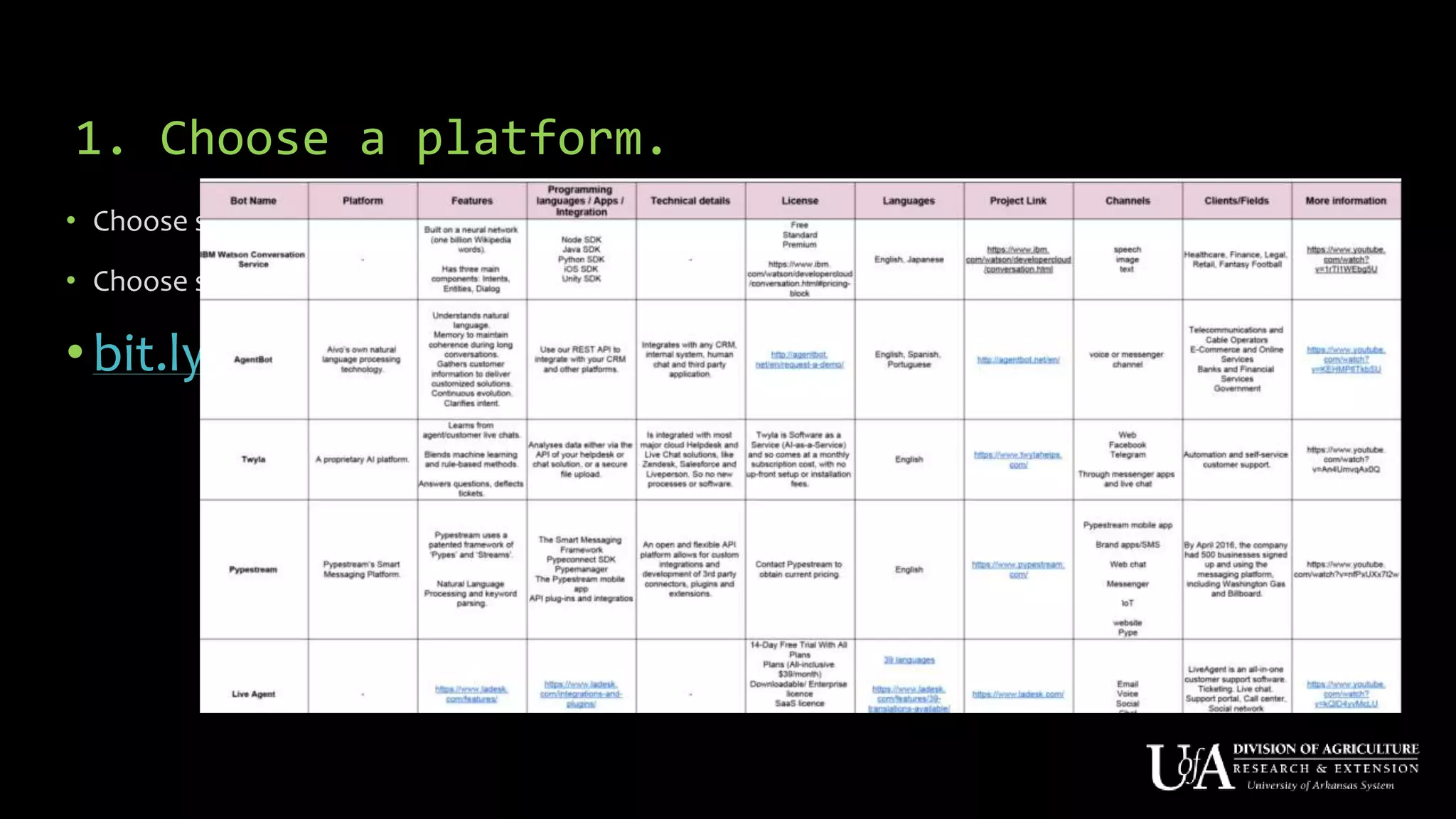
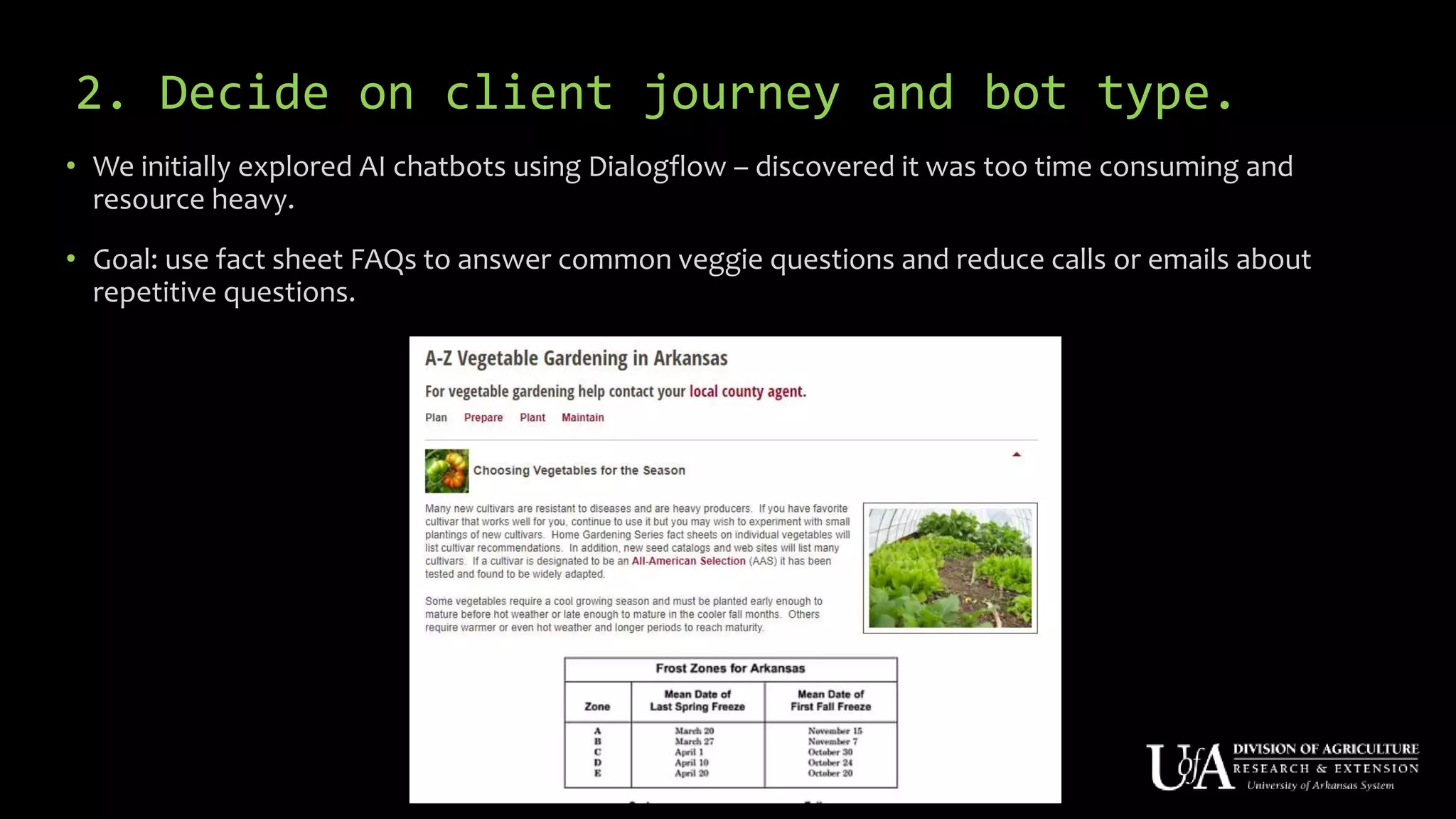
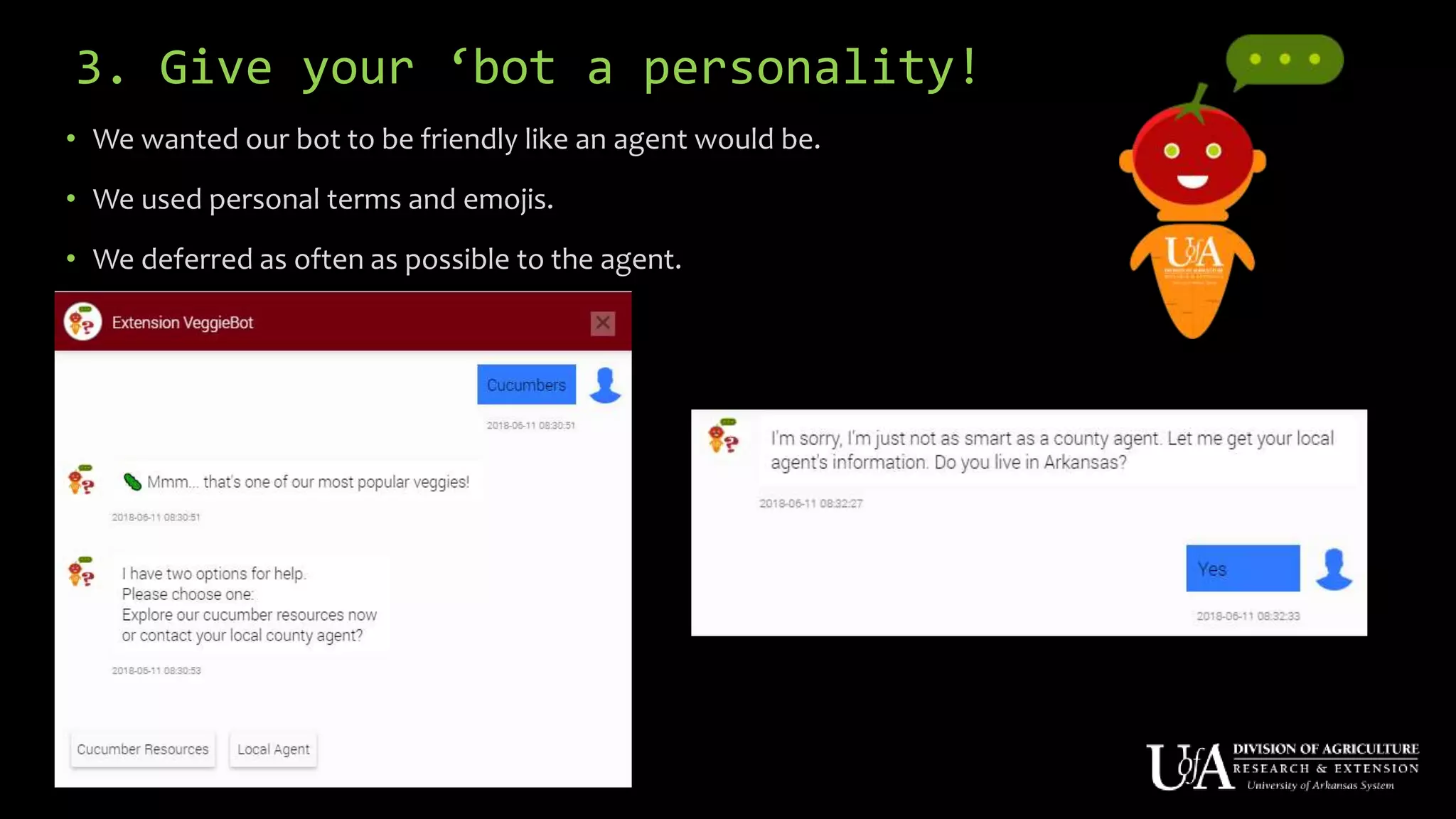
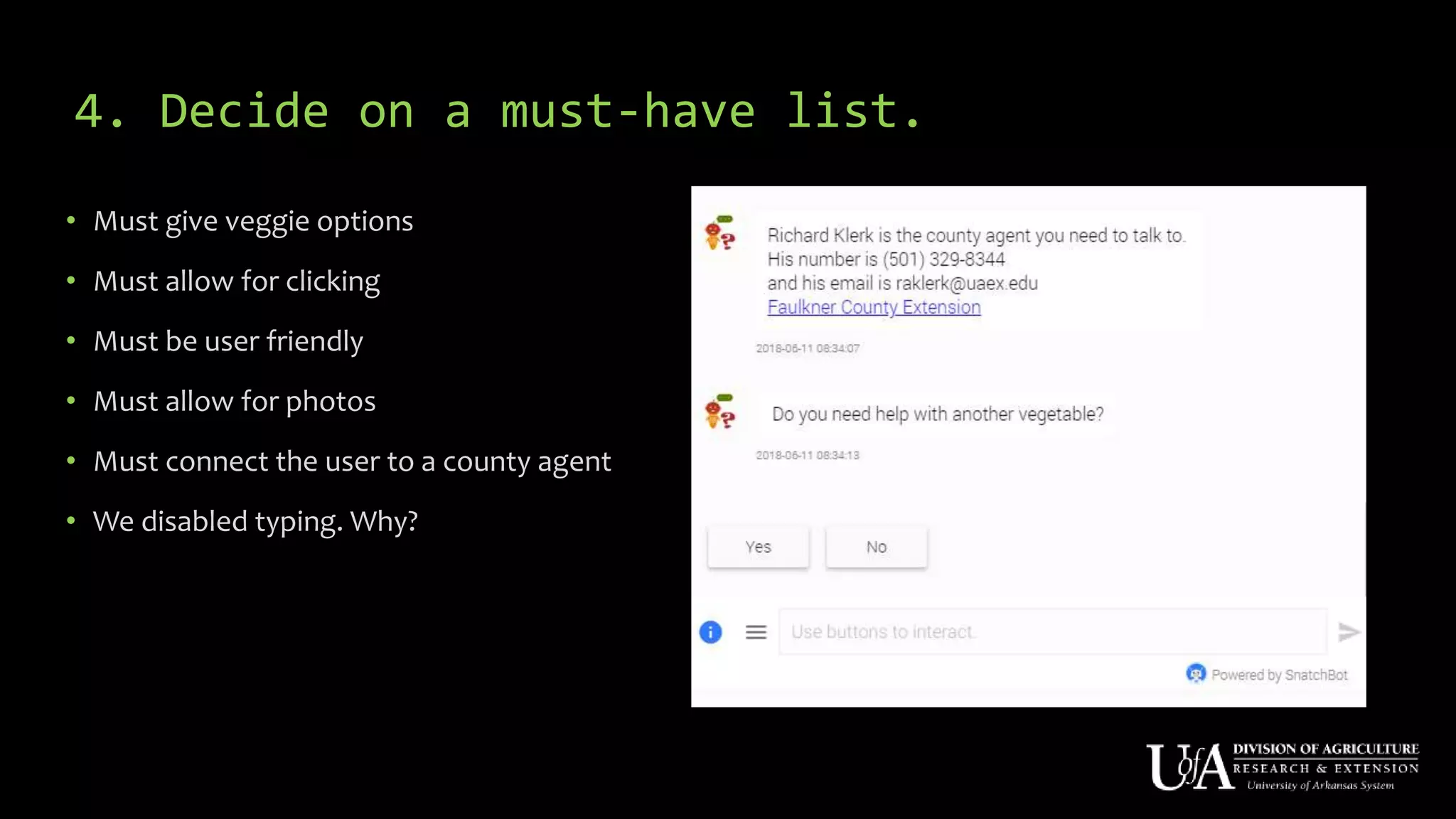
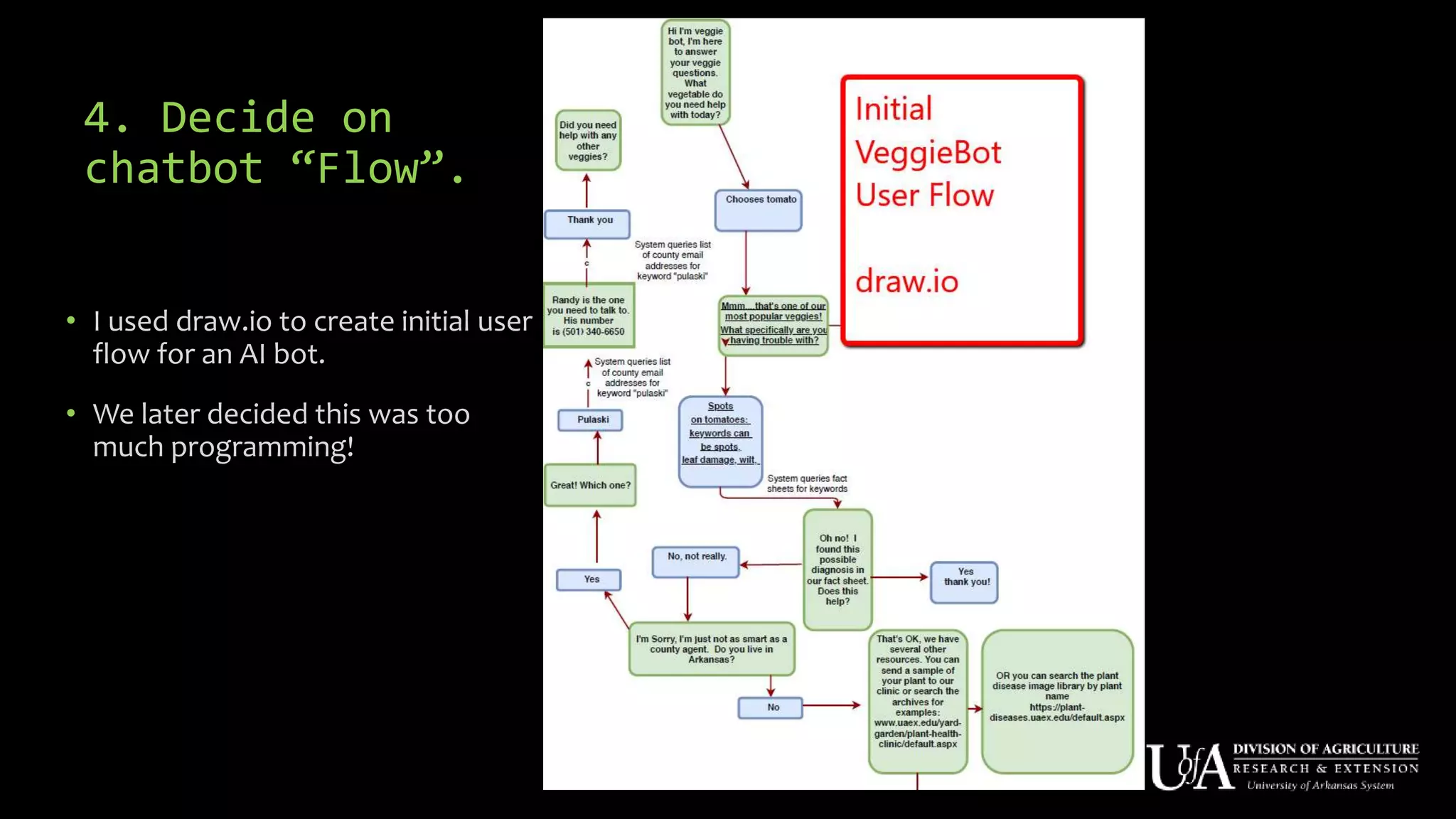
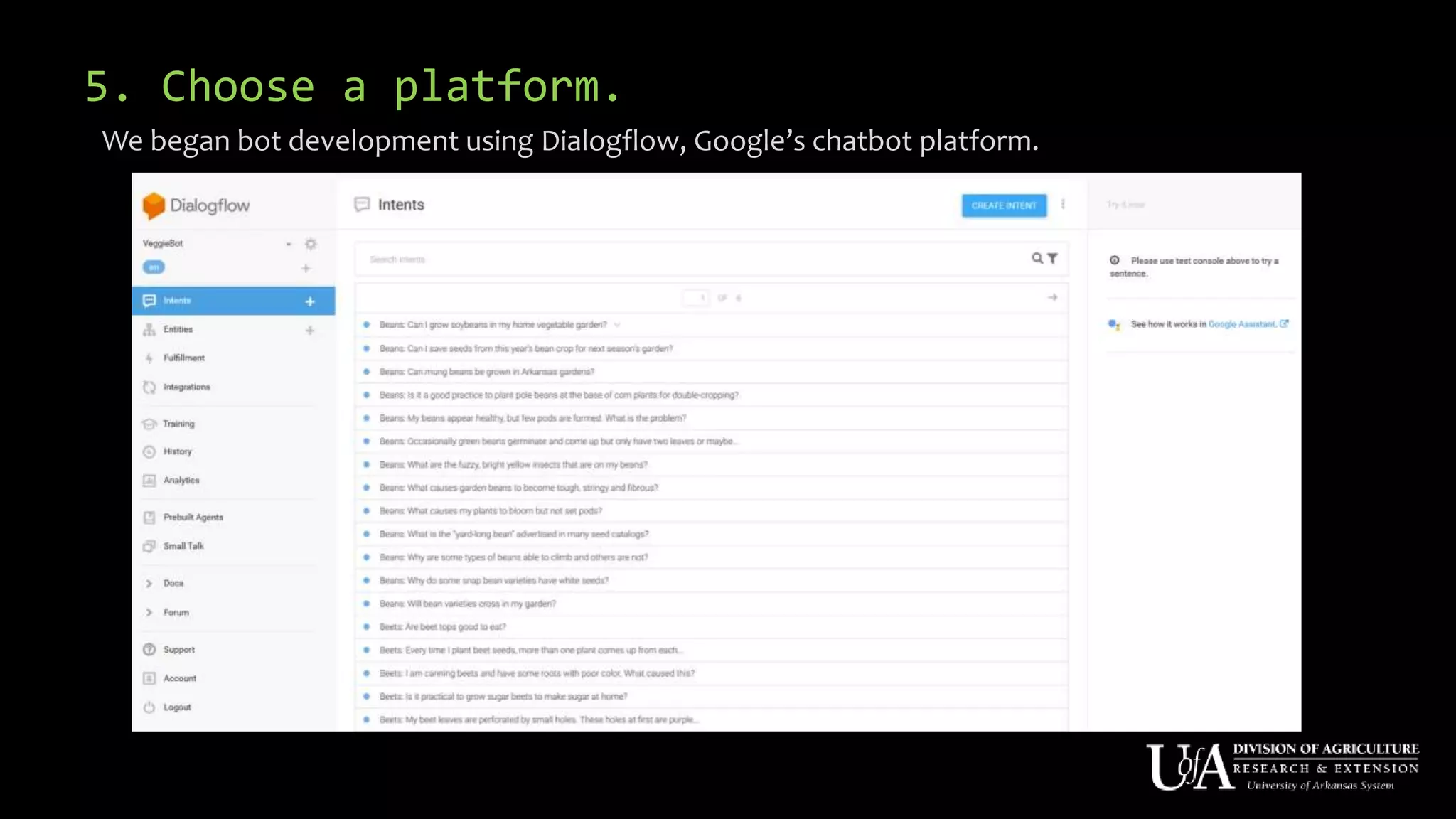
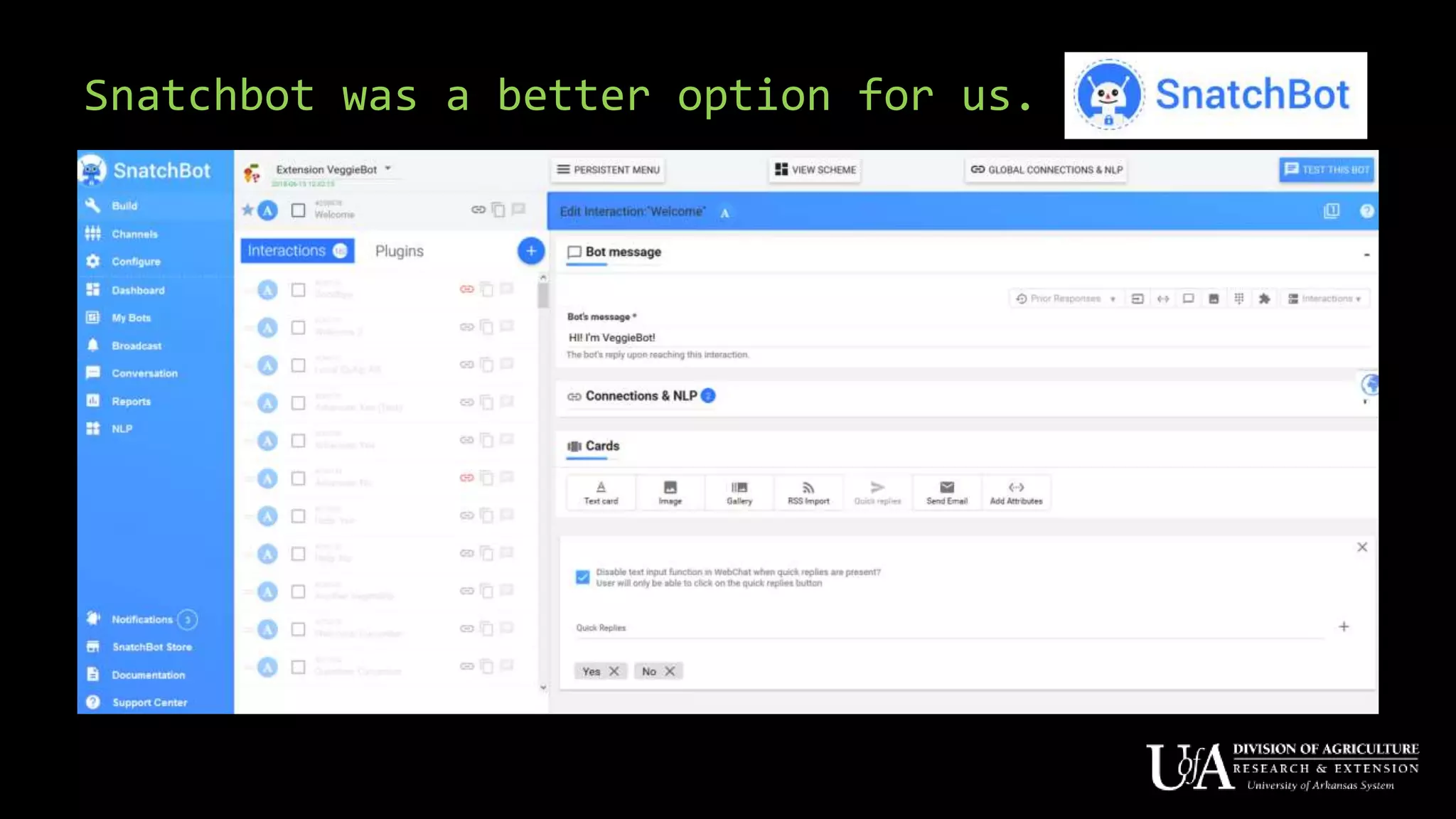
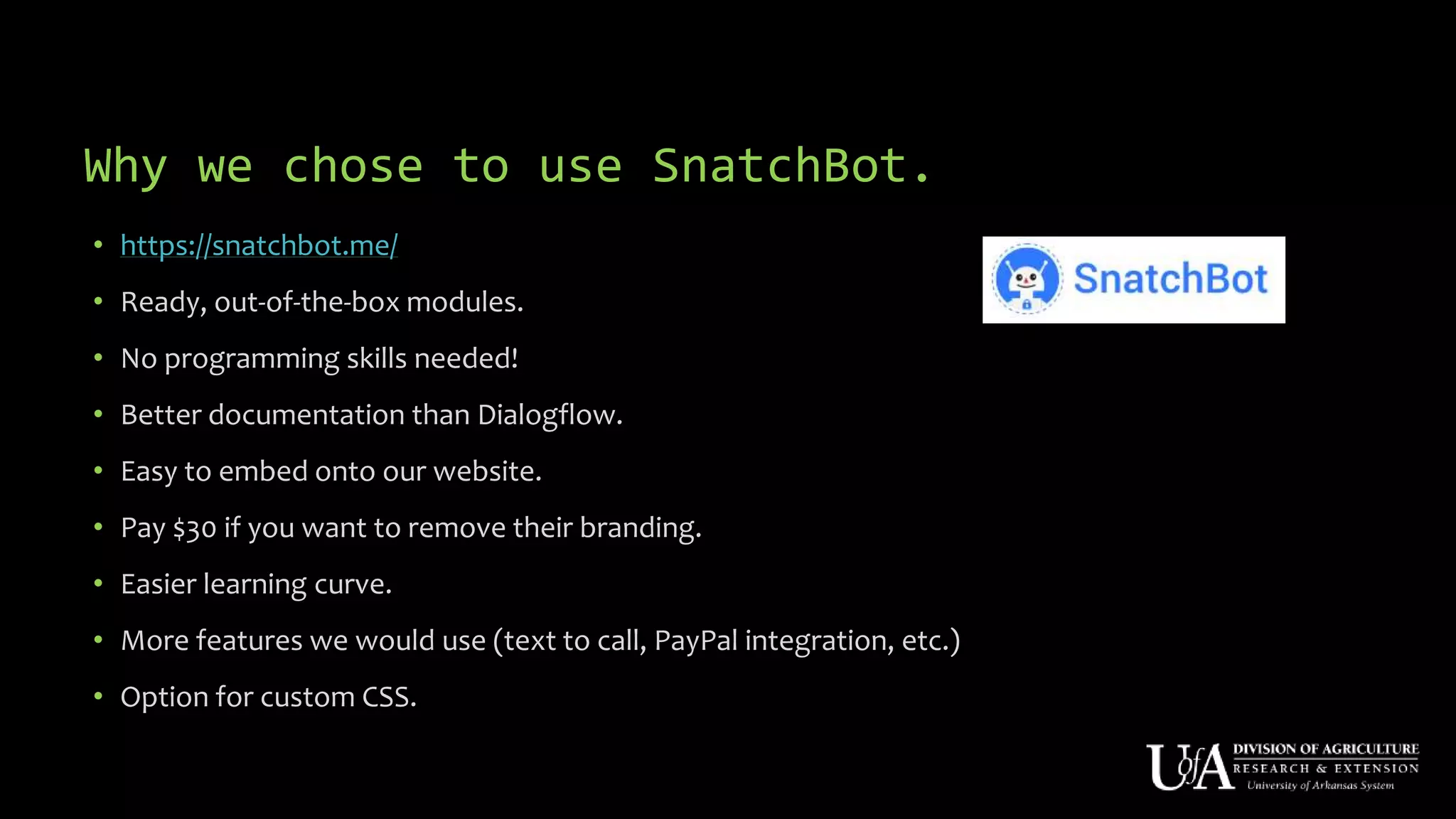
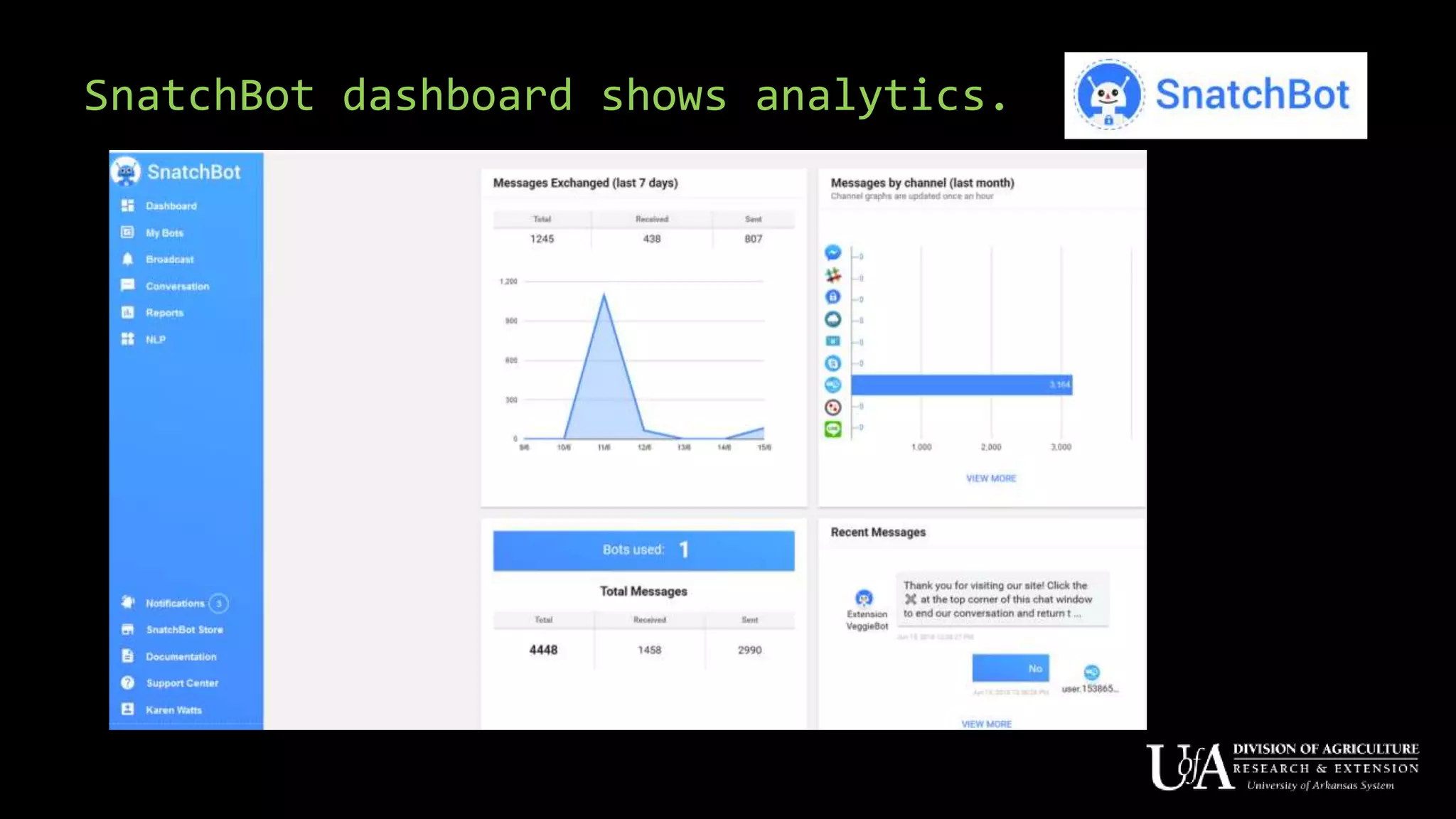
The document discusses the role of chatbots as virtual agents, their various types, and examples of industries benefiting from them, such as sales and healthcare. It outlines the development process for creating a chatbot, sharing insights from the author’s experience using Snatchbot, and emphasizing the importance of user engagement and functionality. Additionally, it suggests potential future uses for chatbots in extension services, such as supporting inquiries and providing resources.