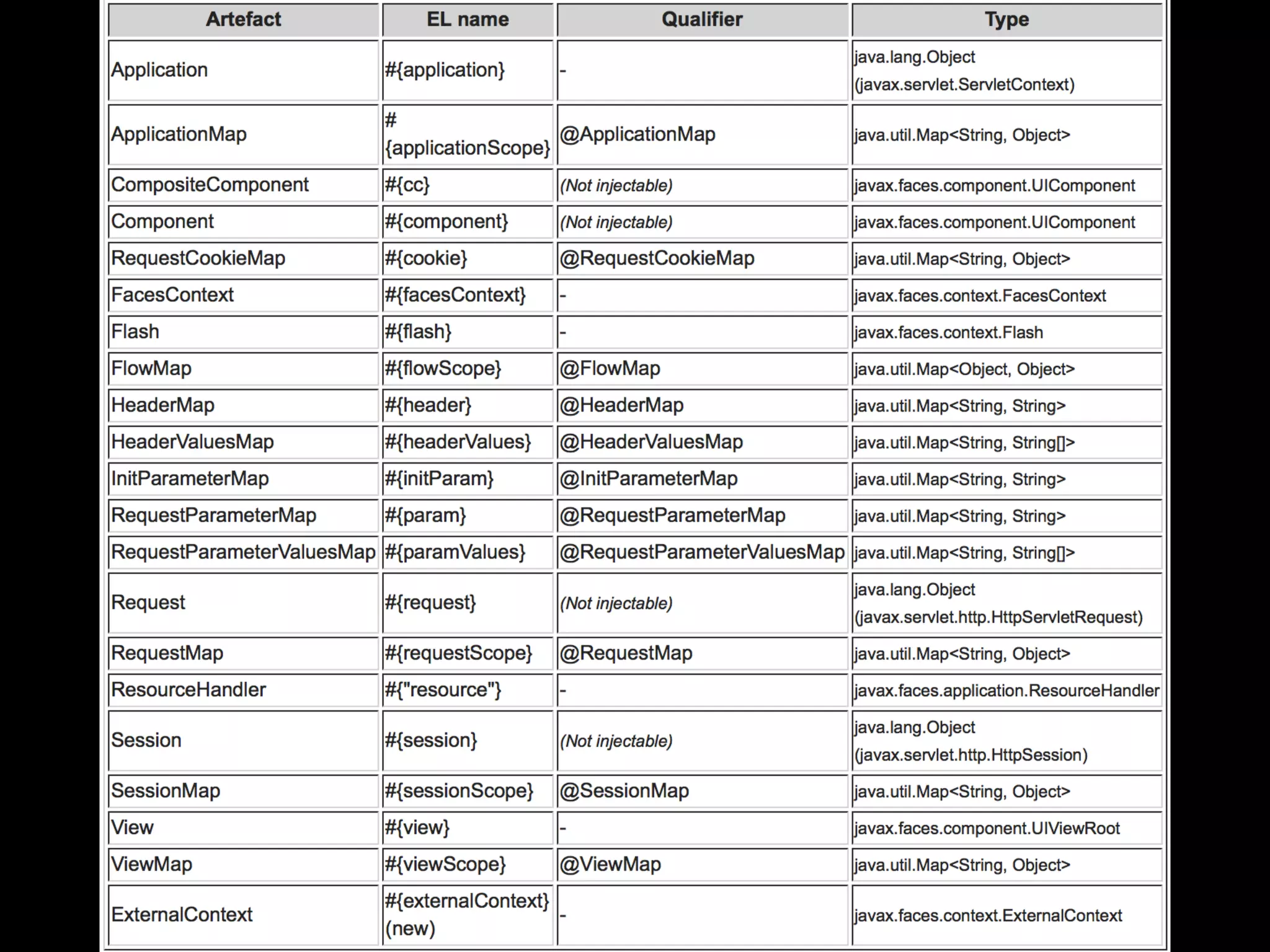
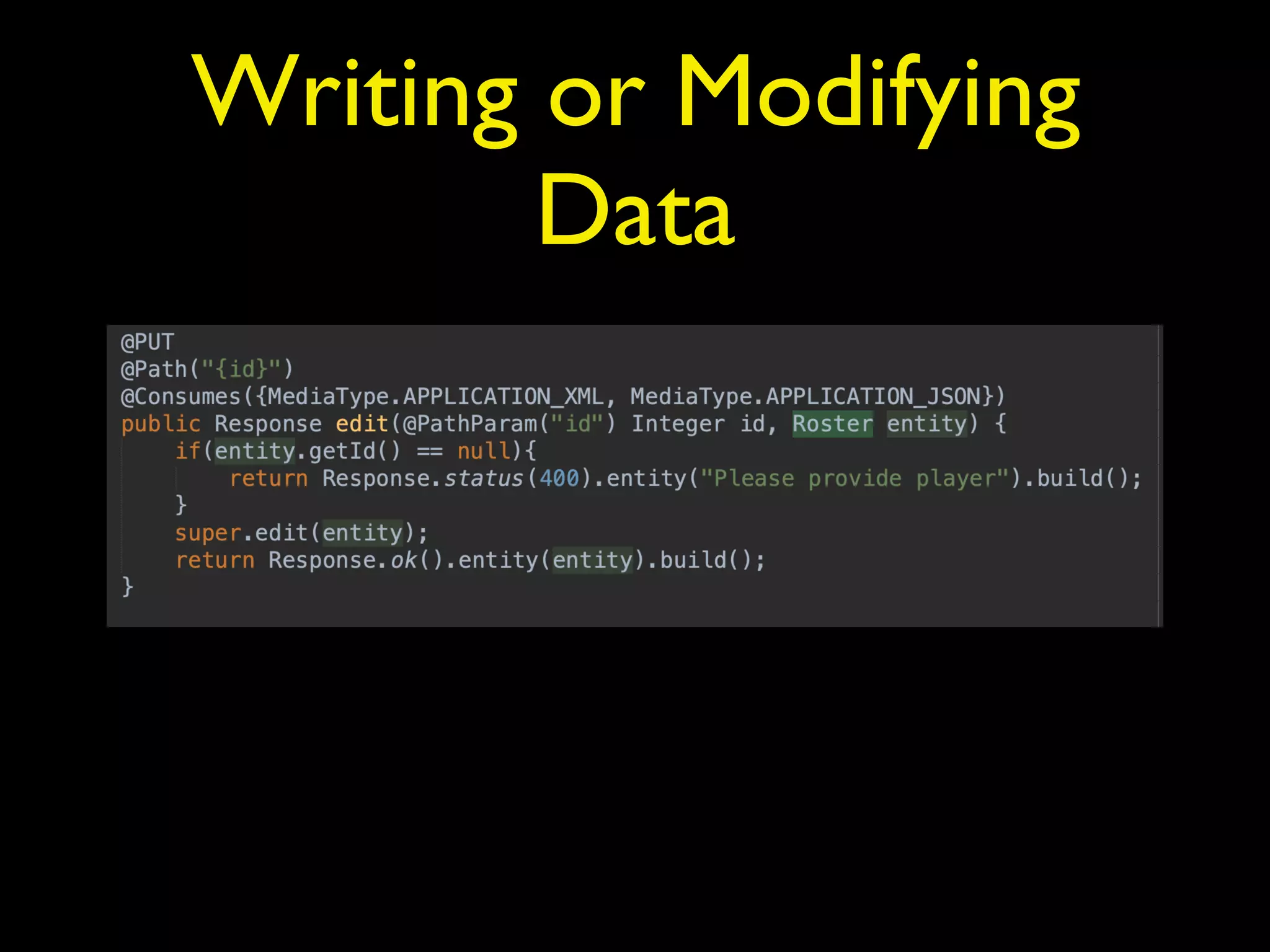
The document discusses utilizing Jakarta Server Faces and Jakarta RESTful Web Services to build front ends for microservices. It provides an overview of the technologies and frameworks, including new features of JSF 2.3 and Jakarta RESTful Web Services. It then demonstrates how to create a simple RESTful service using JAX-RS and JPA, and build a JSF front end to communicate with the service and display database data. The presentation recommends approaches for writing and modifying data via REST, securing services, and using various Java EE and third-party libraries.