This document provides an overview of coding concepts, IF statements, IIF statements, and Select Case statements in VBA for beginners. It explains how to read code, use operators and characters like concatenation and line continuation, and step through code. It provides examples and syntax for IF statements, IIF statements, and Select Case statements.



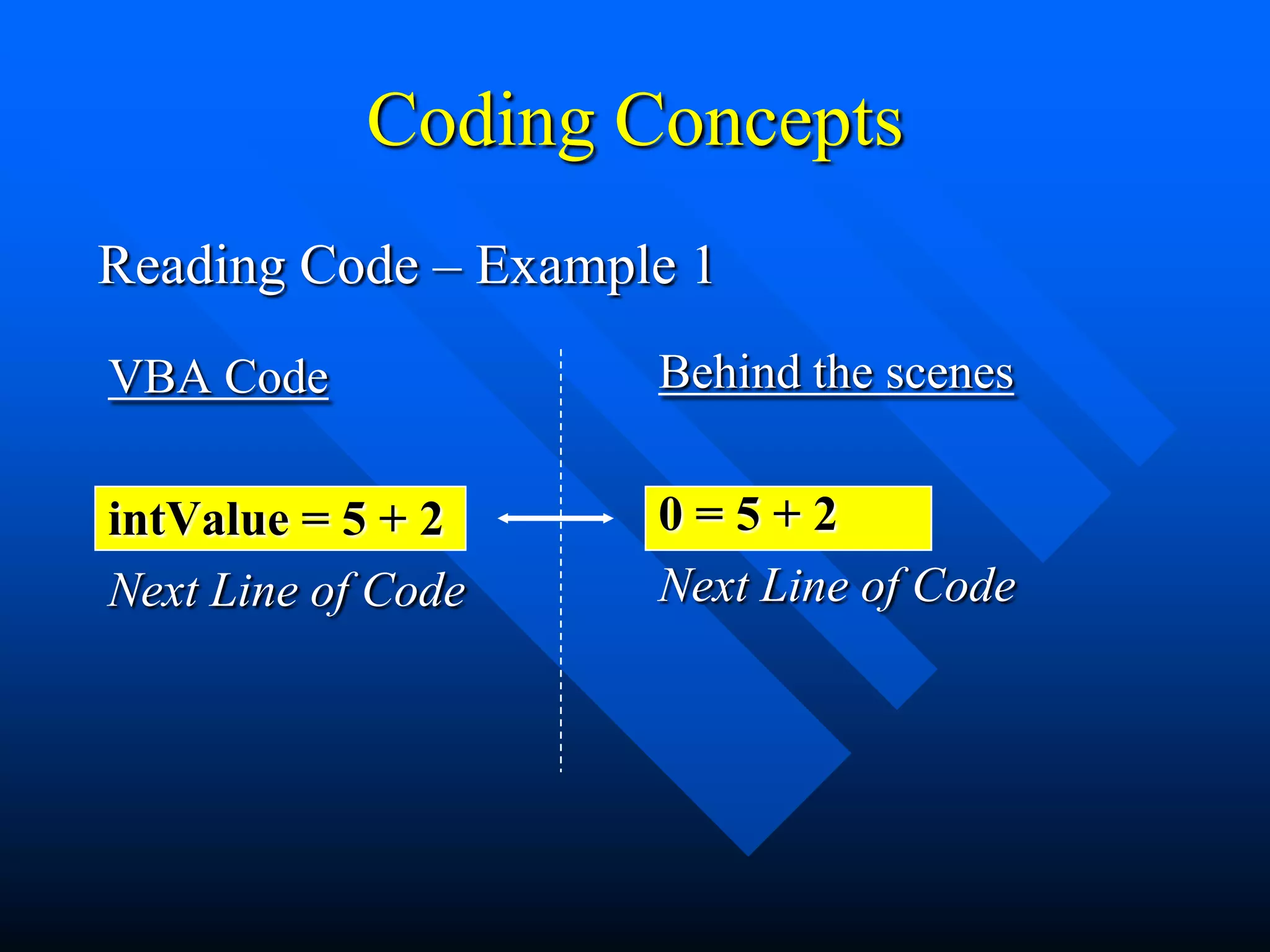
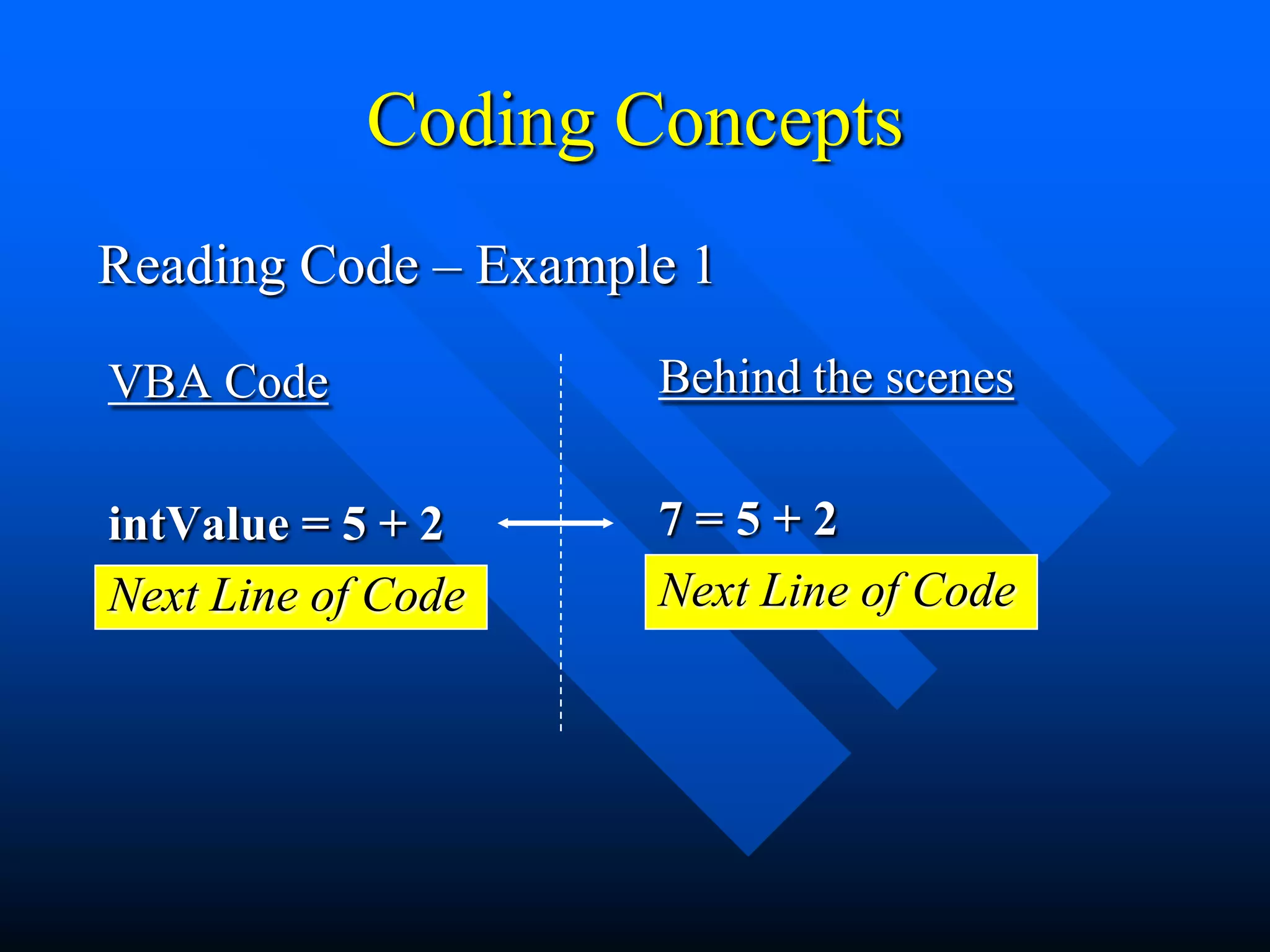
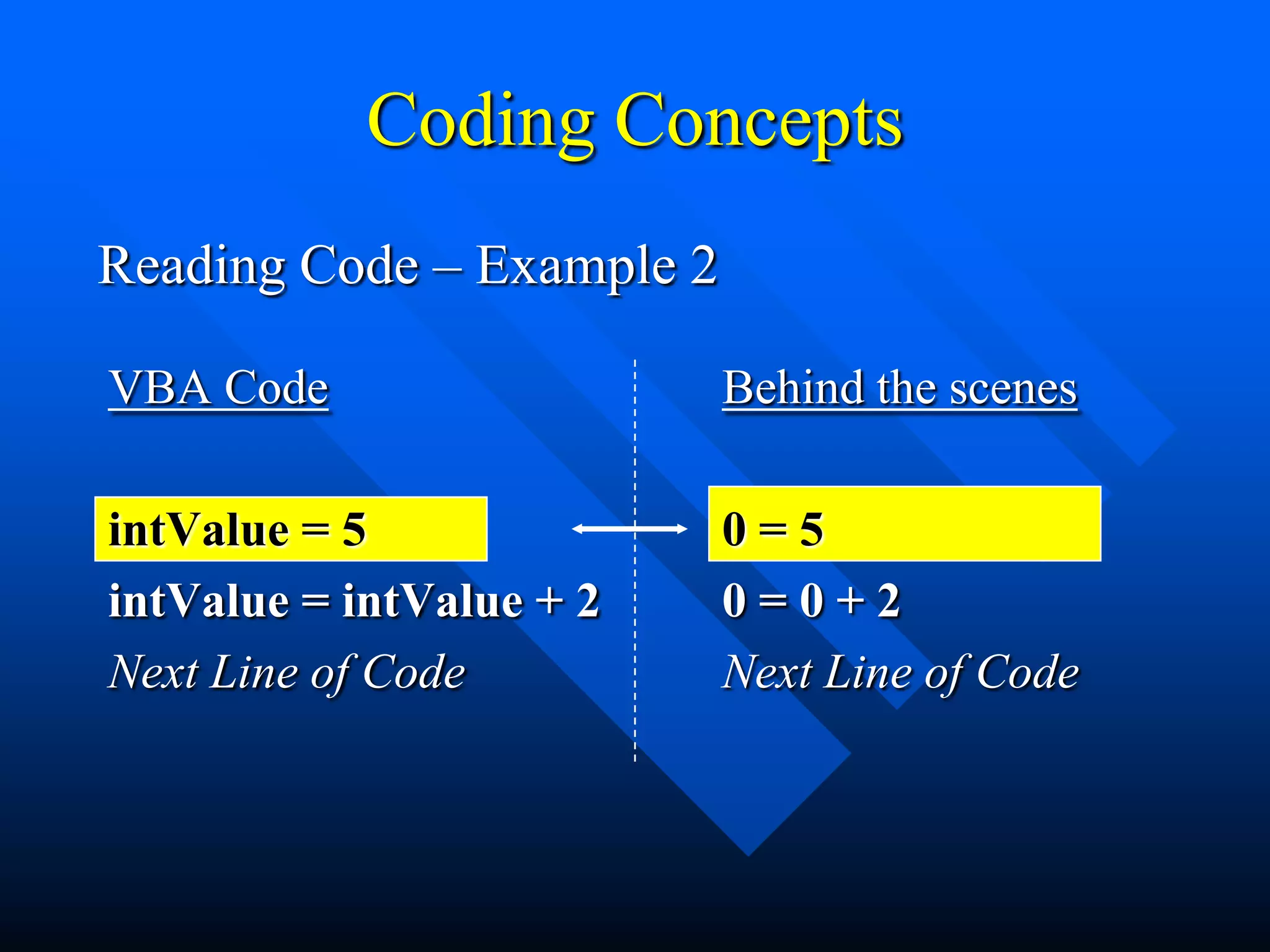
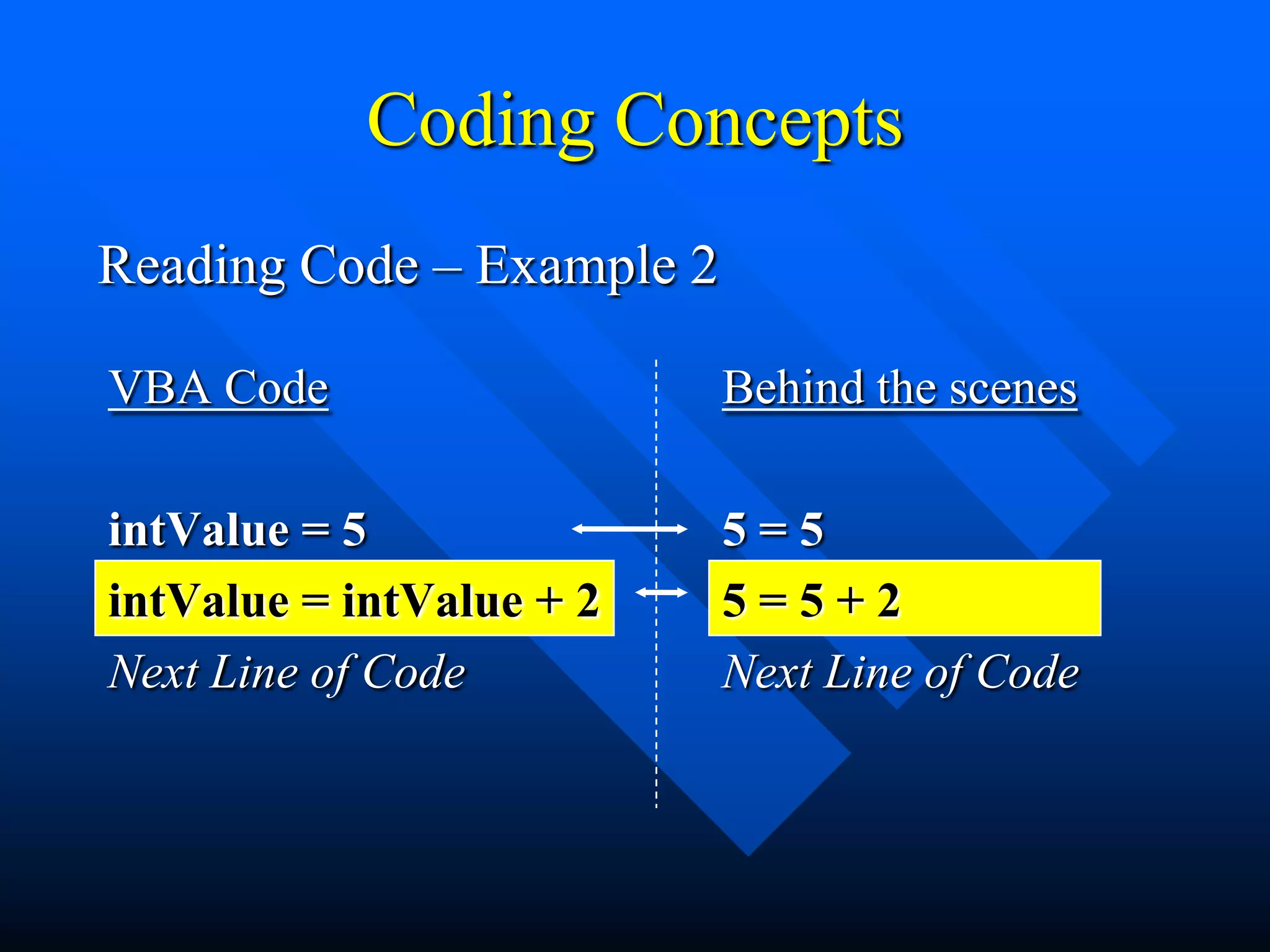
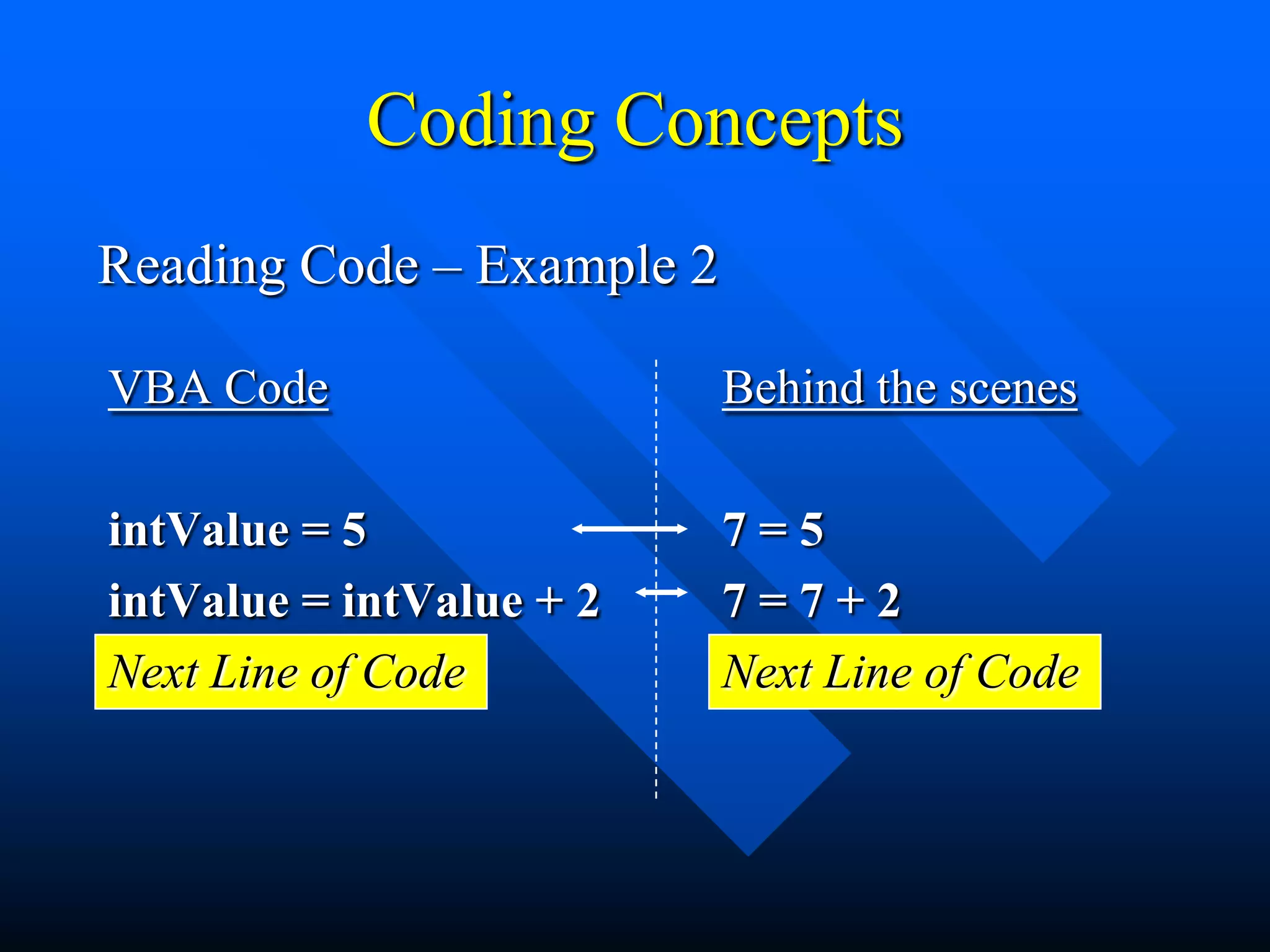


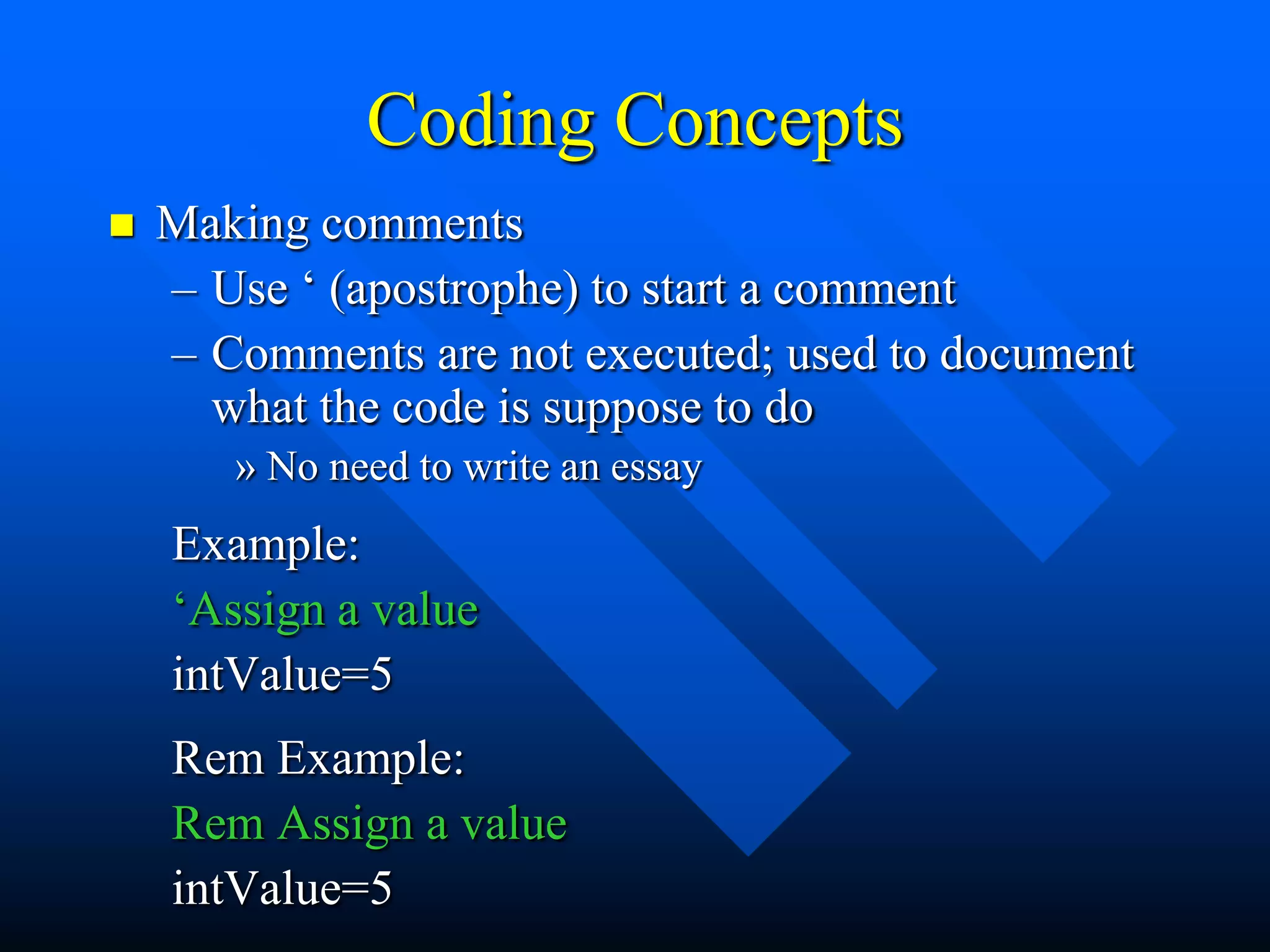
![Coding Concepts
Stepping through code
– Use [F5] in the code window to execute the
code
– Use [F8] in the code window to execute the
code one step at a time
Works in a Standard Module, does not work
in a Form Module.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbaclass4-120314225156-phpapp02/75/Vba-class-4-12-2048.jpg)
![IF Statement
An IF statement evaluates a condition to find
out if it is True or False, then executes the
appropriate statement(s)
Type the word „If‟ in the code window and
press [F1] for help on the topic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbaclass4-120314225156-phpapp02/75/Vba-class-4-13-2048.jpg)
![IF Statement
Syntax (Single Line):
If condition Then [statements] [Else elsestatements]
If Sales>100K Then Bonus=10% Else Bonus=1%
Syntax (Multi-Line) Pseudo-code:
If condition Then If Sales>100K Then
[statements] Bonus=10%
[Else Else
[elsestatements]] Bonus=1%
End If End If](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbaclass4-120314225156-phpapp02/75/Vba-class-4-14-2048.jpg)
![IF Statement
Syntax (If…Then…ElseIf…Then…Else)
If condition Then If Sales>100K Then
[statements] Bonus=10%
[ElseIf condition-n Then ElseIf Sales>50K Then
[elseifstatements] ... Bonus=5%
[Else Else
[elsestatements]] Bonus=1%
End If End If](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbaclass4-120314225156-phpapp02/75/Vba-class-4-15-2048.jpg)
![IF Statement
Nested IF Pseudo-Code:
If condition Then If Sales>100K Then
If condition Then If NewClients>5 Then
[statements] Bonus=15%
[Else Else
[elsestatements]] Bonus=10%
End If End If
[Else Else
[elsestatements]] Bonus=1%
End If End If](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbaclass4-120314225156-phpapp02/75/Vba-class-4-16-2048.jpg)


![Immediate IF
Immediate If is similar to If statements
– Syntax
IIf(expr, truepart, falsepart)
IIf(Sales>100K, Bonus=10%, 1%)
– Can be nested
IIf(expr, truepart, IIf(expr, truepart, falsepart))
IIf(Sales>100K, Bonus=10%, IIf(Sales>50K, Bonus=5%, Bonus=1%))
Type the word „IIf‟ in the code window and press [F1] for
help on the topic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbaclass4-120314225156-phpapp02/75/Vba-class-4-19-2048.jpg)

![Select Case
Select Case is similar to If…Then…ElseIf
statements.
The difference is that it evaluates an
expression once and then compares it to
different values
– Makes it more efficient than multiple ElseIf
statements
Type the word „Select‟ in the code window
and press [F1] for help on the topic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbaclass4-120314225156-phpapp02/75/Vba-class-4-21-2048.jpg)
![Select Case
Syntax: Pseudo-Code:
Select Case testexpression Select Case Sales
[Case expressionlist1] Case >100K
[statements] Bonus=10%
[Case expressionlist2] Case >50K
[statements] Bonus=5%
[Case Else] Case Else
[statements] Bonus=1%
End Select End Select](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbaclass4-120314225156-phpapp02/75/Vba-class-4-22-2048.jpg)