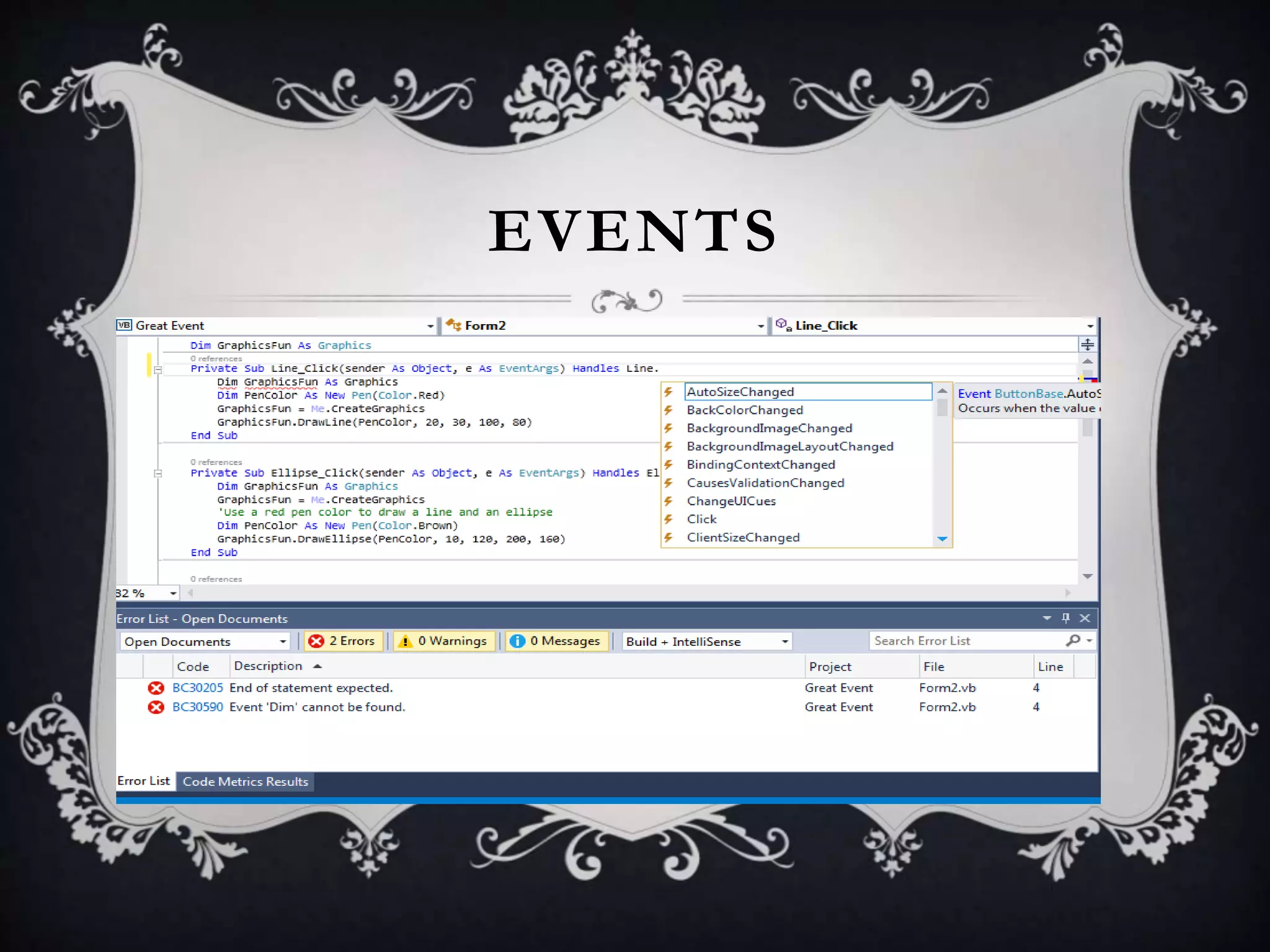
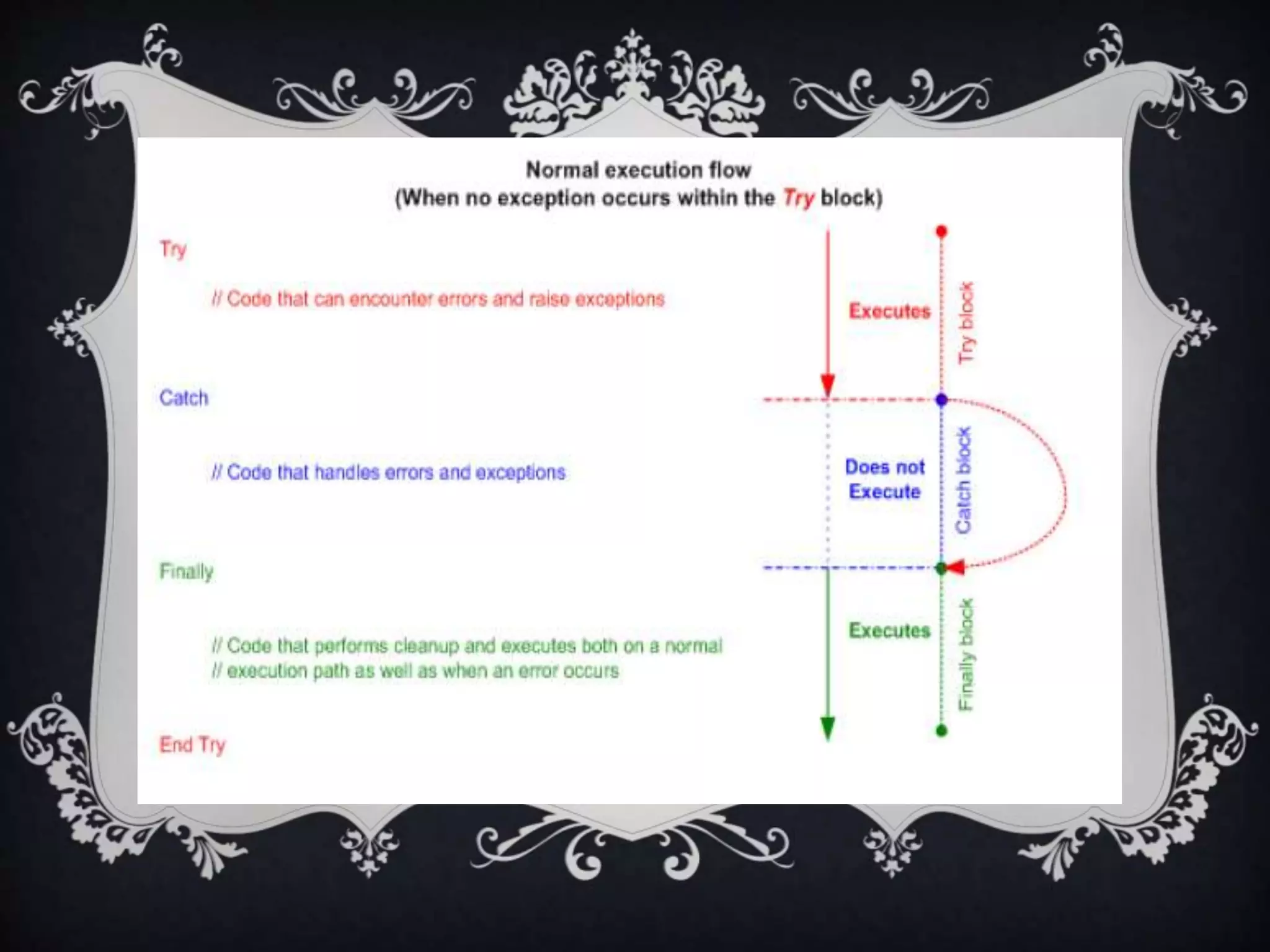
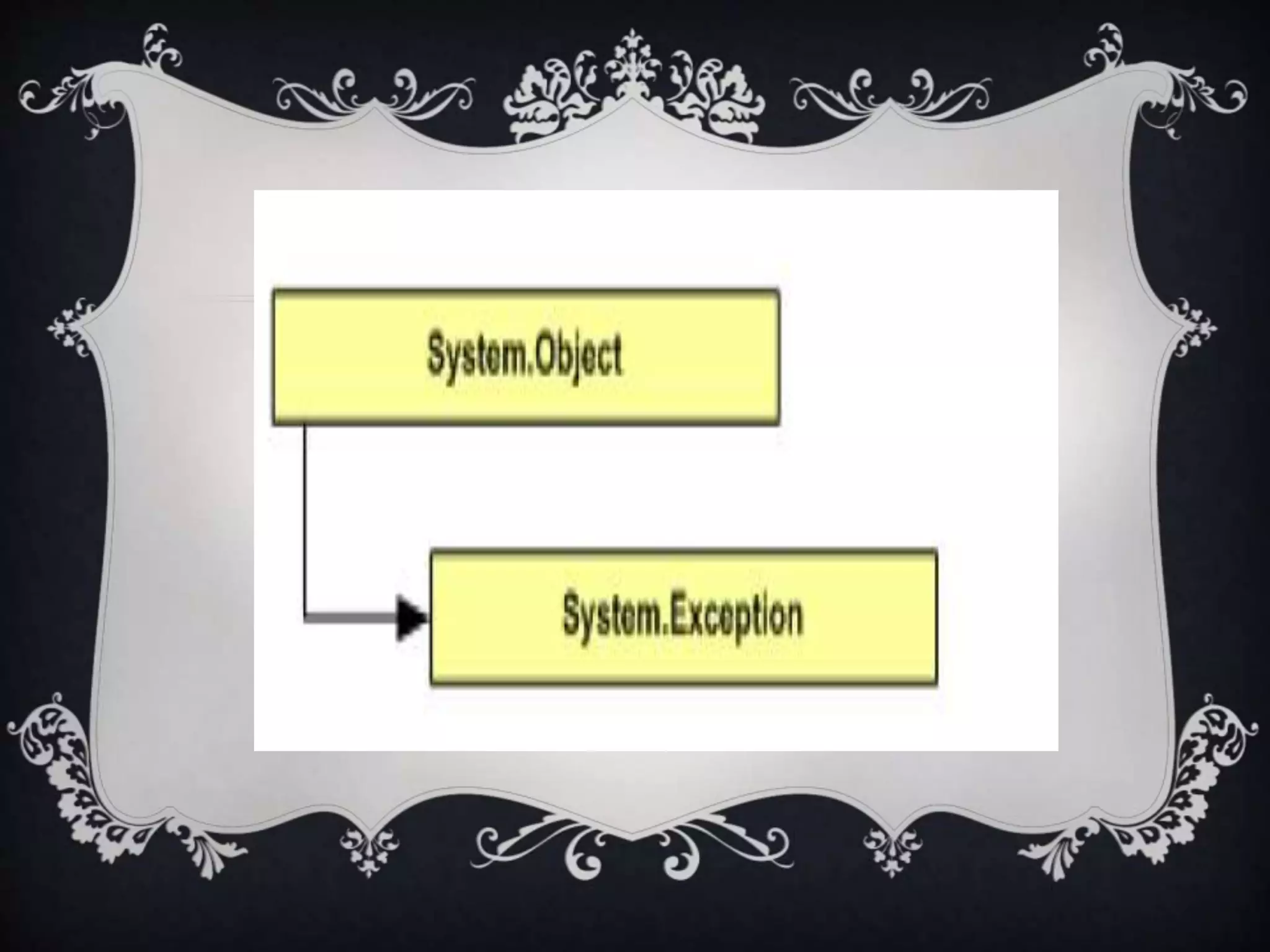
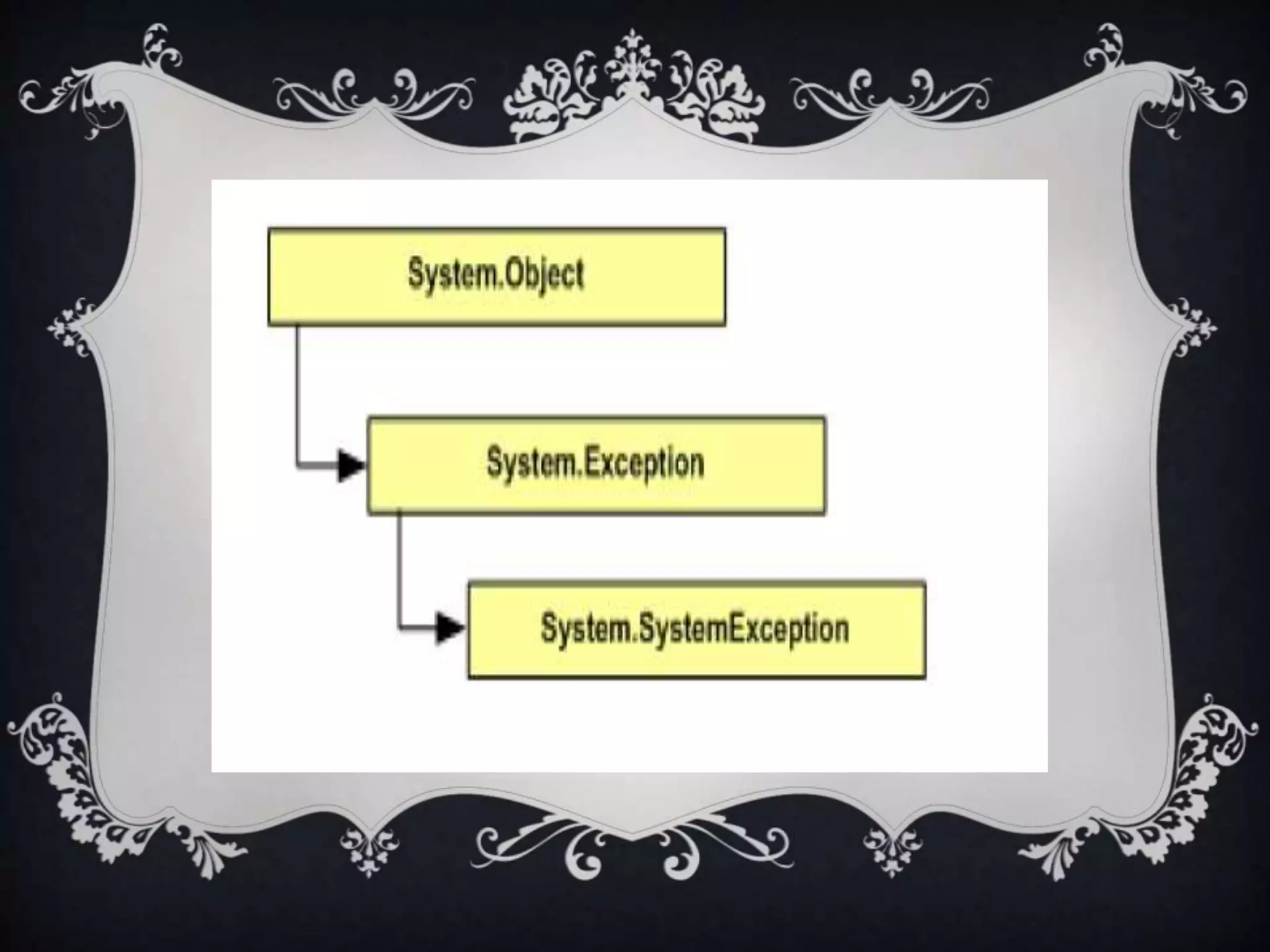
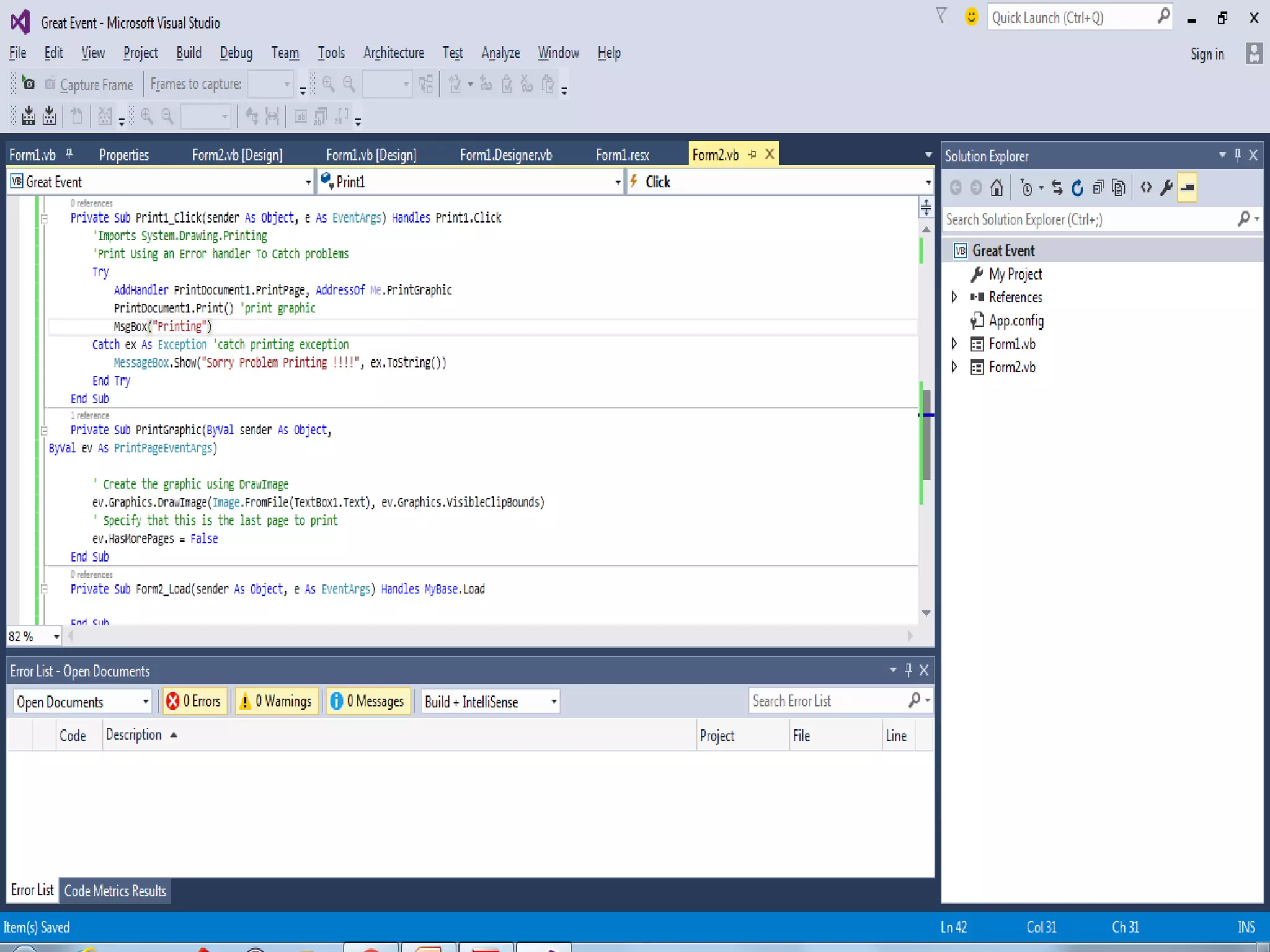
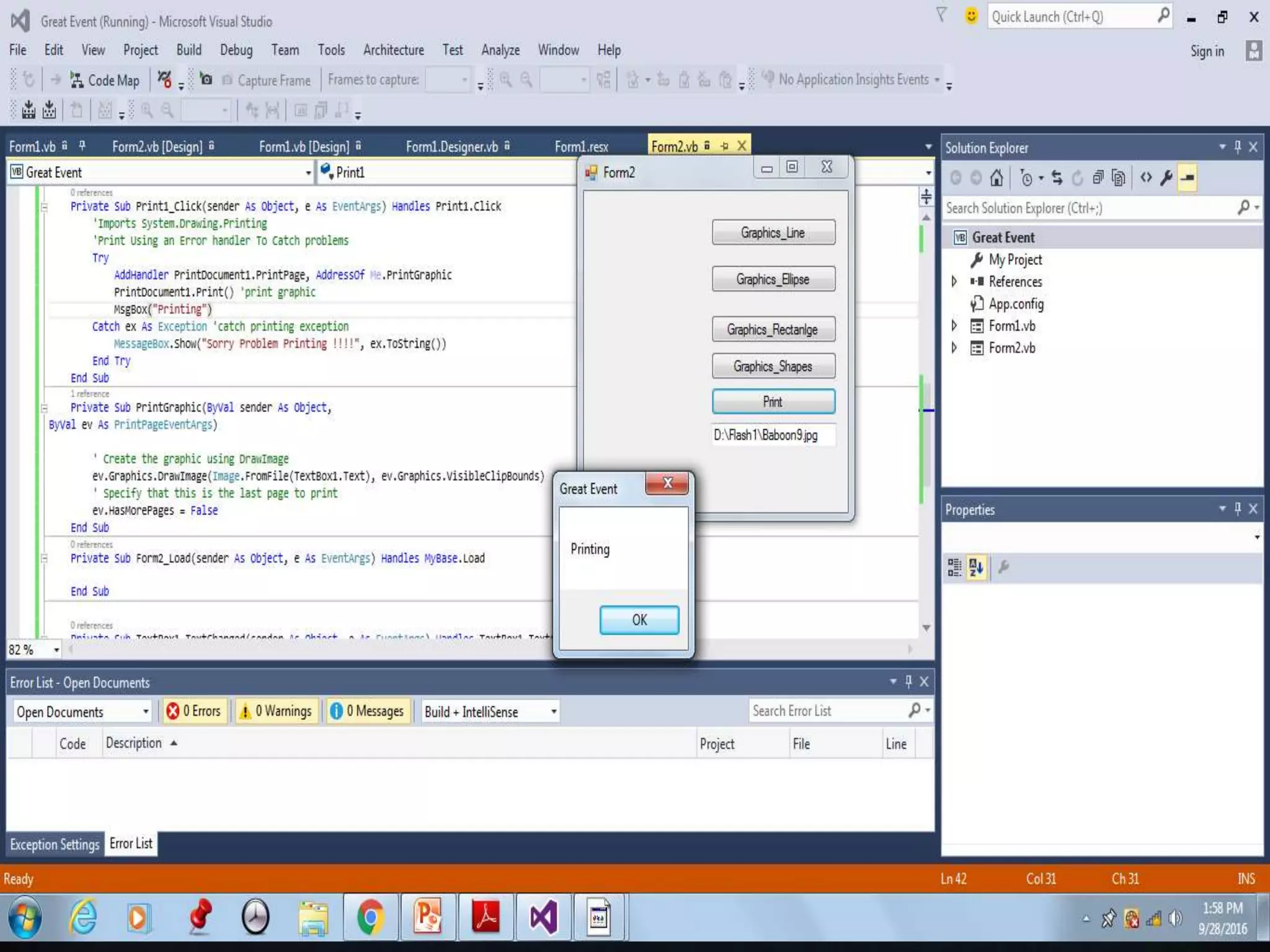
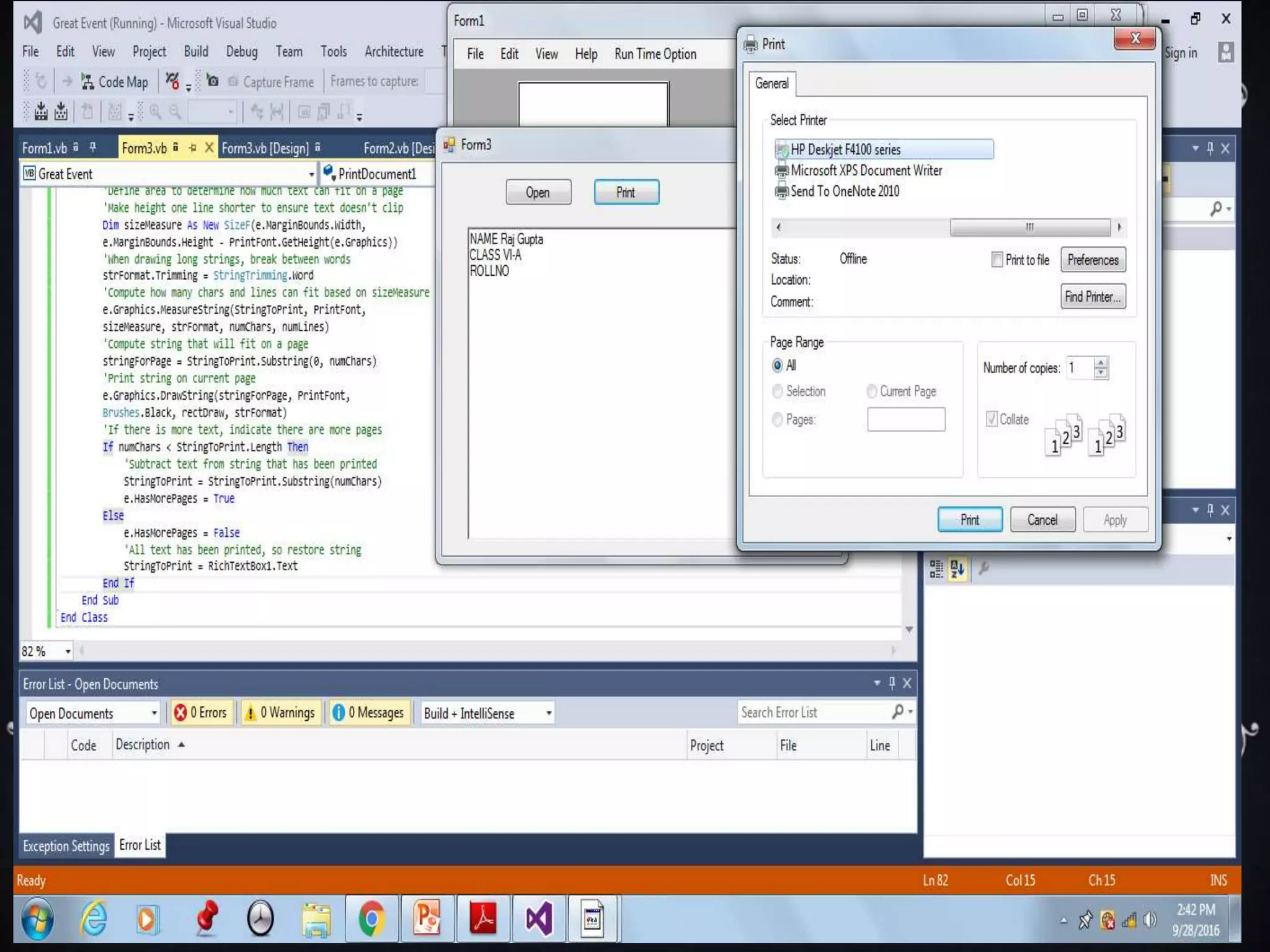
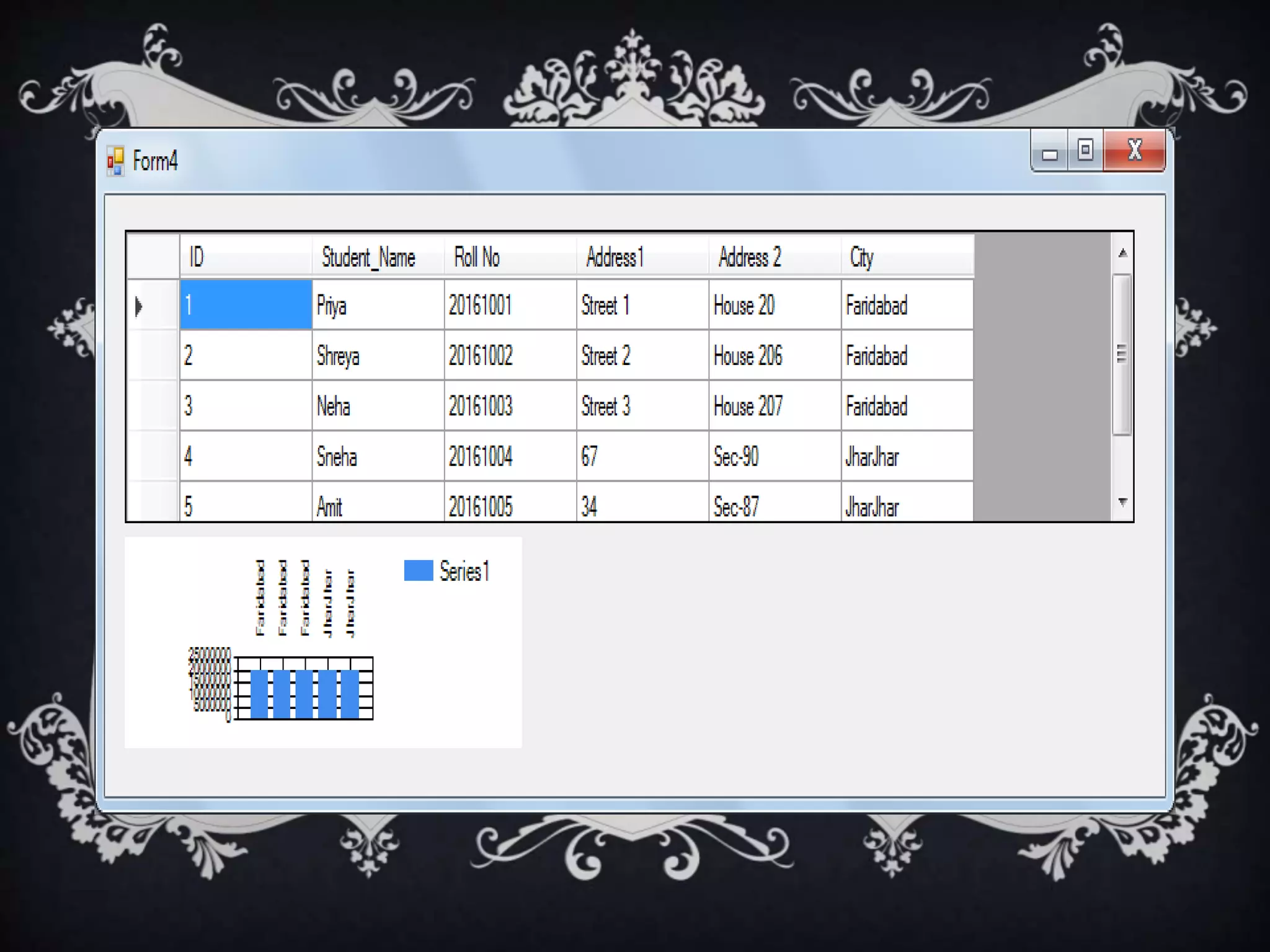
Interfaces allow for multiple inheritance in .NET and contain only method and property definitions without implementations. They are declared using the Interface keyword and implemented using the Implements keyword. Abstract classes can contain implemented members while interfaces cannot. Interfaces are useful when different objects need to share common behaviors. Events allow objects to notify other objects of actions through messages. They are handled by subscribing event handler methods. Exceptions disrupt normal program execution and are handled using try, catch, and finally blocks.