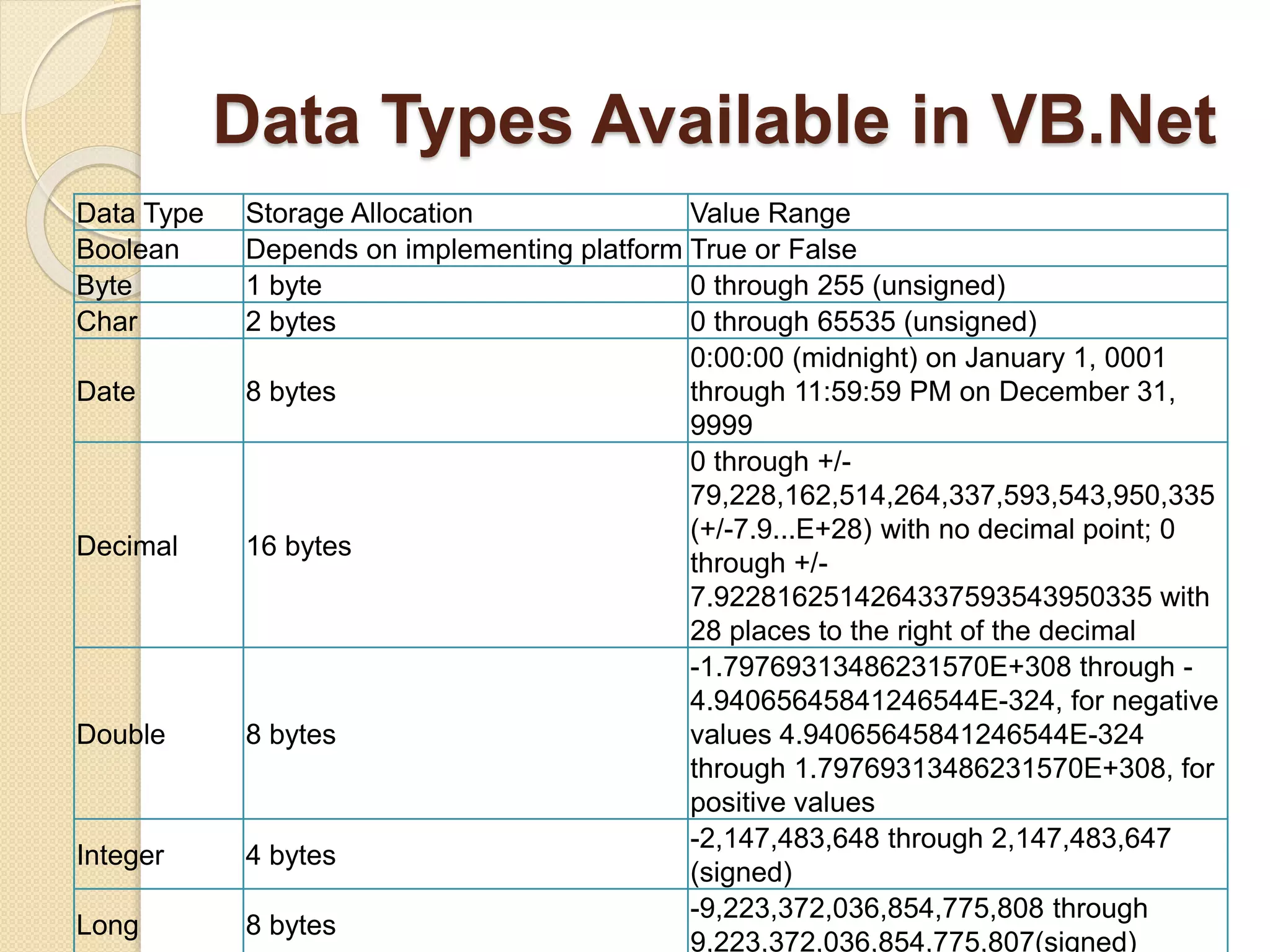
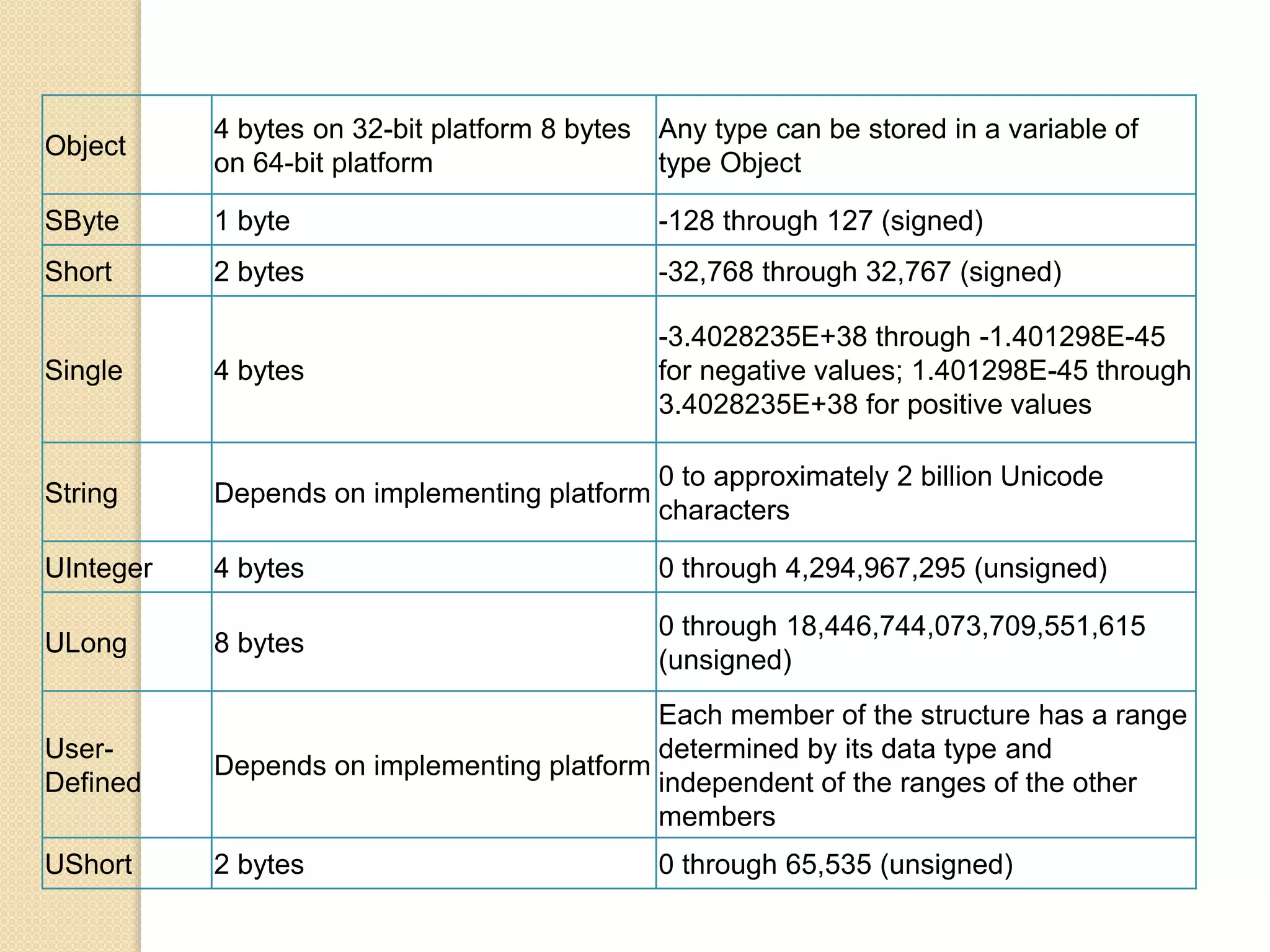
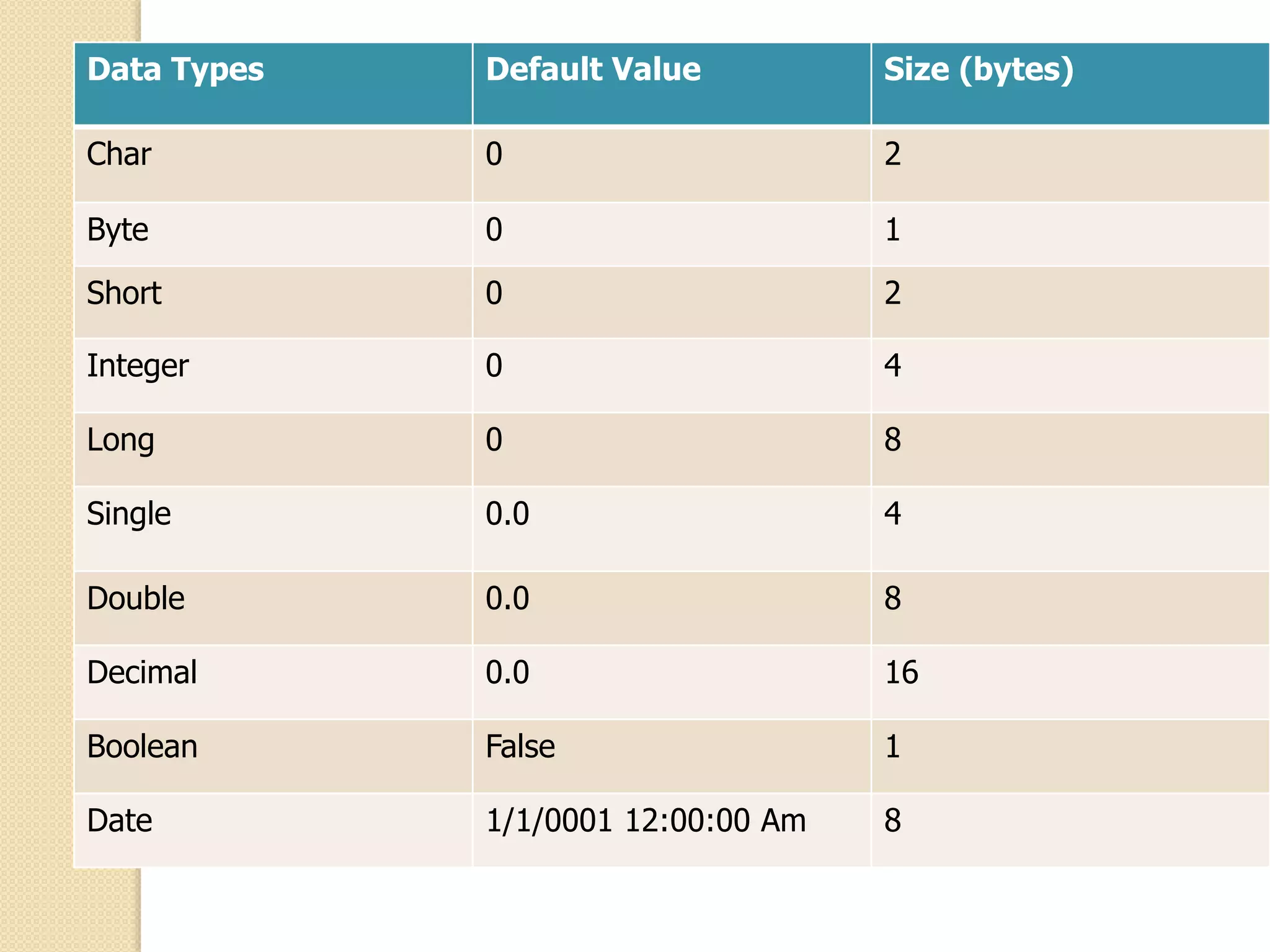
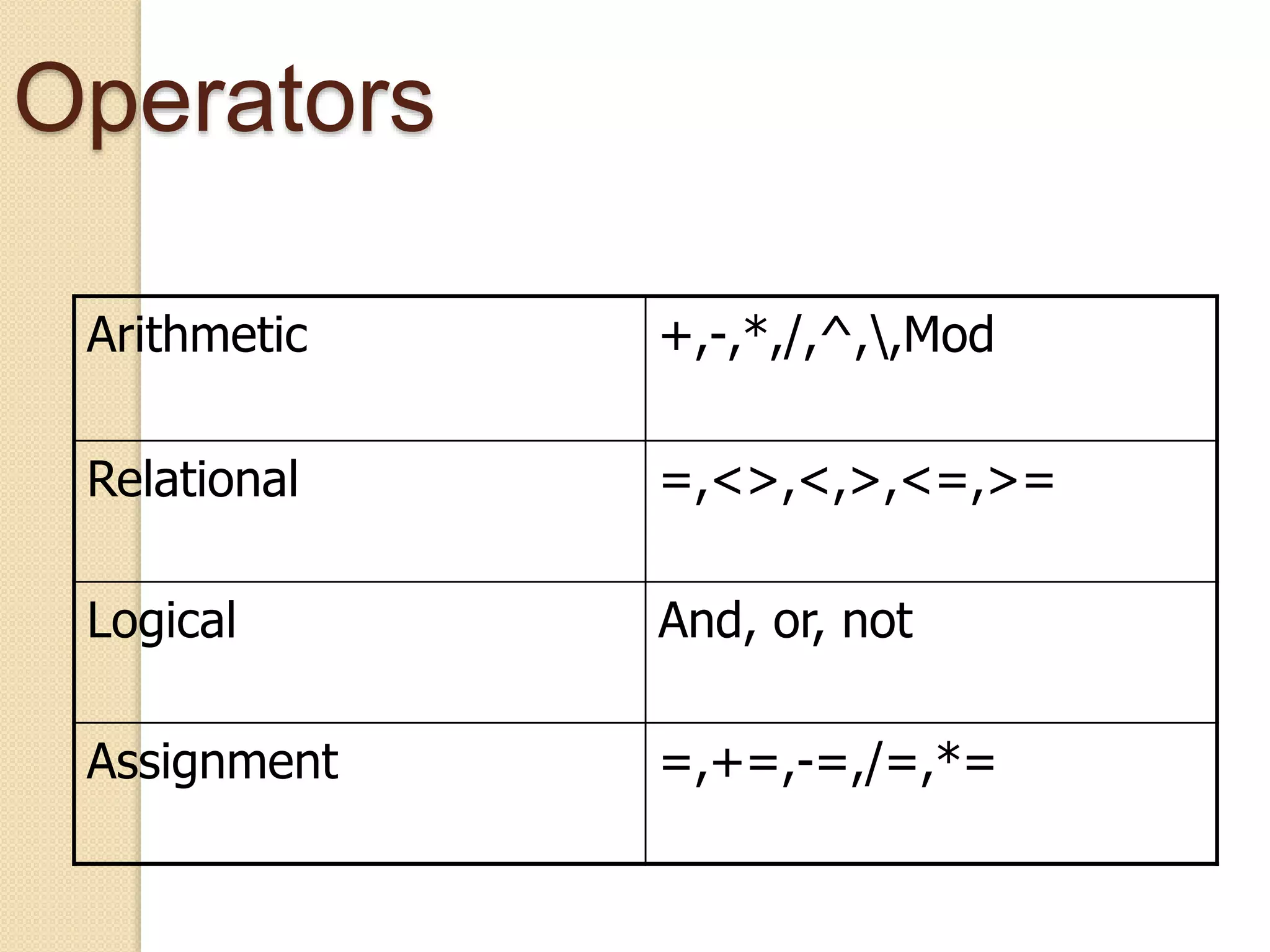
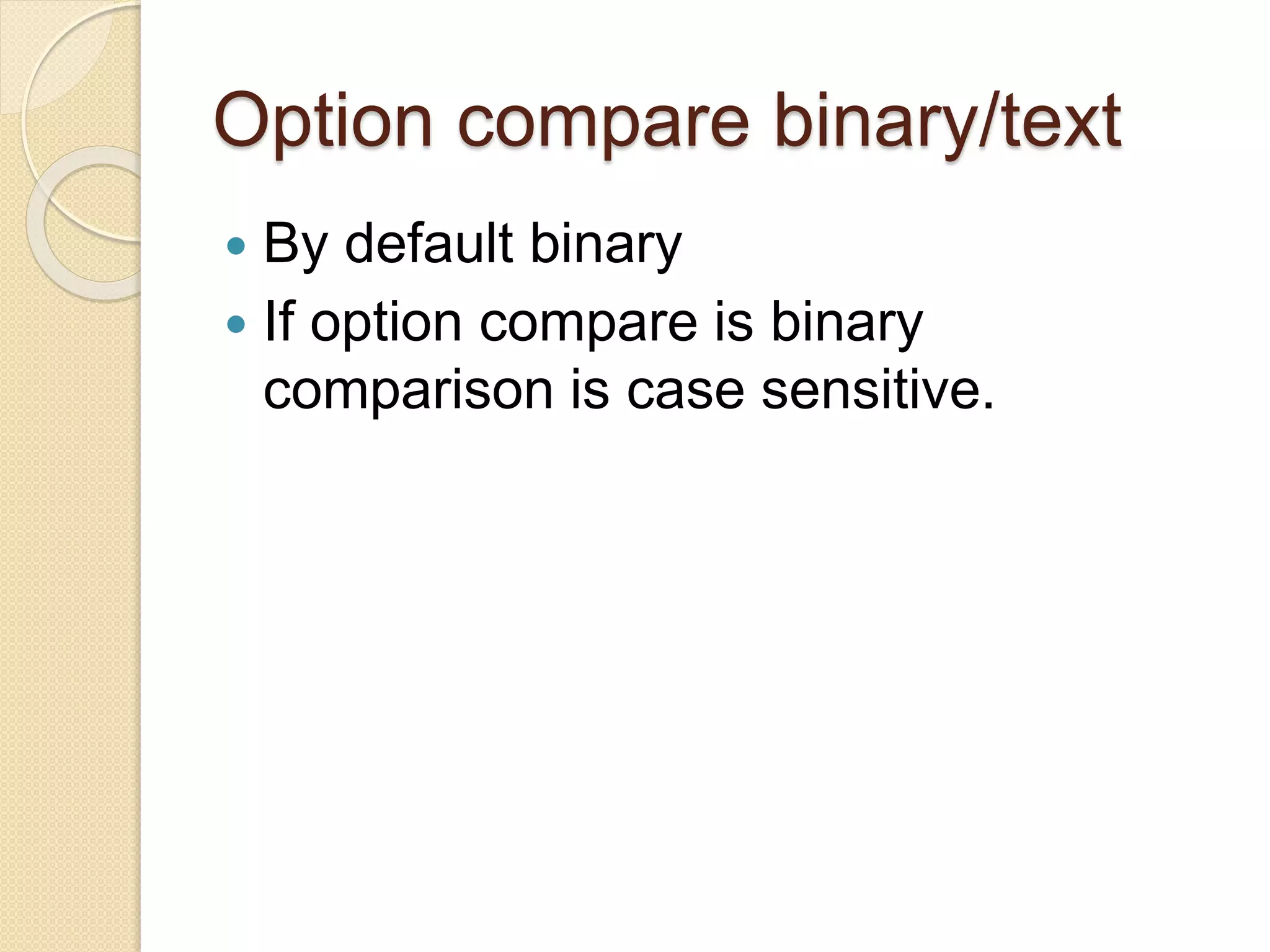
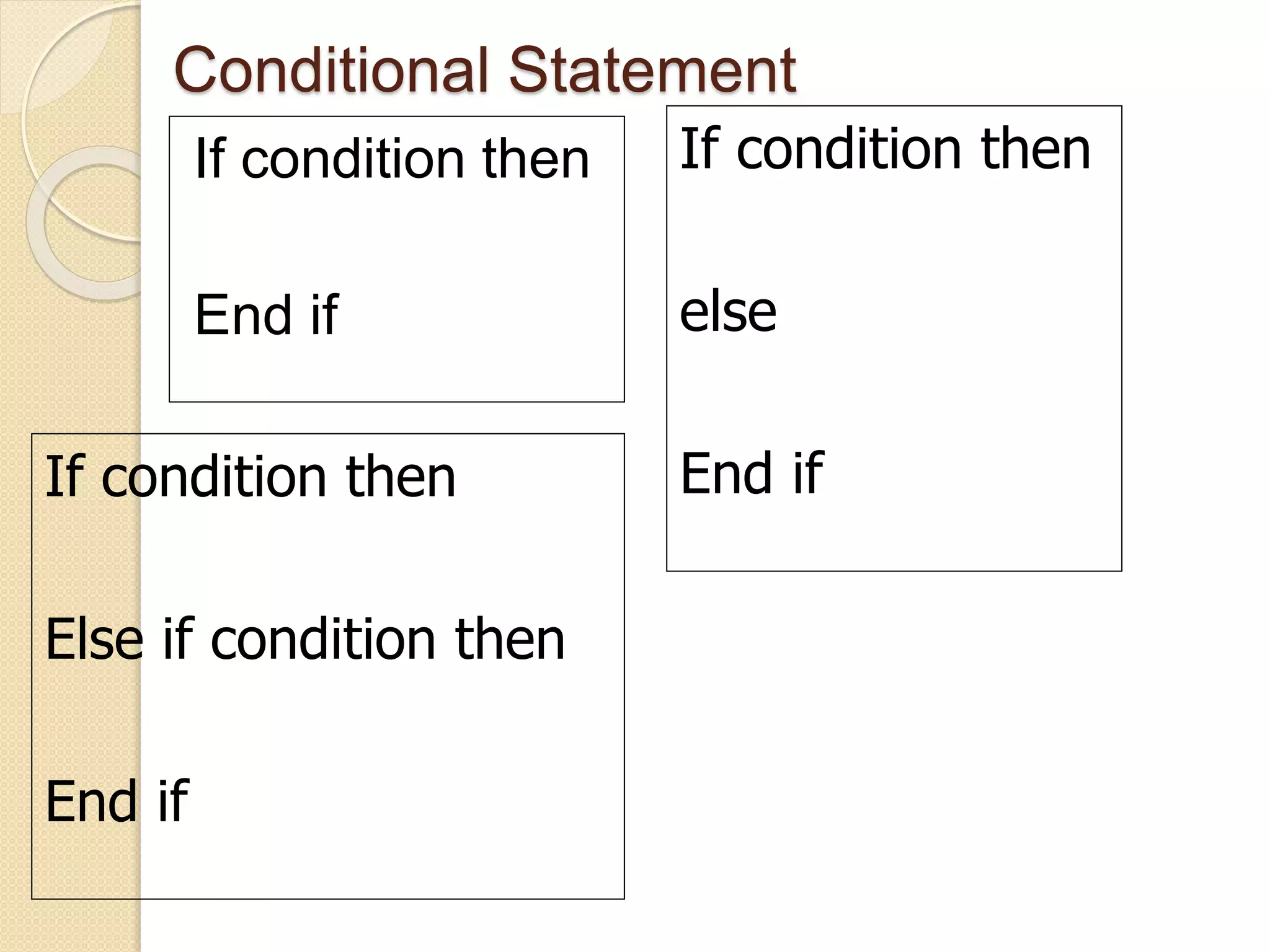
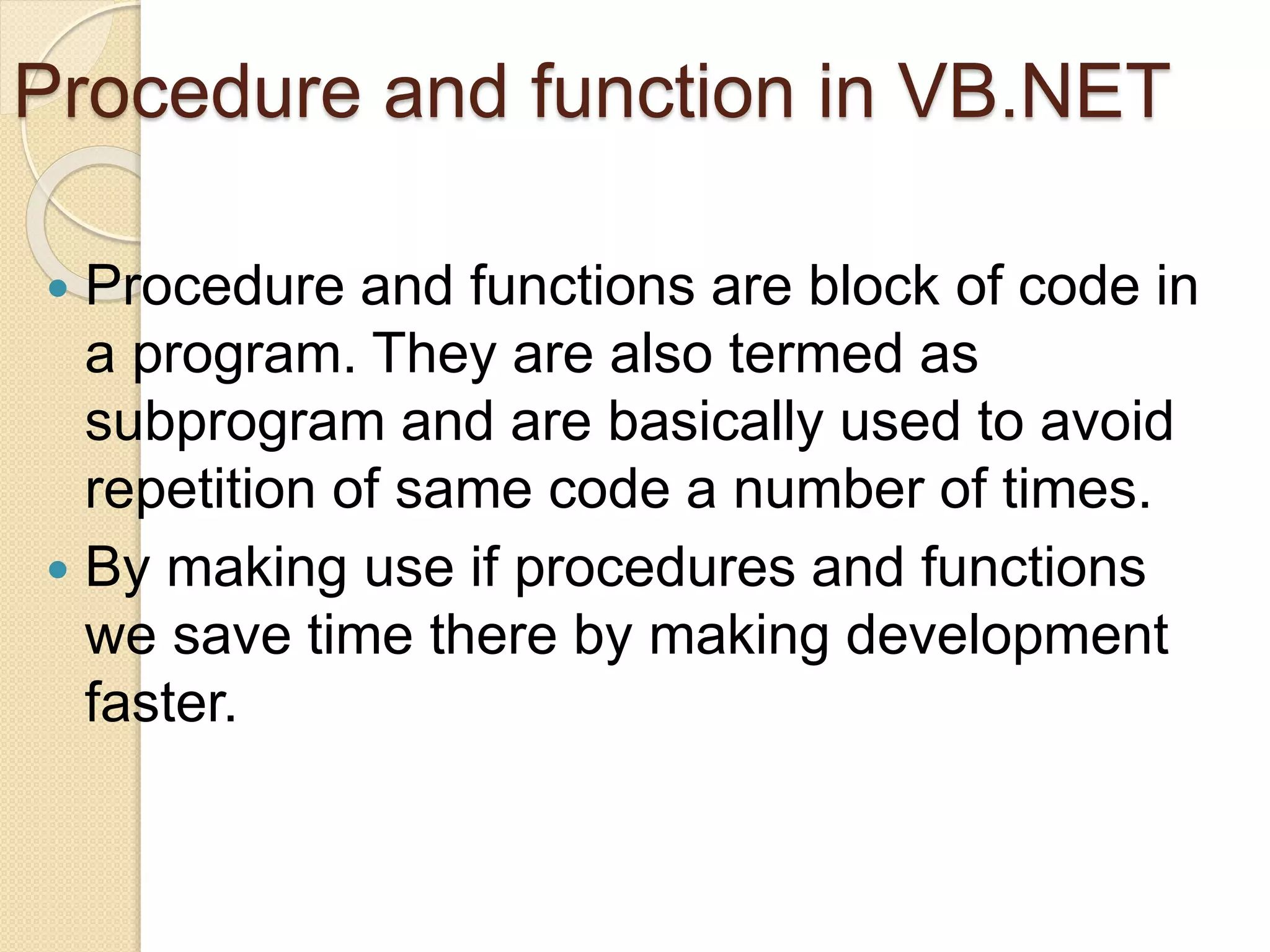
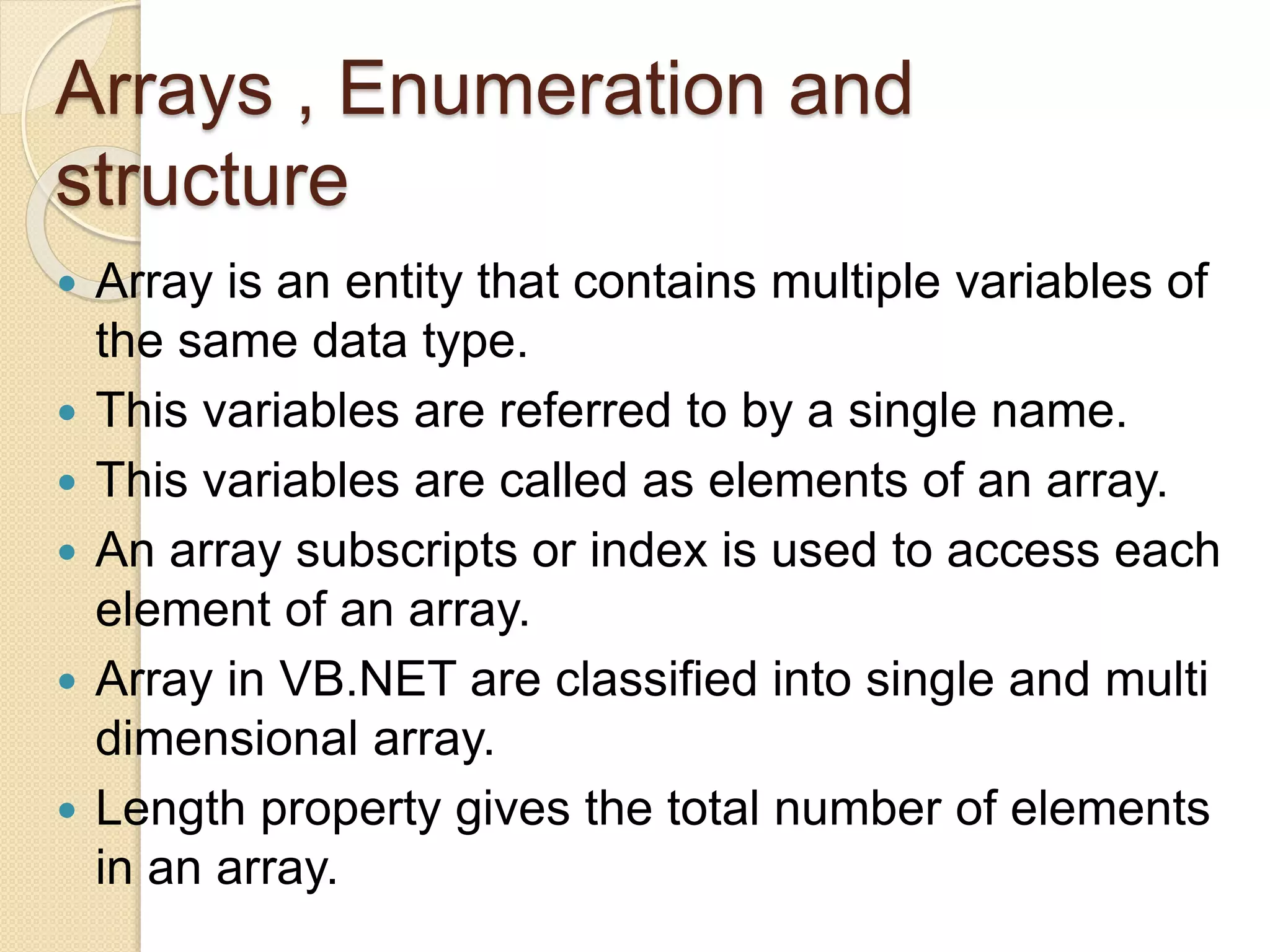
VB.NET is an object-oriented programming language within the .NET framework that treats everything as an object, including primitive types. It includes features such as automatic garbage collection, robust data types, and object-oriented concepts like inheritance, abstraction, and encapsulation. The document also covers programming constructs like loops, procedures, functions, handling events, delegates, multithreading, and memory management.