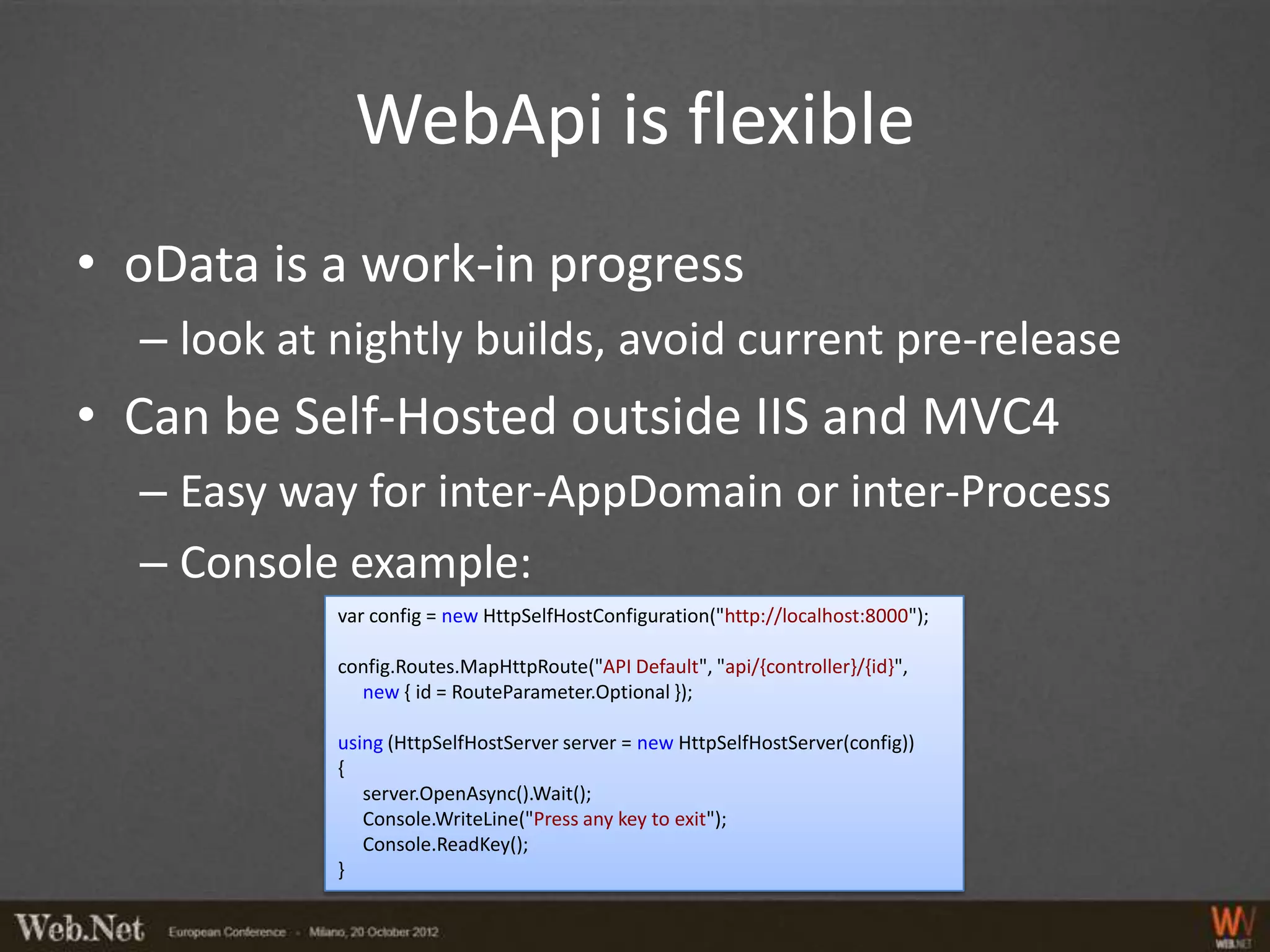
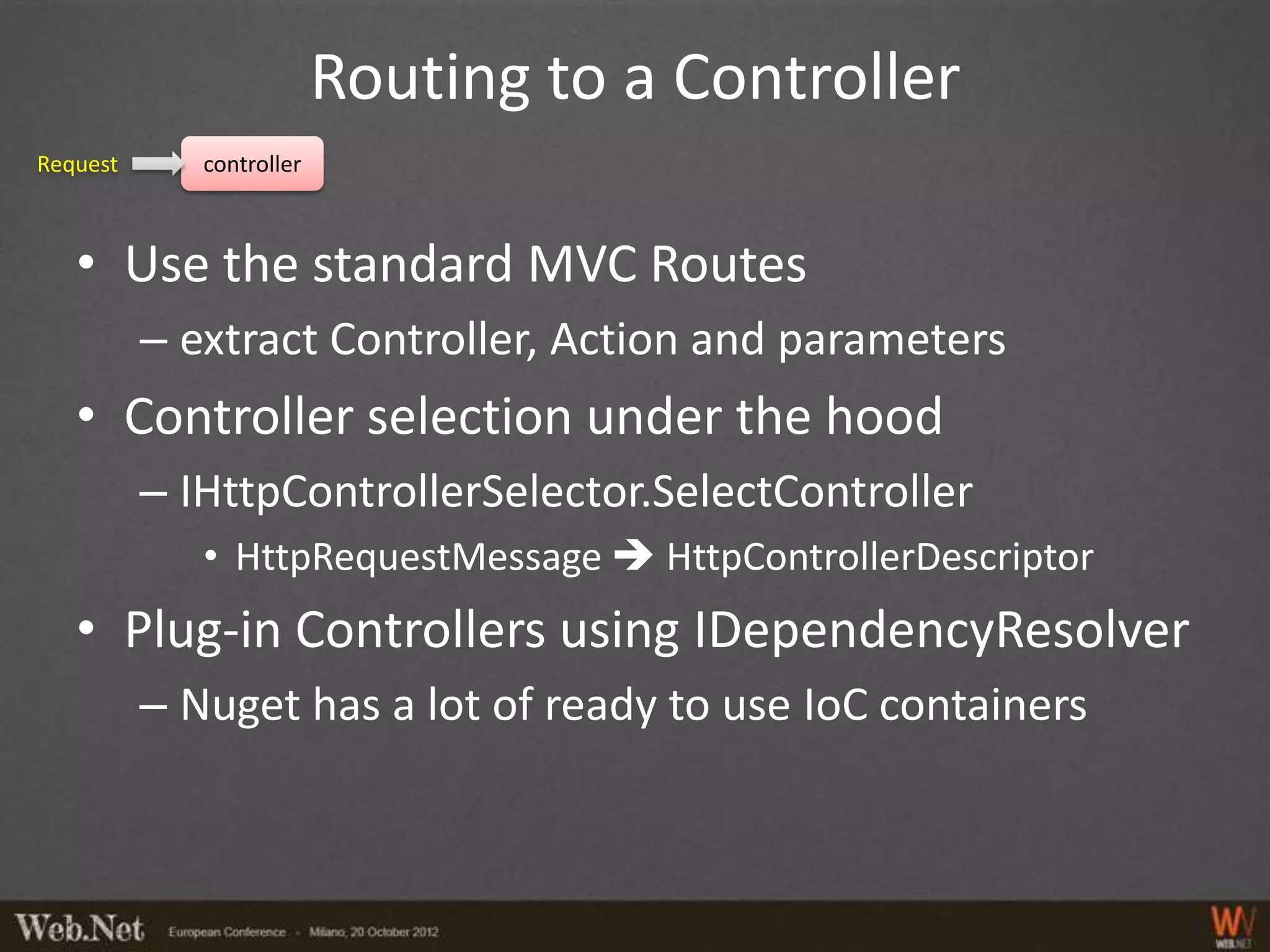
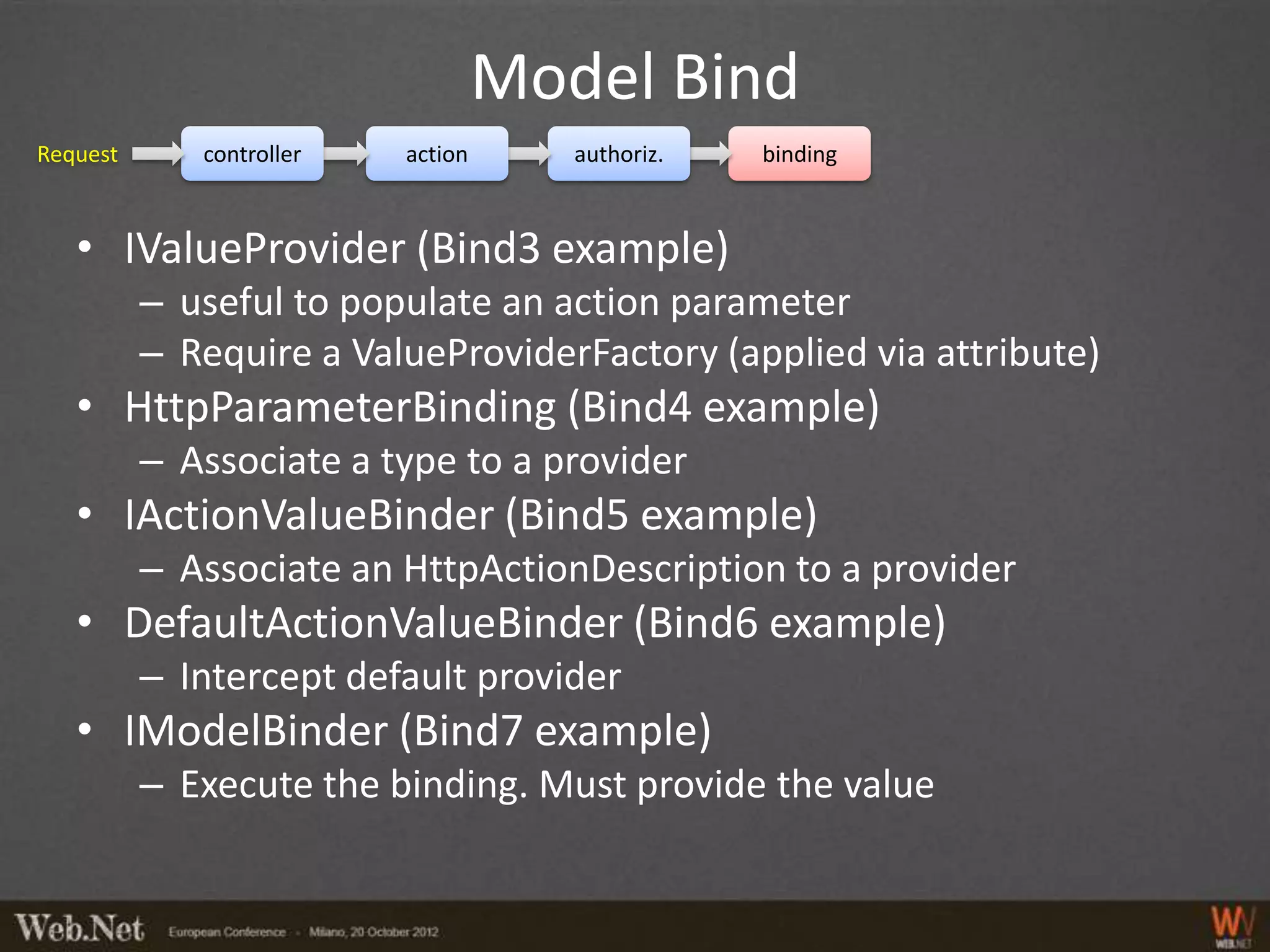
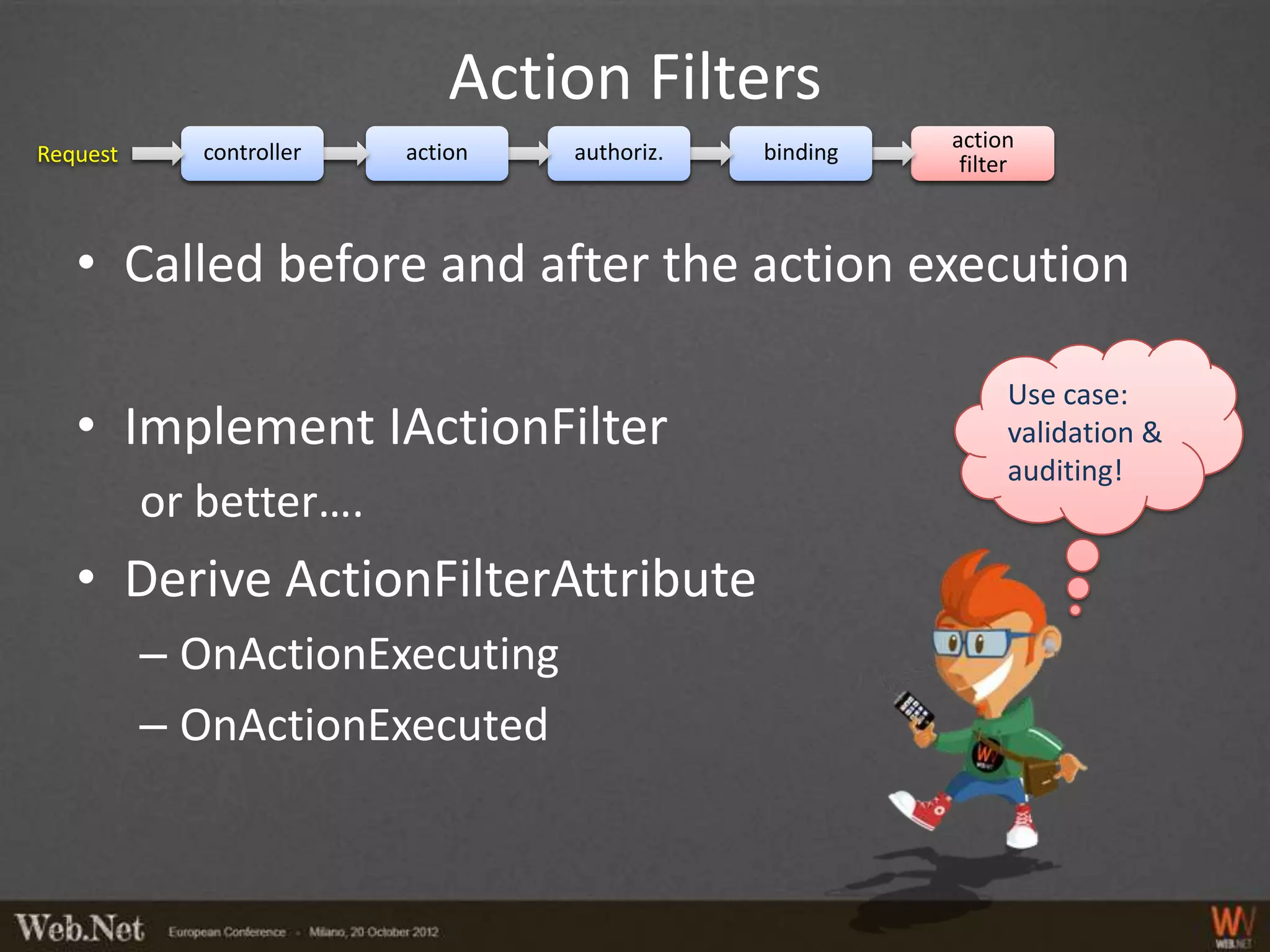
The document provides an overview of using WebAPI, emphasizing its flexibility for creating HTTP services and RESTful applications. It covers topics such as routing, action selection, authorization, data binding, error handling, and custom message processing. Additionally, it highlights the pluggable nature of WebAPI and the capabilities for handling security and custom serialization.



![Selecting an Action
Request controller action
• The easiest way is to modify the default Route
config.Routes.MapHttpRoute(
name: "DefaultApi",
routeTemplate: "api/{controller}/{id}",
defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional }
); config.Routes.MapHttpRoute(
name: "DefaultApi2",
routeTemplate: "api/{controller}/{action}/{x}/{y}" );
• Can use [ActionName("myaction")]
– override the method name as the action name
• Can use [NonAction]
– exclude a method from being an action](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webapifullpower-121030114910-phpapp02/75/How-to-get-full-power-from-WebApi-7-2048.jpg)

![Authorization filter
Request controller action authoriz. I’ll play with
Claims
• [Authorize] is Role oriented
• Derive AuthorizeAttribute to go Claim oriented
• [AllowAnonymous] is self-explanatory
• Starting from Fx4.5 new universal base classes
– ClaimsPrincipal for every Principal
– ClaimsIdentity for every Identity
IPrincipal client = Thread.CurrentPrincipal;
ClaimsPrincipal principal = Thread.CurrentPrincipal as ClaimsPrincipal;
ClaimsIdentity identity = principal.Identity as ClaimsIdentity;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webapifullpower-121030114910-phpapp02/75/How-to-get-full-power-from-WebApi-9-2048.jpg)




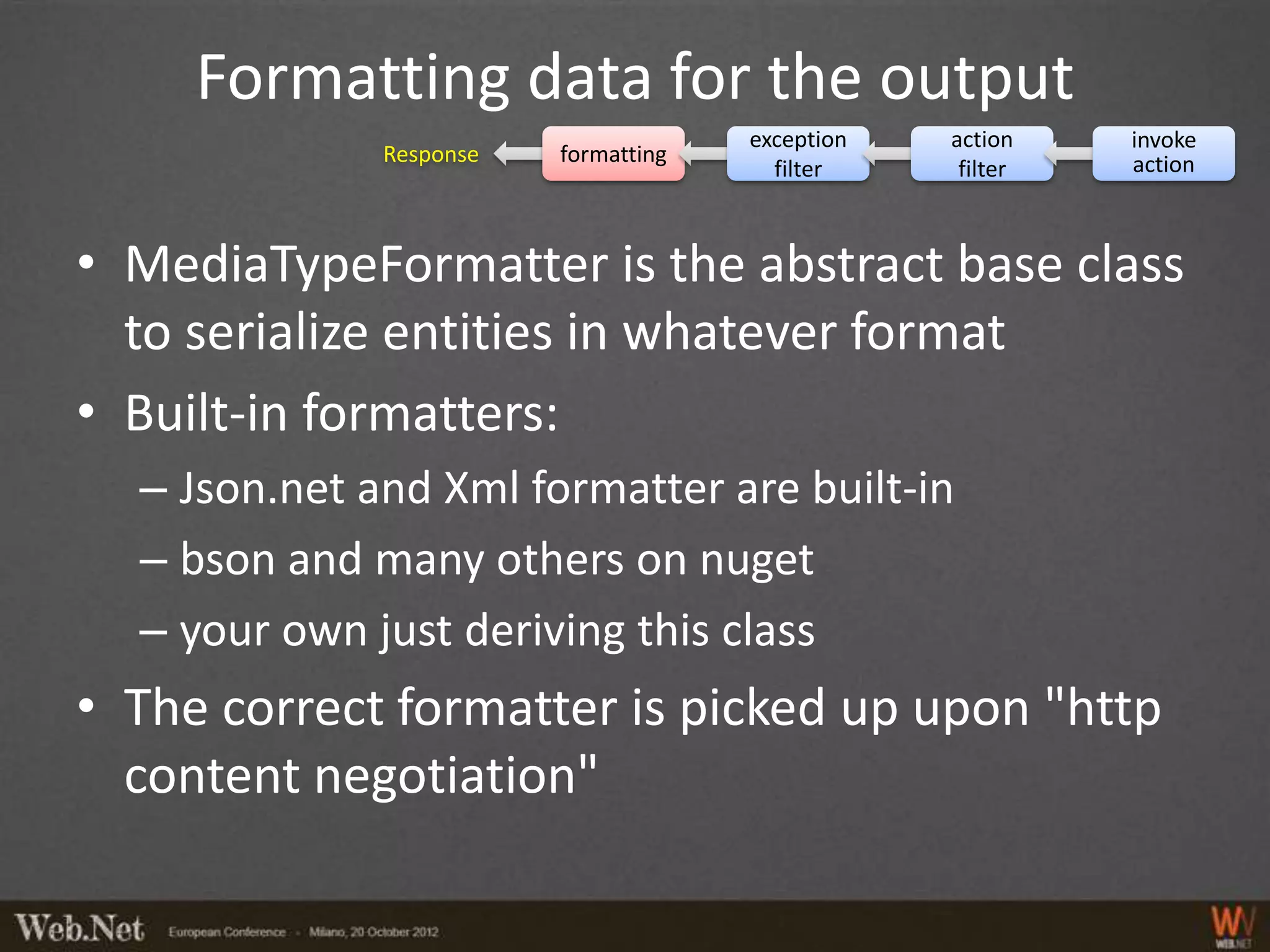
![Exception Filters
exception action invoke
filter filter action
• Do not use MVC [HandleError]
• Transform CLR exceptions in HTTP messages
• Implement IExceptionFilter or better derive
ExceptionFilterAttribute
• Mark actions with the attribute
or
• Change the global configuration
– GlobalConfiguration.Configuration.Filters.Add(new
MyNamespace.NotImplExceptionFilterAttribute());](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webapifullpower-121030114910-phpapp02/75/How-to-get-full-power-from-WebApi-16-2048.jpg)