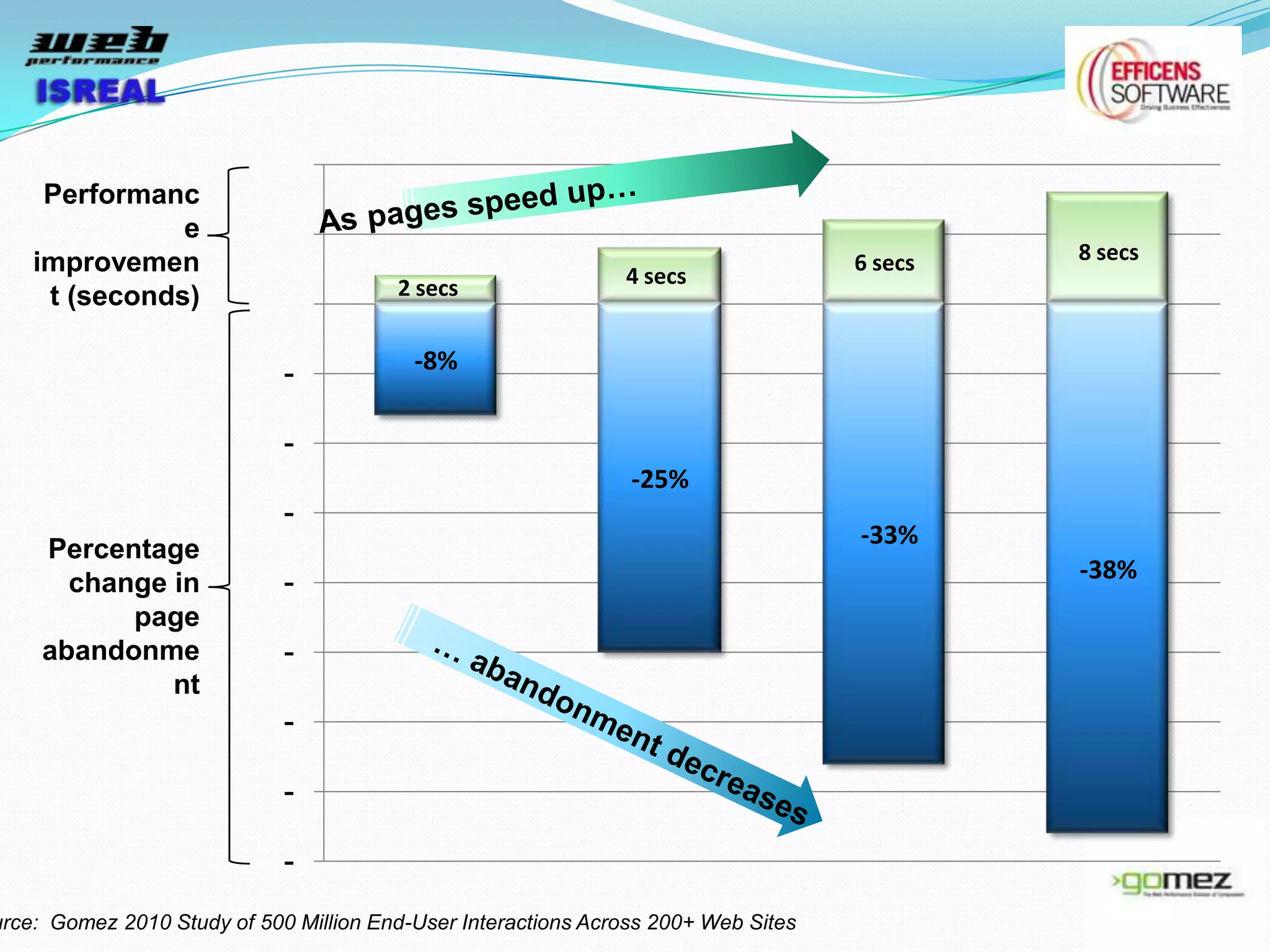
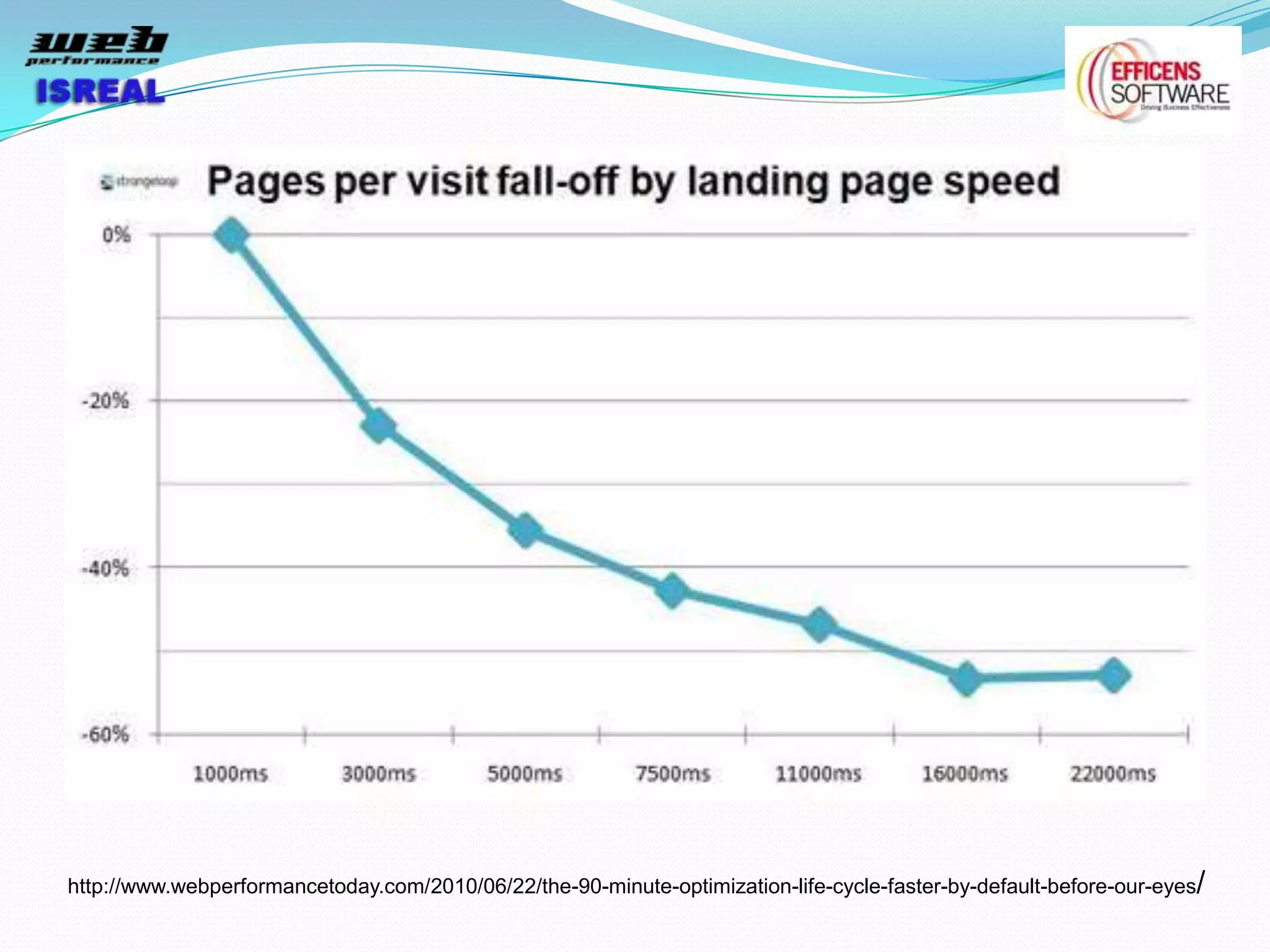
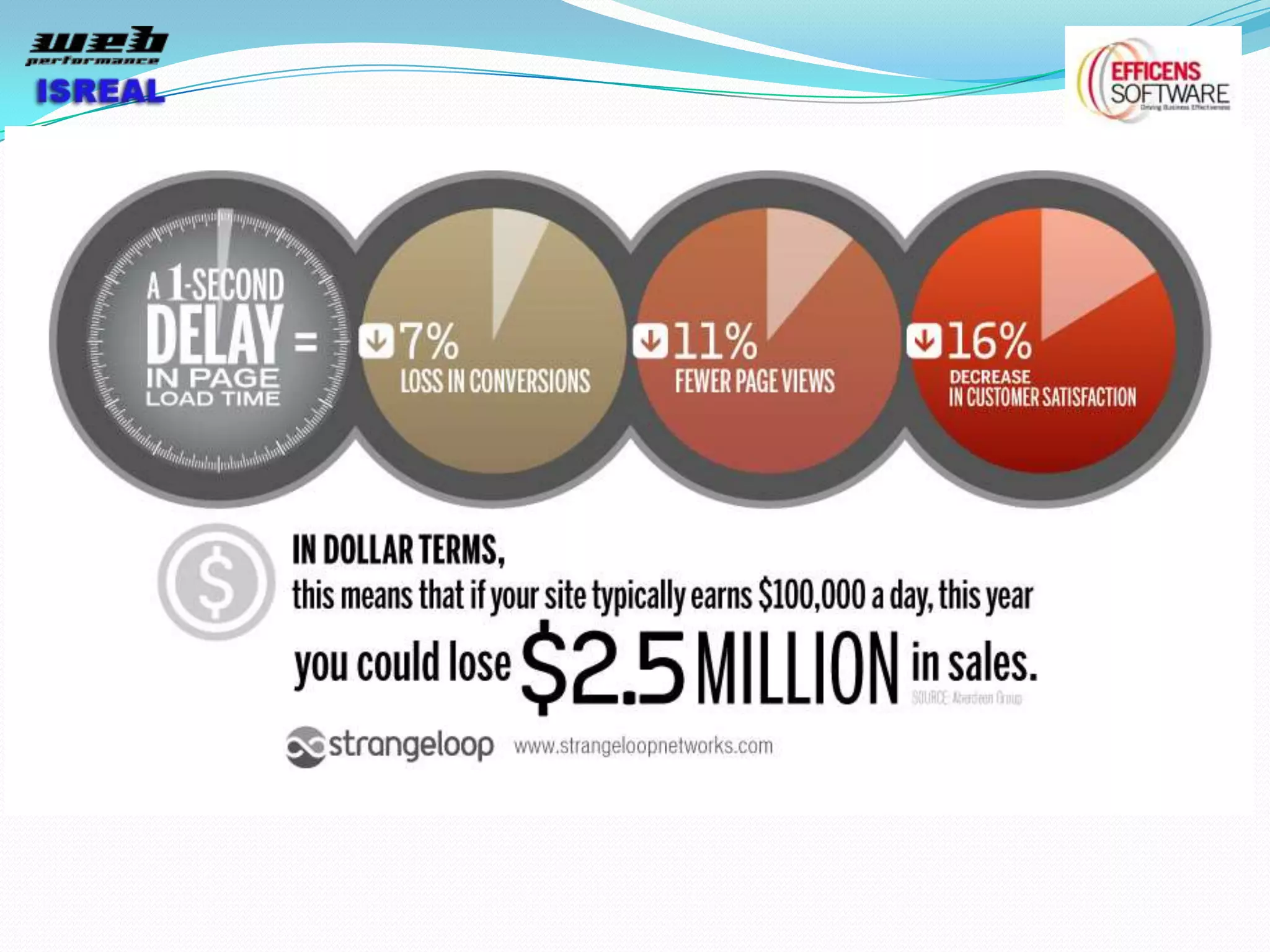
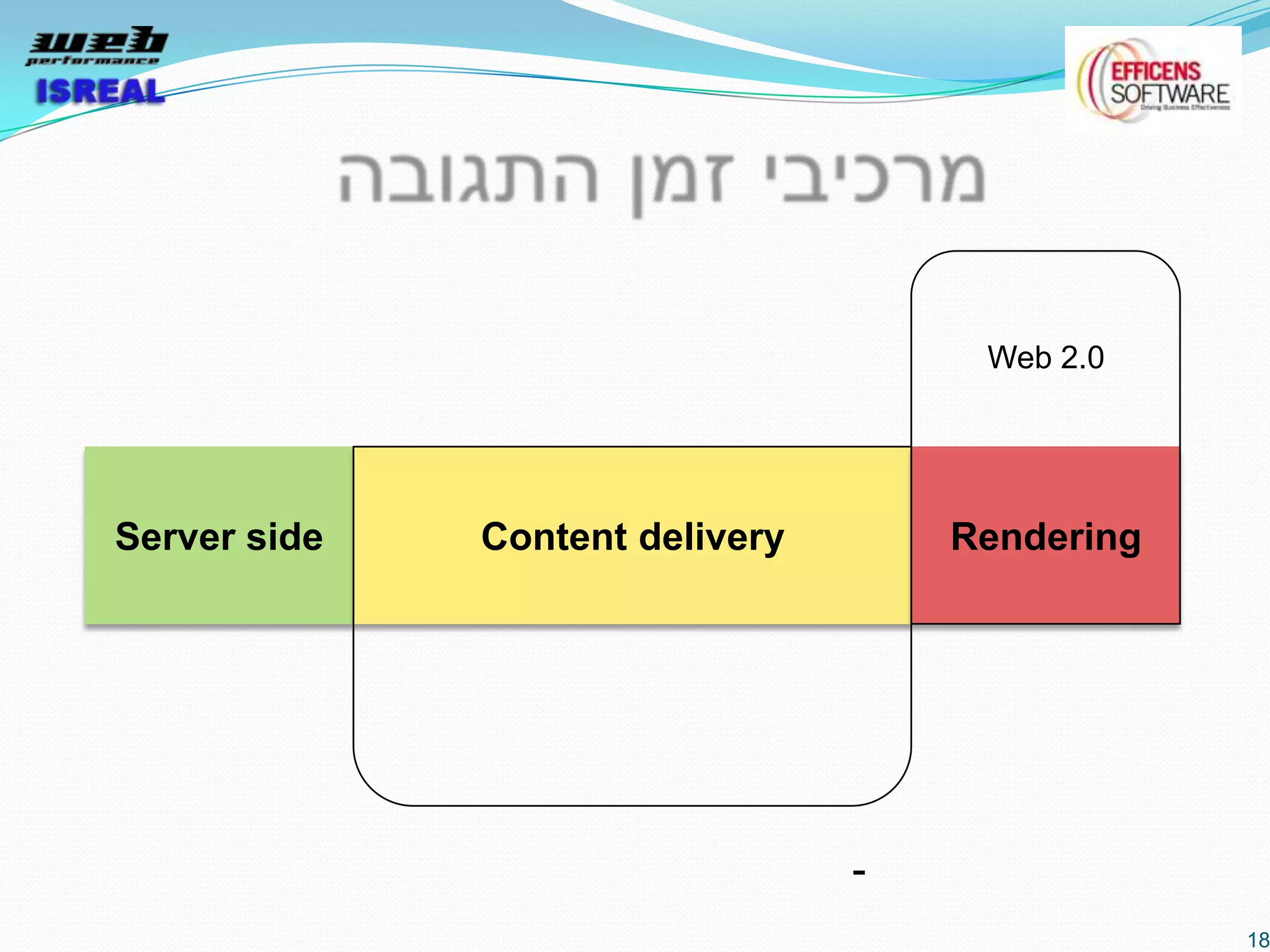
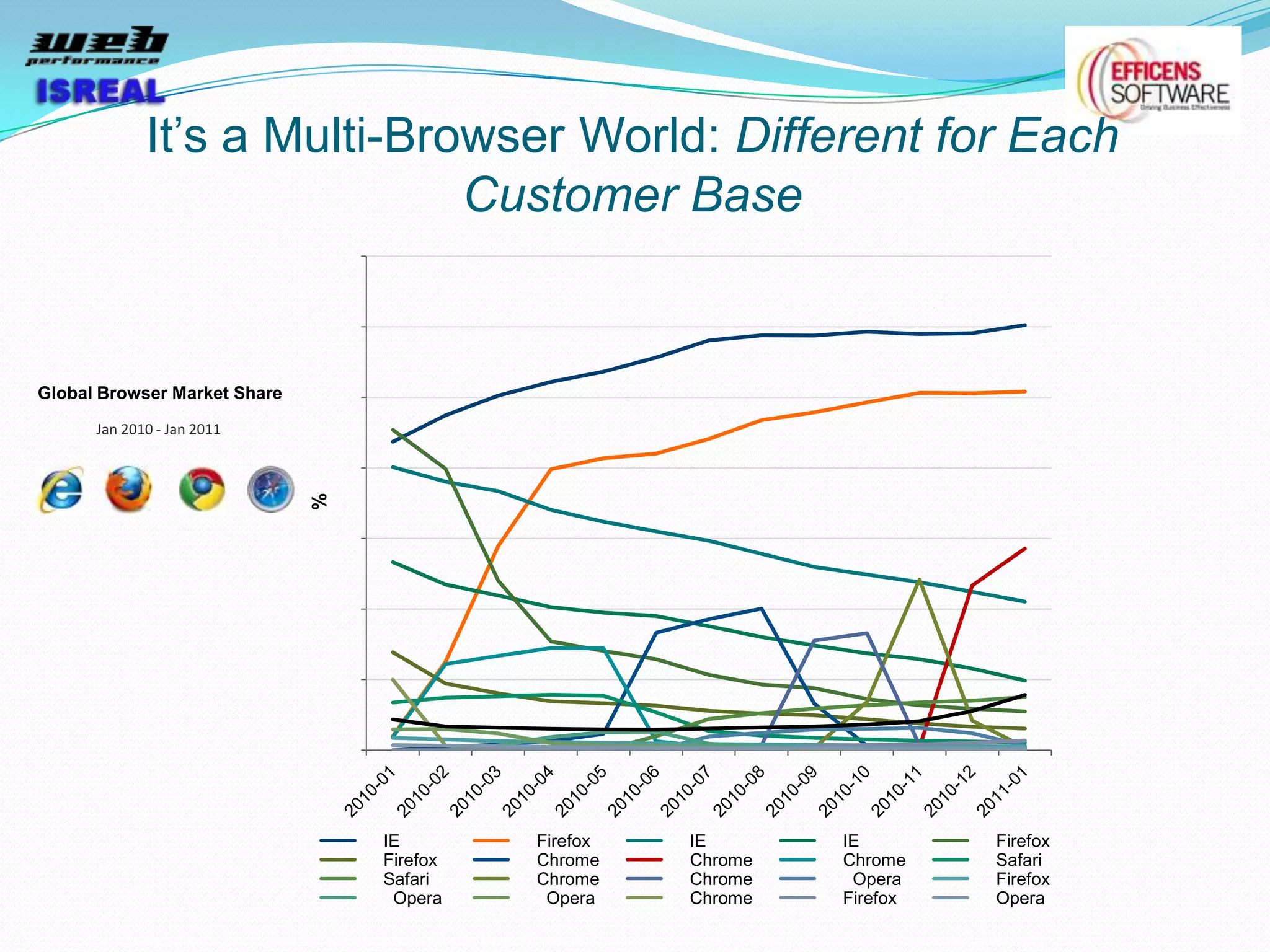
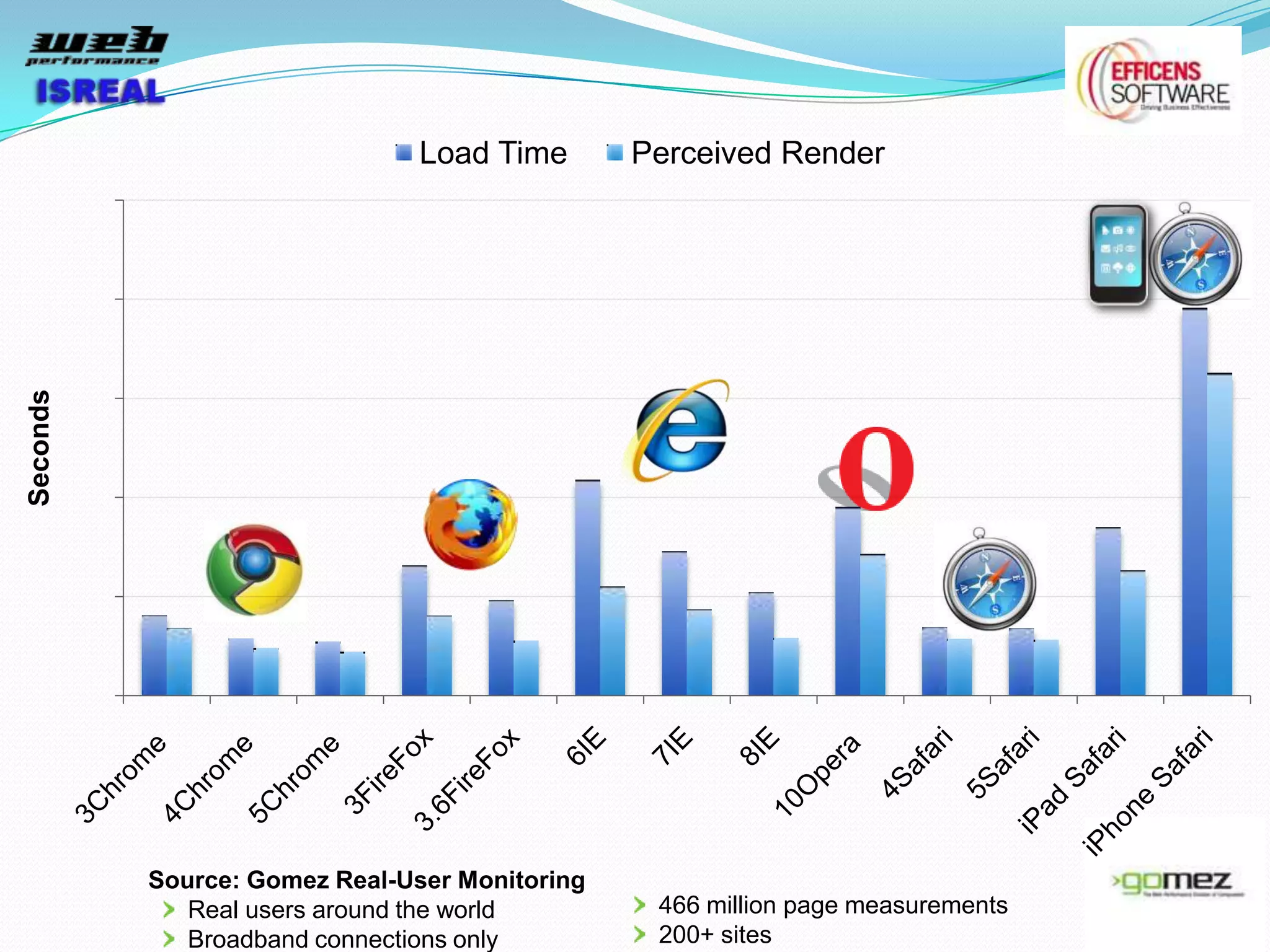
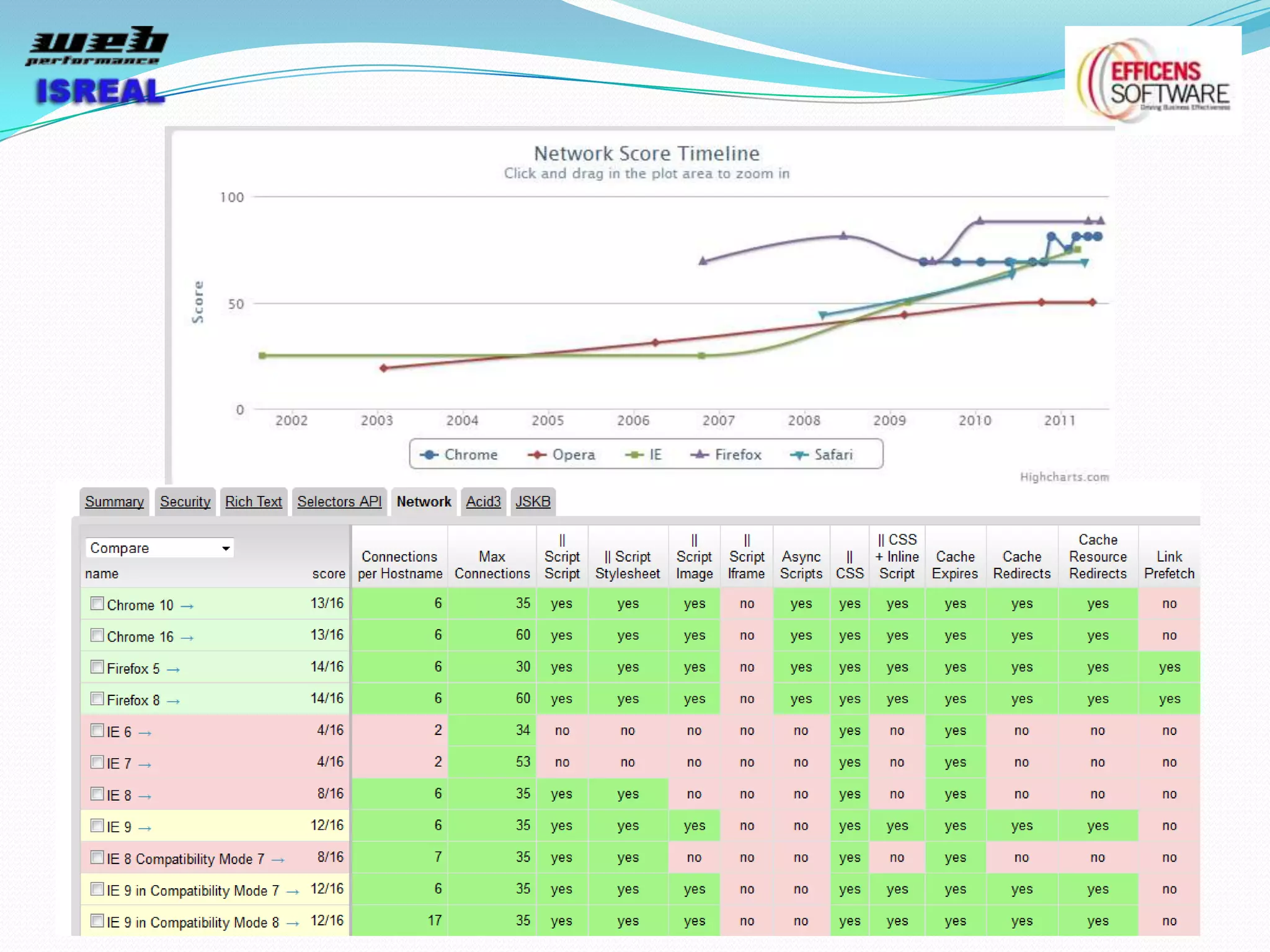
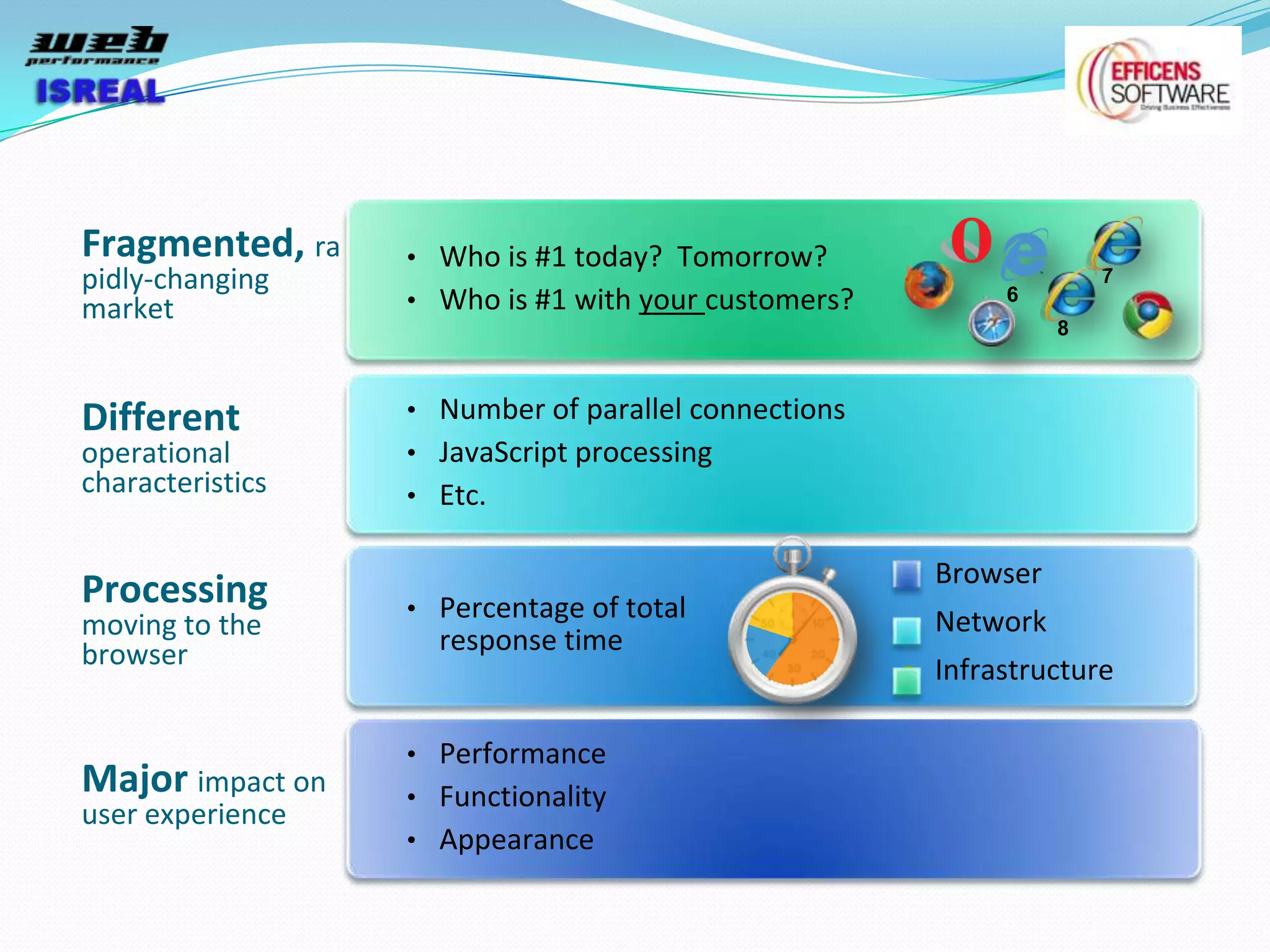
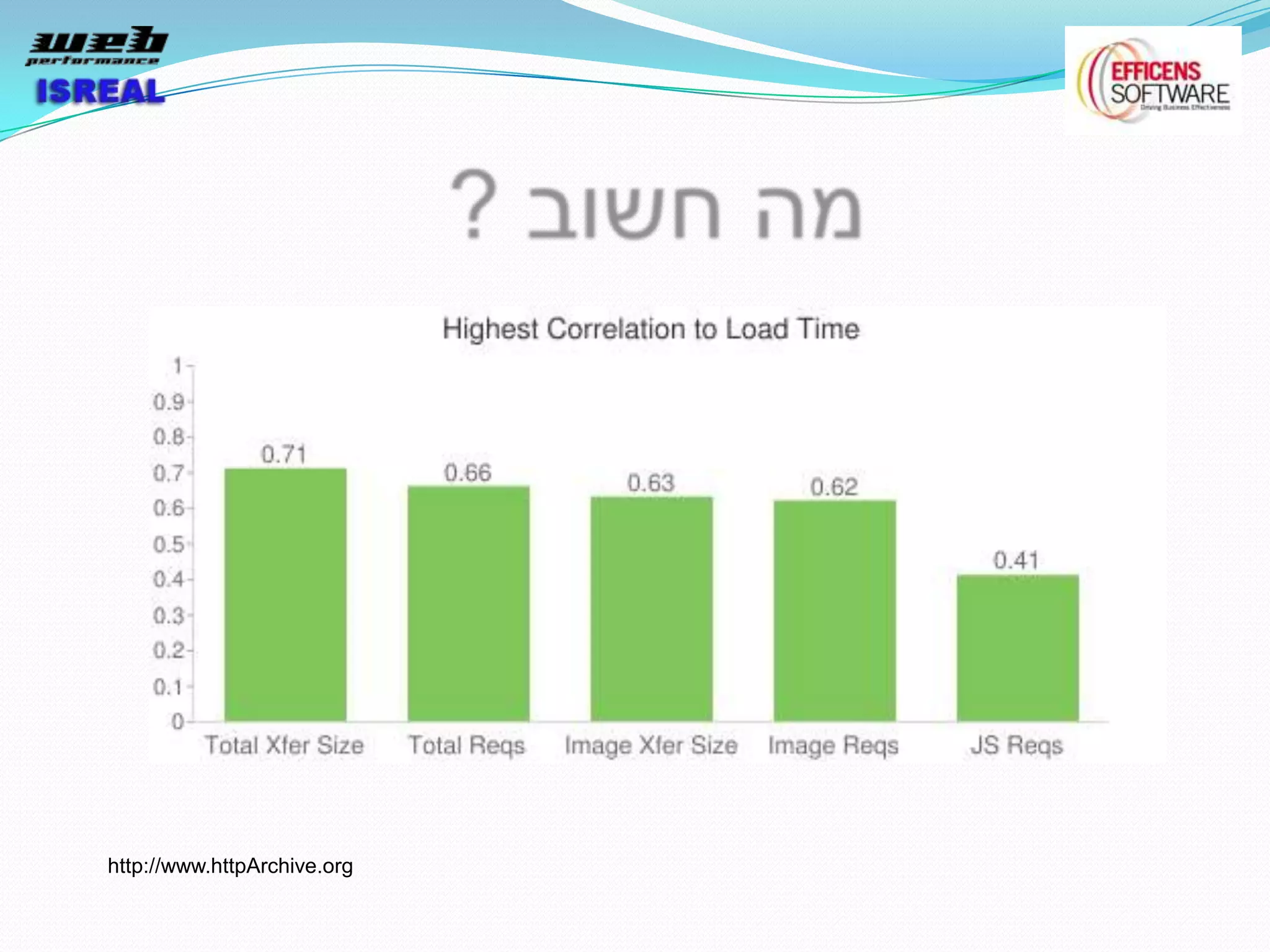
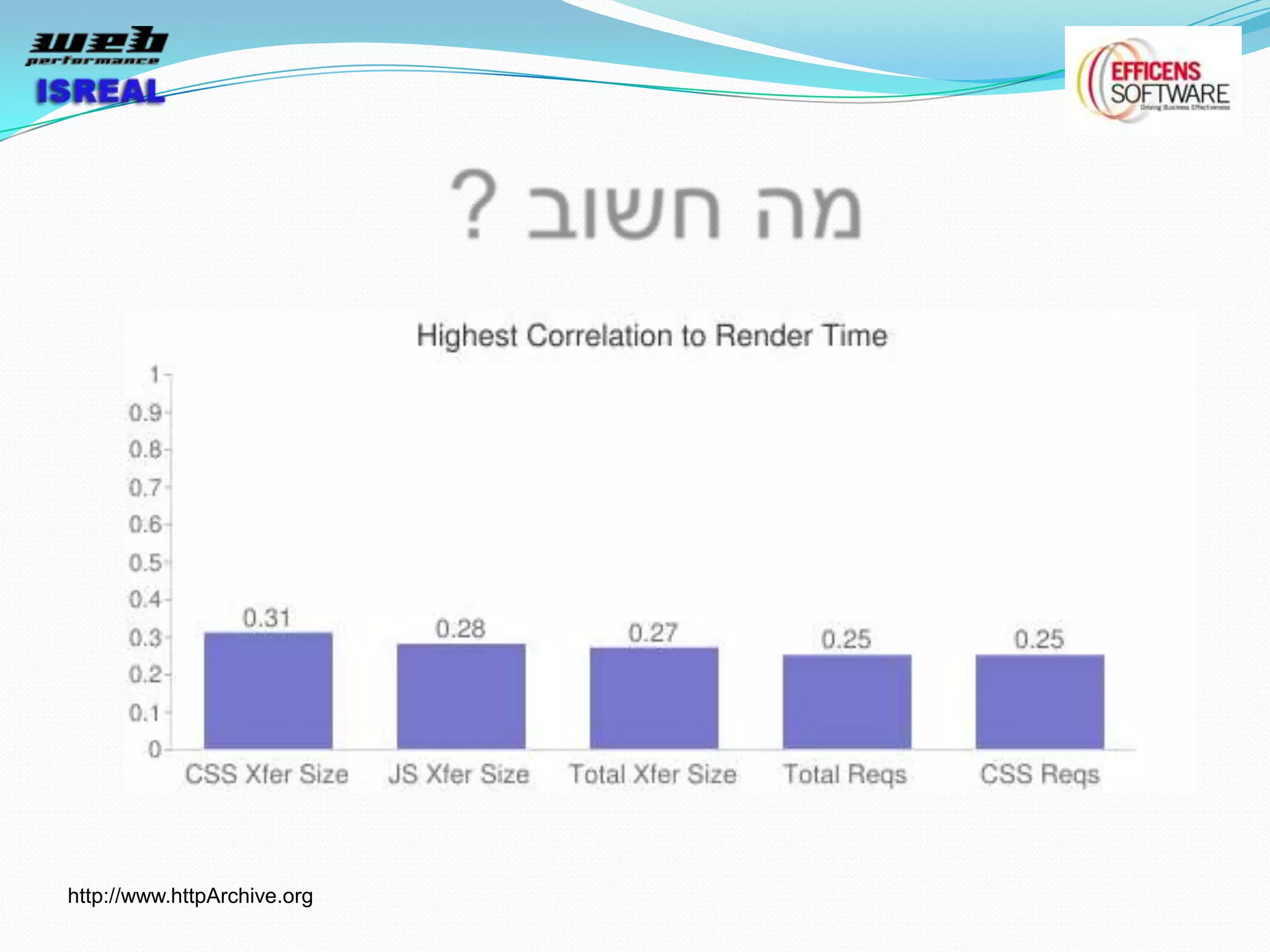
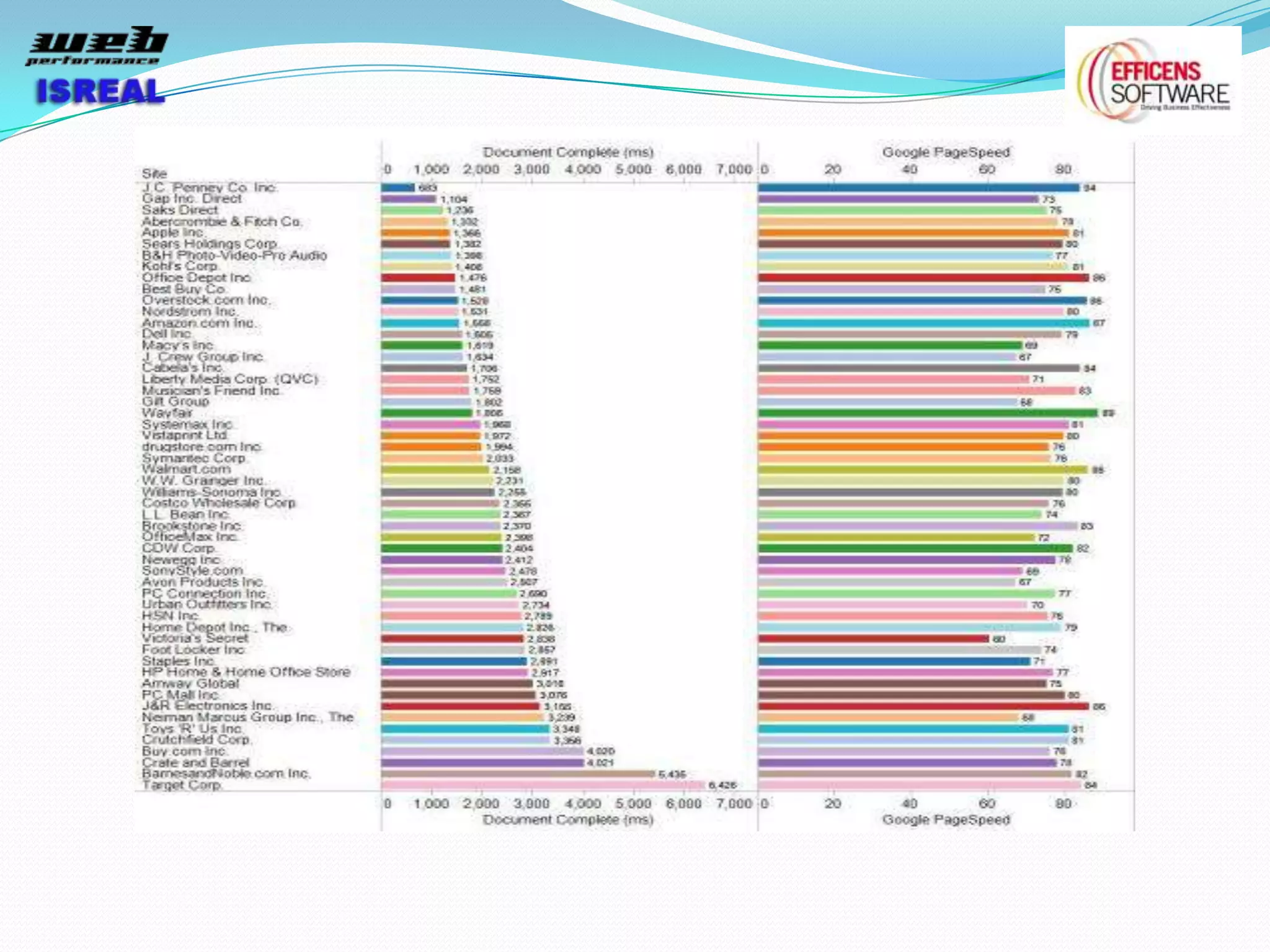
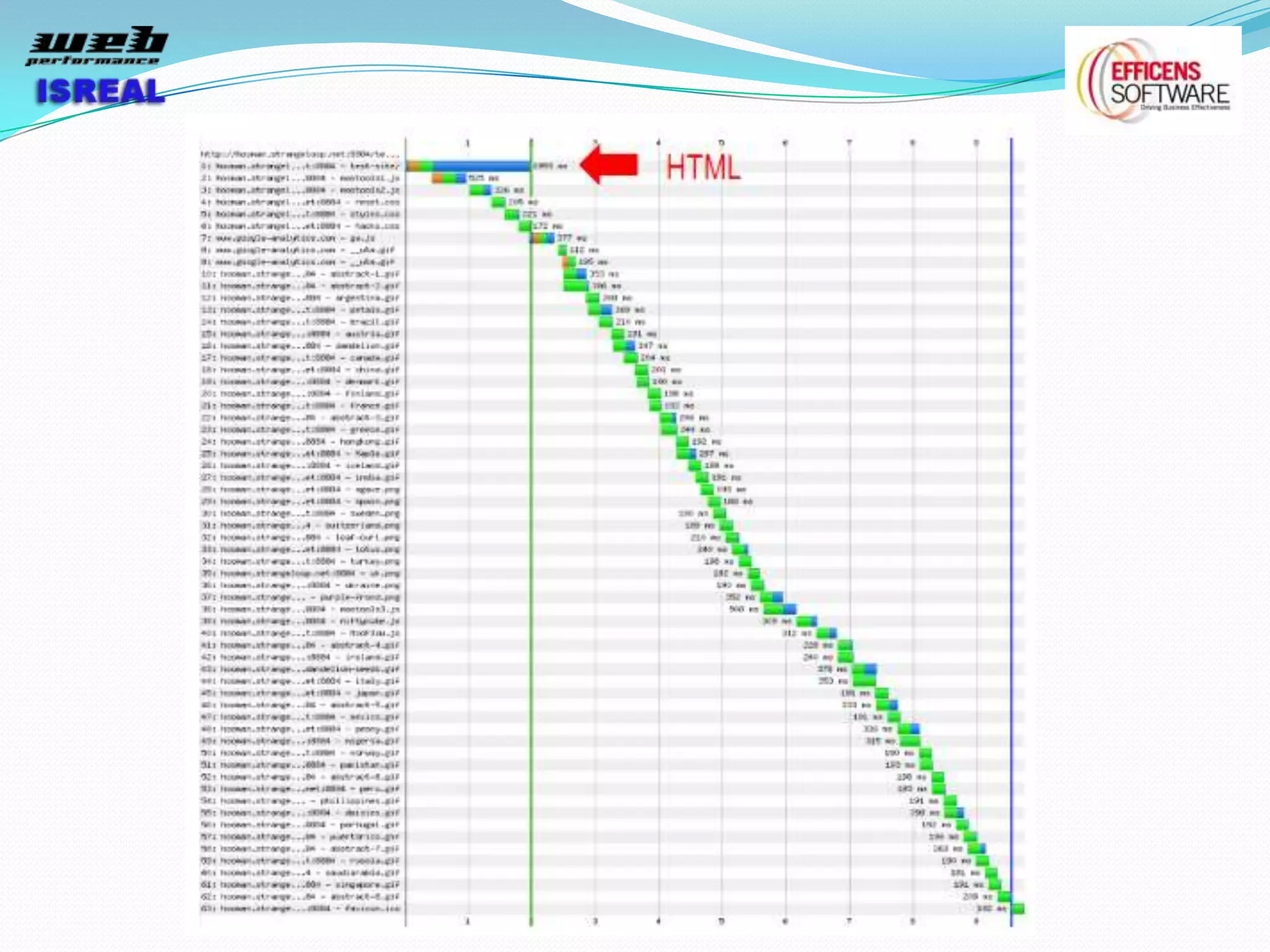
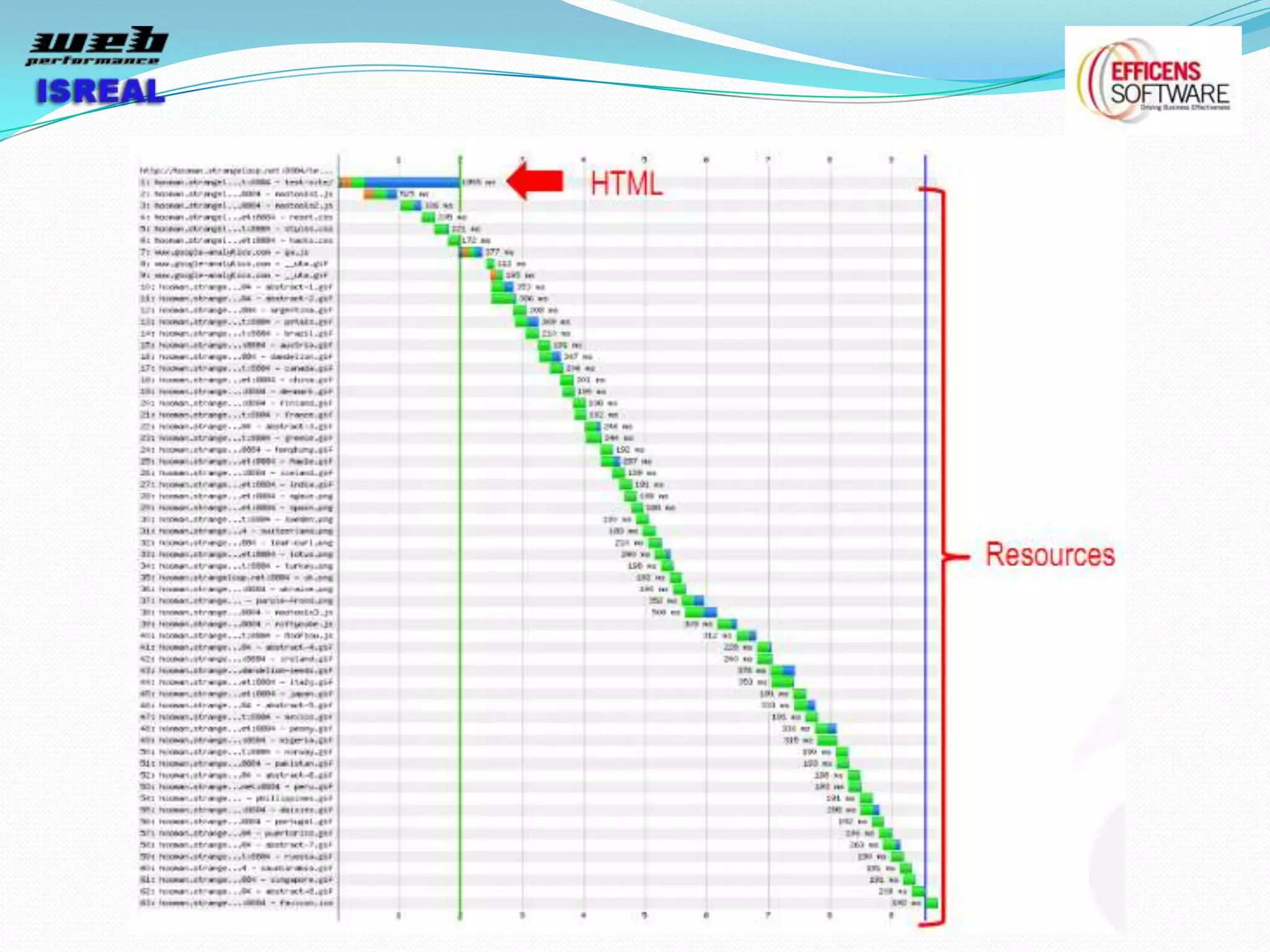
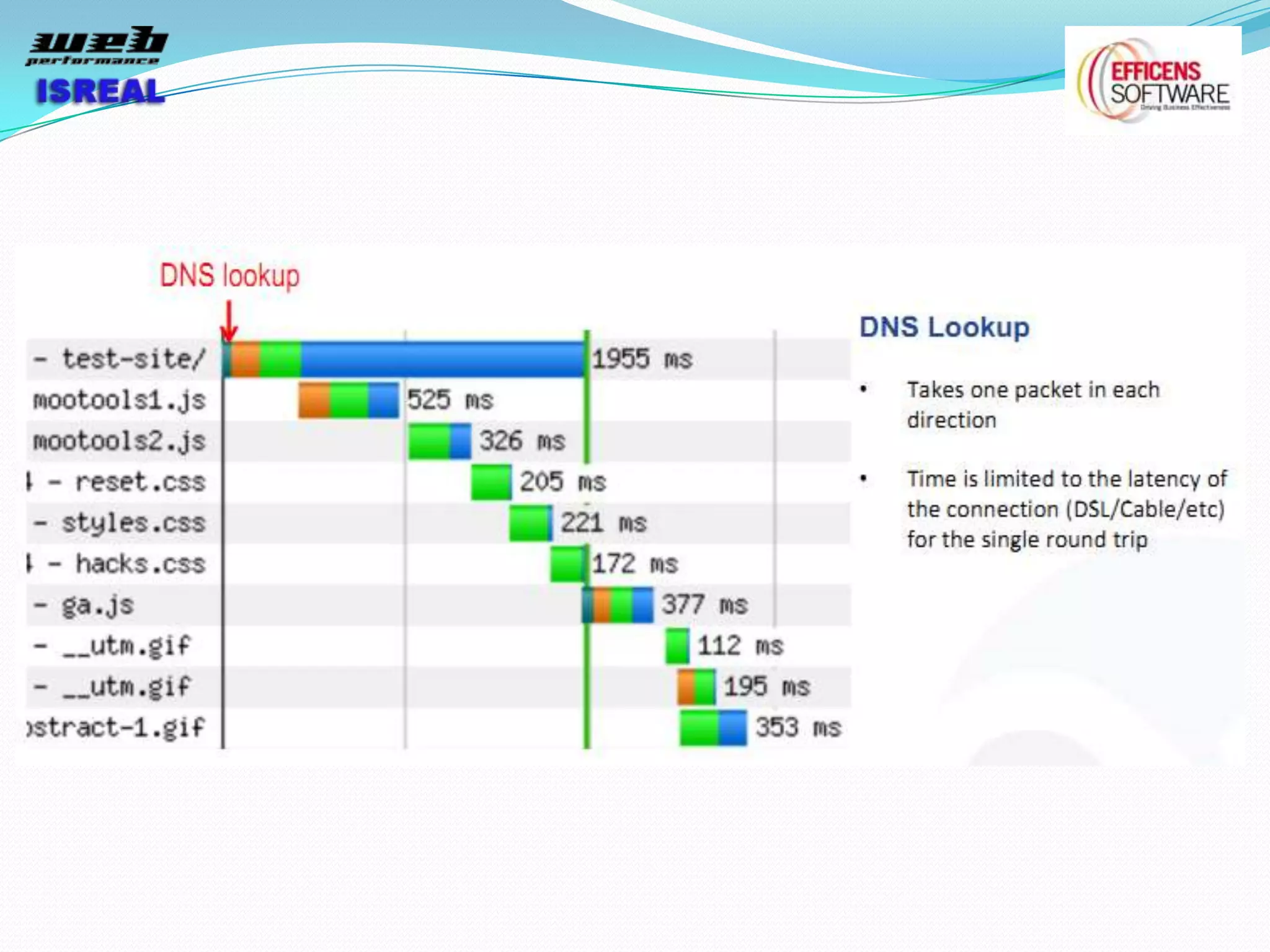
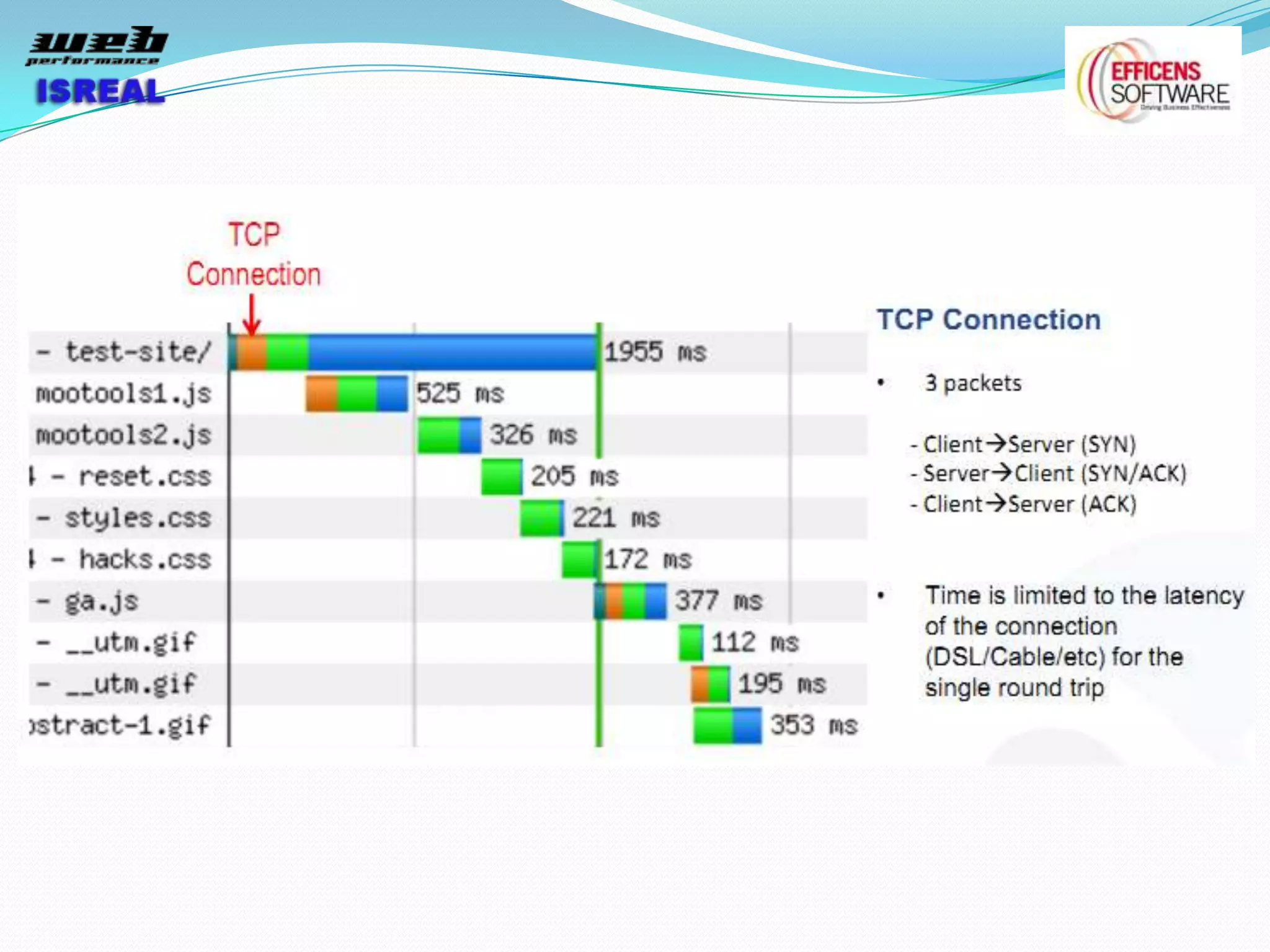
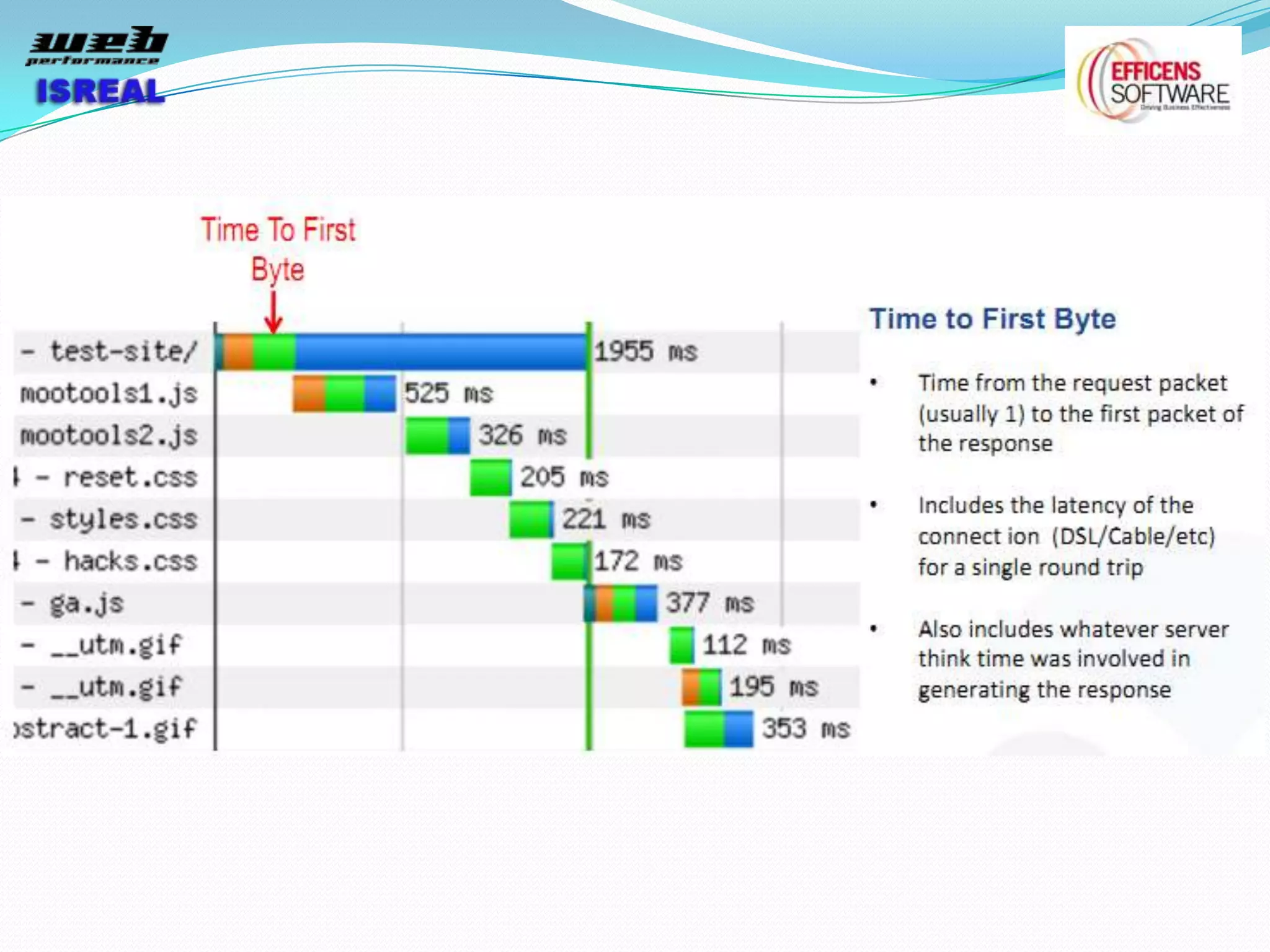
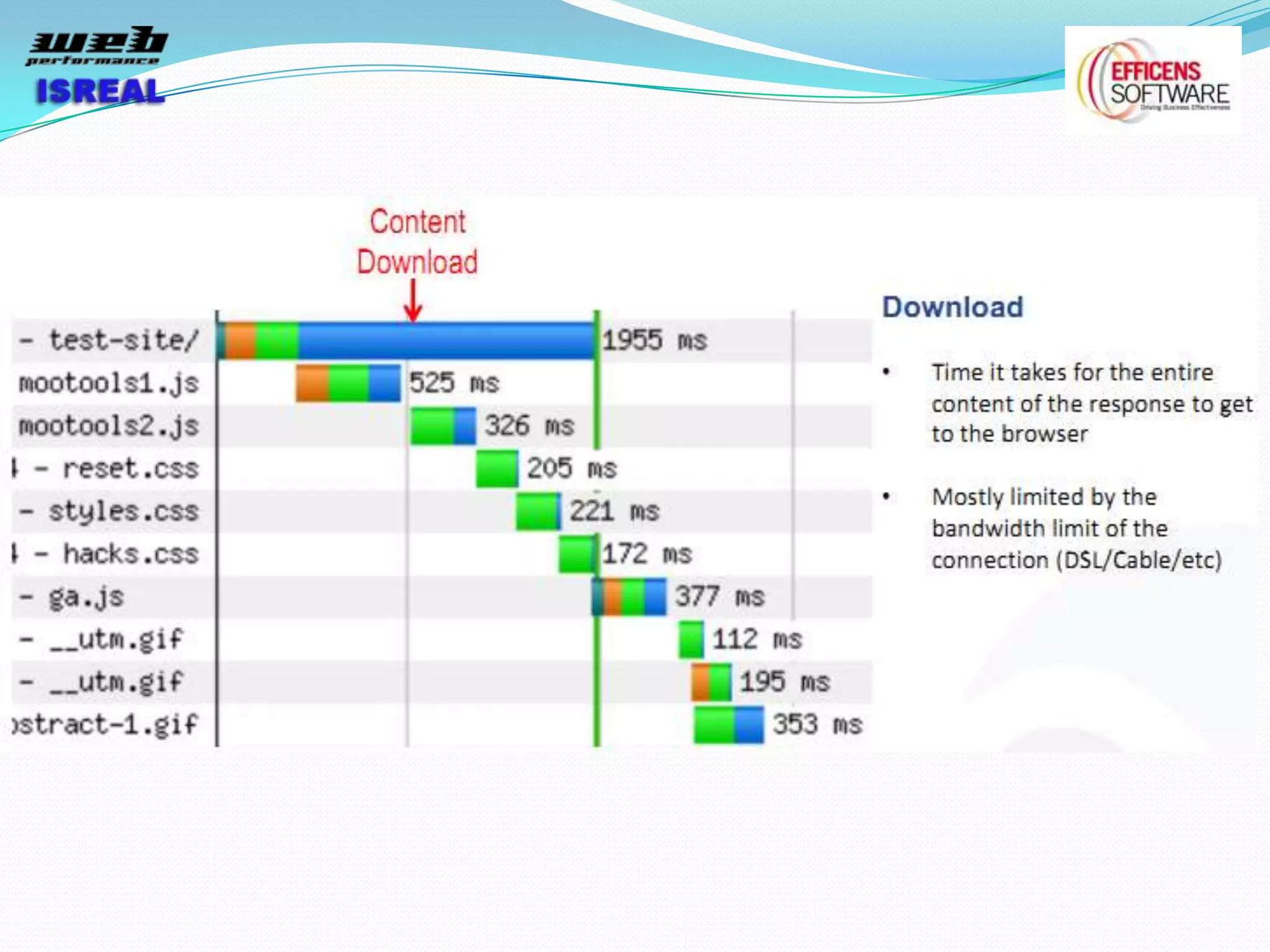
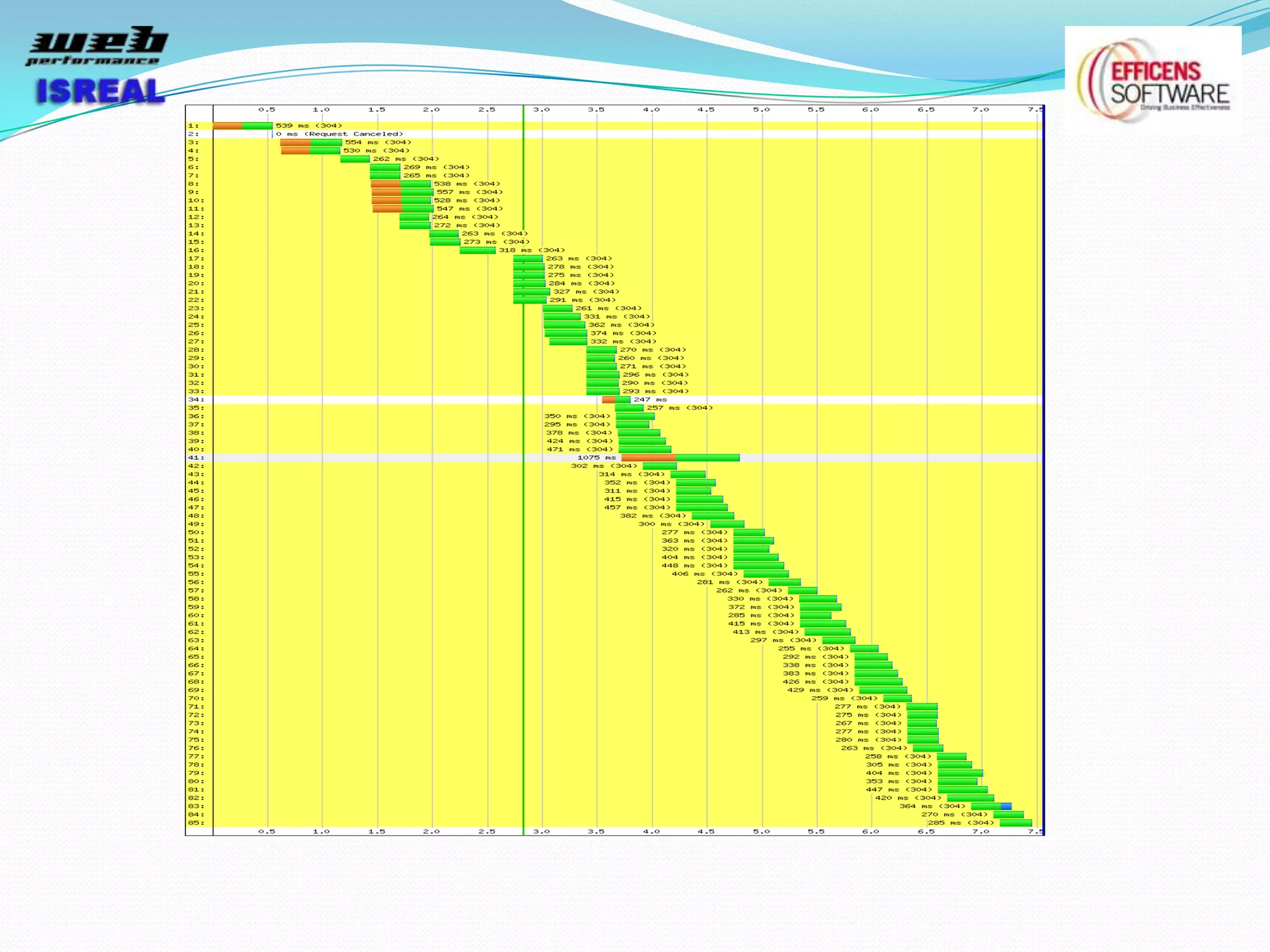
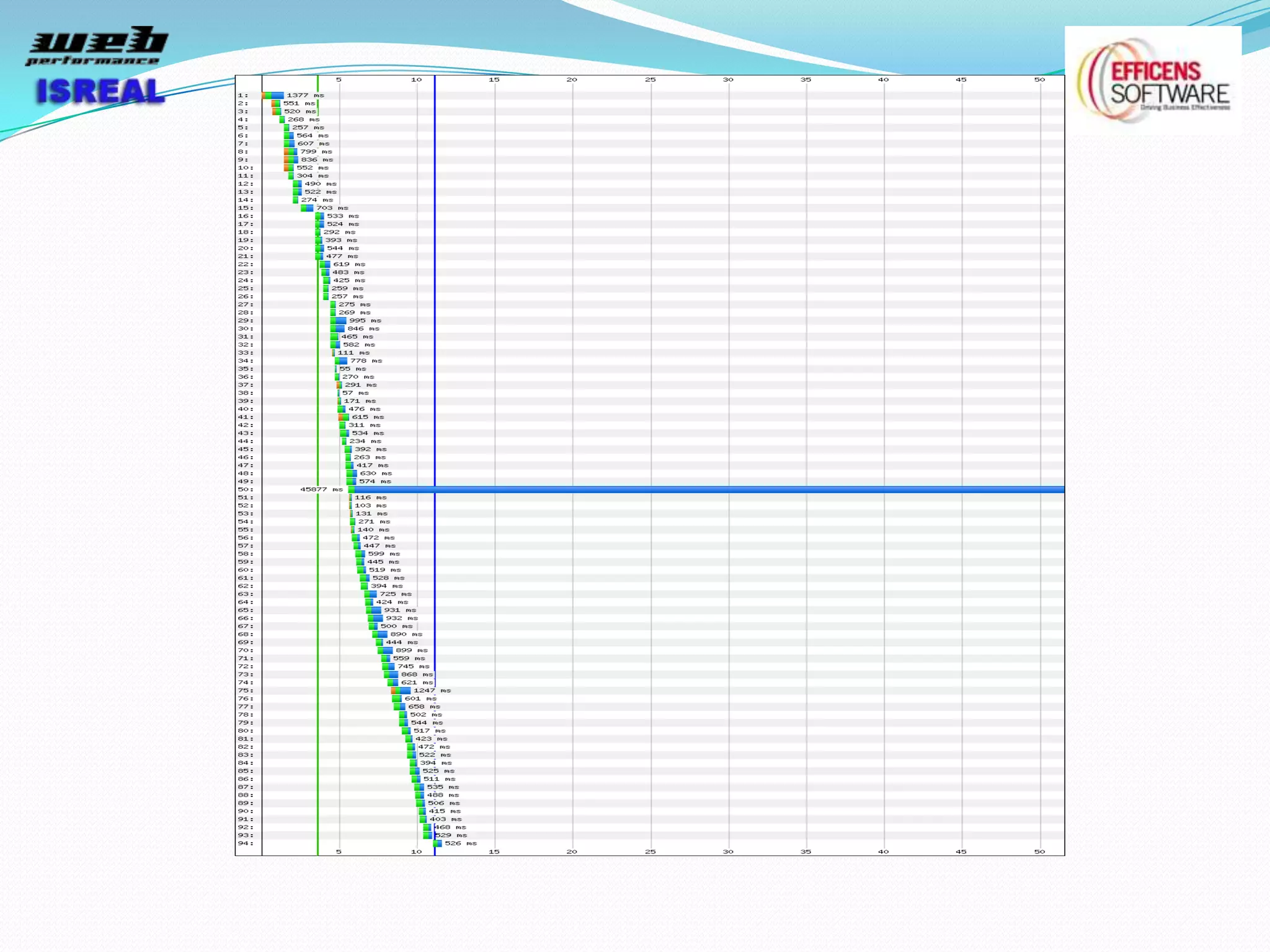
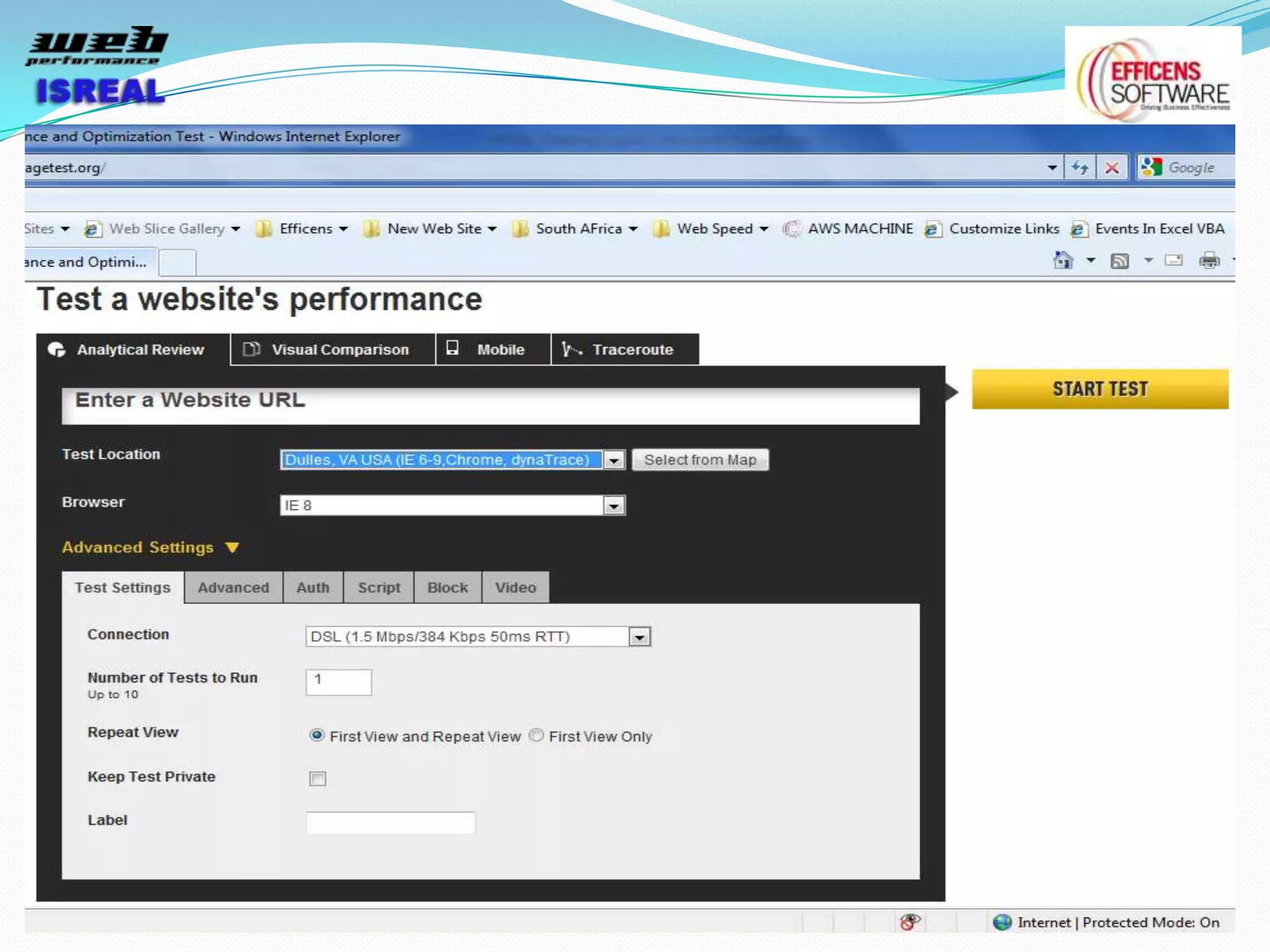
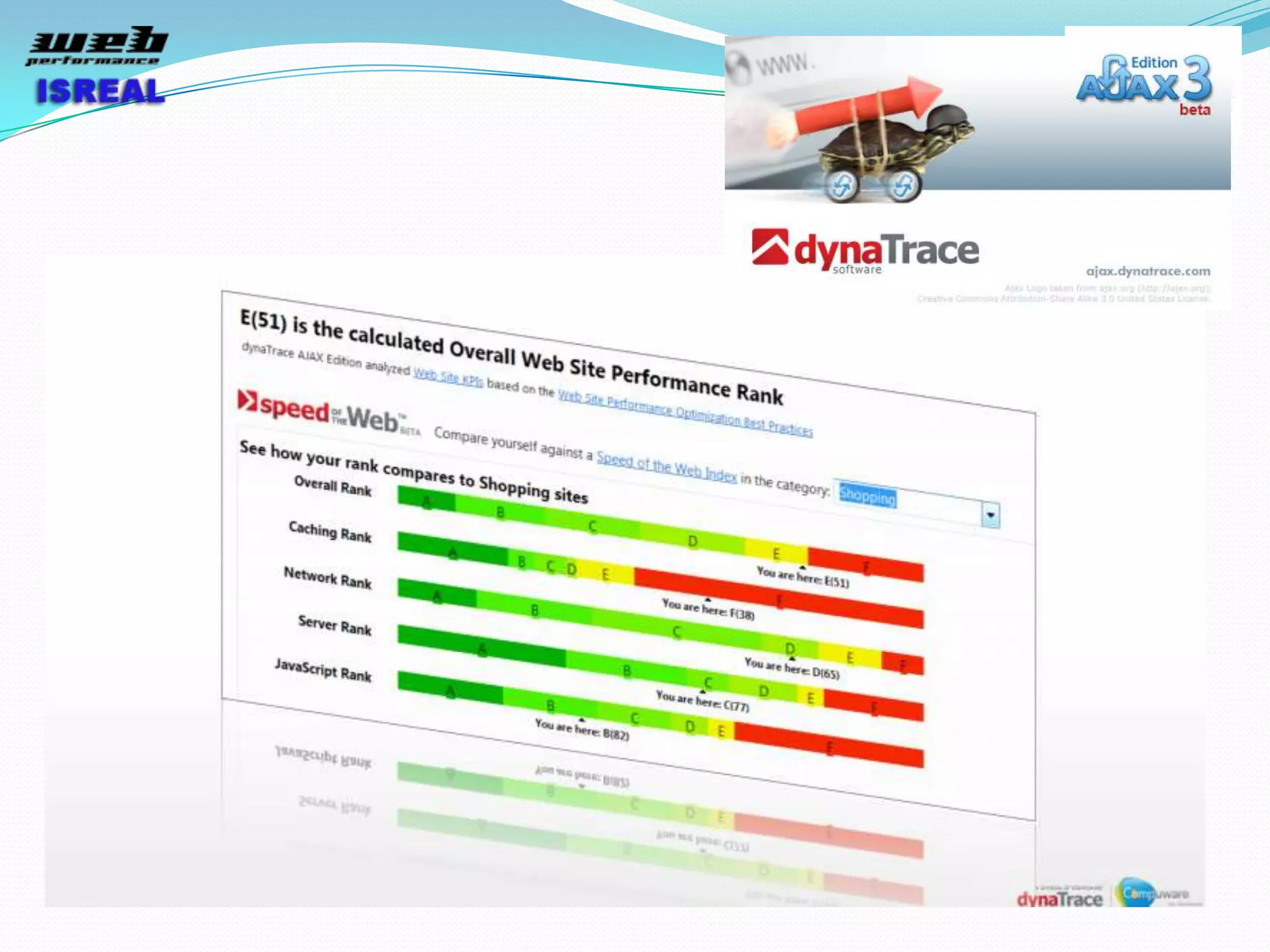
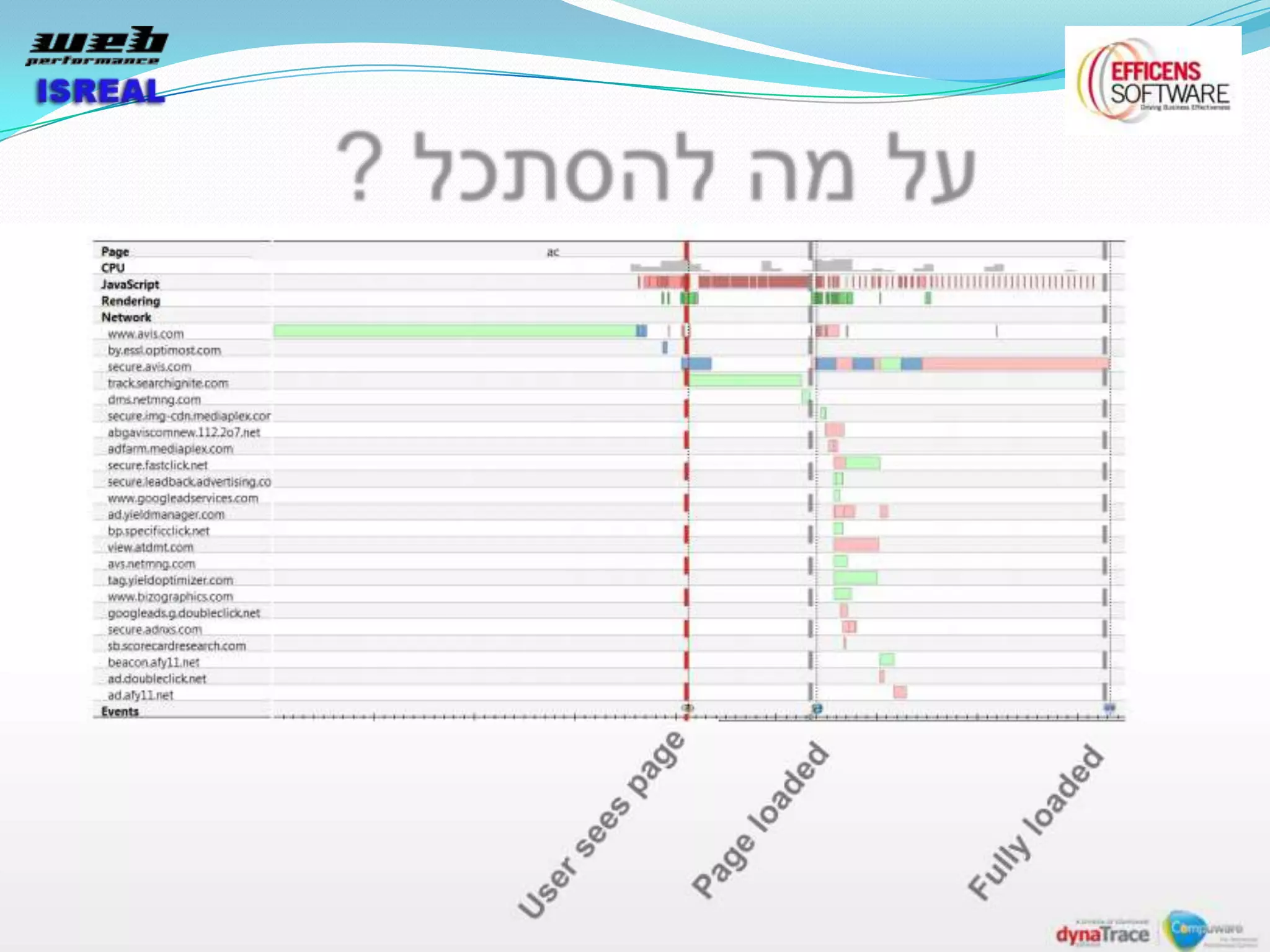
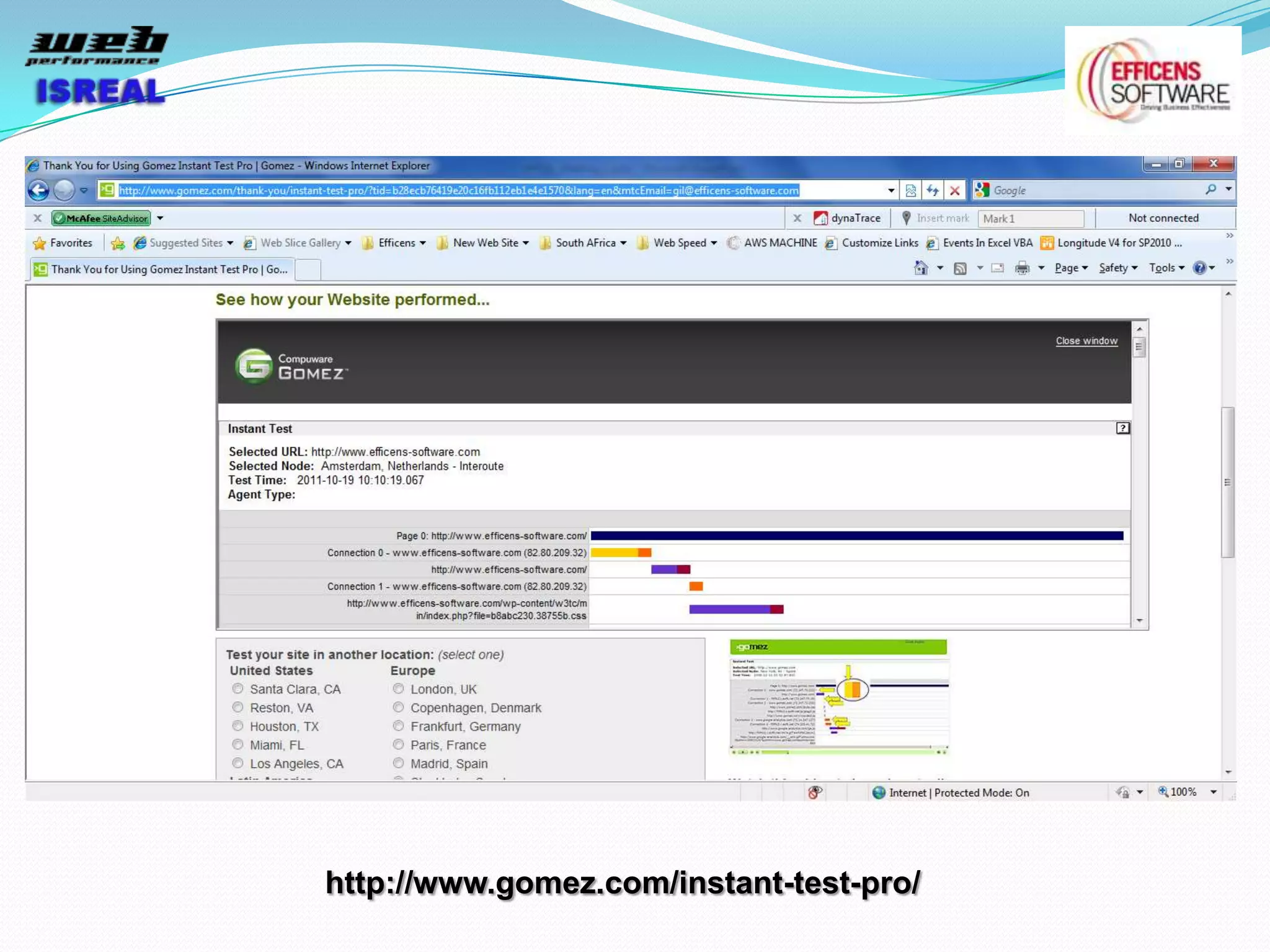
The document discusses various tools and techniques for measuring and improving web performance. It covers topics like understanding how performance affects user experience and business metrics, tools for measuring performance like YSlow and PageSpeed, waterfall charts, browser behaviors, optimization techniques like minification and compression, and monitoring solutions like WebPageTest and dynaTrace. Key tools mentioned include YSlow, PageSpeed, WebPageTest, dynaTrace, Fiddler and HttpWatch. Optimization areas discussed are page size, number of requests, caching, rendering structure, and asynchronous loading.