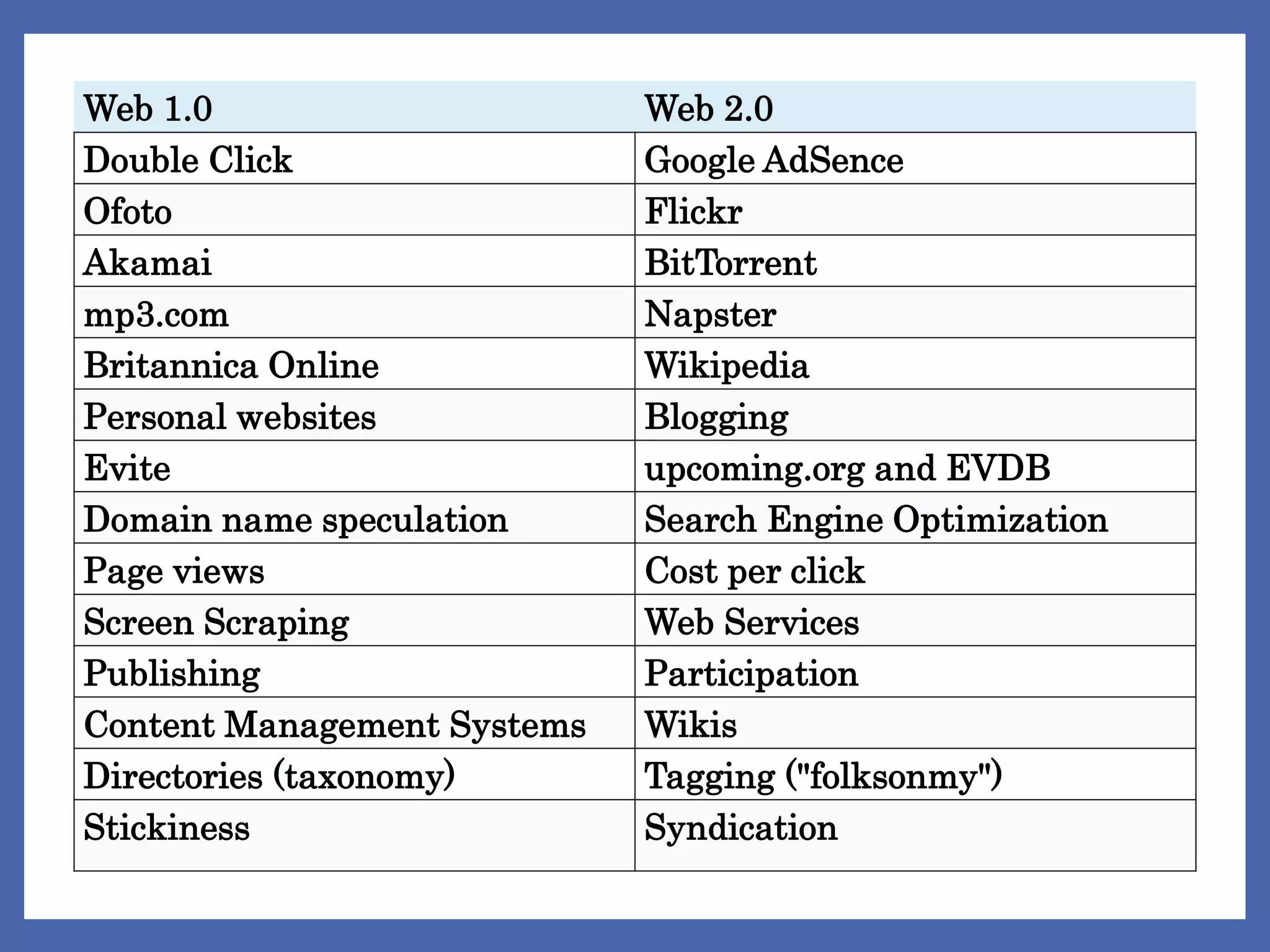
Web 2.0 refers to second-generation internet-based services that allow users to collaborate and share information online. It is characterized by dynamic and user-generated content, as well as the growth of social media. Examples include social networking sites like Facebook, video sharing sites like YouTube, wikis, blogs, and more. The major difference between Web 1.0 and Web 2.0 is that the latter enables users to create, share, and communicate content without needing specialized technical skills. Web 2.0 tools emphasize collective intelligence, sharing of data through open APIs, and constantly evolving software released through lightweight programming models.