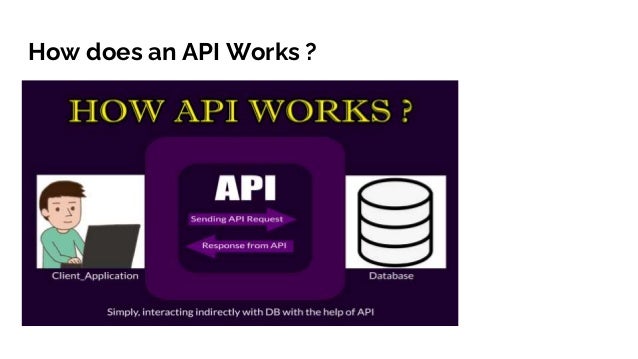
An API, or application programming interface, enables communication between applications for data exchange, exemplified by using Google’s sign-in API for authentication. Various API architectures include REST, which is lightweight and scalable; SOAP, known for its strict standards and security; and RPC, which directly executes server scripts. Each architecture serves different purposes and has unique characteristics, making them suitable for various scenarios in software development.