FIR FILTER USING RECTANGULAR/BOXCAR WINDOW
AIM: To design an FIR filter using Rectangular window technique using MATLAB functions.
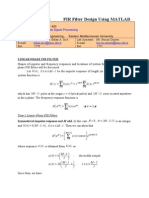
THEORY: The rectangular window sequence is given by
In the design of FIR filters using any window technique, the order can be calculated using the formula given by
where p is the passband ripple, s is the stopband ripple, fp is the passband frequency, fs is the stopband frequency and Fs is the sampling frequency.
BOXCAR Boxcar window: BOXCAR still works but maybe removed in the future. Use RECTWIN instead.
RECTWIN Rectangular window: W = RECTWIN(N) returns the N-point rectangular window.
FIR1 FIR filter design using the window method. B = FIR1(N,Wn) designs an N'th order lowpass FIR digital filter and returns the filter coefficients in length N+1 vector B. The cut-off frequency Wn must be between 0 < Wn < 1.0, with 1.0 corresponding to half the sample rate. The filter B is real and has linear phase. The normalized gain of the filter at Wn is -6 dB.
�B = FIR1(N,Wn,'high') designs an N'th order highpass filter.You can also use B = FIR1(N,Wn,'low') to design a lowpass filter. If Wn is a two-element vector, Wn = [W1 W2], FIR1 returns an order N bandpass filter with passband W1 < W < W2. You can also specify B = FIR1(N,Wn,'bandpass'). If Wn = [W1 W2], B = FIR1(N,Wn,'stop') will design a bandstop filter.
CEIL Round towards plus infinity. CEIL(X) rounds the elements of X to the nearest integers towards infinity.
MATLAB CODE:
%program for the design of FIR Low pass filter using boxcar window method clc; clear all; close all; format long rp=input('Enter the passband ripple'); rs=input('Enter the stopband ripple'); fp=input('Enter the passband frequency'); fs=input('Enter the stopband frequency'); f=input('Enter the sampling frequency'); wp=2*fp/f; ws=2*fs/f; num=-20*log10(sqrt(rp*rs))-13; dem=14.6*(fs-fp)/f; n=ceil(num/dem); n1=n+1; if(rem(n,2)~=0) n1=n; n=n-1; end y=boxcar(n1); %LOW PASS FILTER b=fir1(n,wp,y);%Window-based finite impulse response filter design [h,o]=freqz(b,1,256);%Frequency response of filter m=20*log10(abs(h)); an=angle(h); subplot(2,1,1),plot(o/pi,m); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); ylabel('Gain in dB--->'); title('FIR LOW PASS MAGNITUDE RESPONSE-BOXCAR WINDOW METHOD'); subplot(2,1,2); plot(o/pi,an); ylabel('Phase in radians--->'); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); title('FIR LOW PASS PHASE RESPONSE-BOXCAR WINDOW METHOD');
SAMPLE INPUTS: Enter the passband Enter the stopband Enter the passband Enter the stopband Enter the sampling 2
ripple.05 ripple.04 frequency1500 frequency2000 frequency9000
�%program for the design of FIR High pass filter using boxcar window method clc; clear all; close all; format long rp=input('Enter the passband ripple'); rs=input('Enter the stopband ripple'); fp=input('Enter the passband frequency'); fs=input('Enter the stopband frequency'); f=input('Enter the sampling frequency'); wp=2*fp/f; ws=2*fs/f; num=-20*log10(sqrt(rp*rs))-13; dem=14.6*(fs-fp)/f; n=ceil(num/dem); n1=n+1; if(rem(n,2)~=0) n1=n; n=n-1; end y=boxcar(n1); %HIGH PASS FILTER b=fir1(n,wp,'high',y); [h,o]=freqz(b,1,256); m=20*log10(abs(h)); an=angle(h); subplot(2,1,1); plot(o/pi,m); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); ylabel('Gain in dB--->'); title('FIR HIGH PASS MAGNITUDE RESPONSE-BOXCAR WINDOW METHOD'); subplot(2,1,2); plot(o/pi,an); ylabel('Phase in radians--->'); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); title('FIR HIGH PASS PHASE RESPONSE-BOXCAR WINDOW METHOD');
SAMPLE INPUTS: Enter the passband Enter the stopband Enter the passband Enter the stopband Enter the sampling
ripple.05 ripple.04 frequency1500 frequency2000 frequency9000
FIR FILTER USING BLACKMAN WINDOW
AIM: To design an FIR filter using Blackman window technique using MATLAB functions.
THEORY: The blackman window sequence is given by
�In the design of FIR filters using any window technique, the order can be calculated using the formula given by
where p is the passband ripple, s is the stopband ripple, fp is the passband frequency, fs is the stopband frequency and Fs is the sampling frequency.
BLACKMAN Blackman window: BLACKMAN(N) returns the N-point symmetric Blackman window in a column vector. BLACKMAN(N,SFLAG) generates the N-point Blackman window using SFLAG window sampling. SFLAG may be either 'symmetric' or 'periodic'. By default, a symmetric window is returned.
FIR1 FIR filter design using the window method: B = FIR1(N,Wn) designs an N'th order lowpass FIR digital filter and returns the filter coefficients in length N+1 vector B. The cut-off frequency Wn must be between 0 < Wn < 1.0, with 1.0 corresponding to half the sample rate. The filter B is real and has linear phase. The normalized gain of the filter at Wn is -6 dB. B = FIR1(N,Wn,'high') designs an N'th order highpass filter.You can also use B = FIR1(N,Wn,'low') to design a lowpass filter. If Wn is a two-element vector, Wn = [W1 W2], FIR1 returns an order N bandpass filter with passband W1 < W < W2. You can also specify B = FIR1(N,Wn,'bandpass'). If Wn = [W1 W2], B = FIR1(N,Wn,'stop') will design a bandstop filter.
CEIL Round towards plus infinity: CEIL(X) rounds the elements of X to the nearest integers towards infinity. MATLAB CODE %program for the design of FIR Low pass using blackman window clc; clear all; close all; rp=input('Enter the passband ripple'); rs=input('Enter the stopband ripple'); fp=input('Enter the passband frequency'); fs=input('Enter the stopband frequency'); f=input('Enter the sampling frequency'); wp=2*fp/f; ws=2*fs/f; num=-20*log10(sqrt(rp*rs))-13; dem=14.6*(fs-fp)/f;
�n=ceil(num/dem); n1=n+1; if(rem(n,2)~=0) n1=n; n=n-1; end y=blackman(n1); %LOW PASS FILTER b=fir1(n,wp,y); [h,o]=freqz(b,1,256); m=20*log10(abs(h)); an=angle(h); subplot(2,1,1); plot(o/pi,m); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); ylabel('Gain in dB--->'); title('FIR LOW PASS MAGNITUDE RESPONSE-BLACKMAN WINDOW METHOD'); subplot(2,1,2); plot(o/pi,an); ylabel('Phase in radians--->'); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); title('FIR LOW PASS PHASE RESPONSE-BLACKMAN WINDOW METHOD');
SAMPLE INPUTS: Enter the passband Enter the stopband Enter the passband Enter the stopband Enter the sampling
ripple.03 ripple.01 frequency2000 frequency2500 frequency7000
%program for the design of FIR High pass filter using blackman window clc; clear all; close all; rp=input('Enter the passband ripple'); rs=input('Enter the stopband ripple'); fp=input('Enter the passband frequency'); fs=input('Enter the stopband frequency'); f=input('Enter the sampling frequency'); wp=2*fp/f; ws=2*fs/f; num=-20*log10(sqrt(rp*rs))-13; dem=14.6*(fs-fp)/f; n=ceil(num/dem); n1=n+1; if(rem(n,2)~=0) n1=n; n=n-1; end y=blackman(n1); %HIGH PASS FILTER b=fir1(n,wp,'high',y); [h,o]=freqz(b,1,256); m=20*log10(abs(h)); an=angle(h); subplot(2,1,1); plot(o/pi,m); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); ylabel('Gain in dB--->'); title('FIR HIGH PASS MAGNITUDE RESPONSE-BLACKMAN WINDOW METHOD'); subplot(2,1,2); plot(o/pi,an); ylabel('Phase in radians--->'); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); title('FIR HIGH PASS PHASE RESPONSE-BLACKMAN WINDOW METHOD');
�SAMPLE INPUTS: Enter the passband Enter the stopband Enter the passband Enter the stopband Enter the sampling
ripple.03 ripple.01 frequency2000 frequency2500 frequency7000
FIR FILTER USING HAMMING WINDOW
AIM: To design an FIR filter using Hamming window technique using MATLAB functions.
THEORY: The equation for Hamming window is given by
In the design of FIR filters using any window technique, the order can be calculated using the formula given by
where p is the passband ripple, s is the stopband ripple, fp is the passband frequency, fs is the stopband frequency and Fs is the sampling frequency.
HAMMING Hamming window: HAMMING(N) returns the N-point symmetric Hamming window in a column vector. HAMMING(N,SFLAG) generates the N-point Hamming window using SFLAG window sampling. SFLAG may be either 'symmetric' or 'periodic'. By default, a symmetric window is returned.
FIR1 FIR filter design using the window method:
�B = FIR1(N,Wn) designs an N'th order lowpass FIR digital filter and returns the filter coefficients in length N+1 vector B. The cut-off frequency Wn must be between 0 < Wn < 1.0, with 1.0 corresponding to half the sample rate. The filter B is real and has linear phase. The normalized gain of the filter at Wn is -6 dB. B = FIR1(N,Wn,'high') designs an N'th order highpass filter.You can also use B = FIR1(N,Wn,'low') to design a lowpass filter. If Wn is a two-element vector, Wn = [W1 W2], FIR1 returns an order N bandpass filter with passband W1 < W < W2. You can also specify B = FIR1(N,Wn,'bandpass'). If Wn = [W1 W2], B = FIR1(N,Wn,'stop') will design a bandstop filter.
CEIL Round towards plus infinity: CEIL(X) rounds the elements of X to the nearest integers towards infinity.
MATLAB CODE: %program for the design of FIR Low pass filter using Hamming window clc; clear all; close all; rp=input('Enter the passband ripple'); rs=input('Enter the stopband ripple'); fp=input('Enter the passband frequency'); fs=input('Enter the stopband frequency'); f=input('Enter the sampling frequency'); wp=2*fp/f; ws=2*fs/f; num=-20*log10(sqrt(rp*rs))-13; dem=14.6*(fs-fp)/f; n=ceil(num/dem); n1=n+1; if(rem(n,2)~=0) n1=n; n=n-1; end y=hamming(n1); %LOW PASS FILTER b=fir1(n,wp,y); [h,o]=freqz(b,1,256); m=20*log10(abs(h)); an=angle(h); subplot(2,1,1); plot(o/pi,m); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); ylabel('Gain in dB--->'); title('FIR LOW PASS MAGNITUDE RESPONSE-HAMMING WINDOW METHOD'); subplot(2,1,2); plot(o/pi,an); ylabel('Phase in radians--->'); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); title('FIR LOW PASS PHASE RESPONSE-HAMMING WINDOW METHOD');
SAMPLE INPUTS: Enter the passband ripple.02 Enter the stopband ripple.01 7
�Enter the passband frequency1200 Enter the stopband frequency1700 Enter the sampling frequency9000
%program for the design of FIR High pass filter using Hamming window clc; clear all; close all; rp=input('Enter the passband ripple'); rs=input('Enter the stopband ripple'); fp=input('Enter the passband frequency'); fs=input('Enter the stopband frequency'); f=input('Enter the sampling frequency'); wp=2*fp/f; ws=2*fs/f; num=-20*log10(sqrt(rp*rs))-13; dem=14.6*(fs-fp)/f; n=ceil(num/dem); n1=n+1; if(rem(n,2)~=0) n1=n; n=n-1; end y=hamming(n1); %HIGH PASS FILTER b=fir1(n,wp,'high',y); [h,o]=freqz(b,1,256); m=20*log10(abs(h)); an=angle(h); subplot(2,1,1); plot(o/pi,m); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); ylabel('Gain in dB--->'); title('FIR HIGH PASS MAGNITUDE RESPONSE-HAMMING WINDOW METHOD'); subplot(2,1,2); plot(o/pi,an); ylabel('Phase in radians--->'); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); title('FIR HIGH PASS PHASE RESPONSE-HAMMING WINDOW METHOD');
SAMPLE INPUTS: Enter the passband Enter the stopband Enter the passband Enter the stopband Enter the sampling
ripple.02 ripple.01 frequency1200 frequency1700 frequency9000
FIR FILTER USING KAISER WINDOW
AIM: To design an FIR filter using Kaiser window technique using MATLAB functions.
THEORY: The Kaiser window is given by
�In the design of FIR filters using any window technique, the order can be calculated using the formula given by
where p is the passband ripple, s is the stopband ripple, fp is the passband frequency, fs is the stopband frequency and Fs is the sampling frequency.
KAISER Kaiser window: W = KAISER(N) returns an N-point Kaiser window in the column vector W. W = KAISER(N,BTA) returns the BETA-valued N-point Kaiser window. If omitted, BTA is set to 0.500.
FIR1 FIR filter design using the window method: B = FIR1(N,Wn) designs an N'th order lowpass FIR digital filter and returns the filter coefficients in length N+1 vector B. The cut-off frequency Wn must be between 0 < Wn < 1.0, with 1.0 corresponding to half the sample rate. The filter B is real and has linear phase. The normalized gain of the filter at Wn is -6 dB. B = FIR1(N,Wn,'high') designs an N'th order highpass filter.You can also use B = FIR1(N,Wn,'low') to design a lowpass filter. If Wn is a two-element vector, Wn = [W1 W2], FIR1 returns an order N bandpass filter with passband W1 < W < W2. You can also specify B = FIR1(N,Wn,'bandpass'). If Wn = [W1 W2], B = FIR1(N,Wn,'stop') will design a bandstop filter.
CEIL Round towards plus infinity: CEIL(X) rounds the elements of X to the nearest integers towards infinity. MATLAB CODE %program for the design of FIR Low pass filter using Kaiser window clc; clear all; close all; rp=input('Enter the passband ripple'); rs=input('Enter the stopband ripple'); fp=input('Enter the passband frequency'); fs=input('Enter the stopband frequency'); f=input('Enter the sampling frequency'); wp=2*fp/f; ws=2*fs/f; num=-20*log10(sqrt(rp*rs))-13; dem=14.6*(fs-fp)/f;
�n=ceil(num/dem); n1=n+1; if(rem(n,2)~=0) n1=n; n=n-1; end y=kaiser(n1); %LOW PASS FILTER b=fir1(n,wp,y); [h,o]=freqz(b,1,256); m=20*log10(abs(h)); an=angle(h); subplot(2,1,1); plot(o/pi,m); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); ylabel('Gain in dB--->'); title('FIR LOW PASS MAGNITUDE RESPONSE-KAISER WINDOW METHOD'); subplot(2,1,2); plot(o/pi,an); ylabel('Phase in radians--->'); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); title('FIR LOW PASS PHASE RESPONSE-KAISER WINDOW METHOD');
SAMPLE INPUTS: Enter the passband Enter the stopband Enter the passband Enter the stopband Enter the sampling
ripple.04 ripple.03 frequency1500 frequency2400 frequency8000
%program for the design of FIR High pass filter using Kaiser window clc; clear all; close all; rp=input('Enter the passband ripple'); rs=input('Enter the stopband ripple'); fp=input('Enter the passband frequency'); fs=input('Enter the stopband frequency'); f=input('Enter the sampling frequency'); wp=2*fp/f; ws=2*fs/f; num=-20*log10(sqrt(rp*rs))-13; dem=14.6*(fs-fp)/f; n=ceil(num/dem); n1=n+1; if(rem(n,2)~=0) n1=n; n=n-1; end y=kaiser(n1); %LOW PASS FILTER b=fir1(n,wp,'high',y); [h,o]=freqz(b,1,256); m=20*log10(abs(h)); an=angle(h); subplot(2,1,1); plot(o/pi,m); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); ylabel('Gain in dB--->'); title('FIR HIGH PASS MAGNITUDE RESPONSE-KAISER WINDOW METHOD'); subplot(2,1,2); plot(o/pi,an); ylabel('Phase in radians--->'); xlabel('Normalised frequency--->'); title('FIR HIGH PHASE RESPONSE-KAISER WINDOW METHOD');
10
�SAMPLE INPUTS: Enter the passband Enter the stopband Enter the passband Enter the stopband Enter the sampling
ripple.04 ripple.03 frequency1500 frequency2400 frequency8000
11