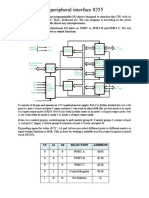
8255 Programmable Peripheral Interface
Block Diagram
�8255 Programmable Peripheral Interface
Modes of 8255
�8255 Programmable Peripheral Interface
�Control Word
�8255 Programmable Peripheral Interface
Bit definitions of the 8255 control register
�8253 Programmable Interval Timer/Counter (PIT)
Block Diagram
�8253 Programmable Interval Timer/Counter (PIT)
Control Word
CONTROL BYTE D7 - D0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
SC1
SC0
RL1
RL0
M2
M1
M0
BCP
D5 D4
R / L Definition
RL1 RL0
D7 D6
Counter Select
SC1 SC0
0
counter 0
counter 1
counter 2
Counter value is latched. This means
that the selected counter has its
contents transferred into a temporary
latch, which can then be read by the CPU.
Read / load least-significant byte only.
Read / load most-significant byte only.
Read / load least-significant byte first,
then most-significant byte.
illegal value
D3 D2 D1
Mode value
M2 M1 M0
0
mode 0: interrupt on terminal count
mode 1: programmable one-shot
mode 2: rate generator
mode 3: square wave generator
mode 4: software triggered strobe
mode 5: hardware triggered strobe
D0 counts down in
0
binary
BCD
8251 UNIVERSAL SYNCHRONOUS ASYNCHRONOUS RECEIVER
TRANSMITTER (USART)
�Block Diagram
�8251 UNIVERSAL SYNCHRONOUS ASYNCHRONOUS RECEIVER
TRANSMITTER (USART)
Bit configuration of Mode Instruction (Asynchronous)
�8251 UNIVERSAL SYNCHRONOUS ASYNCHRONOUS RECEIVER
TRANSMITTER (USART)
Bit configuration of Mode Instruction (Synchronous)
8251 UNIVERSAL SYNCHRONOUS ASYNCHRONOUS RECEIVER
TRANSMITTER (USART)
�Bit configuration of Command
8251 UNIVERSAL SYNCHRONOUS ASYNCHRONOUS RECEIVER
TRANSMITTER (USART)
�Bit configuration of Status Word
�8259 - Programmable Interrupt Controller
Block Diagram
�ICW1 (Initialisation Command Word One)
A0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
A7
A6
A5
LTIM
ADI
SNGL
IC4
D0: IC4: 0=no ICW4, 1=ICW4 required
D1: SNGL: 1=Single PIC, 0=Cascaded PIC
D2: ADI: Address interval. Used only in 8085, not 8086. 1=ISR's are 4 bytes apart (0200,
0204, etc) 0=ISR's are 8 byte apart (0200, 0208, etc)
D3: LTIM: level triggered interrupt mode: 1=All IR lines level triggered. 0=edge triggered
D4-D7: A5-A7: 8085 only. ISR address lower byte segment. The lower byte is
A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
of which A7, A6, A5 are provided by D7-D5 of ICW1 (if ADI=1), or A7, A6 are provided if
ADI=0. A4-A0 (or A5-A0) are set by 8259 itself:
ADI=1 (spacing 4 bytes)
ADI=0 (spacing 8 bytes)
IRQ A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
IRQ A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
IR0 A7 A6 A5 0
IR0 A7 A6 0
IR1 A7 A6 A5 0
IR1 A7 A6 0
IR2 A7 A6 A5 0
IR2 A7 A6 0
IR3 A7 A6 A5 0
IR3 A7 A6 0
IR4 A7 A6 A5 1
IR4 A7 A6 1
IR5 A7 A6 A5 1
IR5 A7 A6 1
IR6 A7 A6 A5 1
IR6 A7 A6 1
IR7 A7 A6 A5 1
IR7 A7 A6 1
�ICW2 (Initialisation Command Word Two)
Higher byte of ISR address (8085), or 8 bit vector address (8086).
A0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
ICW3 (Initialisation Command Word Three)
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
Master
S7
S6
S5
S4
S3
S2
S1
S0
Slave
ID3
ID2
ID1
A0
1
Master mode: 1 indicates slave is present on that interrupt, 0 indicates direct
interrupt
Slave mode: ID3-ID2-ID1 is the slave ID number. Slave 4 on IR4 has ICW3=04h
(0000 0100)
ICW4 (Initialisation Command Word Four)
A0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
SFNM
BUF
M/S
AEOI
Mode
SFNM: 1=Special Fully Nested Mode, 0=FNM
M/S: 1=Master, 0=Slave
AEOI: 1=Auto End of Interrupt, 0=Normal
Mode: 0=8085, 1=8086
OCW1 (Operational Command Word One)
A0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
M7
M6
M5
M4
M3
M2
M1
M0
IRn is masked by setting Mn to 1; mask cleared by setting Mn to 0 (n=0..7)
�OCW2 (Operational Command Word Two)
A0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
SL
EOI
L3
L2
L1
R SL EOI Action
0 0
Non specific EOI (L3L2L1=000)
0 1
Specific EOI command (Interrupt to clear
given by L3L2L1)
1 0
Rotate priorities on non-specific EOI
1 0
Rotate priorities in auto EOI mode set
0 0
Rotate priorities in auto EOI mode clear
1 1
Rotate priority on specific EOI command
(resets current ISR bit)
1 1
Set priority (does not reset current ISR bit)
0 1
No operation
EOI
Auto rotation of priorities
(L3L2L1=000)
Specific rotation of priorities (Lowest
priority ISR=L3L2L1)
OCW3 (Operational Command Word Three)
A0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
D7
ESMM
SMM
MODE
RIR
RIS
ESMM SMM Effect
0
No effect
Reset special mask
Set special mask
8279 Key board display controller
Block Diagrams