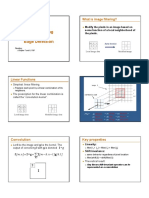
3/1/2017 ConvolutionfunctionHelp|ArcGISforDesktop
Convolution function
ArcMap 10.3
|
Other versions
10.5
10.4
10.3
The Convolution function performs filtering on the pixel values in an image, which can be used for sharpening an image,
blurring an image, detecting edges within an image, or other kernelbased enhancements.
The inputs for this function are the following:
Input Raster
Type
Kernel
Convolution filter types
Filters are used to improve the quality of the raster image by eliminating spurious data or enhancing features in the data.
These convolution filters are applied on a moving, overlapping kernel window or neighborhood, such as 3 by 3.
Convolution filters work by calculating the pixel value based on the weighting of its neighbors.
There are a number of convolution filter types you can choose within this function. You can also specify a User Defined
type and enter your own kernel values.
You can apply a median filter to the image by specifying a weight of 1/9 for a 3 by 3 kernel, thereby giving every pixel in
the kernel an equal weight. This filter can be used to smooth an image. There are other kernels that can be used to
sharpen or enhance edges. You can combine filters to achieve specific results. For example, you may want to apply a filter
that will remove speckle or smooth an image, then apply a filter that will detect edges.
For optimal display results, you may want to apply a histogram stretch to adjust the image's contrast or brightness to help
pull out features.
The examples below are applied on one of these two images:
Unfiltered grayscale image
http://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/10.3/managedata/rasterandimages/convolutionfunction.htm 1/9
�3/1/2017 ConvolutionfunctionHelp|ArcGISforDesktop
Unfiltered color image
Edge detection filters
Gradient types
Gradient filters can be used for edge detection in 45degree increments.
Type Description Example
A 3 by 3 filter
Gradient East 101
202
101
A 3 by 3 filter
Gradient North 121
000
121
http://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/10.3/managedata/rasterandimages/convolutionfunction.htm 2/9
�3/1/2017 ConvolutionfunctionHelp|ArcGISforDesktop
Type Description Example
A 3 by 3 filter
Gradient NorthEast 012
101
210
A 3 by 3 filter
Gradient NorthWest 210
101
012
A 3 by 3 filter
Gradient South 121
000
121
A 3 by 3 filter
Gradient West 101
202
101
http://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/10.3/managedata/rasterandimages/convolutionfunction.htm 3/9
�3/1/2017 ConvolutionfunctionHelp|ArcGISforDesktop
Laplacian types
Laplacian filters are often used for edge detection. It is often applied to an image that has first been smoothed to reduce
its sensitivity to noise.
Type Description Example
A 3 by 3 filter
Laplacian 3x3 010
141
010
A 5 by 5 filter
00100
Laplacian 5x5 01210
121721
01210
00100
Line Detection types
Line detection filters, like the gradient filters, can be used to perform edge detection.
You may get better results if you apply a smoothing algorithm before an edge detection algorithm.
Type Description Example
A 3 by 3 filter
Line Detection Horizontal 111
222
111
http://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/10.3/managedata/rasterandimages/convolutionfunction.htm 4/9
�3/1/2017 ConvolutionfunctionHelp|ArcGISforDesktop
Type Description Example
A 3 by 3 filter
Line Detection Left Diagonal 211
121
112
A 3 by 3 filter
Line Detection Right Diagonal 112
121
211
A 3 by 3 filter
Line Detection Vertical 101
121
121
Sobel types
The Sobel filter is used for edge detection.
Type Description Example
http://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/10.3/managedata/rasterandimages/convolutionfunction.htm 5/9
�3/1/2017 ConvolutionfunctionHelp|ArcGISforDesktop
A 3 by 3 filter
Sobel Horizontal 121
000
121
A 3 by 3 filter
Sobel Vertical 101
202
101
Sharpening and Smoothing filters
Sharpening types
The Sharpening highpass filter accentuates the comparative difference in the values with its neighbors. A highpass filter
calculates the focal sum statistic for each cell of the input using a weighted kernel neighborhood. It brings out the
boundaries between features for example, where a water body meets the forest, thus sharpening edges between objects.
The highpass filter is referred to as an edge enhancement filter. The highpass filter kernel identifies which cells to use in
the neighborhood and how much to weight them multiply them by.
Type Description Example
A 3 by 3 filter
Sharpen 00.250
0.2520.25
00.250
http://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/10.3/managedata/rasterandimages/convolutionfunction.htm 6/9
�3/1/2017 ConvolutionfunctionHelp|ArcGISforDesktop
Type Description Example
A 3 by 3 filter
Sharpen II 0.250.250.25
0.2530.25
0.250.250.25
A highpass 3 by 3 filter
Sharpening 3x3 111
191
111
A highpass 5 by 5 filter
13431
Sharpening 5x5 30603
462164
30603
13431
Smoothing types
Smoothing lowpass filters smooth the data by reducing local variation and removing noise. The lowpass filter calculates
the average mean value for each neighborhood. The effect is that the high and low values within each neighborhood will
be averaged out, reducing the extreme values in the data.
Type Description Example
http://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/10.3/managedata/rasterandimages/convolutionfunction.htm 7/9
�3/1/2017 ConvolutionfunctionHelp|ArcGISforDesktop
A 3 by 3 filter
Smooth Arithmetic Mean 0.1110.1110.111
0.1110.1110.111
0.1110.1110.111
A lowpass 3 by 3 filter
Smoothing 3x3 121
242
121
A lowpass 5 by 5 filter
11111
Smoothing 5x5 14441
141241
14441
11111
Other filters
Point spread type
The point spread function portrays the distribution of light from a point source through a lense. This will introduce a slight
blurring effect.
Type Description Example
http://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/10.3/managedata/rasterandimages/convolutionfunction.htm 8/9
�3/1/2017 ConvolutionfunctionHelp|ArcGISforDesktop
A 3 by 3 filter
Point Spread 0.6270.3520.627
0.3522.9230.352
0.6270.3520.627
Related Topics
What are the functions used by a raster or mosaic dataset?
Editing function chains in a mosaic dataset
http://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/10.3/managedata/rasterandimages/convolutionfunction.htm 9/9