0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views15 pagesOpenmp: Openmp Adds Constructs For Shared-Memory
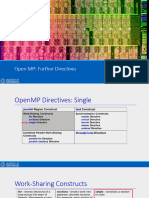
OpenMP is a specification for parallel programming that adds compiler directives to C/C++ and Fortran code. Key directives include:
- #pragma omp parallel to create threads and run code in parallel
- #pragma omp for to parallelize loops across threads
- Reduction clauses to combine private results from each thread
- Worksharing directives like sections to split work among threads
Variables are shared by default, but private, shared, and default clauses control data sharing. The number of threads can be set using the OMP_NUM_THREADS environment variable. OpenMP simplifies parallel programming using compiler directives rather than requiring low-level threading code.
Uploaded by
Aaqib ChCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views15 pagesOpenmp: Openmp Adds Constructs For Shared-Memory
OpenMP is a specification for parallel programming that adds compiler directives to C/C++ and Fortran code. Key directives include:
- #pragma omp parallel to create threads and run code in parallel
- #pragma omp for to parallelize loops across threads
- Reduction clauses to combine private results from each thread
- Worksharing directives like sections to split work among threads
Variables are shared by default, but private, shared, and default clauses control data sharing. The number of threads can be set using the OMP_NUM_THREADS environment variable. OpenMP simplifies parallel programming using compiler directives rather than requiring low-level threading code.
Uploaded by
Aaqib ChCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 15