Microcontroller Page 1 of 9
CPANEL
Search
Home EG Labs About Us Forum Contact Us
HARSHA125
Invite a friend
Microcontroller
My account
A microcontroller is a small and low-cost computer built for the purpose of
Create content dealing with specific tasks, such as displaying information in a microwave LED or
Log out receiving information from a television’s remote control. Microcontrollers are
ACTIVE
mainly used in products that require a degree of control to be exerted by the user.
FORUM
TOPICS
how to
interface
8051 with
8bit serial adc
assembly
language
programming
for min no.
assembly
language
pc controlled
wireless
spybot
more Microcontroller v/s microprocessor
How does a Microcontroller work?
General architecture of a microcontroller
Features of Microcontrollers
Applications
History & Key developments
Comparative study of different families: 8051, AVR/ATmega, PIC
Criteria for choosing a microcontroller
Future of microcontrollers and applications
http://www.engineersgarage.com/microcontroller 9/20/2010
�Microcontroller Page 2 of 9
CPANEL
Microcontroller v/s microprocessor
Microprocessors are used to execute big and generic applications, while a
microcontroller will only be used to execute a single task within one application.
Some of the benefits of microcontrollers include the following:
· Cost advantage: The biggest advantage of microcontrollers against
larger microprocessors is that the design and hardware costs are
much lesser and can be kept to a minimum. A microcontroller is
cheap to replace, while microprocessors are ten times more
expensive.
· Lesser power usage: Microcontrollers are generally built using a
technology known as Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
(CMOS). This technology is a competent fabrication system that
uses less power and is more immune to power spikes than other
techniques.
· All-in-one: A microcontroller usually comprises of a CPU, ROM,
RAM and I/O ports, built within it to execute a single and
dedicated task. On the other hand, a microprocessor generally does
not have a RAM, ROM or IO pins and generally uses its pins as a
bus to interface to peripherals such as RAM, ROM, serial ports,
digital and analog IO.
Top
How does a Microcontroller work?
Microcontroller has an input device in order to get the input and an output device
(such as LED or LCD Display) to exhibit the final process. Let us look into the
illustration of how a microcontroller works in a Television.
The Television has a remote control as an Input device and the TV screen as the
output device. The signal sent from the remote control is captured by the
microcontroller. The microcontroller controls the channel selection, the amplifier
system and picture tube adjustments such as hue, brightness, contrast etc.
Top
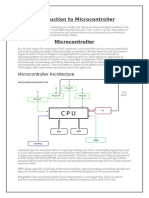
General architecture of a microcontroller
The architecture of a microcontroller depends on the application it is built for. For
example, some designs include usage of more than one RAM, ROM and I/O
functionality integrated into the package.
http://www.engineersgarage.com/microcontroller 9/20/2010
�Microcontroller Page 3 of 9
CPANEL
The architecture of a typical microcontroller is complex and may include the
following:
i. A CPU, ranging from simple 4-bit to complex 64-bit processers.
ii. Peripherals such as timers, event counters and watchdog.
iii. RAM (volatile memory) for data storage. The data is stored in the form
of registers, and the general-purpose registers store information that
interacts with the arithmetic logical unit (ALU).
iv. ROM, EPROM, EEPROM or flash memory for program and operating
parameter storage.
v. Programming capabilities.
vi. Serial input/output such as serial ports.
vii. A clock generator for resonator, quartz timing crystal or RC circuit.
viii. Analog-to-digital convertors.
ix. Serial ports.
x. Data bus to carry information.
Top
Features of microcontrollers
i. Architectural features:
Most microcontrollers built today are based on the CISC (Complex
Instruction Set Computer) platform. A typical CISC microcontroller has
http://www.engineersgarage.com/microcontroller 9/20/2010
�Microcontroller Page 4 of 9
over 80 instructions and it is quite common for the instructions to CPANEL
all
behave quite differently.
The main advantage of CISC architecture is that the instructions are
macro-like, allowing the programmer to use one instruction in place of
many simpler instructions.
ii. Advanced Memory features:
a. Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM)
Many microcontrollers use the economic EEPROM for smaller
amount of memory that have frequently changeable data. This type of
memory is relatively slow, and the number of erase/write cycles
allowed in its lifetime is limited.
b. FLASH (EPROM)
Flash provides microcontrollers with a better solution than EEPROM
for requirements of large amounts in non-volatile program memory.
EPROM is faster and permits more erase/write cycles than EEPROM.
iii. Power Management features
A majority of microcontrollers usually support an operation of 3 - 5.5 V.
As consumer goods become trendier, compact and lighter, the focus is on
microcontrollers to ensure that products with less power usage are
efficiently built and then used by end-users.
Top
Applications
Microcontrollers are used in products that are controlled automatically.
The various products that make use of microcontrollers in our everyday life are
given below:
i. Home: Television, DVD player, Telephone, Fax machine, Cellular
phones, Security systems, Camera, Sewing machine, Musical Instrument,
Exercising machine, Video games, Computer, Microwave oven.
http://www.engineersgarage.com/microcontroller 9/20/2010
�Microcontroller Page 5 of 9
CPANEL
ii. Office: Computers, Printers, Telephones, Fax machine, Security
systems.
Top
History and Key Developments
In 1975, Intel fabricated a chip (Intel 8048) with inbuilt RAM and ROM which
was widely used in numerous applications. The microcontrollers had two variants
namely EPROM which was erasable but expensive and PROM which could be
programmed only once. In 1993, EEPROM memory was introduced in the
microcontrollers which electrically erasable and at affordable price. Atmel used
the Flash memory and launched the first microcontroller. After this, many
companies fabricated microcontrollers with both type of memory.
The microcontroller became popular after Intel Corporation released an 8-bit
version in 1981 called the 8051. Intel allowed other manufacturers to make
alternate versions of the 8051, and this ensured that numerous versions of the
8051 entered the market. Some of these controllers had different speeds with
multiple ROMs mounted on a single chip.
The family of 8051 microcontrollers signalled an electronic revolution with the
end user reaping the benefits in technology and science.
As years passed by, microcontrollers have grown to offer much more to end-users
and businesses. Some of the key developments in the microcontroller lifecycle are
as follows:
i. More ease-of-use and ability to reach market faster.
ii. More energy efficiency.
iii. More integrated features like RF and USB.
iv. Smaller form factors.
v. Increasing processing power.
In future, MRAM (Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory) could be used in
microcontrollers as it can store large amount of data which allows it to access
faster consuming less power of battery.
Top
http://www.engineersgarage.com/microcontroller 9/20/2010
�Microcontroller Page 6 of 9
Comparative study of different families: 8051, AVR/ATmega, PIC CPANEL
8051:
These
microcontrollers are old but still trendy and most of the companies fabricate these
microcontrollers. The older types of 8051 have 12 clocks per instruction that make
it sluggish whereas the recent 8051 have 6 clocks per instruction. The 8051
microcontroller does not have an in built memory bus and A/D converters. In
1980, Intel fabricated the single chip microcontroller 8051 with Harvard
architecture.
PIC: Programmable Interface Controller is usually referred as PIC. They are
slightly older than 8051 microcontrollers but excel cause of their small low pin
count devices. They perform well and are affordable. The Microchip technology
fabricated the single chip microcontroller PIC with Harvard architecture. The
programming part is very tedious and hence it is not recommended.
AVR: In 1996, Atmel fabricated this single chip microcontroller with a modified
Harvard Architecture. This chip is loaded with C- compiler, Free IDE and many
more features. This microcontroller is a bit difficult for the starters to handle.
Top
Criteria for choosing a microcontroller
The most important factor is that the microcontroller should be cost-efficient and
work capably to handle the dedicated task. Some questions that should be asked
while deciding on a microcontroller are as follows:
i. What is the maximum speed of the microcontroller?
ii. What is the amount of RAM and ROM on chip?
iii. How easy it is to upgrade to higher upgrade or lower consumption
versions?
http://www.engineersgarage.com/microcontroller 9/20/2010
�Microcontroller Page 7 of 9
iv. Is the microcontroller readily available at cheaper rates? CPANEL
v. What is the number of I/O pins and timer on the chip?
vi. How easy is it to develop applications around a microcontroller?
Top
Future of microcontrollers and applications
The future is bright and shining for microcontroller manufacturers. This is because
the global economies are booming and microcontrollers have a role to play in
almost every gadget present on earth. The list of applications for these
microcontrollers is:
i. Energy Management:
Technology for energy management is in great demand due to
government initiatives that focus on energy. Efficient metering systems
help in controlling energy usage in homes and industrial applications.
These metering systems are made capable by incorporating
microcontrollers.
ii. Touch screens:
A touch screen is accepted as the most efficient method to implement
user control. They enable dynamic user interfaces and allow increased
productivity. Touch screen controller implementation is microcontroller
-based and therefore, ample opportunities lie ahead for microcontroller
providers that incorporate touch-sensing capabilities in their designs.
Portable electronics such as home appliances, cell phones, media
players, gaming devices are some of the domains where microcontroller
-based touch screens will be in demand.
iii. Automobiles:
Microcontrollers find wide usage in hybrid vehicles, especially to
ensure smooth and simultaneous functioning of electric and petrol
engines. Additionally, almost every car manufacturer uses
microcontrollers to control functions within their vehicles and to ensure
error-free rides for their customers.
http://www.engineersgarage.com/microcontroller 9/20/2010
�Microcontroller Page 8 of 9
iv. LED Lighting: CPANEL
Microcontrollers are used for led lighting in residential and industrial
locations to enable greater control and power savings.
v. Personal Medical Devices
The rise and popularity of portable medical devices such as blood
pressure and glucose monitors have ensured that microcontrollers will
have a role in the medical industry. Microcontrollers are used to display
date and increase reliability in providing medical results.
Top
236 reads
Comments (0)
Post new comment
Your name:
Harsha125
Comment: *
http://www.engineersgarage.com/microcontroller 9/20/2010
�Microcontroller Page 9 of 9
CPANEL
Font Size
Disable rich-text
Web page addresses and e-mail addresses turn into links automatically.
Lines and paragraphs break automatically.
More information about formatting options
Notify me when new comments are posted
All comments Replies to my comment
Save
Copyright © 2010 EngineersGarage. All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
http://www.engineersgarage.com/microcontroller 9/20/2010