0% found this document useful (0 votes)
167 views16 pagesMaths Probability
This document provides examples of probability questions from the CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 on Probability.
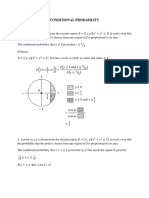
1) The first question asks for the probability that the minute and hour hands of a clock will form an acute angle at any given time, and the answer is less than 0.5 because some positions result in 0 or 180 degree angles.
2) Another question asks for the probability of getting different values when throwing two dice, and the answer is 5/6 because there is only a 1/6 probability of getting the same value on both dice.
3) A third question provides that the probability of event A is 0.15, and asks for the probability of the complementary event not A,
Uploaded by
Adhi AdhiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
167 views16 pagesMaths Probability
This document provides examples of probability questions from the CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 on Probability.
1) The first question asks for the probability that the minute and hour hands of a clock will form an acute angle at any given time, and the answer is less than 0.5 because some positions result in 0 or 180 degree angles.
2) Another question asks for the probability of getting different values when throwing two dice, and the answer is 5/6 because there is only a 1/6 probability of getting the same value on both dice.
3) A third question provides that the probability of event A is 0.15, and asks for the probability of the complementary event not A,
Uploaded by
Adhi AdhiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16