Unit 1 Notes For Visual Basic Part 1 PDF
Uploaded by
vipul kumarUnit 1 Notes For Visual Basic Part 1 PDF
Uploaded by
vipul kumarlOMoARcPSD|4339219
Unit-1- Notes FOR Visual Basic PART 1
Visual Programming (Bangalore University)
StuDocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
NOTES FOR VISUAL BASIC PART 1
1.Introduction to vb
What is vb?
vb is a user friendly event driven and partly objected oriented programming
language using which we can develop:
database application.
web enabled application.
and variety of other window based application.
Who developed vb?
vb is developed by Microsoft in 1991 as Visual Basic 1.0.
Why vb was developed?
before vb window based application was being done using c and window based
compiler which was a slow and tedious process. it required lots of coding. to
speed up development of window based application vc++ and Microsoft
foundation class were developed. but the development process was still tedious
and slow. to boost development of window based application easily and fastly vb
was introduced.
What are the different editions of vb?
there are three editions of vb:-
standard or learning edition: contains basic language feature and tools.
professional edition: contains more feature and tools when compared to
standard edition.
enterprise edition: contains most advance feature and tools.
the edition which we are using is enterprise edition.
What are the hardware requirement to use vb?
the hardware requirement are as follows:
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
cd-rom drive
cd-rom (1 to 7 cds). first cd rom contains compilers for various languages like vb,
vc++, visual foxpro, visual internet developer etc. remaining cds contains help,
client server tools, samples etc.
windows 9x Os.
80 to 120 mb for installation of vb.
40 mb free hard disk space for user generated program.
16 mb ram minimum ( 32 mb ram recommended)
80486 based micro processor ( Pentium 166 mhz recommended)
What is Event Driven programming?
when a program consists of one or more than one event procedures and those
procedures accomplish the task to be done by program it is know as event driven
programming.
What is event?
Event is any action performed by either performed by user or performed by
program itself. for example mouse-click, key press, window resize etc.
What is the difference between structured/procedure oriented and event
driven programming
Structured/Procedure Oriented Event Driven Programming
Program consists of one or more procedure.Program consists of one or more event
procedure.
Programming task is completed byProgramming task is completed by event
procedure. procedure.
The order of execution of procedure is moreThe order of execution of event procedure
or less predictable. depends on user performed action.
Procedure oriented programming is notEvent driven programming is suitable for
suitable for window based application. window based application.
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
What do you mean by IDE ?
Ide stands for integrated development environment. it is
collection of program allowing to compose and edit the program, test the
program, run the program and debug the program.
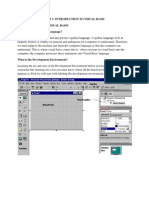
Describe working environment of vb?
Working environment of vb is compsed of many elements:
title bar: where program title, project name and program mode is displayed
menu bar: contains menu and related commands.
tool bar: consists of icons which are short cuts to frequently used commands
some toolbars are : standard, formatting etc.
toolbox: on the left side toolbox appears which contains controls.
form designer: appears in middle where graphical user interface
element(controls) are placed.
properties window: using this we can set properties of controls.
project explorer window: displays files which make up the project
form layout window: displays form-icon used to set start up position of form.
immediate window: useful to test any statement or to print value of variable.
What are the different modes of vb program?
there are three modes of vb program:
design: ( when designing form and writing code)
run : when a program is running.
break: when any occurred in program.
What is project file? why it is needed?
project file contains information about all those file which make the project. it
stores location of individual file with path. when saving project it saves all files
one by one inside project. when we open project it automatically opens all files
which are part of project we need not to open each file one by one thus saving
time. project file has extension “vbp”.
What is executable file. how it is made?
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
to make executable file (exe) we have to go to file menu and have to select make
exe.
copying of exe file to another computer and running the exe file does not
guarantee that the executable file will run there because a window based
program depends on many different file. it better to run distributable package
using package and deployment wizard.
What is module?
module is collection of procedures and functions corresponding to a file in disk
will generate. benefits are:
it provides code reusability and shariblity.
avoids code repetition.
testing and debugging becomes easier.
type of module:
form module: normally contains event procedures, other procedure and function
which will be used inside the same form module. extension is .frm
basic module: normally contains global variables, procedure and function which
can be accessed across other modules. extension is .bas
class module: contains definition of class, member function and properties.
extension is .cls
How to use code editor window?
code editor window can be brought forward using either of these methods:
select view-> view code
right click on form and select view code
double click on any control or on double click on form.
from project explorer window select the form name and click on button view
code.
navigation of code editor window:
control+left arrow : move one word left
control+right arrow : move one word right
control +home : move to beginning of code view
control +end : move to end of code view
home : move to beginning of line
end : move to end of line
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
control+up arrow : move one procedure up
control+down arrow : move one procedure down
shift+f2: view definition of function or procedure under cursor
control+shift+f2: go to last position of cursor
what is documentation? why it is needed?
documention of code is very necessary. using documention we can increase
readability of our program. using documentation we can store addition
information like:
date and time of program
version no. of program
company for which it was created
author of the code
variables used and purpose
algorithm of program
explaination of statment
documentation makes the program easily understable. in future if we are going
to make modification in program it will help greatly. we use ‘(apostrophe) to
write comments or rem keyword.
how formatting of code is done?
formatting of code make program easy to read. indentation makes easy to follow
closing of control structure. different background and foreground colors, fonts,
font size can be assigned to normal text, keywords etc. using tool->options-
>editor format tab. procedure seperator line can also be turned on to help to
identify where one procedure is beginning and ending.
describe environment options in vb?
select tools->options->environment tab
under when visual basic starts
if option button selected is prompt for project: each time visual basic starts a
dialog box appears which lets us select type of project.
if option button selected create default project: each time visual basic starts it
automatically open standard exe project.
under a program starts:
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
if save changes: is selected when program is about to start it saves the changes
made in project.
if selected prompt to save changes: is selected when program is about to start it
will ask to save the changes.
if selected don’t save changes: it will not save the changes made in project and
will run program.
show templates for: we can have many templates available for use as starting
point for form, mdi forms, modules etc.
Describe editor options.
select tools->options->editor tab.
auto syntax check: if checked , when writing a statement and pressing enter
check the statement for error.
require variable declaration: puts ‘option explicit’ statement in module’s general
declaration section which forces declaration of variable before use as in c-
language.
auto list member: if checked gives popup list consisting of properties, methods
supported by object.
auto quick info.: if checked gives information about function parameter and data
type of parameter which current function will work on.
auto data tips: if checked gives list of constant which can be assigned to a
variable or to parameter of a procedure or function.
dim b as Boolean
type b= then you will get true, false in a list
auto indent: if checked starts new line just below the previous line.
tab width: specify the amount of space generated by a tab key.
drag and drop text editing: if checked supports drag and drop in code editor
window.
default to full module view: if not checked only one procedure will be visible at a
time.
procedure separator: if checked draws line among procedures.
Describe automatic code completion feature of vb.
when we have to use any object property or any method of object we have to
type just a few letter of that property or method as soon as the property or
method is selected from popup list we can press control+space key combination
to complete the whole property or method thus saving key stroke.
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
2. Creating programs
What is Object?
object is class variable which is composition of properties, methods and data
member. object is fundamental requirement of any object oriented language.
object has three characteristics:
state: state of any object it defines identity of object.
behaviour: behaviour of any object is decided by member functions(methods) to
which object can respond.
method: it is also known as member function it performs computation on data
member or any kind of action.
What is property?
property of any object is actually member procedure which allows to set value in
data member ( working as mutator) or allows to retrieve value of data member
( working as accessor).
How to create program in vb?
steps are as follows:
first decide the controls which will be used to create graphical user interface.
set properties of controls
write event procedure coding.
How to get print of visual basic program.
save the project
select file->print
from the dialog box specify:
under range:
selection – to print selected code
current module- to print current module
current project- to print all modules in current project
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
under print what:
form image- to print the image of form.
code- to print code
form as text- to print form as text format , resulting of printing of controls along
with properties and code
under setup, specify paper size, orientation of paper and printer to use
Describe controlling objects. or describe toolbox.
control depend on interface which are properties,events and methods.
normally there are many controls found in visual basic. some controls are activex
controls which can be included in toolbox using project->component dialog.
there are some control already available in toolbox which are also known as
intrinsic controls or standard controls. description of standard controls are as
follows:
label control: it is useful to give user a prompt.
text box: it is useful to input/output data for program.
list box: it is useful to give list of items and user can select items from list.
combo box: it is combination of text box and list box user can type new item or
can select an existing item from combo box list portion.
image box: can display picture
picture box: can display picture.
directory , drive and file list box: allows to create a dialog box to save , open file
ole control: allows to use feature of other existing application.
data control: useful to write data base program
option button or radio button : allows to select only one of several available
choices.
check box: allows to select many choices of several available choices.
frame: acts as container to place related controls together.
command button or push button: useful to confirm action like close, open, apply
etc.
timer: useful to execute certain piece of code after specified interval. default
property is enabled which takes true or false value.
shape: useful to decorate form
line : useful to draw line to decorate form
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
scrollbar: useful to take input/output or scrolling data.
3.Variables Procedures
What is variable?
variable is name given to computer memory location where we can store value
and retrieve the stored value by name.
variable is fundamental requirement of any programming language.
rule of naming variable or identifier:
variable name must start with alphabet.
later on digits can be used, under score can also appear.
variable name is not case sensitive
only a-z, 0-9 and _ can appear in variable Name
space and special are not allowed.
variable name must not match with keyword
we can have variable name 255 characters long
name of control must not exceed 40 characters
What is data type?
data type of variable defines range, memory and valid operation for a variable
Data type Range Memory
1.Byte 0 , 255 1
2.Integer % 32767 , 0 , -32768 2
3.Single ! +/- 3.4 e +34 4
4.Double # +/- 1.7 e+308 8
5.Date 1-1-100 to 31-12-9999 8
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
6.string(variable) $ 2 billion characters
6.string(fixed) $
7.boolean True, false 2
8.object Reference of any object
9. variant Range for number is same as
double
Range for string is same as 2
billion characters
How to declare variable?
(a) dim x as integer, y as integer
or
dim x%,y%
(b) dim x, y as integer
then x will be variant and y will be integer
(c) dim b as Boolean
Describe scope of variable.
scope specifies the code range where value of variable is accessible.
local variable: accessible inside a function or procedure. we use dim keyword to
declare local variable.
module level global variable: accessible inside a module but not outside from
other module. we use dim or private keyword to declare module level global
variable and declare it inside general declaration of module.
global variable : accessible from every where. we use public or global keyword
to declare global variable inside general declaration of module.
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
What do you mean by shadowing of variable?
if global variable or module level global variable exists with name ‘a’ and a local
variable also exists in a procedure or function it prevents accessing of global or
module level global variable because local variable is given preference. to access
value of global variable we can use
modulename.globalvariable e.g. form1.a
what are the operators in vb?
arithmetic operator:
+ for addition,
- for subtraction.
* for multiplication
\ for integer division c=10\3 c will be 3
/ for float division c= 10/3 c will be 3.333
^ for power e.g. c=10^3 therefore c will be 1000
mod for modulo division c=10 mod 3 c will be 1
relation operator
>,>=,<,<=,=, <>
3. logical operator
and, or, not
assignment
=
4 .Controlling program Execution
Why do we need control structure?
We all need to alter our action depending on changing circumstances. For
example If weather is fine I will go Dongargarh on bike otherwise I will go by
train. In the same way ‘vb’ language too must be able to perform different action
under one condition and different action under another condition and this is
made possible by control structure. Sometimes a given set of statements are
needed to run repeatedly this is done using loop control structure.
Write notes on if control structure./ explain branching structure in vb./ write
short notes on if statement/ write short note on select case.. end select.
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
The general form of if statement is:
(a)if-endif statement
the general format of if statement is
if (condition is true) then
execute this statement
end if
The keyword if tells the compiler that what follows, is a decision control
instruction. The condition following the keyword if is optionally enclosed within
a pair of parentheses. If the condition, whatever it is, is true, then the statement
is executed. If the condition is not true then the statement is not executed;
instead the program skips past it.
(b) if –else-endif statement
if statement by itself can execute only one statement if condition is true. If it
required running a group of statements when condition is true we have to
enclose those statements inside curly brace known as compound statement.
The above form of if statement mentioned in (a) will not do anything when
condition is false. If we want to run statement when condition is false we need
if-else construct.
General format of if-else construct is
If (condition is true) then
Execute this statement
Else
Execute this statement if condition is false
end if
Condition is specified using relational operator
x= y means x is equal to y.
x<>y means x is not equal to y.
x< y means x is less than y.
x>y means x is greater than y.
x<=y means x is less than or equal to y.
x>=y means x is greater than or equal to y
What is the use of logical operator?/what is meant by logical testing?
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
Logical operator and, or, not are useful to join more than one condition whereas
not operator negates meaning of condition. these are required in following
situations:
* When it is be tested whether a value falls within a particular range or not.
* When after testing several conditions the outcome is either true or false.
* Reverse the logic of condition using ‘not’ logical operator.
control structure mostly depend on logical testing to perform some piece of
code either selectively or repeatedly.
What are the different forms of if –else statements?
Different forms of if-else statement are as follows:
1. if (condition) then
do this
and this
end if
2. if (condition) then
do this
do this
else
do this
do this
end if
3. if (condition) then single-true statement
4. if (condition) then single-true statement else single-false-statement
5. if (condition) then
if (condition) then
statement
else
statement
end if
else
if (condition) then
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
statements
else
statements
end if
end if
if condition then
statements
elseif condition then
statements
elseif condition then
statements
else
statements
end if
program to find division given percentage
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim a!, b$
a = Text1.Text
If a < 33 Then
b = "fail"
Else
If a < 45 Then
b = "third"
Else
If a < 60 Then
b = "second"
Else
b = "first"
End If
End If
End If
Text2 = b
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
End Sub
place label : having caption enter percentage
place text1: having text property cleared
place label2 : having caption division
place text2: having text property cleared
place command1: having caption find division
program to check leap year
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim a%
a = Text1
If a Mod 100 = 0 Then
If a Mod 400 = 0 Then
Text2 = "leap"
Else
Text2 = "not leap"
End If
else
If a Mod 4 = 0 Then
Text2 = "leap"
Else
Text2 = "not leap"
End If
End If
End Sub
place label : having caption enter year
place text1: having text property cleared
place label2 : having caption result of testing
place text2: having text property cleared
place command1: having caption check for leap year
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
program to print message teenage, child, old etc. according to given age
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim a!
a = Text1
Select Case (a)
Case Is <= 8
Text2 = "child"
Case 9 To 14
Text2 = "teenager"
Case 15 To 20
Text2 = "young"
Case 21 To 28
Text2 = "adult"
Case Is > 28
Text2 = "old"
End Select
End Sub
place label : having caption enter age
place text1: having text property cleared
place label2 : having caption state
place text2: having text property cleared
place command1: having caption check age
State the difference between select case and if
select-case if-else
1.All programs made using select-case canAll programs made by ‘if’ are not possible to
be solved using if. select case takessolve by ‘select-case’.
different action depending on value of a
single variable.‘if’ leads to less structured programming
and level of indentation is difficult to
2. ‘select-case’ leads to more structuredmanage if using nested ‘ifs’.
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
programming and level of indentation is
manageable even if we have nested select-
case.
Multiple ifNested if..else
1.multiple ‘if..else’ contains more than one1.nested ‘if..else’ contains more than one
end if. Each ‘end if’ corresponds to each ‘if’.‘else if’ but just one ‘end if’..
2. multiple if requires more comparison.2. nested if requires less comparison.
Therefore it is not efficient. Therefore it is efficient.
Write short notes on goto statement and its limitations.
‘goto’ is a statement which is quite common in monolithic programming
paradigm. some languages like basic, fortran etc. use it deliberately. using goto
we can do :
skipping of some statement without executing them.
transferring of control to a labeled statement.
coming out of loop whatever level of nesting of loop may be.
note that break statement can take out of loop inside which it lies but goto
statement can take out of loops irrespective of level of nesting of loops.
different type of goto can be:
conditional-goto : if it is used with ‘if’ statement.
unconditional-goto : if it is not used with ‘if’ statement.
limitations of goto: unwise use of goto make it difficult to trace logic flow
of program and makes it difficult to remove logical error of program therefore,
as far as possible, we must avoid use of goto.
program to print 1 to 10 using goto statement
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim a%, b%, c%, t$
a = Text1
b = Text2
c = Text3
mm: t = t & a & " "
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
a=a+c
If a <= b Then GoTo mm
Text4 = t
End Sub
place label1 : having caption enter starting term
place text1: having text property cleared
place label2 : having caption enter stopping term
place text2: having text property cleared
place label3: having caption enter value to step by
place text3: having text property cleared
place text4: having text property cleared
place command1: having caption print series in text box
Why loop control structure is needed?
Without loops we execute the same series of actions, in the same way, exactly
once. Loops allows to execute same portion of program code repeatedly a
specified no. of times or until a particular condition is being satisfied. This
repetitive operation is done through a loop control structure.
There are four methods using which we can repeat a part of a program which
are:
* for statement
* while statement
* do-while statement
* goto statement (not recommended)
Write short notes on ‘while’ (entry level control structure/test and do) loop.
In programming we require to execute same set of instructions a fixed number
of times. E.g. we want to calculate gross salary of ten different persons, we want
to convert temperatures from centigrade to Fahrenheit for 15 different cities.
The ‘while’ loop is suited for this.
‘ program to print 1 to 10 on form
private sub command1_click()
dim a%
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
a=1
do while a<=10
print a
a=a+1
loop
end sub
General format is
1.
initialize loop counter
do while(condition is true)
do this;
increment loop counter;
loop
Write short notes on ‘while’ (entry level control structure/test and do) loop.
In programming we require to execute same set of instructions a fixed number
of times. E.g. we want to calculate gross salary of ten different persons, we want
to convert temperatures from centigrade to Fahrenheit for 15 different cities.
The ‘while’ loop is suited for this.
‘ program to print 1 to 10 on form
private sub command1_click()
dim a%
a=1
do
print a
a=a+1
loop while a<=10
end sub
General format is
initialize loop counter
do
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
do this
increment loop counter
loop while(condition is true)
Differentiate between while/while..wend and do-while loop.
Body of loop in case of ‘while’ loop will not execute even once if condition of
while loop is false but in case of ‘do-while’ loop body of loop will run at least
once because condition is tested at the end of loop body.
format of do..loop is
initialize loop counter
do
do this
increment loop counter
loop while(condition is true)
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
format of while loop:
initialize loop counter
while condition
do this
increment loop counter
loop
format of while.. wend loop:
initialize loop counter
while condition
do this
increment loop counter
wend
Do while loop must test a condition that will eventually become false, otherwise
the loop would be executed forever, indefinitely known as infinite or indefinite
loop.
while loop or while..wend loop test condition and if condition is true then
statements are executed if condition is false statements are not executed even
once.
do.. while loop test condition later therefore if condition is false statements are
executed at least once.
while..wend statement can not use ‘exit do’ statement to come out of loop
whereas do..while and do..loop…while can use ‘exit do’ statement to come out
of loop.
Write short notes on for loop.
‘for’ loop is most popular loop. ‘for’ loop allows us to specify three things about a
loop in a single line which are:
1. Setting a loop counter to initial value.
2. Testing the loop counter to determine whether its value has reached the
number of repetitions desired.
3. Increasing the value of loop counter each time the program segment within
the loop have been executed.
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
The general format of for statement is as us under:
for variable= intialvalue to endvalue step stepvalue
do this
and this
and this
next
Write short notes on odd loop.
The loops in which no. of times statements inside loop body will execute are
known as finite or determinate loop. The loops which will never terminate
execution of statements inside loop body are known as infinite loop. The loop
about which we are not certain how many times statements inside loop body
will execute but we are sure that it will terminate after some time is known as
odd loop.
Write program to demonstrate loops to solve Fibonacci series up to n terms.
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim i%, term1&, term2&, term3&, t$, nterms
term1 = 0
term2 = 1
nterms = Text1
' method A- using for loop
‘For i = 1 To nterms
't = t & term1 & " "
'term3 = term1 + term2
'term1 = term2
'term2 = term3
'Next
‘method B-using do-while…loop
'i = 1
'Do While i <= nterms ' do loop until i>nterms
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
't = t & term1 & " "
'term3 = term1 + term2
'term1 = term2
'term2 = term3
'i = i + 1
'Loop
‘ method C- using do…loop while
'i = 1
'Do
't = t & term1 & " "
'term3 = term1 + term2
'term1 = term2
'term2 = term3
'i = i + 1
'Loop While i <= nterms ' loop while until>nterms
‘method D-using while … wend
i=1
While i <= nterms
t = t & term1 & " "
term3 = term1 + term2
term1 = term2
term2 = term3
i=i+1
Wend
Text2 = t ‘series will go into a text box
End Sub
place label1 : having caption enter no. of terms of Fibonacci series
place text1: having text property cleared
place label2 : having caption series is
place command1: having caption print series in text box
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
Write short Notes on ‘exit do / exit for’ in Loop/write program to check
primality.
We often come across situations when we want to jump out of a loop instantly,
without waiting to get back to the conditional test. The keyword ‘exit do / exit
for’ allows us to do this. When the keyword ‘‘exit do / exit for’’ is encountered
inside any loop statement, control automatically passed to the first statement
after the loop. An ‘exit do / exit for’ is usually associated with an ‘if’ statement
applicable to loop.
The keyword ‘exit do / exit for’ takes the control out of the loop inside which it
is placed.
What is use of const keyword?
const keyword is useful to declare a constant with a given symbolic name whose
value can not change during program run time.
const pi =3.1415
What do you mean by nested loop?
nested loop is a special case in which one loop contains other loop inside its loop
body. for each value of outer loop counter , inner loop counter changes
frequently.
program to print prime series between 1 to 100 using for loop and exit for
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim a%, b%, c%, n%, t$, i%
a=1
b = 100
For n = a To b
For i = 2 To n - 1
If n Mod i = 0 Then
Exit For
End If
Next
If i >= n Then
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
t=t&""&n
End If
Next
Text1 = t
End Sub
place label1 : having caption set to prime series is
place text1: having text property cleared
place command1: having caption print series in text box
Define Array.
Array or Subscripted variables:
Array is collection of variables having common name and common data type.
Individual variable in collection is identified by index or subscript. Elements of
array occupy contiguous memory location.
How can we declare a single dimension Array?
Declaration (single dimension numeric array):
dim a(5) as integer
or
dim a%(5)
‘a’ is name of array.
it means there are 6 variables viz. a(0),a(1),a(2),a(3),a(4),a(5) index or subscript
will ange from 0 to 5. All variables will be integers.
dim b!(10)
or
dim b(10) as single
It means there are 11 variables viz. b(0),b(1)… b(5) index or subscript will
change from 0 to 10. All variables will be single.
How we can initalise an array?
Initialization of array is not supported by vb.
What are the usages/Applications of Array?
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
Application of arrays:
* It is useful to solve simultaneous equation.
* It is useful to solve problems of data structure like searching, sorting, linked
list, graph etc.
* Its is useful to solve such problems requiring variable of same data type in
contiguous memory location.
What is Multi Dimension Arrays? What are their usages?
Array declared with more than one dimension is known as multi-dimension
array.
Often multi dimension array is needed to store data for table and matrices. Multi
-dimension array has more than one subscript. Two dimension array contains
two subscript, three dimension array has three subscript and so on.
program to add two matrix of order 3x3
place three command buttons on form labeled input, sort, print
Dim a%(2, 2), b%(2, 2), c%(2, 2), i%, j%
Private Sub Command1_Click()
MsgBox "enter value for array a"
For i = 0 To 2
For j = 0 To 2
a(i, j) = InputBox("enter value")
Next
Next
MsgBox "enter value for array b"
For i = 0 To 2
For j = 0 To 2
b(i, j) = InputBox("enter value")
Next
Next
End Sub
Private Sub Command2_Click()
For i = 0 To 2
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
For j = 0 To 2
c(i, j) = a(i, j) + b(i, j)
Next
Next
End Sub
Private Sub Command3_Click()
For i = 0 To 2
For j = 0 To 2
Print c(i, j) & " ";
Next
Next
End Sub
Program to sort a given array
place three command buttons on form labeled input,add,print
Dim a%(4)
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim i%
For i = 0 To 4
a(i) = InputBox("enter value", "data entry", 1)
Next
End Sub
Private Sub Command2_Click()
Dim i%, j%
For i = 0 To 3
For j = 0 To 3 - i
If a(j) > a(j + 1) Then
t = a(j)
a(j) = a(j + 1)
a(j + 1) = t
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
End If
Next
Next
End Sub
Private Sub Command3_Click()
Dim i%
For i = 0 To 4
Print a(i)
Next
End Sub
What is dynamic array?
dynamic array is an array whose no. of elements are not specified earlier. no. of
elements can be requested from user at program run time. redim keyword can
be used to allocate memory for such no. of elements. after allocating memory
we can store value in elements of array.
dynamic array saves memory because we have to allocate memory for such
many elements which we want to use.
Program to sort an array using dynamic array
Dim a%(), n 'note element is not specified
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim i%
' take no. of elements required
n = InputBox("enter no. of elements")
'allocate memory
ReDim a(n - 1) ' workout
For i = LBound(a) To UBound(a)
a(i) = InputBox("enter value", "data entry", 1)
Next
End Sub
Private Sub Command2_Click()
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
Dim i%, j%
For i = LBound(a) To UBound(a) - 1
For j = LBound(a) To UBound(a) - 1 - i
If a(j) > a(j + 1) Then
t = a(j)
a(j) = a(j + 1)
a(j + 1) = t
End If
Next
Next
End Sub
Private Sub Command3_Click()
Dim i%
For i = LBound(a) To UBound(a)
Print a(i)
Next
End Sub
place command1:having caption set to input
place command1:having caption set to sort
place command1:having caption set to print
Program to add two matrix using non-dynamic array.
Dim a%(2, 2), b%(2, 2), c%(2, 2), i%, j%,t$
Private Sub Command1_Click()
MsgBox "enter value for array a"
For i = 0 To 2
For j = 0 To 2
a(i, j) = InputBox("enter value")
Next
Next
MsgBox "enter value for array b"
For i = 0 To 2
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
For j = 0 To 2
b(i, j) = InputBox("enter value")
Next
Next
End Sub
Private Sub Command2_Click()
For i = 0 To 2
For j = 0 To 2
c(i, j) = a(i, j) + b(i, j)
Next
Next
End Sub
Private Sub Command3_Click()
For i = 0 To 2
For j = 0 To 2
t=t & c(i, j) & " "
Next
t=t & vbcrlf
Next
End Sub
place command1:having caption set to input
place command1:having caption set to add
7place text1: having multiline property true and scrollbars set to 2 for both
place command1:having caption set to print
Program to multiply two matrix using dynamic array.
Dim a%(), b%(), c%(), i%, j%, m%, n%, p%, q%
Private Sub Command1_Click()
m = InputBox("enter no of rows in matrix a")
n = InputBox("enter no. of columns in matrix a")
p = InputBox("enter no of rows in matrix b")
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
q = InputBox("enter no. of columns in matrix b")
If n <> p Then
MsgBox "invalid matrix order for multiplication"
Exit Sub ' come out of event
End If
MsgBox "enter value" & m * n & " for array a"
ReDim a(m - 1, n - 1) 'allocate memory before storing value
For i = LBound(a, 1) To UBound(a, 1)
For j = LBound(a, 2) To UBound(a, 2)
a(i, j) = InputBox("enter value")
Next
Next
MsgBox "enter value" & p * q & " for array b"
ReDim b(p - 1, q - 1) 'allocate memory before storing value
For i = LBound(b, 1) To UBound(b, 1)
For j = LBound(b, 2) To UBound(b, 2)
b(i, j) = InputBox("enter value")
Next
Next
End Sub
Private Sub Command2_Click()
ReDim c(m - 1, q - 1)
For i = LBound(a, 1) To UBound(a, 1)
For k = LBound(b, 2) To UBound(b, 2)
c(i, k) = 0
For j = LBound(a, 2) To UBound(a, 2)
c(i, k) = c(i, k) + a(i, j) * b(j, k)
Next
Next
Next
End Sub
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
Private Sub Command3_Click()
For i = LBound(c, 1) To UBound(c, 1)
For j = LBound(c, 2) To UBound(c, 2)
Print c(i, j) & " ";
Next
Next
End Sub
place command1:having caption set to input
place command1:having caption set to multiply
place command1:having caption set to print
what is use of preserve keyword?
preserve keyword is useful to let the dynamic array remember the older
contents it has.
e.g.
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim a%()
'redimension
ReDim a(2)
a(0) = 10
a(1) = 20
a(2) = 30
Print a(0), a(1), a(2)
'resize array without using redim
ReDim a(3)
a(3) = 40
Print a(0), a(1), a(2), a(3)
End Sub
Private Sub Command2_Click()
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
Dim a%()
'redimension
ReDim a(2)
a(0) = 10
a(1) = 20
a(2) = 30
Print a(0), a(1), a(2)
'change array size and use preserve
ReDim Preserve a(3)
a(3) = 40
Print a(0), a(1), a(2), a(3)
End Sub
place command1:having caption set to test without preserve
place command1:having caption set to test with preserve
What is function?
a number of statements grouped into a single logical unit is
referred to as a function which returns a value and which is
made to complete a specific task. A program can be made of
many functions.
Types of functions:
User defined function: these are those functions which are made by
programmer for his programming convenience.
Library function: these are those functions which are readymade and are
provided by compiler, uses of which are possible by including corresponding
header files. Source code of library function is not available to programmer but
its object codes are available in precompiled form.
What is procedure?
a number of statements grouped into a single logical unit is
referred to as a procedure or subroutine which does not return
any value and which is made to complete a specific task. A
program can be made of many procedures.
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
What are the usages/applications of functions/procedures?
Usages are as follows:
Function/procedure avoids code repetition:- once a function/procedure has
been made we can call the function/procedure to complete the task when and
where necessary.
Function/procedure used carefully makes the process of error removing easier
called debugging.
Once function/procedure is tested and satisfies the one’s needs, one can convert
it in to library, and can distribute it others for use.
Function/procedure allows breaking bigger task into smaller manageable
subtasks which is soul of modular programming.
Recursive function/procedure (function/procedure calling itself at least once)
solves some typical programming tasks easily and with few lines of coding which
otherwise would have taken several lines of code.
What do you mean by recursion?/what are recursive function explain with an
example.
Expressing an entity in terms of itself is known as recursion. When
function/procedure calls itself at least once the function/procedure is called
recursive function/procedure. Recursive function/procedure contains a function/
procedure call statement to call itself normally kept inside if-else construct.
Putting function/procedure call inside if-else construct allows termination of
recursive function/procedure call after some time.
While defining a recursive function/procedure we must take care of these two
points
* Each time a function/procedure calls itself it must be closer, in some sense to a
solution.
* There must be a decision criterion for stopping recursive function/procedure
call otherwise it will execute till the stack overflows.
write program to find factorial using recursive function
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim n%, m&
n = Text1
m = fact(n)
Text2 = m
End Sub
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
Private Function fact&(n As Integer)
If n <= 1 Then
fact = 1
Else
fact = n * fact(n - 1)
End If
user interface:
create a command button: having caption find factorial
create text1: having text property clear
create text2: having text property clear
create label1: having caption property set to enter a value
create label2: having caption property set to factorial is
write program to find factorial using function.
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim n%, f&
n = Text1
f = fact(n)
Text2 = f
End Sub
'Private Function fact&(byref x%) ‘ by default calling by reference
'Dim i%, f&
'f = 1
'For i = 1 To x
'f=f*i
'Next
'fact = f
'End Function
Private Function fact&(ByVal x%)
Dim i%, f&
f=1
For i = 1 To x
f=f*i
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
Next
fact = f
End Function
user interface:
create a command button: having caption find factorial
create text1: having text property clear
create text2: having text property clear
create label1: having caption property set to enter a value
create label2: having caption property set to factorial is
Explain call by value and call by reference
'when called routine is not able to change value of actual argument
'through dummy argument it is known as call by value
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim a%, b%
a = Text1
b = Text2
swap a, b
'after call
Text5 = a
Text6 = b
End Sub
Private Sub swap(ByVal a%, ByVal b%)
'default is call by reference
Text3 = a
Text4 = b
Dim temp%
'interchange
temp = a
a=b
b = temp
End Sub
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|4339219
call by reference:
'when called routine is able to change value of actual argument
'through dummy argument it is known as call by reference
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim a%, b%
a = Text1
b = Text2
swap a, b
'after call
Text5 = a
Text6 = b
End Sub
Private Sub swap(Byref a%, Byref b%)
'default is call by reference
Text3 = a
Text4 = b
Dim temp%
'interchange
temp = a
a=b
b = temp
End Sub
user interface:
6 textboxes: having text property clear and having default name text1,text2…
6 labels: having caption enter value of a, enter value of b, within called
subroutine value of a, within called subroutine value of b, after call to swap value
of a, after call to swap value of b
1 command button: having caption swap and having default name command1
Downloaded by vipul kumar (vipulkumar7710@gmail.com)
You might also like
- 1 Visual Programming Summary Notes of VBNo ratings yet1 Visual Programming Summary Notes of VB7 pages
- College of Science and Technology: Covenant University, Canaan Land, Ota, NigeriaNo ratings yetCollege of Science and Technology: Covenant University, Canaan Land, Ota, Nigeria33 pages
- CHAPTER 1 - Introduction To Visual Basic ProgrammingNo ratings yetCHAPTER 1 - Introduction To Visual Basic Programming28 pages
- Visual Basic - Unit 1 History of Visual Basic 6.0No ratings yetVisual Basic - Unit 1 History of Visual Basic 6.06 pages
- Session 1 - Introduction To Visual Basic 6.0No ratings yetSession 1 - Introduction To Visual Basic 6.026 pages
- To Visual Basic: Prepared By: Mercy Ann G. GiereNo ratings yetTo Visual Basic: Prepared By: Mercy Ann G. Giere20 pages
- Visual Basic (III CS III BCA III IT-Sem5) - 240620 - 220422No ratings yetVisual Basic (III CS III BCA III IT-Sem5) - 240620 - 220422110 pages
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To VB ProgrammingNo ratings yetChapter 1 - Introduction To VB Programming16 pages
- SIT301 VP LEC 1n2 SLIDES - VISUAL PARADIGMNo ratings yetSIT301 VP LEC 1n2 SLIDES - VISUAL PARADIGM8 pages
- Lesson 3-Part I - Visual Basic 2008 ExpressNo ratings yetLesson 3-Part I - Visual Basic 2008 Express24 pages
- Microsoft Visual Basic 6.0: Applied ScienceNo ratings yetMicrosoft Visual Basic 6.0: Applied Science54 pages
- DataAnalyticsforBusinessProfessionals CertificateOfCompletion PDFNo ratings yetDataAnalyticsforBusinessProfessionals CertificateOfCompletion PDF1 page
- Bhartiya International LTD: IT Security Foundations: Core ConceptsNo ratings yetBhartiya International LTD: IT Security Foundations: Core Concepts1 page
- ITSecurityFoundations CoreConcepts CertificateOfCompletion PDFNo ratings yetITSecurityFoundations CoreConcepts CertificateOfCompletion PDF1 page
- Bhartiya International LTD: Data Analytics For Business ProfessionalsNo ratings yetBhartiya International LTD: Data Analytics For Business Professionals1 page
- Exam May 2016, Questions Exam May 2016, QuestionsNo ratings yetExam May 2016, Questions Exam May 2016, Questions3 pages
- Bhartiya International LTD: Python Automation and TestingNo ratings yetBhartiya International LTD: Python Automation and Testing1 page
- From Bhartiya International LTD Po Number 0560006597No ratings yetFrom Bhartiya International LTD Po Number 056000659736 pages
- Exam May 2017, Questions Exam May 2017, QuestionsNo ratings yetExam May 2017, Questions Exam May 2017, Questions4 pages
- Exam May 2015, Questions Exam May 2015, QuestionsNo ratings yetExam May 2015, Questions Exam May 2015, Questions4 pages
- Unit 3 Notes For Visual Basic Part 3 PDFNo ratings yetUnit 3 Notes For Visual Basic Part 3 PDF23 pages
- Unit 1 Notes For Visual Basic Part 1 PDFNo ratings yetUnit 1 Notes For Visual Basic Part 1 PDF38 pages
- IEEE Cloud Computing - November-December 2016No ratings yetIEEE Cloud Computing - November-December 201694 pages
- C.K.T. University of Techology and Applied Sciences: Ckt-Utas Student Mis ManualNo ratings yetC.K.T. University of Techology and Applied Sciences: Ckt-Utas Student Mis Manual9 pages
- Inyector de Medios de Contraste Ge Presicion Rxi Usuario EspañolNo ratings yetInyector de Medios de Contraste Ge Presicion Rxi Usuario Español12 pages
- LS6 PPT-AE-JHS (Troubleshoot Basic Computer Software)No ratings yetLS6 PPT-AE-JHS (Troubleshoot Basic Computer Software)28 pages
- Rukmini Basic Science and Engineering Drawing RRB ALP CBT 2 HindiNo ratings yetRukmini Basic Science and Engineering Drawing RRB ALP CBT 2 Hindi378 pages
- EEE 3132 - Microprocessors Lecture NotesNo ratings yetEEE 3132 - Microprocessors Lecture Notes56 pages
- Top 50 Tableau Interview Questions and Answers in 2022 - Edureka100% (1)Top 50 Tableau Interview Questions and Answers in 2022 - Edureka16 pages
- Linksys RV042 & GreenBow IPsec VPN Configuration100% (2)Linksys RV042 & GreenBow IPsec VPN Configuration12 pages
- 08 NetNumen U31 Alarm Management Operation - 50PNo ratings yet08 NetNumen U31 Alarm Management Operation - 50P50 pages