0% found this document useful (0 votes)
418 views4 pagesUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 5 (Chapter 5)
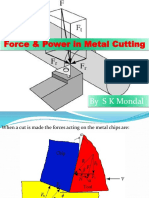
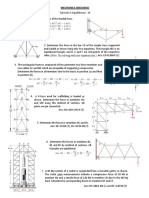
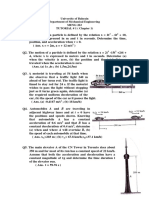
This document contains 16 questions from a tutorial on mechanical engineering concepts related to angular velocity, acceleration, and kinematics of rotating bodies. The questions involve determining velocities, accelerations, angular velocities, and other kinematic properties of points on rotating disks, gears, cranks, and other mechanisms at specific times or angular positions. Sample solutions are provided for each question.
Uploaded by
Vivin MathewCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
418 views4 pagesUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 5 (Chapter 5)
This document contains 16 questions from a tutorial on mechanical engineering concepts related to angular velocity, acceleration, and kinematics of rotating bodies. The questions involve determining velocities, accelerations, angular velocities, and other kinematic properties of points on rotating disks, gears, cranks, and other mechanisms at specific times or angular positions. Sample solutions are provided for each question.
Uploaded by
Vivin MathewCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4