0% found this document useful (0 votes)
219 views29 pagesSDN Implementation Guide
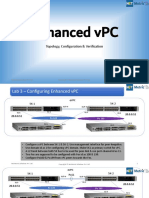
This document provides an overview of a module on implementing software defined networking. It discusses SDN and its benefits, network virtualization using NVGRE, and implementing a network controller. The module includes lessons on SDN overview, network virtualization, and deploying a network controller. It provides information on planning an SDN configuration, deploying SDN scripts, and demonstrates preparing and deploying a network controller to manage network services and devices in a test lab environment.
Uploaded by
SanitaracCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
219 views29 pagesSDN Implementation Guide
This document provides an overview of a module on implementing software defined networking. It discusses SDN and its benefits, network virtualization using NVGRE, and implementing a network controller. The module includes lessons on SDN overview, network virtualization, and deploying a network controller. It provides information on planning an SDN configuration, deploying SDN scripts, and demonstrates preparing and deploying a network controller to manage network services and devices in a test lab environment.
Uploaded by
SanitaracCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 29