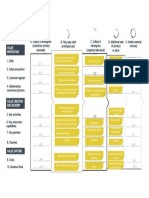
MINING EQUIPMENT MANAGEMENT METRICS
Numerical Benchmarks -- Metrics
What is needed?
Metrics Calculation / Method How do we use it? What Will I Have Benchmark
Operated Hours;
Operated Hours Service Downtime Hrs. Production Estimating Aid:
1 Mechanical Availability MA = -------------------------------------------- x 100 (%) Collect & enter: Daily; - Can production requirements be met today? 92% - new fleet
(Equipment Management Operated Hrs. + Service Downtime. Analyze: Monthly; - Is the trend in MA as desired? 88% - old fleet
Focus) Monitor/Trend: 12 – 24 months
Operated Hours;
Operated Hours Total Hours in Period Asset Utilization:
2 Utilization U = -------------------------------- x 100 (%) Collect & enter: Daily; - Fleet burden indicator; 90%
Total Hours in Period Analyze: Monthly; - Operation performance indicator.
Monitor/Trend: 12 – 24 months
Operated Hours;
Operated Hours Stoppage Count Machine Reliability & Equipment Management Effectiveness; 80 hrs. – new fleet
3 Mean Time Between MTBS = -------------------------------- Collect & enter: Daily; Impact of MTBS on Mechanical Availability. 60 hrs. – old fleet
Stoppages (MTBS) Number of Stoppages Analyze: Monthly;
Monitor/Trend: 12 months
Service Downtime;
Service Downtime Stoppage Count Service Turnaround/Efficiency;
4 Mean Time To Repair MTTR = ----------------------------------- Collect & enter: Daily; Machine Serviceability; 3 – 6 hours
(MTTR) No. of Stoppages Analyze: Monthly; Impact of MTTR on Mechanical Availability
Trend: 12 months
Service Man-hours;
Service Man-hours Operated Hours. Manpower management tool; 0.2 new fleet
5 Maintenance Ratio MR = ------------------------------ Collect & enter: Daily; Labor needed; 0.3 old fleet
(MR) Operated Hours Analyze: Monthly; Service & labor efficiency.
Trend: Every 5,000 hr increment.
Service Downtime with scheduled
Scheduled Service Downtime / unscheduled identification. Service system effectiveness:
6 Percent of Scheduled Service SS = ------------------------------------ x 100% Collect & enter: With every WO; - Who is in control? Maintenance department or the machines? 80%
(SS) Total Service Downtime Analyze: Monthly; - Is the system proactive or reactive?
Trend: 12 months
No. of Scheduled Services within ± 5% Actual Service Intervals (SMU) Planning / Scheduling efficiency
7 Service Accuracy SA = ----------------------------------------------- x 100% Scheduled Service Intervals Are Repair Centers following the schedule? 95%
(SA) No. of Scheduled Services (SMU) General planning accomplishment
Visual Method: Collect & enter: With every WO;
Scatter Diagram of Nominal Interval & ± 5%Limits Analyze: Monthly;
Trend: 12 months
Parts Order Count identified as
Number of Parts Orders Closed at 1st Request “Closed at 1st Request” and/or
8 Warehouse Parts Fill Level PFL = ------------------------------------------------------- “Backorder”. Parts Management Efficiency Indicator > 85%
(PFL) Total Number of Parts Orders Collect & enter: With every PO;
Analyze: Monthly;
Trend: 12 months
512944813.doc 03/04/aa 1
� MINING EQUIPMENT MANAGEMENT METRICS
Compliance Benchmarks -- Service Records & Data
Records & Data What Data & Records Needed? What Will I Have Benchmark
- Date & SMU of the machine start-up; - Reference point of machine & component life;
1 Commissioning Report - Component identification; - Component tracking system input; Summary Report
- Machine system performance data; - Benchmarks for further system performance tests; on File
- Custom product & retrofits identification; - Input for extra parts, tools, literature order;
- Production Data;
- Operator Shift Report - Downtime Data;
- Mechanical Condition Records;
- Operating Condition Report. All suggested
- Problem Indicator; methods used;
- Fuel & Oil Consumption Data - Application Severity Indicator;
- Component Management Aid.
2 Condition Monitoring - Contamination Indicator;
- Oil Sampling Data - Oil Condition Indicator;
- Mechanical Condition Indicator. Effectiveness
- Mechanical Inspection Report (including operating tests) - Detailed Condition indicator; evaluated through
- Test Data. service history
- Fault Codes; analysis
- Onboard Monitoring System (if available) - System Integrity Report;
- Operating Parameter Analysis.
- Diagnostic Test Reports - Data for Statistical Analysis and Trending.
- Machine & System Identifier;
- Statistical Data - Date / Time (In / Out), SMU;
- Labor Data; All shop services
3 Work Orders (WO) - Parts Usage. documented in a
- Problem Description; unique Work
- Technical Data - Problem Resolution; Order.
- Failure Cause;
- Afterservice Test Data.
Production Data: The ability to analyze & prioritize the problems by component, system, machine, fleet:
- Downtime Count per machine; - Downtime; Pareto Analysis
- Downtime Count per component (system); - Repair frequency; reviewed monthly.
- Downtime Hours per machine & component. - Parts Cost;
- Labor Cost and Time; Problem
4 Pareto Analysis Work Order Data: - Total Cost; management
(Top 10 Problems) - Machine System Identity; - Chronological Repair History. process in
- Date, SMU; Problem Management Capability: operation.
- Labor Applied; - Problem Identification;
- Parts Consumed. - Impact & Severity Quantification.
Work Order Data:
- Machine System Identity; Effective Service Backlog Management Capability:
- Date, SMU; - Efficient use of labor;
5 Backlog Management - Description; - Efficient use of downtime;
- Priority (Urgency) - Effective planning for the shop & production supervisors;
- Estimated Labor Needed; - Capability to match the workload to available resources.
- Estimated Downtime Required;
- Parts Availability & Delivery Status.
512944813.doc 03/04/aa 2