0% found this document useful (0 votes)
55 views4 pagesAnswer 1:: Computer Science and Engineering Department Computer Organisation and Architecture (SE-204)
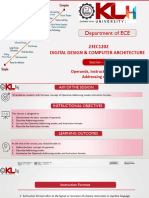
This document contains a tutorial sheet submitted by Aseem Sangalay to Dr. Pawan Singh Mehra for the course Computer Organisation and Architecture. It discusses different addressing modes used in computer instructions, including implied, immediate, register, register indirect, direct, indirect, PC relative, indexed, auto-increment, auto-decrement, and base address register addressing modes. It also provides examples of three address, two address, one address, and zero address instructions and their operation codes, destination addresses, source addresses, and modes.
Uploaded by
Hariom SharmaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
55 views4 pagesAnswer 1:: Computer Science and Engineering Department Computer Organisation and Architecture (SE-204)
This document contains a tutorial sheet submitted by Aseem Sangalay to Dr. Pawan Singh Mehra for the course Computer Organisation and Architecture. It discusses different addressing modes used in computer instructions, including implied, immediate, register, register indirect, direct, indirect, PC relative, indexed, auto-increment, auto-decrement, and base address register addressing modes. It also provides examples of three address, two address, one address, and zero address instructions and their operation codes, destination addresses, source addresses, and modes.
Uploaded by
Hariom SharmaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4