0% found this document useful (0 votes)
98 views16 pagesMat3012 Numerical Analysis (Lab Applicatoins) : Bahcesehir University
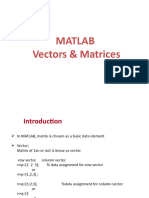
This document provides a syllabus for a Numerical Analysis lab course at Bahcesehir University that uses MATLAB. It covers 5 topics: [1] the MATLAB environment, [2] useful commands, [3] input-output functions, [4] arrays/vectors/matrices, and [5] mathematical functions and operations. The instructor is Research Assistant Aysun Soysal and the course materials are provided online. Students will complete quizzes and MATLAB homework assignments as part of their grading.
Uploaded by
drogoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
98 views16 pagesMat3012 Numerical Analysis (Lab Applicatoins) : Bahcesehir University
This document provides a syllabus for a Numerical Analysis lab course at Bahcesehir University that uses MATLAB. It covers 5 topics: [1] the MATLAB environment, [2] useful commands, [3] input-output functions, [4] arrays/vectors/matrices, and [5] mathematical functions and operations. The instructor is Research Assistant Aysun Soysal and the course materials are provided online. Students will complete quizzes and MATLAB homework assignments as part of their grading.
Uploaded by
drogoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16