0% found this document useful (0 votes)
388 views3 pagesDma Operation in An 8086 Based System
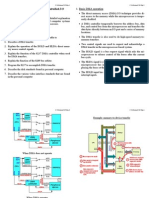
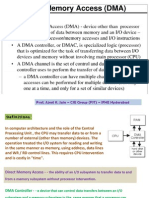
The document describes how DMA operation works in an 8086-based system. It explains that the DMA controller temporarily takes control of the address, data, and control buses from the microprocessor to directly transfer data between peripherals and memory. This is faster than programmed I/O because the transfer is handled by hardware instead of the microprocessor. It also provides step-by-step details of the sequence followed to perform a disk read operation using DMA.
Uploaded by
Sowmya PCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
388 views3 pagesDma Operation in An 8086 Based System
The document describes how DMA operation works in an 8086-based system. It explains that the DMA controller temporarily takes control of the address, data, and control buses from the microprocessor to directly transfer data between peripherals and memory. This is faster than programmed I/O because the transfer is handled by hardware instead of the microprocessor. It also provides step-by-step details of the sequence followed to perform a disk read operation using DMA.
Uploaded by
Sowmya PCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3